Free energy principle
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 22 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 22 min
The free energy principle is a theoretical framework suggesting that the brain reduces surprise or uncertainty by making predictions based on internal models and updating them using sensory input. It highlights the brain's objective of aligning its internal model and the external world to enhance prediction accuracy. This principle integrates Bayesian inference with active inference, where actions are guided by predictions and sensory feedback refines them. It has wide-ranging implications for comprehending brain function, perception, and action.[1]
Overview
[edit]In biophysics and cognitive science, the free energy principle is a mathematical principle describing a formal account of the representational capacities of physical systems: that is, why things that exist look as if they track properties of the systems to which they are coupled.[2] It establishes that the dynamics of physical systems minimise a quantity known as surprisal (which is the negative log probability of some outcome); or equivalently, its variational upper bound, called free energy. The principle is used especially in Bayesian approaches to brain function, but also some approaches to artificial intelligence; it is formally related to variational Bayesian methods and was originally introduced by Karl Friston as an explanation for embodied perception-action loops in neuroscience.[3]
The free energy principle models the behaviour of systems that are distinct from, but coupled to, another system (e.g., an embedding environment), where the degrees of freedom that implement the interface between the two systems is known as a Markov blanket. More formally, the free energy principle says that if a system has a "particular partition" (i.e., into particles, with their Markov blankets), then subsets of that system will track the statistical structure of other subsets (which are known as internal and external states or paths of a system).
The free energy principle is based on the Bayesian idea of the brain as an “inference engine.” Under the free energy principle, systems pursue paths of least surprise, or equivalently, minimize the difference between predictions based on their model of the world and their sense and associated perception. This difference is quantified by variational free energy and is minimized by continuous correction of the world model of the system, or by making the world more like the predictions of the system. By actively changing the world to make it closer to the expected state, systems can also minimize the free energy of the system. Friston assumes this to be the principle of all biological reaction.[4] Friston also believes his principle applies to mental disorders as well as to artificial intelligence. AI implementations based on the active inference principle have shown advantages over other methods.[4]
The free energy principle is a mathematical principle of information physics: much like the principle of maximum entropy or the principle of least action, it is true on mathematical grounds. To attempt to falsify the free energy principle is a category mistake, akin to trying to falsify calculus by making empirical observations. (One cannot invalidate a mathematical theory in this way; instead, one would need to derive a formal contradiction from the theory.) In a 2018 interview, Friston explained what it entails for the free energy principle to not be subject to falsification:[5]
I think it is useful to make a fundamental distinction at this point—that we can appeal to later.
The distinction is between a state and process theory; i.e., the difference between a normative principle that things may or may not conform to, and a process theory or hypothesis about how that principle is realized. Under this distinction, the free energy principle stands in stark distinction to things like predictive coding and the Bayesian brain hypothesis. This is because the free energy principle is what it is — a principle. Like Hamilton's principle of stationary action, it cannot be falsified. It cannot be disproven. In fact, there’s not much you can do with it, unless you ask whether measurable systems conform to the principle. On the other hand, hypotheses that the brain performs some form of Bayesian inference or predictive coding are what they are—hypotheses. These hypotheses may or may not be supported by empirical evidence.
There are many examples of these hypotheses being supported by empirical evidence.[6]
Background
[edit]The notion that self-organising biological systems – like a cell or brain – can be understood as minimising variational free energy is based upon Helmholtz’s work on unconscious inference[7] and subsequent treatments in psychology[8] and machine learning.[9] Variational free energy is a function of observations and a probability density over their hidden causes. This variational density is defined in relation to a probabilistic model that generates predicted observations from hypothesized causes. In this setting, free energy provides an approximation to Bayesian model evidence.[10] Therefore, its minimisation can be seen as a Bayesian inference process. When a system actively makes observations to minimise free energy, it implicitly performs active inference and maximises the evidence for its model of the world.
However, free energy is also an upper bound on the self-information of outcomes, where the long-term average of surprise is entropy. This means that if a system acts to minimise free energy, it will implicitly place an upper bound on the entropy of the outcomes – or sensory states – it samples.[11][12]
Relationship to other theories
[edit]Active inference is closely related to the good regulator theorem[13] and related accounts of self-organisation,[14][15] such as self-assembly, pattern formation, autopoiesis[16] and practopoiesis.[17] It addresses the themes considered in cybernetics, synergetics[18] and embodied cognition. Because free energy can be expressed as the expected energy of observations under the variational density minus its entropy, it is also related to the maximum entropy principle.[19] Finally, because the time average of energy is action, the principle of minimum variational free energy is a principle of least action. Active inference allowing for scale invariance has also been applied to other theories and domains. For instance, it has been applied to sociology,[20][21][22][23] linguistics and communication,[24][25][26] semiotics,[27][28] and epidemiology [29] among others.
