Hebron Governorate
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 10 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 10 min
31°30′N 35°06′E / 31.5°N 35.1°E
Hebron Governorate | |
|---|---|
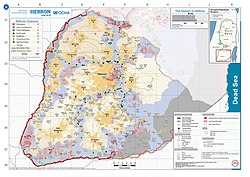 2018 United Nations map of the area, showing the Israeli occupation arrangements in the governorate | |
 | |
 | |
| Country | |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,060 km2 (410 sq mi) |
| Population (2017 Census)[1] | |
• Total | 711,223 |
| This figure excludes the Israeli West Bank settlements | |
| ISO 3166 code | PS-HBN |
| Governorates of the West Bank (Palestine) |
|---|
The Hebron Governorate (Arabic: محافظة الخليل, romanized: Muḥāfaẓat al-Khalīl) is an administrative district of Palestine in the southern West Bank.
The governorate's land area is 1,060 square kilometres (410 sq mi) and its population according to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics in mid-year 2019 was 1,004,510. This makes the Hebron Governorate the largest of 16 governorates in both population and land area in the Palestinian territories.[2] The city of Hebron is the district capital or muhfaza (seat) of the governorate. The governor is Hussein al-Araj and its district commander[ambiguous] is Abdel Fattah al-Ju’eidi.[3]
During the first six months of the First Intifada 42 people in Hebron Governorate were killed by the Israeli army.[4]
Emirates proposal
[edit]The Wall Street Journal reported in July 2025 that a group of sheikhs of the Jaabari clan in Hebron, led by Wadee’ al-Jaabari, had penned a joint letter to Israeli economy minister Nir Barkat proposing to leave the Palestinian Authority to join the Abraham Accords and set up an "Emirate of Hebron". This plan had previously been proposed by Israeli scholar Mordechai Kedar, which would have Palestinian clans rule their local territories, rather than the PA or Hamas, modeled on the United Arab Emirates system. Jaabari met with a WSJ writer and later a Jerusalem Post writer, and said the sheikhs reject the Oslo Accords, do not trust the Palestinian Authority, and want a new solution. The plan will create a special economic zone and allow thousands of Hebron residents to work in Israel, which stopped after the October 7 attacks.[5][6]
Localities
[edit]The Hebron Governorate has a total of seven cities and eighteen towns. The governorate also contains more than 100 Bedouin villages and settlements that are not listed below.[2]
Cities
[edit]- Dura
- Halhul
- Hebron (capital)
- Yatta
- ad-Dhahiriya
Municipalities
[edit]The following localities have municipality status from the Ministry of Local Government of the Palestinian National Authority.
|
|
Village councils
[edit]The following have populations over 1,000 persons.
|
|
Refugee camps
[edit]Demographics
[edit]| Year | Muslims | Christians | Jews | Total | Notes and sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1538 | 749 h | 7 h | 20 h | 776 h | (h = households), Cohen & Lewis[7] |
| 1774 | 300 | Azulai[8] | |||
| 1817 | 500 | Israel Foreign Ministry[9] | |||
| 1820 | 1,000 | William Turner[10] | |||
| 1824 | 60 h | (40 h Sephardim, 20 h Ashkenazim), The Missionary Herald[11] | |||
| 1832 | 400 h | 100 h | 500 h | (h = households), Augustin Calmet, Charles Taylor, Edward Robinson[12] | |
| 1837 | 423 | Montefiore census | |||
| 1838 | c. 6000–7,000 | "few" | 700 | 7–8,000 | William McClure Thomson[13] |
| 1839 | 1295 f | 1 f | 241 | (f = families), David Roberts[14][15] | |
| 1840 | 700–800 | James A. Huie[16] | |||
| 1851 | 11,000 | 450 | Official register[17] | ||
| 1851 | 400 | Clorinda Minor[18] | |||
| 1866 | 497 | Montefiore census | |||
| 1871–2 | 2,800 h | 200 h | 3,000 h | Ottoman records for the Syrian provincial sālnāme for these years[19] | |
| 1875 | 8,000–10,000 | 500 | Albert Socin[17] | ||
| 1875 | 17,000 | 600 | Hebron Kaymakam[17] | ||
| 1881 | 1,000–1,200 | PEF Survey of Palestine[17] | |||
| 1881 | 800 | 5,000 | The Friend[20] | ||
| 1890 | 1,490 | Jewish Encyclopedia | |||
| 1895 | 1,400 | [21] | |||
| 1906 | 1,100 | 14,000 | (690 Sephardim, 410 Ashkenazim), Jewish Encyclopedia | ||
| 1922 | 16,074 | 73 | 430 | 16,577 | 1922 census of Palestine[22] |
| 1929 | 700 | Israel Foreign Ministry[9] | |||
| 1930 | 0 | Israel Foreign Ministry[9] | |||
| 1931 | 17,277 | 109 | 134 | 17,532 | 1931 census of Palestine[23] |
| 1938 | 0 | 20,400 | Village Statistics, 1938[24] | ||
| 1945 | 24,400 | 150 | 0 | 24,560 | Village Statistics, 1945[25] |
| 1961 | 37,868 | Jordanian census[26][27] | |||
| 1967 | 38,073 | 136 | 38,348 | Israeli census[28] | |
| 1997 | n/a | n/a | 119,093 | Palestinian census[29] | |
| 2007 | n/a | n/a | 163,146 | Palestinian census[30] |
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Main Indicators by Type of Locality - Population, Housing and Establishments Census 2017" (PDF). Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2021-01-28. Retrieved 2021-01-19.
