Gulf of Thailand
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 15 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 15 min
| Gulf of Thailand | |
|---|---|
| |
 Location of the Gulf of Thailand | |
| Location | Southeast Asia |
| Coordinates | 09°30′N 102°00′E / 9.500°N 102.000°E |
| Type | Gulf |
| Primary inflows | South China Sea |
| Basin countries | |
| Surface area | 320,000 km2 (120,000 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 58 m (190 ft) |
| Max. depth | 85 m (279 ft) |
The Gulf of Thailand (Thai: อ่าวไทย), historically known as the Gulf of Siam (Thai: อ่าวสยาม), is a shallow inlet[1][2] adjacent to the southwestern South China Sea, bounded between the southwestern shores of the Indochinese Peninsula and the northern half of the Malay Peninsula. It is around 800 km (500 mi) in length and up to 560 km (350 mi) in width, and has a surface area of 320,000 km2 (120,000 sq mi).[3][4] The gulf is surrounded on the north, west and southwest by the coastlines of Thailand (hence the name), on the northeast by Cambodia and the Mekong Delta region of Vietnam, and opens to the South China Sea in the southeast.
Names
[edit]The modern Thai name of the gulf is Ao Thai (Thai: อ่าวไทย, [ʔàːw tʰāj] ⓘ, 'Thai Gulf') and "Gulf of Thailand" has been adopted as the official name of the body by the International Hydrographic Organization.[5][when?] Its name in Malay is "Gulf of Siam", Teluk Siam or in Jawi script: تلوق سيم, and in Khmer: ឈូងសមុទ្រសៀម, Chhoung Samut Siem. In Thai, the gulf is historically known as Ao Sayam (Thai: อ่าวสยาม).[6] In Vietnamese it is known as Vịnh Thái Lan.
It is generally identified with the Great Gulf (Latin: Magnus Sinus) known to Greek, Roman, Arab, Persian, and Renaissance cartographers before the influx of Portuguese explorers removed the phantom Dragon Tail peninsula from European world maps in the 16th century.
Etymology
[edit]
The Gulf of Thailand, historically known as the Gulf of Siam, derives its name from the historical kingdom of Siam, the former name of modern-day Thailand. The term "Gulf of Siam" was widely used in Western cartography and geographical references up until the mid-20th century, reflecting the colonial-era practice of naming regions based on the prevalent local political entities at the time.
"Siam" itself is an exonym, believed to have origins in the Sanskrit word "Syama," which means "dark" or "brown," referring to the skin tone of the region's inhabitants. The term "Siam" was used internationally until 1939, when the country officially changed its name to Thailand. Following this renaming, "Gulf of Thailand" gradually became the more commonly used term, especially in official contexts, although "Gulf of Siam" is still occasionally used.
Geography
[edit]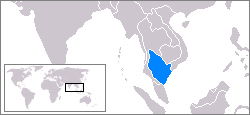
The Gulf of Thailand is bordered by Cambodia, Thailand, Malaysia, and Vietnam.[7][8] It occupies a seabed area of 304,000 km2 from 6° N to 13°30' N latitude and 99°E to 104° E longitude.[9]: 250 The northern tip of the gulf is the Bay of Bangkok at the mouth of the Chao Phraya River. The southern boundary of the gulf is defined by a line from Cape Bai Bung in southern Vietnam (just south of the mouth of the Mekong River) to the town of Tumpat and Pengkalan Chepa on the Malaysian coast.
The gulf is relatively shallow: its mean depth is 58 metres (190 ft) and the maximum depth is only 85 metres (279 ft).[9]: 250 This makes water exchange slow, and the strong water inflow from the rivers reduces the level of salinity in the gulf (3.05–3.25 percent) and enriches the sediments. Only at greater depths does water with a higher salinity (3.4 percent) flow into the gulf from the South China Sea. It fills the central depression below a depth of 50 metres (160 ft). The main rivers which empty into the gulf are the Chao Phraya, including its distributary Tha Chin River, the Mae Klong, and Bang Pakong rivers at the Bay of Bangkok, and to a lesser degree the Tapi River flowing into Bandon Bay in the southwest of the gulf.
The International Hydrographic Organization defines the southern limit of the gulf as "[a] line running from the Western extreme of Cambodia or Camau Point (8°36'N) to the Northern extreme of the point on the East side of the estuary of the Kelantan River (6°14′N 102°15′E / 6.233°N 102.250°E)".[5]
Seabed morphology
[edit]The seabed morphology in the central depression of the gulf is characterised by the presence of elongated mounds and ridges arranged parallel to the axis of the basin. This morphology, widespread within the gulf in water depths exceeding 50 m, covers an area of tens of thousands of square kilometres.