Negative free energy is formally equivalent to the evidence lower bound, which is commonly used in machine learning to train generative models, such as variational autoencoders.
Action and perception
[edit]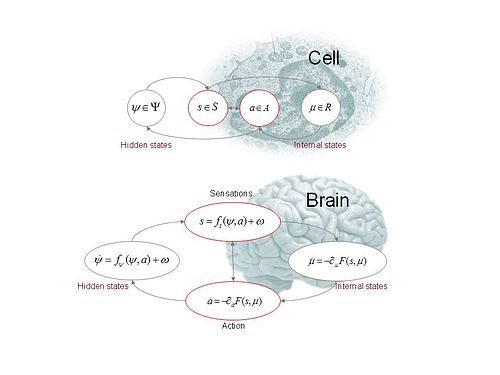
Active inference applies the techniques of approximate Bayesian inference to infer the causes of sensory data from a 'generative' model of how that data is caused and then uses these inferences to guide action. Bayes' rule characterizes the probabilistically optimal inversion of such a causal model, but applying it is typically computationally intractable, leading to the use of approximate methods. In active inference, the leading class of such approximate methods are variational methods, for both practical and theoretical reasons: practical, as they often lead to simple inference procedures; and theoretical, because they are related to fundamental physical principles, as discussed above.
These variational methods proceed by minimizing an upper bound on the divergence between the Bayes-optimal inference (or 'posterior') and its approximation according to the method. This upper bound is known as the free energy, and we can accordingly characterize perception as the minimization of the free energy with respect to inbound sensory information, and action as the minimization of the same free energy with respect to outbound action information. This holistic dual optimization is characteristic of active inference, and the free energy principle is the hypothesis that all systems which perceive and act can be characterized in this way.
In order to exemplify the mechanics of active inference via the free energy principle, a generative model must be specified, and this typically involves a collection of probability density functions which together characterize the causal model. One such specification is as follows. The system is modelled as inhabiting a state space , in the sense that its states form the points of this space. The state space is then factorized according to , where is the space of 'external' states that are 'hidden' from the agent (in the sense of not being directly perceived or accessible), is the space of sensory states that are directly perceived by the agent, is the space of the agent's possible actions, and is a space of 'internal' states that are private to the agent.
Keeping with the Figure 1, note that in the following the and are functions of (continuous) time . The generative model is the specification of the following density functions:
- A sensory model, , often written as , characterizing the likelihood of sensory data given external states and actions;
- a stochastic model of the environmental dynamics, , often written , characterizing how the external states are expected by the agent to evolve over time , given the agent's actions;
- an action model, , written , characterizing how the agent's actions depend upon its internal states and sensory data; and
- an internal model, , written , characterizing how the agent's internal states depend upon its sensory data.
These density functions determine the factors of a "joint model", which represents the complete specification of the generative model, and which can be written as
- .
Bayes' rule then determines the "posterior density" , which expresses a probabilistically optimal belief about the external state given the preceding state and the agent's actions, sensory signals, and internal states. Since computing is computationally intractable, the free energy principle asserts the existence of a "variational density" , where is an approximation to . One then defines the free energy as
and defines action and perception as the joint optimization problem
where the internal states are typically taken to encode the parameters of the 'variational' density and hence the agent's "best guess" about the posterior belief over . Note that the free energy is also an upper bound on a measure of the agent's (marginal, or average) sensory surprise, and hence free energy minimization is often motivated by the minimization of surprise.
Free energy minimisation
[edit]Free energy minimisation and self-organisation
[edit]Free energy minimisation has been proposed as a hallmark of self-organising systems when cast as random dynamical systems.[30] This formulation rests on a Markov blanket (comprising action and sensory states) that separates internal and external states. If internal states and action minimise free energy, then they place an upper bound on the entropy of sensory states:
This is because – under ergodic assumptions – the long-term average of surprise is entropy. This bound resists a natural tendency to disorder – of the sort associated with the second law of thermodynamics and the fluctuation theorem. However, formulating a unifying principle for the life sciences in terms of concepts from statistical physics, such as random dynamical system, non-equilibrium steady state and ergodicity, places substantial constraints on the theoretical and empirical study of biological systems with the risk of obscuring all features that make biological systems interesting kinds of self-organizing systems.[31]
Free energy minimisation and Bayesian inference
[edit]All Bayesian inference can be cast in terms of free energy minimisation[32][failed verification]. When free energy is minimised with respect to internal states, the Kullback–Leibler divergence between the variational and posterior density over hidden states is minimised. This corresponds to approximate Bayesian inference – when the form of the variational density is fixed – and exact Bayesian inference otherwise. Free energy minimisation therefore provides a generic description of Bayesian inference and filtering (e.g., Kalman filtering). It is also used in Bayesian model selection, where free energy can be usefully decomposed into complexity and accuracy:
Models with minimum free energy provide an accurate explanation of data, under complexity costs (c.f., Occam's razor and more formal treatments of computational costs[33]). Here, complexity is the divergence between the variational density and prior beliefs about hidden states (i.e., the effective degrees of freedom used to explain the data).
