Judaeo-Spanish
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 52 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 52 min
| Judaeo-Spanish | |
|---|---|
| Ladino | |
| |
 Judeoespañol in Solitreo and Rashi scripts | |
| Pronunciation | [dʒuˈðeo‿spaˈɲol] ⓘ[a] |
| Native to | Spain, Israel, Turkey, Greece (12 reported 2017), Bosnia and Herzegovina (2 as of 2022), Morocco (Ḥaketía dialect), Brazil (Ḥaketía dialect), Algeria (Tetuani Dialect) |
| Region | Mediterranean Basin (native region), formerly also the Americas |
| Ethnicity | Sephardic Jews |
Native speakers | 51,000 (2018)[1] |
Indo-European
| |
Early forms | |
| Dialects | |
| Mainly Latin alphabet; also Hebrew (normally using Rashi or Solitreo); formerly Greek, Cyrillic and Aljamiado (Perso-Arabic) | |
| Official status | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | lad Ladino |
| ISO 639-3 | lad Ladino |
| Glottolog | ladi1251 Ladino |
| ELP | Ladino |
| Linguasphere | … 51-AAB-bd 51-AAB-ba … 51-AAB-bd |
| IETF | lad |
 Historical Judeo-Spanish speech communities in the Mediterranean. Ringed circles represent modern speech communities. | |
Judaeo-Spanish or Judeo-Spanish (autonym Djudeo-Espanyol, Hebrew script: גֿודֿיאו-איספאנייול),[3] also known as Ladino or Judezmo or Spaniolit, is a Romance language derived from Castilian Old Spanish.
Originally spoken in Spain, and then after the Edict of Expulsion spreading through the Ottoman Empire (the Balkans, Turkey, West Asia, and North Africa) as well as France, Italy, the Netherlands, Morocco, and England, it is today spoken mainly by Sephardic minorities in more than 30 countries, with most speakers residing in Israel.[4] Although it has no official status in any country, it has been acknowledged as a minority language in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Israel, and France. In 2017, it was formally recognised by the Royal Spanish Academy.[5]
The core vocabulary of Judaeo-Spanish is Old Spanish, and it has numerous elements from the other old Romance languages of the Iberian Peninsula: Old Aragonese, Asturleonese, Old Catalan, Galician-Portuguese, and Andalusi Romance.[6] The language has been further enriched by Ottoman Turkish and Semitic vocabulary, such as Hebrew, Aramaic, and Arabic—especially in the domains of religion, law, and spirituality—and most of the vocabulary for new and modern concepts has been adopted through French and Italian. Furthermore, the language is influenced to a lesser degree by other local languages of the Balkans, such as Greek, Bulgarian, and Serbo-Croatian.[7]
Historically, the Rashi script and its cursive form Solitreo have been the main orthographies for writing Judaeo-Spanish. However, today it is mainly written with the Latin alphabet, though some other alphabets such as Hebrew and Cyrillic are still in use. Judaeo-Spanish has been known also by other names, such as: Español (Espanyol, Spaniol, Spaniolish, Espanioliko), Judió (Judyo, Djudyo) or Jidió (Jidyo, Djidyo), Judesmo (Judezmo, Djudezmo), Sefaradhí (Sefaradi) or Ḥaketía (in North Africa).[8] In Turkey, and formerly in the Ottoman Empire, it has been traditionally called Yahudice in Turkish, meaning the 'Jewish language.' In Israel, Hebrew speakers usually call the language Ladino, Espanyolit or Spanyolit.
Judaeo-Spanish, once the Jewish lingua franca of the Adriatic Sea, the Balkans, and the Middle East, and renowned for its rich literature, especially in Salonika, today is under serious threat of extinction. Most native speakers are elderly, and the language is not transmitted to their children or grandchildren for various reasons; consequently, all Judeo-Spanish-speaking communities are undergoing a language shift. In 2018, four native speakers in Bosnia were identified;[9] however, two of them have since died, David Kamhi in 2021[10] and Moris Albahari in late 2022.[11] In some expatriate communities in Spain, Latin America, and elsewhere, there is a threat of assimilation by modern Spanish. It is experiencing, however, a minor revival among Sephardic communities, especially in music.