It reflects an interaction between sediment dewatering and the erosional activity of the present-day bottom currents.[10] The sediment dewatering and fluid seepage result in the formation of numerous small pits and pockmarks. The long-term erosion imposed by currents of stable orientation modifies pockmarks into long runnels and depressions, and ultimately leads to the formation of the large fields of elongated mounds and ridges, as well as the residual outliers of un-eroded mud and clay sheets.[10]
Bays
[edit]- Thailand
- Cambodia
- Bay of Kompong Som (Chhak Kompong Som)
- Veal Rinh Bay
- Kep Bay
- Chhak Koh Kong
- Vietnam
- Vinh Thuan Yen
- Vinh Ba Hon
- Vinh Hon Chong
Islands
[edit]The larger islands in the gulf include:
- Ko Chang
- Ko Mak
- Ko Kut
- Ko Samui
- Ko Pha Ngan
- Ko Tao
- Ko Phaluai
- Ko Sichang
- Ko Lan
- Ko Phai
- Ko Khram
- Ko Samae San
- Ko Samet
- Ko Rang
- Ko Khangkhao
- Ko Man Nok
- Ko Wai
- Ko Phi
- Ko Kham
- Ko Sai
- Ko Kra
- Ko Losin
- Phú Quốc
- Thổ Chu Islands
- Hà Tiên Islands
- Bà Lụa Islands
- Nam Du Islands
- Koh Kong
- Koh Rong
- Koh Sdach
- Koh Rong Sanloem
- Koh Puos
- Koh Dek Koul
- Koh Russei
- Koh Ta Kiev
- Koh Preab
- Koh Thmei
- Koh Seh
- Koh Ach Seh
- Koh Tonsay
- Koh Tang
- Koh Pring
- Koh Poulo Wai
History
[edit]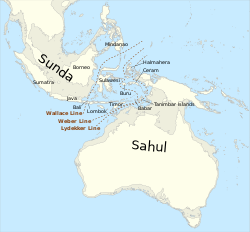
During the Last Glacial Maximum (26,000-20,000 years ago) the 3-4 km thick ice sheets in the Northern hemisphere lowered the global sea level by about 120 meters. The climate was -6 Celsius colder in Thailand. There was no seawater in the Gulf of Thailand since the sea-level was below the max depth of 85 meters. There was a great lake filled with fresh water from rivers and rain. The Mainland was connected by land with the former islands of Western Indonesia in Maritime Southeast Asia. The landmass Sundaland existed until circa 15000 years ago.
Environment
[edit]
Coral reefs
[edit]There are 75,590 rai of coral reef in the gulf, of which five percent are considered to be in fertile condition. In 2010 severe coral bleaching occurred at most reef sites in the country. Bleaching of reefs in the Andaman Sea was more severe and extensive than that in the Gulf of Thailand.[11] In 2016, coral bleaching was detected at Ko Thalu and Ko Lueam in Prachuap Khiri Khan Province for the first time.[12] Scientists have determined that bleaching starts when seawater temperature rises beyond 30 °C for more than three weeks. Given the prolonged period of temperatures up to 32 °C at Ko Thalu in Prachuap Khiri Khan, five to ten percent of corals in the area are already bleached.[13]
Water quality
[edit]Coastal water monitoring results in 2015 from 202 sampling locations, collected twice annually, indicate that no Thai coastal waters were found to be in excellent condition. Sixteen percent of coastal water was of good quality, 72 percent was of fair quality, 9 percent was of poor quality and 3 percent was of very poor quality. The quality of all coastal waters exhibited similar percentages — most were of fair quality — except for the Inner Gulf of Thailand, where the coastal water was poor to very poor. In comparison to coastal water quality as measured in 2014, water quality has deteriorated.[14]: 52 Some gulf waters off Chachoengsao Province, Samut Sakhon Province, Samut Prakan Province, Bangkok, Rayong Province, Chonburi Province, Phetchaburi Province, Prachuap Khiri Khan Province, and Surat Thani Province were judged to have coastal waters in "poor" or "very poor" condition.[14]: 54 Songkhla was the only province on the gulf with coastal water rated "good" quality.[14]: 56
Fisheries
[edit]Of Thailand's total marine catch, 41 percent is caught in the Gulf of Thailand and 19 percent in the Andaman Sea. Forty percent is caught in waters outside Thailand's EEZ.[11]
Coastal erosion
[edit]Thailand has 1,660 kilometres of coastline bordering the gulf. "Severe erosion", more than five metres of coastline loss per year, afflicts 670 kilometres of that total. At least some of the erosion is attributable to the clearing of mangrove forests to make way for shrimp farms.[15]
Plastic pollution