Free energy minimisation and thermodynamics
[edit]Variational free energy is an information-theoretic functional and is distinct from thermodynamic (Helmholtz) free energy.[34] However, the complexity term of variational free energy shares the same fixed point as Helmholtz free energy (under the assumption the system is thermodynamically closed but not isolated). This is because if sensory perturbations are suspended (for a suitably long period of time), complexity is minimised (because accuracy can be neglected). At this point, the system is at equilibrium and internal states minimise Helmholtz free energy, by the principle of minimum energy.[35]
Free energy minimisation and information theory
[edit]Free energy minimisation is equivalent to maximising the mutual information between sensory states and internal states that parameterise the variational density (for a fixed entropy variational density). This relates free energy minimization to the principle of minimum redundancy.[36][12]
Free energy minimisation in neuroscience
[edit]Free energy minimisation provides a useful way to formulate normative (Bayes optimal) models of neuronal inference and learning under uncertainty[37] and therefore subscribes to the Bayesian brain hypothesis.[38] The neuronal processes described by free energy minimisation depend on the nature of hidden states: that can comprise time-dependent variables, time-invariant parameters and the precision (inverse variance or temperature) of random fluctuations. Minimising variables, parameters, and precision correspond to inference, learning, and the encoding of uncertainty, respectively.
Perceptual inference and categorisation
[edit]Free energy minimisation formalises the notion of unconscious inference in perception[7][9] and provides a normative (Bayesian) theory of neuronal processing. The associated process theory of neuronal dynamics is based on minimising free energy through gradient descent. This corresponds to generalised Bayesian filtering (where ~ denotes a variable in generalised coordinates of motion and is a derivative matrix operator):[39]
Usually, the generative models that define free energy are non-linear and hierarchical (like cortical hierarchies in the brain). Special cases of generalised filtering include Kalman filtering, which is formally equivalent to predictive coding[40] – a popular metaphor for message passing in the brain. Under hierarchical models, predictive coding involves the recurrent exchange of ascending (bottom-up) prediction errors and descending (top-down) predictions[41] that is consistent with the anatomy and physiology of sensory[42] and motor systems.[43]
Perceptual learning and memory
[edit]In predictive coding, optimising model parameters through a gradient descent on the time integral of free energy (free action) reduces to associative or Hebbian plasticity and is associated with synaptic plasticity in the brain.
Perceptual precision, attention and salience
[edit]Optimizing the precision parameters corresponds to optimizing the gain of prediction errors (c.f., Kalman gain). In neuronally plausible implementations of predictive coding,[41] this corresponds to optimizing the excitability of superficial pyramidal cells and has been interpreted in terms of attentional gain.[44]

With regard to the top-down vs. bottom-up controversy, which has been addressed as a major open problem of attention, a computational model has succeeded in illustrating the circular nature of the interplay between top-down and bottom-up mechanisms. Using an established emergent model of attention, namely SAIM, the authors proposed a model called PE-SAIM, which, in contrast to the standard version, approaches selective attention from a top-down position. The model takes into account the transmission of prediction errors to the same level or a level above, in order to minimise the energy function that indicates the difference between the data and its cause, or, in other words, between the generative model and the posterior. To increase validity, they also incorporated neural competition between stimuli into their model. A notable feature of this model is the reformulation of the free energy function only in terms of prediction errors during task performance:
where is the total energy function of the neural networks entail, and is the prediction error between the generative model (prior) and posterior changing over time.[45] Comparing the two models reveals a notable similarity between their respective results while also highlighting a remarkable discrepancy, whereby – in the standard version of the SAIM – the model's focus is mainly upon the excitatory connections, whereas in the PE-SAIM, the inhibitory connections are leveraged to make an inference. The model has also proved to be fit to predict the EEG and fMRI data drawn from human experiments with high precision. In the same vein, Yahya et al. also applied the free energy principle to propose a computational model for template matching in covert selective visual attention that mostly relies on SAIM.[46] According to this study, the total free energy of the whole state-space is reached by inserting top-down signals in the original neural networks, whereby we derive a dynamical system comprising both feed-forward and backward prediction error.