Name
[edit]
The scholar Joseph Nehama, author of the comprehensive Dictionnaire du judéo-espagnol, referred to the language as Judeo-Espagnol.[12] The 1903 Hebrew–Judeo-Spanish Haggadah entitled "Seder Haggadah shel pesaḥ ʿim pitron be-lashon sefaradi" (סדר הגדה של פסח עם פתרון בלשון ספרדי), from the Sephardic community of Livorno, Italy, refers to the language used for explanation as the Sefaradi language.[13] The rare Judeo-Spanish-language textbook entitled Nuevo Silibaryo Espanyol, published in Salonica in 1929, referred to the language as Espanyol and lingua Djudeo-Espanyola.[14]
The language is also called Judeo-Espanyol,[note 1] Judeoespañol,[15] Sefardí, Judío, and Espanyol or Español sefardita; Haketia (from Arabic: حكى, romanized: ḥakà 'tell') refers to the dialect of North Africa, especially Morocco. Judeo-Spanish has also been referred to as Judesmo (also Judezmo, Djudesmo or Djudezmo).[16] The dialect of the Oran area of Algeria was called Tétuani after the Moroccan city of Tétouan since many Orani Jews came from there. In Israel, the language is known as Spanyolit or Espanyolit.[17]: 325 The names Djidio, Kasteyano Muestro, and Spanyol de mozotros have also been proposed to refer to the language;[18] regional names to refer to the language include kastiyano viejo, sepharadit, ekseris romeka, yahudije, and musevije.[19]: 98
An entry in Ethnologue claims, "The name 'Judesmo' is used by Jewish linguists and Turkish Jews and American Jews; 'Judeo-Spanish' by Romance philologists; 'Ladino' by laymen, initially in Israel; 'Haketia' by Moroccan Jews; 'Spanyol' by some others."[1] That does not reflect the historical usage. In the Judaeo-Spanish press of the 19th and 20th centuries the native authors referred to the language almost exclusively as Espanyol, which was also the name that its native speakers spontaneously gave to it for as long as it was their primary spoken language. More rarely, the bookish Judeo-Espanyol has also been used since the late 19th century.[20]
In recent decades in Israel, followed by the United States and Spain, the language has come to be referred to as Ladino (Ladino: לאדינו), literally meaning 'Latin'. This name for the language was promoted by the Autoridad Nasionala del Ladino. However, speakers of the language in Israel referred to their mother tongue as Espanyolit or Spanyolit. Native speakers of the language consider the name Ladino to be incorrect, having for centuries reserved the term for the "semi-sacred" language used in word-by-word translations from the Bible, which is distinct from the spoken vernacular.[8] According to linguist Paul Wexler, Ladino is a written language that developed in the eighteenth century and is distinct from spoken Judeo-Spanish.[21] According to the website of the Jewish Museum of Thessaloniki, the cultural center of Sephardic Judaism after the expulsion from Spain,
Ladino is not spoken, rather, it is the product of a word-for-word translation of Hebrew or Aramaic biblical or liturgical texts made by rabbis in the Jewish schools of Spain. In these translations, a specific Hebrew or Aramaic word always corresponded to the same Spanish word, as long as no exegetical considerations prevented this. In short, Ladino is only Hebrew clothed in Spanish, or Spanish with Hebrew syntax. The famous Ladino translation of the Bible, the Biblia de Ferrara (1553), provided inspiration for the translation of numerous Spanish Christian Bibles.[8]
The derivation of the name Ladino is complicated. Before the expulsion of Jews from Spain, the word meant "literary Spanish" as opposed to other dialects,[citation needed] or "Romance" distinct from Arabic.[22] One derivation has Ladino as derived from the verb enladinar, meaning "to translate", from when Jews, Christians and Arabs translated works from Hebrew, Greek, and Arabic into Spanish during the times of Alfonso X of Castile.[19]: 97 (The first European language grammar and dictionary, of Spanish referred to it as ladino or ladina. In the Middle Ages, the word Latin was frequently used to mean simply 'language', particularly one understood: a latiner or latimer meant a translator.) Following the Expulsion, Jews spoke of "the Ladino" to mean the word-for-word translation of the Bible into Old Spanish. By extension, it came to mean that style of Spanish generally in the same way that (among Kurdish Jews) Targum has come to refer to Judeo-Aramaic languages and Arab Jews, sharḥ has come to mean Judeo-Arabic.[citation needed]
Judaeo-Spanish Ladino should not be confused with the Ladin language (Italian: ladino), spoken in part of Northeast Italy. Ladin has nothing to do with Jews or with Spanish beyond being a Romance language, a property that it shares with French, Italian, Portuguese and Romanian.