- ^ a b Hebron Governorate Statistical Yearbook No. 2; Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine. pp. 59, 60. PCBS, November 2010.
- ^ Hébron
- ^ B'Tselem information sheet (July 1989). p. 4.
- ^ Bob, Yonah Jeremy (July 6, 2025). "Reporter's Notebook: 'Post' meets with top Hebron sheikh who wants to pull out of PA". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved July 6, 2025.
- ^ "The unusual letter from the sheikhs of Hebron: Recognize the 'Emirate of Hebron' and we will recognize Israel". Ynet. Yedioth Ahronoth. Retrieved July 6, 2025.
- ^ Lewis, Bernard; Cohen, Amnon (March 8, 2015). Population and Revenue in the Towns of Palestine in the Sixteenth Century. Princeton University Press. p. 109. ISBN 978-1-4008-6779-0.
- ^ רבי חיים יוסף דוד אזולאי, Meir Benayhu, Mosad Harav Kook, 1959.
- ^ a b c "Hebron". Jewish Virtual Library.
- ^ Turner, W. (1820). Journal of a tour in the Levant. Vol. 2. John Murray. p. 261. Retrieved February 21, 2012.
- ^ "American Board of Foreign Missions: Palestine Mission". The Missionary Herald. March 1825. p. 65.
- ^ Augustin Calmet (1832). Dictionary of the Holy Bible. Crocker and Brewster. p. 488. ISBN 978-1-4047-8796-4.
{{cite book}}: ISBN / Date incompatibility (help) - ^ William McClure Thomson, The Land and the Book, Southern Palestine and Jerusalem, p. 275
- ^ Robinson, p. 88
- ^ David Roberts, The Holy Land – 123 Coloured Facsimile Lithographs and The Journal from his visit to the Holy Land. Terra Sancta Arts. 1982. ISBN 978-965-260-001-1. Plate III – 13. Journal entry March 17, 1839.
- ^ James A. Huie (1840). The history of the Jews, from the taking of Jerusalem by Titus to the present time [by J.A. Huie]. p. 242.
- ^ a b c d PEF Survey of Western Palestine, Volume III, p. 309
- ^ Clorinda Minor (1851). Meshullam!: Or, Tidings from Jerusalem. Arno Press. p. 58. ISBN 978-0-405-10302-5.
{{cite book}}: ISBN / Date incompatibility (help) - ^ Alexander Scholch (Schölch), "The Demographic Development of Palestine, 1850-1882". International Journal of Middle East Studies Vol. 17, No. 4. (November 1985). p. 486.
- ^ "Jewish Life in the East". The Friend. Vol. 54–55. May 28, 1881. p. 333.
- ^ Tzvi Rabinowicz (1996). The Encyclopedia of Hasidism. Jason Aronson. ISBN 978-1-56821-123-7.
- ^ Barron, 1923, Table V, Sub-district of Hebron, p. 10
- ^ Jessie Sampter (2007). Modern Palestine – A Symposium. Read Books. ISBN 978-1-4067-3834-6.
- ^ Village Statistics (PDF). 1938. p. 52.
- ^ Government of Palestine (1945), A Survey of Palestine, Vol. 1, p. 151
- ^ First Census, Government of Jordan. 1964, p. 06
- ^ West Bank, Volume 1 Table I – West Bank population according to 1967 census and Jordanian 1961 census, Levy Economics Institute
- ^ West Bank, Volume 1 Table 4 – Population by religion, sex, age, and type of settlement, Levy Economics Institute
- ^ "Palestinian Census 1997". Archived from the original on November 15, 2010.
- ^ The last official census in 2007 gave 165,000.2007 Locality Population Statistics Archived 2010-12-10 at the Wayback Machine Hebron Governorate Population, Housing and Establishment Census 2007 Archived 2012-03-04 at the Wayback Machine. Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS).
 KSF
KSF