Active inference
[edit]When gradient descent is applied to action , motor control can be understood in terms of classical reflex arcs that are engaged by descending (corticospinal) predictions. This provides a formalism that generalizes the equilibrium point solution – to the degrees of freedom problem[47] – to movement trajectories.
Active inference and optimal control
[edit]Active inference is related to optimal control by replacing value or cost-to-go functions with prior beliefs about state transitions or flow.[48] This exploits the close connection between Bayesian filtering and the solution to the Bellman equation. However, active inference starts with (priors over) flow that are specified with scalar and vector value functions of state space (c.f., the Helmholtz decomposition). Here, is the amplitude of random fluctuations and cost is . The priors over flow induce a prior over states that is the solution to the appropriate forward Kolmogorov equations.[49] In contrast, optimal control optimises the flow, given a cost function, under the assumption that (i.e., the flow is curl free or has detailed balance). Usually, this entails solving backward Kolmogorov equations.[50]
Active inference and optimal decision (game) theory
[edit]Optimal decision problems (usually formulated as partially observable Markov decision processes) are treated within active inference by absorbing utility functions into prior beliefs. In this setting, states that have a high utility (low cost) are states an agent expects to occupy. By equipping the generative model with hidden states that model control, policies (control sequences) that minimise variational free energy lead to high utility states.[51]
Neurobiologically, neuromodulators such as dopamine are considered to report the precision of prediction errors by modulating the gain of principal cells encoding prediction error.[52] This is closely related to – but formally distinct from – the role of dopamine in reporting prediction errors per se[53] and related computational accounts.[54]
Active inference and cognitive neuroscience
[edit]Active inference has been used to address a range of issues in cognitive neuroscience, brain function and neuropsychiatry, including action observation,[55] mirror neurons,[56] saccades and visual search,[57][58] eye movements,[59] sleep,[60] illusions,[61] attention,[44] action selection,[52] consciousness,[62][63] hysteria[64] and psychosis.[65] Explanations of action in active inference often depend on the idea that the brain has 'stubborn predictions' that it cannot update, leading to actions that cause these predictions to come true.[66]
See also
[edit]- Action-specific perception – Psychological theory that people perceive their environment and events within it
- Affordance – Possibility of an action on an object or environment
- Autopoiesis – System capable of producing itself
- Bayesian approaches to brain function – Explaining the brain's abilities through statistical principles
- Constructal law - Law of design evolution in nature, animate and inanimate
- Decision theory – Branch of applied probability theory
- Embodied cognition – Interdisciplinary theory
- Entropic force – Physical force that originates from thermodynamics instead of fundamental interactions
- Principle of minimum energy – thermodynamic formulation based on the second law
- Info-metrics – Interdisciplinary approach to scientific modelling and information processing
- Optimal control – Mathematical way of attaining a desired output from a dynamic system
- Adaptive system – System that can adapt to the environment
- Predictive coding – Theory of brain function
- Self-organization – Process of creating order by local interactions
- Surprisal – Basic quantity derived from the probability of a particular event occurring from a random variable
- Synergetics (Haken) – school of thought on thermodynamics and systems phenomena developed by Hermann Haken
- Variational Bayesian methods – Mathematical methods used in Bayesian inference and machine learning
References
[edit]- ^ Bruineberg, Jelle; Kiverstein, Julian; Rietveld, Erik (2018). "The anticipating brain is not a scientist: the free-energy principle from an ecological-enactive perspective". Synthese. 195 (6): 2417–2444. doi:10.1007/s11229-016-1239-1. PMC 6438652. PMID 30996493.
- ^ Friston, Karl (2010). "The free-energy principle: a unified brain theory?". Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 11 (2): 127–138. doi:10.1038/nrn2787. PMID 20068583. S2CID 5053247. Retrieved July 9, 2023.
- ^ Friston, Karl; Kilner, James; Harrison, Lee (2006). "A free energy principle for the brain" (PDF). Journal of Physiology-Paris. 100 (1–3): 70–87. doi:10.1016/j.jphysparis.2006.10.001. PMID 17097864. S2CID 637885.
- ^ a b Shaun Raviv: The Genius Neuroscientist Who Might Hold the Key to True AI. In: Wired, 13. November 2018
- ^ Friston, Karl (2018). "Of woodlice and men: A Bayesian account of cognition, life and consciousness. An interview with Karl Friston (by Martin Fortier & Daniel Friedman)". ALIUS Bulletin. 2: 17–43.
- ^ Friston, Karl (2022). Active Inference: The Free Energy Principle in Mind, Brain, and Behavior. MIT Press. ISBN 9780262045353.