Origins
[edit]At the time of the expulsion from Spain, the day-to-day language of the Jews of different regions of the peninsula was hardly, if at all, different from that of their Christian neighbours. There may have been some dialect mixing to form a sort of Jewish lingua franca. There was, however, a special style of Spanish used for purposes of study or translation, featuring a more archaic dialect, a large number of Hebrew and Aramaic loanwords and a tendency to render Hebrew word order literally (hal-layla haz-ze "this night" was rendered la noche la esta instead of the normal Spanish esta noche[23]). As mentioned above, authorities confine the term Ladino to that style.[24]
Following the Expulsion of Jews from Spain, the process of dialect mixing continued, but Castilian Spanish remained by far the largest contributor. The daily language was increasingly influenced by both the language of study and the local non-Jewish vernaculars, such as Greek and Turkish. It came to be known as Judesmo and, in that respect, the development is parallel to that of Yiddish. However, many speakers, especially among community leaders, also had command of a more formal style, "castellano", which was closer to the Spanish at the time of the Expulsion.
Source languages
[edit]Spanish
[edit]The grammar, the phonology, and about 60% of the vocabulary of Judaeo-Spanish is essentially Spanish but, in some respects, it resembles the dialects in southern Spain and South America, rather than the dialects of Central Spain. For example, it has yeísmo ("she" is eya/ella [ˈeja] (Judaeo-Spanish), instead of ella) as well as seseo.
In many respects, it reproduces the Spanish of the time of the Expulsion, rather than the modern variety, as it retains some archaic features such as the following:
- Modern Spanish j, pronounced [x], corresponds to two different phonemes in Old Spanish: x, pronounced /ʃ/, and j, pronounced /ʒ/. Judaeo-Spanish retains the original sounds. Similarly, g before e or i remains [d͡ʒ] or /ʒ/, not [x].
- Contrast basho ('low' or 'down,' with /ʃ/, modern Spanish bajo) and mujer ('woman' or 'wife,' spelled the same, with /ʒ/).
- Modern Spanish z (c before e or i), pronounced [s] or [θ], like the th in English think, corresponds to two different phonemes in Old Spanish: ç (c before e or i), pronounced [ts]; and z (in all positions), pronounced [dz]. In Judaeo-Spanish, they are pronounced [s] and [z], respectively.
- Contrast korasón ('heart,' with /s/, modern Spanish corazón) and dezir ('to say,' with /z/, modern Spanish decir).
- In modern Spanish, the use of the letters b and v is determined partly based on earlier forms of the language and partly based on Latin etymology. Both letters represent one phoneme, (/b/), realised as [b] or as [β] according to its position. In Judaeo-Spanish, /b/ and /v/ are different phonemes: boz /bɔs/ 'voice' vs. vos /vɔs/ 'you'. v is a labiodental "v," like in English, rather than a bilabial.
Portuguese and other Iberian languages
[edit]However, the phonology of both the consonants and part of the lexicon is, in some respects, closer to Portuguese and Catalan than to modern Spanish. That is explained by direct influence but also because Portuguese, Old Spanish and Catalan retained some of the characteristics of medieval Ibero-Romance languages that Spanish later lost. There was a mutual influence with the Judaeo-Portuguese of the Portuguese Jews.
Contrast Judaeo-Spanish daínda ('still') with Portuguese ainda (Galician ainda or aínda, Asturian aína or enaína) and Spanish aún or the initial consonants in Judaeo-Spanish fija, favla ('daughter,' 'speech'), Portuguese filha, fala Galician filha or filla, fala, Asturian fía, fala, Aragonese filla, fabla, Catalan filla), Spanish hija, habla. It sometimes varied with dialect, as in Judaeo-Spanish popular songs, both fijo and hijo ('son') are found.
The Judaeo-Spanish pronunciation of s as "[ʃ]" before a "k" sound or at the end of certain words (such as seis, pronounced [seʃ], for 'six') is shared with Portuguese (as spoken in Portugal, most of Lusophone Asia and Africa, and in a plurality of Brazilian varieties and registers with either partial or total forms of coda |S| palatalization) but not with Spanish.
Hebrew and Aramaic
[edit]Like other Jewish vernaculars, Judaeo-Spanish incorporates many Hebrew and Aramaic words, mostly for religious concepts and institutions. Examples are haham ('rabbi', from Hebrew ḥakham) and kal ('synagogue', from Hebrew qahal). Some Judeo-Spanish words of Hebrew or Aramaic origin have more poetic connotations than their Spanish equivalents. Compare gaava ('pride, arrogance') from Hebrew ga'avá with arrogansya ('arrogance') from Spanish arrogancia.