[edit]In February 2017, a 10 kilometer-long patch of plastic refuse was found floating off Chumphon Province.[16] Thailand is among the world's worst plastic polluters. More than half of "land-based plastic waste leakage" into the sea originates from just five countries: China, Indonesia, the Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam.[17]
The Thai Marine and Coastal Resources Department has noted that at least 300 sea animals on average—60 per cent of which are whales and dolphins—die from eating plastic fishing gear and trash each year.[16] Filter feeding invertebrates tested off the coast of Chonburi Province showed high levels of microplastics, leading the authors to warn that, "Health risks are possible when people consume these contaminated marine organisms, particularly shellfish."[18]
Thailand's Pollution Control Department (PCD) estimates that plastic waste in the country is increasing at an annual rate of 12 percent, or around two million tonnes per year.[16]
Oil spills
[edit]In 2013, a pipeline leak resulted in an oil slick that went on to coat a beach on the nearby Ka Samet island.[19]
In late January 2022, a leak in the pipeline operated by the Star Petroleum Refining Public Company Ltd caused a spill of 20 to 50 tonnes across 47 km2 of water, with some oil reaching the coast of Rayong province 20 km away.[19][20]
Tourism
[edit]

The gulf's many coral reefs have made it attractive to divers. The tropical warmth of the water attracts many tourists. Some of the most important tourist destinations in the Gulf of Thailand are the islands of Ko Samui and Ko Pha Ngan in Surat Thani Province, Pattaya in Chonburi Province, Cha-am in Phetchaburi Province, Hua Hin in Prachuap Khiri Khan Province, and Ko Samet in Rayong Province.
In recent years, the bay has become known for its whale watching activities, targeting the endemic, critically endangered populations of cetaceans (Eden's whales, newly described Omura's whales,[21] Chinese white dolphins, and Irrawaddy dolphins showing unique feeding behaviors), and dugongs.[22][23][24] It was first classified by Müller in 1776 as Trichechus dugon.[25] Five species of the sea turtles have been found in the Gulf of Thailand and the Andaman sea coast, including olive ridley turtles, green turtles, hawksbill turtles, loggerhead turtles, and leatherback turtles.[26]
Territorial disputes
[edit]The area between Malaysia, Thailand, Cambodia, and Vietnam is subject to several territorial disputes. Malaysia and Thailand have chosen to jointly develop the disputed areas, which include the islands of Ko Kra and Ko Losin.[27] A long-standing dispute between Cambodia and Vietnam in the Gulf of Thailand concerns mainly the island of Phú Quốc or Koh Tral in Khmer, which is off the Cambodian coast.[28] Cambodia also claims 48,000 square kilometres (19,000 sq mi) of shelf area.[29][30]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Marine Gazetteer browser". Marineregions org. Retrieved June 6, 2016.
- ^ "Thailand, Gulf of". Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on October 30, 2014. Retrieved June 6, 2016.
- ^ "Marine Gazetteer Placedetails - Gulf of Thailand". Marineregions org. Retrieved June 6, 2016.
- ^ "Gulf of Thailand". Deepseawaters.com. Retrieved June 7, 2016.
- ^ a b "Limits of Oceans and Seas" (PDF) (3 ed.). International Hydrographic Organization. 1953. p. 23. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 October 2011. Retrieved 28 December 2020.
- ^ ระยะทางเสด็จฯ ประพาสชายทะเลอ่าวสยาม พ.ศ. 2470 [A report on the royal travel through the Gulf of Siam, 1927] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette (in Thai). 88 (D): 44. 1927-05-22. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 8, 2014. Retrieved 2014-03-08.
- ^ "Map of Gulf of Thailand, Gulf of Thailand Location Facts, Major Bodies of Water, South China Sea". World Atlas. Retrieved 29 July 2018.
- ^ "Gulf of Thailand". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 29 July 2018.
- ^ a b Khongchai, Narongsak; Vibunpant, Somchai; Eiamsa-ard, Monton; Supongpan, Mala. "Preliminary Analysis of Demersal Fish Assemblages in Coastal Waters of the Gulf of Thailand" (PDF). Worldfish. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 19 Feb 2015.