- ^ a b Helmholtz, H. (1866/1962). Concerning the perceptions in general. In Treatise on physiological optics (J. Southall, Trans., 3rd ed., Vol. III). New York: Dover. Available at https://web.archive.org/web/20180320133752/http://poseidon.sunyopt.edu/BackusLab/Helmholtz/
- ^ Gregory, R. L. (1980-07-08). "Perceptions as hypotheses". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. B, Biological Sciences. 290 (1038): 181–197. Bibcode:1980RSPTB.290..181G. doi:10.1098/rstb.1980.0090. JSTOR 2395424. PMID 6106237.
- ^ a b Dayan, Peter; Hinton, Geoffrey E.; Neal, Radford M.; Zemel, Richard S. (1995). "The Helmholtz Machine" (PDF). Neural Computation. 7 (5): 889–904. doi:10.1162/neco.1995.7.5.889. hdl:21.11116/0000-0002-D6D3-E. PMID 7584891. S2CID 1890561.
- ^ Beal, M. J. (2003). Variational Algorithms for Approximate Bayesian Inference. Ph.D. Thesis, University College London.
- ^ Sakthivadivel, Dalton (2022). "Towards a Geometry and Analysis for Bayesian Mechanics". arXiv:2204.11900 [math-ph].
- ^ a b Ramstead, Maxwell; Sakthivadivel, Dalton; Heins, Conor; Koudahl, Magnus; Millidge, Beren; Da Costa, Lancelot; Klein, Brennan; Friston, Karl (2023). "On Bayesian mechanics: A physics of and by beliefs". Interface Focus. 13 (3). arXiv:2205.11543. doi:10.1098/rsfs.2022.0029. PMC 10198254. PMID 37213925. S2CID 249017997.
- ^ Conant, Roger C.; Ross Ashby, W. (1970). "Every good regulator of a system must be a model of that system". International Journal of Systems Science. 1 (2): 89–97. doi:10.1080/00207727008920220.
- ^ Kauffman, S. (1993). The Origins of Order: Self-Organization and Selection in Evolution. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- ^ Nicolis, G., & Prigogine, I. (1977). Self-organization in non-equilibrium systems. New York: John Wiley.
- ^ Maturana, H. R., & Varela, F. (1980). Autopoiesis: the organization of the living. In V. F. Maturana HR (Ed.), Autopoiesis and Cognition. Dordrecht, Netherlands: Reidel.
- ^ Nikolić, Danko (2015). "Practopoiesis: Or how life fosters a mind". Journal of Theoretical Biology. 373: 40–61. arXiv:1402.5332. Bibcode:2015JThBi.373...40N. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.03.003. PMID 25791287. S2CID 12680941.
- ^ Haken, H. (1983). Synergetics: An introduction. Non-equilibrium phase transition and self-organisation in physics, chemistry and biology (3rd ed.). Berlin: Springer Verlag.
- ^ Jaynes, E. T. (1957). "Information Theory and Statistical Mechanics" (PDF). Physical Review. 106 (4): 620–630. Bibcode:1957PhRv..106..620J. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.106.620. S2CID 17870175.
- ^ Veissière, Samuel P. L.; Constant, Axel; Ramstead, Maxwell J. D.; Friston, Karl J.; Kirmayer, Laurence J. (2020). "Thinking through other minds: A variational approach to cognition and culture". Behavioral and Brain Sciences. 43: e90. doi:10.1017/S0140525X19001213. ISSN 0140-525X. PMID 31142395. S2CID 169038428.
- ^ Ramstead, Maxwell J. D.; Constant, Axel; Badcock, Paul B.; Friston, Karl J. (2019-12-01). "Variational ecology and the physics of sentient systems". Physics of Life Reviews. Physics of Mind. 31: 188–205. Bibcode:2019PhLRv..31..188R. doi:10.1016/j.plrev.2018.12.002. ISSN 1571-0645. PMC 6941227. PMID 30655223.
- ^ Albarracin, Mahault; Demekas, Daphne; Ramstead, Maxwell J. D.; Heins, Conor (April 2022). "Epistemic Communities under Active Inference". Entropy. 24 (4): 476. Bibcode:2022Entrp..24..476A. doi:10.3390/e24040476. ISSN 1099-4300. PMC 9027706. PMID 35455140.
- ^ Albarracin, Mahault; Constant, Axel; Friston, Karl J.; Ramstead, Maxwell James D. (2021). "A Variational Approach to Scripts". Frontiers in Psychology. 12: 585493. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2021.585493. ISSN 1664-1078. PMC 8329037. PMID 34354621.
- ^ Friston, Karl J.; Parr, Thomas; Yufik, Yan; Sajid, Noor; Price, Catherine J.; Holmes, Emma (2020-11-01). "Generative models, linguistic communication and active inference". Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews. 118: 42–64. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.07.005. ISSN 0149-7634. PMC 7758713. PMID 32687883.