Turkish
[edit]The majority of Judaeo-Spanish speaking people resided in the Ottoman Empire, although a large minority on the northern Coast of Morocco and Algeria existed. As such, words of Turkish origin were incorporated into the local dialect of the language. Examples include emrenear ('rejoice') from Turkish imrenmek.
Some of these words themselves were inherited into Turkish from Arabic or Persian. Examples include bilbiliko ('nightingale'), from Persian (via Turkish) bülbül and gam ('sorrow, anxiety, grief') from Arabic (via Persian then Turkish) ġamm.
The Turkish agentive suffix -ci (denoting a profession) was borrowed into Judaeo-Spanish as the suffix -djí. It can be found in words like halvadjí ('candyman'), derived from halva + -djí.
French
[edit]Due to the influence of the Alliance Israélite Universelle in the westernization and modernization of Judaeo-Spanish speaking communities, many words of French origin were adopted. Most of these words refer to Western European innovations and introductions. Examples include: abazur ('lampshade'), from French abat-jour, fardate ('apply makeup'), from French se farder, and fusil ('gun') from French fusil.[25] Some French political and cultural elements are present in Judaeo-Spanish. For example, ir al Bismark ('to go to the Bismark') was a phrase used in some Judaeo-Spanish communities in the late 20th century to mean 'to go to the restroom', referring to the German Chancellor, Otto von Bismarck (an unpopular figure in France), as a euphemism for toilet.[25]
Arabic
[edit]Because of the large number of Arabic words in Spanish generally, it is not always clear whether some of these words were introduced before the Expulsion or adopted later; modern Spanish replaced some of these loans with Latinisms after the Reconquista, where Judaeo-Spanish speakers had no motivation to do so. Some Arabic words were borrowed via Turkish or Persian.
Haketia, the variety of Judaeo-Spanish spoken in the Maghreb, has substantial influence from Moroccan and Algerian Arabic, as well as local Amazigh languages. The varieties of Judaeo-Spanish spoken in the Levant and Egypt have some influence from Levantine Arabic and Egyptian Arabic respectively.
Other source languages
[edit]Judeao-Spanish speaking communities often incorporated words or phrases from surrounding languages. Greek, South Slavic, Italian, and Romanian borrowings can be found in those respective communities.[26]
Varieties
[edit]
A common way of dividing Judaeo-Spanish is by splitting first Haketia, or "Western Judaeo-Spanish", from other varieties, collectively referred to as "Eastern Judaeo-Spanish".[27] Within Eastern Judaeo-Spanish, further division is made based on city of origin.[28]
Aldina Quintana split Eastern Ladino into three groups:
- Grupo noroccidental (Northwest group), centered around Sarajevo (Bosnia). It also includes the dialects of Bitola (Macedonia) and Kastoria (Greece). The most distinct characteristics of this group are: the reduction of /r/ and /ɾ/ into /ɾ/ and the conservation of ⟨rd⟩ as in ⟨gordo⟩.
- Grupo nororiental (Northeast group) that includes most of (northern) Bulgaria and Romania including Sofia and Bucharest. It represented an intermediate state between the other varieties: the reduction of /r/ and /ɾ/ into /ɾ/, but the metathesis of ⟨rd⟩ into ⟨dr⟩ as in ⟨godro⟩.
- Grupo suroriental (Southeast group) that included the main Sephardic cultural hubs of Salonika (Greece) and Istanbul (Turkiye), as well as the remainder of Anatolia, and Eastern Greece. The varieties of this group maintain the gradient in difference between /e : i/ and /o : u/ in the final position, as well as maintaining a difference between /r/ : /ɾ/. The metathesis of ⟨rd⟩ into ⟨dr⟩ is also present.[29]
While unsorted, the variety of spoken in Judeo-Spanish in Italy (Venice, Trieste, Ferrera) and Budapest more closely followed the Northwest group. Egyptian Judeo-Spanish (Alexandria, Cairo) followed more the patterns of the Southeast Group. Levantine Judeo-Spanish (Jerusalem, Jaffa, Hebron) and Rhodesli Judeo-Spanish represented intermediate states, more similar to the Northeast group. Although Levantine Judeo-Spanish phonology and syntax, especially its usage of [ħ], [ʕ], [ʔ], and [h] was unique enough to be defined separately.