- ^ a b Puchala, R. (2014), Morphology and origin of modern seabed features in the central basin of the Gulf of Thailand, doi:10.13140/RG.2.1.3891.0808
- ^ a b Oceans in the Balance, Thailand in Focus (PDF). Bangkok: Greenpeace Southeast Asia (Thailand). c. 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 September 2015. Retrieved 11 July 2017.
- ^ Wipatayotin, Apinya (2016-04-04). "Rising sea temps bring coral bleaching to Gulf". Bangkok Post. Retrieved 4 April 2016.
- ^ Rujivanarom, Pratch (2018-05-29). "More coral reefs damaged by mass bleaching". The Nation. Archived from the original on 2022-08-15. Retrieved 2 June 2018.
- ^ a b c Thailand State of Pollution Report 2015 (PDF). Bangkok: Pollution Control Department, Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment (Thailand). 2016. ISBN 978-616-316-327-1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 September 2017. Retrieved 5 September 2017.
- ^ Wipatayotin, Apinya (10 December 2017). "Shoring up defences". Bangkok Post Spectrum. Vol. 10, no. 50. Retrieved 10 December 2017.
- ^ a b c Wonggruang, Piyaporn (6 May 2018). "SPECIAL REPORT: Alarm raised as Thailand drowns in plastic trash". The Nation. Archived from the original on 28 May 2022. Retrieved 6 May 2018.
- ^ Stemming the Tide: Land-based strategies for a plastic- free ocean (PDF). Ocean Conservancy-McKinsey Center for Business and Environment. September 2015. p. 3. Retrieved 6 May 2018.
- ^ Thushari, GGN; Senevirathna, JDM; Yakupitiyage, A; Chavanich, S (2017-11-15). "Effects of microplastics on sessile invertebrates in the eastern coast of Thailand: An approach to coastal zone conservation". Marine Pollution Bulletin. 124 (1): 349–355. Bibcode:2017MarPB.124..349T. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.06.010. PMID 28760587.
- ^ a b "Thailand rushes to contain oil spill after undersea leak". France 24. Agence France-Presse. 27 January 2022.
- ^ Wongcha-um, Panu (29 January 2022). Coates, Stephen (ed.). "Thai beach declared disaster area after oil spill". Reuters.
- ^ "มารู้จักวาฬโอมูระ สัตว์ทะเลในบัญชีสัตว์สงวนชุดใหม่" [Come to know Omura's whale, marine animal in the new reserve animal account]. DMCR (in Thai). 2019-05-13.
- ^ "Dugongs and seagrass in Thailand: Present status and future challenges" (PDF). Phuket Marine Biological Center and Department of Marine and Coastal Resources. pp. 41–50. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 4, 2016. Retrieved June 7, 2016.
- ^ "Conservation of the Dugong (Dugong Dugon) on the Eastern Coast of the Gulf of Thailand" (PDF). Ocean Park Conservation Foundation Aberdeen, Hong Kong & Project Aware, Australia. May 1, 2004. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 8, 2015. Retrieved June 7, 2016.
- ^ Marsh, H. et al. (2002). Dugong: status reports and action plans for countries and territories Archived 2007-05-08 at the Wayback Machine. IUCN.
- ^ Dugong dugon. The Paleobiology Database. Retrieved on 22 July 2007.
- ^ Boonngok, Papitchaya (22 June 2009). "Threatened sea turtles have Thai navy for protection". Reuters. Retrieved 11 August 2021.
- ^ "Defining areas for joint development in disputed waters - Malaysia–Thailand p. 13". University of Wollongong. Retrieved June 7, 2016.
- ^ Prescott, J. R. V. (1978). Boundaries and Frontiers. Rowman and Littlefield. ISBN 978-0847660865.
- ^ Dzurek, Daniel J. (2005). "Maritime Agreements and Oil Exploration in the Gulf of Thailand". In Ganster, Paul; Lorey, David E. (eds.). Borders and Border Politics in a Globalizing World. Lanham: S.R. Books. pp. 301–313. ISBN 0-8420-5104-X. [Reprint of Dzurek, Daniel J. (1998). "Maritime Agreements and Oil Exploration in the Gulf of Thailand". In Blake, Gerald; Pratt, Martin; Schofield, Clife; Brown, Janet Allison (eds.). Boundaries and Energy: Problems and Prospects. London: Kluwer Law. pp. 117–135. ISBN 90-411-0690-1.]
- ^ Schofield, Clive (2008). "Maritime Claims, Conflicts and Cooperation in the Gulf of Thailand". Ocean Yearbook Online. 22: 75–116. doi:10.1163/221160008x00064.
 KSF
KSF