- ^ Tison, Remi; Poirier, Pierre (2021-10-02). "Communication as Socially Extended Active Inference: An Ecological Approach to Communicative Behavior". Ecological Psychology. 33 (3–4): 197–235. doi:10.1080/10407413.2021.1965480. ISSN 1040-7413. S2CID 238703201.
- ^ Friston, Karl J.; Frith, Christopher D. (2015-07-01). "Active inference, communication and hermeneutics". Cortex. Special issue: Prediction in speech and language processing. 68: 129–143. doi:10.1016/j.cortex.2015.03.025. ISSN 0010-9452. PMC 4502445. PMID 25957007.
- ^ Kerusauskaite, Skaiste (2023-06-01). "Role of Culture in Meaning Making: Bridging Semiotic Cultural Psychology and Active Inference". Integrative Psychological and Behavioral Science. 57 (2): 432–443. doi:10.1007/s12124-022-09744-x. ISSN 1936-3567. PMID 36585542. S2CID 255366405.
- ^ García, Adolfo M.; Ibáñez, Agustín (2022-11-14). The Routledge Handbook of Semiosis and the Brain. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-000-72877-4.
- ^ Bottemanne, Hugo; Friston, Karl J. (2021-12-01). "An active inference account of protective behaviours during the COVID-19 pandemic". Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience. 21 (6): 1117–1129. doi:10.3758/s13415-021-00947-0. ISSN 1531-135X. PMC 8518276. PMID 34652601.
- ^ Crauel, Hans; Flandoli, Franco (1994). "Attractors for random dynamical systems". Probability Theory and Related Fields. 100 (3): 365–393. doi:10.1007/BF01193705. S2CID 122609512.
- ^ Colombo, Matteo; Palacios, Patricia (2021). "Non-equilibrium thermodynamics and the free energy principle in biology". Biology & Philosophy. 36 (5). doi:10.1007/s10539-021-09818-x. S2CID 235803361.
- ^ Roweis, Sam; Ghahramani, Zoubin (1999). "A Unifying Review of Linear Gaussian Models" (PDF). Neural Computation. 11 (2): 305–345. doi:10.1162/089976699300016674. PMID 9950734. S2CID 2590898.
- ^ Ortega, Pedro A.; Braun, Daniel A. (2013). "Thermodynamics as a theory of decision-making with information-processing costs". Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 469 (2153). arXiv:1204.6481. Bibcode:2013RSPSA.46920683O. doi:10.1098/rspa.2012.0683. S2CID 28080508.
- ^ Evans, Denis J. (2003). "A non-equilibrium free energy theorem for deterministic systems" (PDF). Molecular Physics. 101 (10): 1551–1554. Bibcode:2003MolPh.101.1551E. doi:10.1080/0026897031000085173. S2CID 15129000.
- ^ Jarzynski, C. (1997). "Nonequilibrium Equality for Free Energy Differences". Physical Review Letters. 78 (14): 2690–2693. arXiv:cond-mat/9610209. Bibcode:1997PhRvL..78.2690J. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.78.2690. S2CID 16112025.
- ^ Sakthivadivel, Dalton (2022). "Towards a Geometry and Analysis for Bayesian Mechanics". arXiv:2204.11900 [math-ph].
- ^ Friston, Karl (2010). "The free-energy principle: A unified brain theory?" (PDF). Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 11 (2): 127–138. doi:10.1038/nrn2787. PMID 20068583. S2CID 5053247.
- ^ Knill, David C.; Pouget, Alexandre (2004). "The Bayesian brain: The role of uncertainty in neural coding and computation" (PDF). Trends in Neurosciences. 27 (12): 712–719. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2004.10.007. PMID 15541511. S2CID 9870936. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2013-05-31.
- ^ Friston, Karl; Stephan, Klaas; Li, Baojuan; Daunizeau, Jean (2010). "Generalised Filtering". Mathematical Problems in Engineering. 2010: 1–34. doi:10.1155/2010/621670.
- ^ Knill, David C.; Pouget, Alexandre (2004). "The Bayesian brain: The role of uncertainty in neural coding and computation" (PDF). Trends in Neurosciences. 27 (12): 712–719. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2004.10.007. PMID 15541511. S2CID 9870936.
- ^ a b Mumford, D. (1992). "On the computational architecture of the neocortex" (PDF). Biological Cybernetics. 66 (3): 241–251. doi:10.1007/BF00198477. PMID 1540675. S2CID 14303625.