Differences between varieties usually include phonology and lexicon. The dialect spoken in the Macedonian city of Bitola (traditionally referred to as Monastir) has relatively many lexical differences as compared with other varieties of Judeao-Spanish.[25] An example of this can be seen is the word for 'carriage'. In many dialects, such as those that were spoken in Istanbul and Thessaloniki, araba is used, a loanword from Arabic via Turkish, while the Monastir dialect uses karrose, possibly from Italian.[25] The dialect spoken in the Greek island of Rhodes has the unique difference that when a word ends with o, it is pronounced as u.[30]
Phonology
[edit]The number of phonemes in Judaeo-Spanish varies by dialect. Its phonemic inventory consists of 24-26 consonants and 5 vowels.
Consonants
[edit]| Bilabial | Labio- dental |
Dental | Alveolar | Post- alveolar |
Palatal | Velar | Glottal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | (ɲ) | (ŋ) | ||||
| Stop | p b | t d | k ɡ | |||||
| Affricate | t͡ʃ d͡ʒ | |||||||
| Fricative | (β) | f v | (ð) | s z | ʃ ʒ | x (ɣ) | (h) | |
| Trill | r | |||||||
| Tap | (ɾ) | |||||||
| Approximant | l | j | w |
| Bilabial | Labio- dental |
Dental | Alveolar | Post- alveolar |
Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Pharyngeal | Glottal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | |||||||
| Stop | p b | t d | k g | (q) | ||||||
| Affricate | (t͡s) | t͡ʃ d͡ʒ | ||||||||
| Fricative | f v | (ð) | s z | ʃ ʒ | x | (ħ) (ʕ) | (h) | |||
| Trill | (r) | |||||||||
| Tap | ɾ | |||||||||
| Approximant | (ð̞) | j | ||||||||
| Lateral | l |
Notes:
- Most dialects merge /ð~ð̞/ with /d/ and /ħ/ with /x/.
- Some dialects merge the rhotic phonemes. The realization of the merged rhotic is variable, though speakers typically pronounce it as a tap.
- /t͡s/ and /h/ only appear in loanwords. Some dialects merge /t͡s/ with /s/.
- /q/ and /ʕ/ only appear in dialects heavily influenced by Arabic, such as Haketia.
Vowels
[edit]| Front | Back | |
|---|---|---|
| Close | i (y) | u |
| Mid | e (ø) | o |
| Open | a | |
Notes:
- Front rounded vowels only appear in French loanwords. They do not exist in every dialect.
Phonological differences from Spanish
[edit]As exemplified in the Sources section above, much of the phonology of Judaeo-Spanish is similar to that of standard modern Spanish. Here are some exceptions:
- It is claimed that, unlike all other non-creole varieties of Spanish, Judaeo-Spanish does not contrast the trill /r/ and the tap/flap /ɾ/.[33] However, that claim is not universally accepted.[34]
- The Spanish /nue-/ is /mue-/ in some dialects of Judaeo-Spanish: nuevo, nuestro → muevo, muestro.[33]
- The Judaeo-Spanish phoneme inventory includes separate [d͡ʒ] and [ʒ]: jurnal /ʒuɾˈnal/ ('newspaper') vs jugar/djugar /d͡ʒuˈgar/ ('to play'). Neither phoneme is used in modern Spanish,[33] where they have been replaced by the jota [x]: jornal /xor'nal/, jugar /xu'gar/.
- While Spanish pronounces both b and v as /b/ ([b] or [β]), Judeo-Spanish distinguishes between the two, with b representing [b~β] and v representing [v]: bivir /biˈviɾ/ ('to live').
- Judaeo-Spanish has (at least in some varieties) little or no diphthongization of tonic vowels, e.g. in the following lullaby:
- (Judaeo-Spanish text) Durme, durme, kerido ijiko, [...] Serra tus lindos ojikos, [...]
- (Equivalent Spanish) Duerme, duerme, querido hijito, [...] Cierra tus lindos ojitos, [...]
- (Translation) Sleep, Sleep, beloved little son, [...] close your beautiful little eyes, [...]
- There is a tendency to drop [s] at the end of a word or syllable, as in Andalusian Spanish and many other Spanish dialects in Spain and the Americas: amargasteis -> amargátex/amargatesh ('you have embittered').