- ^ Bastos, Andre M.; Usrey, W. Martin; Adams, Rick A.; Mangun, George R.; Fries, Pascal; Friston, Karl J. (2012). "Canonical Microcircuits for Predictive Coding". Neuron. 76 (4): 695–711. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2012.10.038. PMC 3777738. PMID 23177956.
- ^ Adams, Rick A.; Shipp, Stewart; Friston, Karl J. (2013). "Predictions not commands: Active inference in the motor system". Brain Structure and Function. 218 (3): 611–643. doi:10.1007/s00429-012-0475-5. PMC 3637647. PMID 23129312.
- ^ a b Friston, Karl J.; Feldman, Harriet (2010). "Attention, Uncertainty, and Free-Energy". Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. 4: 215. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2010.00215. PMC 3001758. PMID 21160551.
- ^ Abadi, Alireza Khatoon; Yahya, Keyvan; Amini, Massoud; Friston, Karl; Heinke, Dietmar (2019). "Excitatory versus inhibitory feedback in Bayesian formulations of scene construction". Journal of the Royal Society Interface. 16 (154). doi:10.1098/rsif.2018.0344. PMC 6544897. PMID 31039693.
- ^ "12th Biannual Conference of the German Cognitive Science Society (KogWis 2014)". Cognitive Processing. 15: 107. 2014. doi:10.1007/s10339-013-0597-6. S2CID 10121398.
- ^ Feldman, Anatol G.; Levin, Mindy F. (1995). "The origin and use of positional frames of reference in motor control" (PDF). Behavioral and Brain Sciences. 18 (4): 723–744. doi:10.1017/S0140525X0004070X. S2CID 145164477. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-03-29. Retrieved 2013-05-31.
- ^ Friston, Karl (2011). "What is Optimal about Motor Control?" (PDF). Neuron. 72 (3): 488–498. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2011.10.018. PMID 22078508. S2CID 13912462.
- ^ Friston, Karl; Ao, Ping (2012). "Free Energy, Value, and Attractors". Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine. 2012: 1–27. doi:10.1155/2012/937860. PMC 3249597. PMID 22229042.
- ^ Kappen, H. J. (2005). "Path integrals and symmetry breaking for optimal control theory". Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment. 2005 (11): P11011. arXiv:physics/0505066. Bibcode:2005JSMTE..11..011K. doi:10.1088/1742-5468/2005/11/P11011. S2CID 87027.
- ^ Friston, Karl; Samothrakis, Spyridon; Montague, Read (2012). "Active inference and agency: Optimal control without cost functions". Biological Cybernetics. 106 (8–9): 523–541. doi:10.1007/s00422-012-0512-8. hdl:10919/78836. PMID 22864468.
- ^ a b Friston, Karl J.; Shiner, Tamara; Fitzgerald, Thomas; Galea, Joseph M.; Adams, Rick; Brown, Harriet; Dolan, Raymond J.; Moran, Rosalyn; Stephan, Klaas Enno; Bestmann, Sven (2012). "Dopamine, Affordance and Active Inference". PLOS Computational Biology. 8 (1): e1002327. Bibcode:2012PLSCB...8E2327F. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002327. PMC 3252266. PMID 22241972.
- ^ Fiorillo, Christopher D.; Tobler, Philippe N.; Schultz, Wolfram (2003). "Discrete Coding of Reward Probability and Uncertainty by Dopamine Neurons" (PDF). Science. 299 (5614): 1898–1902. Bibcode:2003Sci...299.1898F. doi:10.1126/science.1077349. PMID 12649484. S2CID 2363255. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2013-05-31.
- ^ Frank, Michael J. (2005). "Dynamic Dopamine Modulation in the Basal Ganglia: A Neurocomputational Account of Cognitive Deficits in Medicated and Nonmedicated Parkinsonism" (PDF). Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 17 (1): 51–72. doi:10.1162/0898929052880093. PMID 15701239. S2CID 7414727.
- ^ Friston, Karl; Mattout, Jérémie; Kilner, James (2011). "Action understanding and active inference" (PDF). Biological Cybernetics. 104 (1–2): 137–160. doi:10.1007/s00422-011-0424-z. PMC 3491875. PMID 21327826.
- ^ Kilner, James M.; Friston, Karl J.; Frith, Chris D. (2007). "Predictive coding: An account of the mirror neuron system" (PDF). Cognitive Processing. 8 (3): 159–166. doi:10.1007/s10339-007-0170-2. PMC 2649419. PMID 17429704.
- ^ Friston, Karl; Adams, Rick A.; Perrinet, Laurent; Breakspear, Michael (2012). "Perceptions as Hypotheses: Saccades as Experiments". Frontiers in Psychology. 3: 151. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00151. PMC 3361132. PMID 22654776.