- The form Dios -> Dio ('God') is sometimes explained as an example of dropping the final [s], or more often as an example of folk etymology: taking the s as a plural ending (which it is not) and attributing it to Christian trinitarianism. Thus, removing the s supposedly produced a more clearly monotheistic word for God. This is probably a folk etymology, however, as dio is an Old Spanish alternative spelling of dios, the former derived from the Latin accusative form deum and the latter from the nominative form deus.
Morphology
[edit]Judaeo-Spanish is distinguished from other Spanish dialects by the presence of the following features:
- Judaeo-Spanish maintains the second-person pronouns tú/tu (informal singular), vos (formal singular) and vosotros/vozotros (plural); the third-person él/ella/ellos/ellas / el/eya/eyos/eyas are also used in the formal register.[33] The Spanish pronouns usted and ustedes do not exist.
- In verbs, the preterite indicates that an action taken once in the past was also completed at some point in the past. That is as opposed to the imperfect, which refers to any continuous, habitual, unfinished or repetitive past action. Thus, "I ate falafel yesterday" would use the first-person preterite form of 'eat', comí/komí but "When I lived in Izmir, I ran five miles every evening" would use the first-person imperfect form, corría/koria. Though some of the morphology has changed, usage is just as in normative Spanish.
- In general, Judaeo-Spanish uses the Spanish plural morpheme /-(e)s/. The Hebrew plural endings /-im/ and /-ot/ are used with Hebrew loanwords, as well as with a few words from Spanish: ladrón/ladron ('thief'): ladrones, ladronim; hermano/ermano ('brother'): hermanos/hermanim / ermanos/ermanim.[35] Similarly, some loaned feminine nouns ending in -á can take either the Spanish or Hebrew plural: quehilá/keilá ('synagogue'): quehilás/quehilot / keilas/keilot.
- Judaeo-Spanish contains more gendering cases than standard Spanish, prominently in adjectives, (grande/-a, inferior/-ra) as well as in nouns (vozas, fuentas) and in the interrogative qualo/quala / kualo/kuala.[33]
Verb conjugation
[edit]Regular conjugation for the present tense:
| -er verbs (comer/komer: "to eat") |
-ir verbs (bivir: "to live") |
-ar verbs (favlar: "to speak") | |
|---|---|---|---|
| yo | -o : como/komo, bivo, favlo | ||
| tú/tu | -es : comes/komes, bives | -as : favlas | |
| él/el, ella/eya | -e : come/kome, bive | -a : favla | |
| mosotros/mozotros, mosotras/mozotras | -emos : comemos/komemos | -imos : bivimos | -amos : favlamos |
| vos, vosotros/vozotros, vosotras/vozotras | -ex/esh : comex/komesh | -ix/ish : bivix/bivish | -ax/ash : favlax/favlash |
| ellos/eyos, ellas/eyas | -en : comen/komen, biven | -an : favlan | |
Regular conjugation in the preterite:
| -er verbs (comer/komer: "to eat") |
-ir verbs (bivir: "to live") |
-ar verbs (favlar: "to speak") | |
|---|---|---|---|
| yo | -í : comí/komi, biví/bivi, favli/favlí | ||
| tú/tu | -ites : comites/komites, bivites | -ates : favlates | |
| él/el, ella/eya | -yó : comió/komió, bivió/bivio | -ó : favló | |
| mosotros/mozotros, mosotras/mozotras | -imos : comimos/komimos, bivimos, favlimos | ||
| vos, vosotros/vozotros, vosotras/vozotras | -ítex/itesh : comítex/komitesh, bivítex/bivitesh | -átex/atesh : favlátex/favlatesh | |
| ellos/eyos, ellas/eyas | -ieron : comieron/komieron, bivieron | -aron : favlaron | |
Regular conjugation in the imperfect:
| -er verbs (comer/komer: "to eat") |
-ir verbs (bivir: "to live") |
-ar verbs (favlar: "to speak") | |
|---|---|---|---|
| yo | -ía : comía/komia, bivía/bivia | -ava : favlava | |
| tú/tu | -ías : comías/komias, bivías/bivias | -avas : favlavas | |
| él/el, ella/eya | -ía : comía/komia, bivía/bivia | -ava : favlava | |
| mosotros/mozotros, mosotras/mozotras | -íamos : comíamos/komiamos, bivíamos/biviamos | -ávamos : favlavamos | |
| vos, vosotros/vozotros, vosotras/vozotras | -íax/iash : comíax/komiash, bivíax/biviash | -avax/avash : favlavax/favlavash | |
| ellos/eyos, ellas/eyas | -ían : comían/komian, bivían/bivian | -avan : favlavan | |
Syntax
[edit]Judaeo-Spanish follows Spanish for most of its syntax. (That is not true of the written calque language involving word-for-word translations from Hebrew, which scholars refer to as "Ladino", as described above.) Like Spanish, it generally follows a subject–verb–object word order, has a nominative-accusative alignment, and is considered a fusional or inflected language.
Orthography
[edit]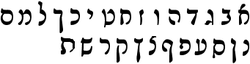
Two Israeli organizations, the Akademia Nasionala del Ladino and the Autoridad Nasionala del Ladino, jointly regulate Judaeo-Spanish orthography. The organizations allow speakers to choose between the Hebrew script, which was historically the most prevalent writing system for the language, and the Latin script, which gained prominence after the fall of the Ottoman Empire.
Hebrew script
[edit]Printed works in Judæo-Spanish use the Rashi script, whereas the handwritten language uses a cursive form of the Hebrew alphabet called Solitreo. In the Hebrew script, a silent ⟨א⟩ must precede word-initial vowels. Moreover, it is necessary to separate adjacent vowels with ⟨א⟩ or ⟨י⟩. Whereas ⟨א⟩ can separate any pair of vowels, ⟨י⟩ can only separate front vowels (/i/ and /e/, both represented by ⟨י⟩) from adjacent vowels. Furthermore, ⟨י⟩ cannot separate diphthongs that include a non-syllabic /u/ ([w]).
Hebrew and Aramaic loanwords and morphemes (except those that were borrowed indirectly through other languages) are spelled according to Hebrew orthography. The rest of the language's lexicon is spelled as illustrated in the following table:
| Grapheme | Name | Phoneme (IPA) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| א | אָלֶף |
|
|
| בּ | בֵּית | /b/ | Only appears in Hebrew and Aramaic loanwords. In native words, the dagesh is unnecessary. |
| ב | בֵית | ||
| (ב׳) בﬞ | בֵית רָפֶה | /v/ | |
| ג | גִימֶל | /g/ | |
| (ג׳) גﬞ | גִﬞימֶל | /d͡ʒ/ | |
| ג׳׳ | גִ׳׳ימֶל | /t͡ʃ/ | |
| ד | דָּלֶת | /d/ | |
| (ד׳) דﬞ | דָּלֶת רָפֶה | /ð/~/ð̞/ | Most dialects merge /ð/~/ð̞/ with /d/. Therefore, Judaeo-Spanish orthography does not always distinguish the two phonemes. |
| ה | הֵא | ||
| ו | וָאו | ||
| ז | זַיִן | /z/ | |
| (ז׳) זﬞ | זַיִן רָפֶה | /ʒ/ | |
| ח | חֵית | /ħ/ | Most dialects merge /ħ/ with /x/. |
| ט | טֵית | /t/ | In Hebrew and Aramaic loanwords, ⟨ט⟩ represents an etymologically pharyngealized /t/. |
| י | יוֹד | ||
| יי | יוֹד ג׳׳יפﬞטי | /j/ | /j/ is represented by a double ⟨יי⟩, except when it is adjacent to a front vowel (/i/ or /e/, both represented by ⟨י⟩). |
| כּ | כַּף | /k/ | Only appears in Hebrew and Aramaic loanwords. |
| כ | כַף | /x/ | Only appears in Hebrew and Aramaic loanwords. |
| ל | לָמֶד | /l/ | |
| מ | מֵם | /m/ | |
| נ | נוּן | /n/ | |
| ני |
|
| |
| ניי | |||
| ס | סָמֶךְ | /s/ | |
| ע | עַיִן | silent | Represents an etymological /ʕ/ in Hebrew and Aramaic loanwords. |
| פּ | פֵּא | /p/ | Only appears in Hebrew and Aramaic loanwords. In native words, the dagesh is unnecessary. |
| פ | פֵא | Cannot represent /f/ in native words (see ⟨פﬞ⟩). | |
| (פ׳) פﬞ | פֵא רָפֶה | /f/ | |
| צ | צָדִי | /t͡s/ | |
| ק | קוֹף | /k/ | Represents an etymological /q/ in Hebrew and Aramaic loanwords. |
| ר | רֵיש | /ɾ/ | |
| ש | שין | /ʃ/ | |
| שׁ | שִׁין | /ʃ/ | Only appears in Hebrew and Aramaic loanwords. |
| שׂ | שִׂין | /s/ | Only appears in Hebrew and Aramaic loanwords, wherein it represents an etymological /ɬ/. |
| ת | תָו | /t/ | Only appears in Hebrew and Aramaic loanwords. |
Notes:
- The Hebrew geresh diacritic is used most often when typing, as it is the most accessible, whereas the diacritic rafe is used in handwriting.