- ^ Mirza, M. Berk; Adams, Rick A.; Mathys, Christoph; Friston, Karl J. (2018). "Human visual exploration reduces uncertainty about the sensed world". PLOS ONE. 13 (1): e0190429. Bibcode:2018PLoSO..1390429M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0190429. PMC 5755757. PMID 29304087.
- ^ Perrinet, Laurent U.; Adams, Rick A.; Friston, Karl J. (2014). "Active inference, eye movements and oculomotor delays". Biological Cybernetics. 108 (6): 777–801. doi:10.1007/s00422-014-0620-8. PMC 4250571. PMID 25128318.
- ^ Hobson, J.A.; Friston, K.J. (2012). "Waking and dreaming consciousness: Neurobiological and functional considerations". Progress in Neurobiology. 98 (1): 82–98. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2012.05.003. PMC 3389346. PMID 22609044.
- ^ Brown, Harriet; Friston, Karl J. (2012). "Free-Energy and Illusions: The Cornsweet Effect". Frontiers in Psychology. 3: 43. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00043. PMC 3289982. PMID 22393327.
- ^ Rudrauf, David; Bennequin, Daniel; Granic, Isabela; Landini, Gregory; Friston, Karl; Williford, Kenneth (2017-09-07). "A mathematical model of embodied consciousness" (PDF). Journal of Theoretical Biology. 428: 106–131. Bibcode:2017JThBi.428..106R. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2017.05.032. PMID 28554611.
- ^ K, Williford; D, Bennequin; K, Friston; D, Rudrauf (2018-12-17). "The Projective Consciousness Model and Phenomenal Selfhood". Frontiers in Psychology. 9: 2571. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02571. PMC 6304424. PMID 30618988.
- ^ Edwards, M. J.; Adams, R. A.; Brown, H.; Parees, I.; Friston, K. J. (2012). "A Bayesian account of 'hysteria'" (PDF). Brain. 135 (11): 3495–3512. doi:10.1093/brain/aws129. PMC 3501967. PMID 22641838.
- ^ Adams, Rick A.; Perrinet, Laurent U.; Friston, Karl (2012). "Smooth Pursuit and Visual Occlusion: Active Inference and Oculomotor Control in Schizophrenia". PLOS ONE. 7 (10): e47502. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...747502A. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0047502. PMC 3482214. PMID 23110076.
- ^ Yon, Daniel; Lange, Floris P. de; Press, Clare (2019-01-01). "The Predictive Brain as a Stubborn Scientist". Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 23 (1): 6–8. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2018.10.003. PMID 30429054. S2CID 53280000.
 KSF
KSF



























![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\underset {\mathrm {free-energy} }{\underbrace {F(\mu ,a\,;s)} }}&={\underset {\text{expected energy}}{\underbrace {\mathbb {E} _{q({\dot {\psi }})}[-\log p({\dot {\psi }},s,a,\mu \mid \psi )]} }}-{\underset {\mathrm {entropy} }{\underbrace {\mathbb {H} [q({\dot {\psi }}\mid s,a,\mu ,\psi )]} }}\\&={\underset {\mathrm {surprise} }{\underbrace {-\log p(s)} }}+{\underset {\mathrm {divergence} }{\underbrace {\mathbb {KL} [q({\dot {\psi }}\mid s,a,\mu ,\psi )\parallel p_{\text{Bayes}}({\dot {\psi }}\mid s,a,\mu ,\psi )]} }}\\&\geq {\underset {\mathrm {surprise} }{\underbrace {-\log p(s)} }}\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/79cb2e8de6a300308d27a3f3d57f752de677151e)

![{\displaystyle \lim _{T\to \infty }{\frac {1}{T}}{\underset {\text{free-action}}{\underbrace {\int _{0}^{T}F(s(t),\mu (t))\,dt} }}\geq \lim _{T\to \infty }{\frac {1}{T}}\int _{0}^{T}{\underset {\text{surprise}}{\underbrace {-\log p(s(t)\mid m)} }}\,dt=H[p(s\mid m)]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/45e9af1ac3447400ff76b1a3d8d09dbae0ea2542)
![{\displaystyle {\underset {\text{free-energy}}{\underbrace {F(s,\mu )} }}={\underset {\text{complexity}}{\underbrace {D_{\mathrm {KL} }[q(\psi \mid \mu )\parallel p(\psi \mid m)]} }}-{\underset {\mathrm {accuracy} }{\underbrace {E_{q}[\log p(s\mid \psi ,m)]} }}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1485673d77ce7c702ff0e37885de968ebae63e26)