Latin script
[edit]This orthography uses an interpunct ⟨·⟩ to distinguish the sequence /s+x/ (written ⟨s·h⟩) from the /ʃ/ phoneme (written ⟨sh⟩). Writers may also use acute accents to mark irregular stress. The regular stress pattern is as follows:
- Words that end with a vowel or with /n/, /s/, or /ʃ/ are paroxytones.
- Words that end with any other consonant are oxytones.
| Grapheme | Name | Phoneme (IPA) |
|---|---|---|
| a | A | /a/ |
| b | Be | /b/ |
| ch | Che | /t͡ʃ/ |
| d | De | /d/ |
| dj | Dje | /d͡ʒ/ |
| e | E | /e/ |
| f | Ef | /f/ |
| g | Ge | /g/ |
| h | He | /x/ |
| 'h | 'He | /h/ |
| i | I | /i/ |
| j | Je | /ʒ/ |
| k | Ka | /k/ |
| l | El | /l/ |
| m | Em | /m/ |
| n | En | /n/ |
| ny | Nye | /ɲ/ |
| o | O | /o/ |
| ö | Ö | /ø/ |
| p | Pe | /p/ |
| r | Er | /ɾ/ |
| rr | /r/ | |
| s | Es | /s/ |
| sh | She | /ʃ/ |
| t | Te | /t/ |
| ts | /t͡s/ | |
| u | U | /u/ |
| ü | Ü | /y/ |
| v | Ve | /v/ |
| x | Iks | /g+z/ |
| y | Ye | /j/ |
| z | Zed | /z/ |
Historical orthographies
[edit]Prior to the adoption of the official orthographies, the following systems of writing Judaeo-Spanish had been used or proposed.
- Formerly, the Hebrew-script orthography represented an etymological /ʎ/, which has merged with /j/.
- Historically, the most common form of written Ladino was Rashi script, as well as its cursive form, Solitreo.
- The Greek alphabet and the Cyrillic script were used in the past,[37] but this is rare or nonexistent nowadays.
- In Turkey, Judaeo-Spanish was most commonly written in the Turkish variant of the Latin alphabet. That may have been the most widespread system in use prior to the adoption of the official orthography, as following the decimation of Sephardic communities throughout much of Europe (particularly in Greece and the Balkans) during the Holocaust, the greatest proportion of speakers remaining were Turkish Jews.
- The American Library of Congress has published the romanization standard it uses.
- Works published in Spain usually adopted the standard orthography of modern Spanish to make them easier for modern Spanish speakers to read.[38] The editions often used diacritics to show where the Judaeo-Spanish pronunciation differs from modern Spanish.
- Pablo Carvajal Valdés and others suggested adopting the orthography that was used at the time of the Expulsion
History
[edit]In the medieval Iberian Peninsula, now Spain and Portugal, Jews spoke a variety of Romance dialects. Jews in the Middle Ages were instrumental in the development of Spanish into a prestige language. Erudite Jews translated Arabic and Hebrew works, often translated earlier from Greek, into Spanish. Christians translated them again into Latin for transmission to Europe.
Following the 1490s expulsion from Spain and Portugal, most of the Iberian Jews resettled in the Ottoman Empire. Jews in the Ottoman Balkans, Western Asia (especially Turkey), and North Africa (especially Morocco) developed their own Romance dialects, with some influence from Hebrew and other languages, which became what is now known as Judaeo-Spanish. Until recent times, the language was widely spoken throughout the Balkans, Turkey/Western Asia and North Africa, as Judaeo-Spanish had been brought there by the Jewish refugees.[39] Later on, many Portuguese Jews also escaped to France, Italy, the Netherlands and England, establishing small groups in those nations as well, but these spoke Early Modern Spanish or Portuguese rather than Judaeo-Spanish. The contact among Jews of different regions and languages, including Catalan, Leonese and Portuguese developed a unified dialect, differing in some aspects from the Spanish norm that was forming simultaneously in Spain, but some of the mixing may have already occurred in exile rather than in the Iberian Peninsula.
In the 16th century, the development Judeo-Spanish was significantly influenced by the extensive mobility of Sephardic Jews. By the end of the century, Spanish had become the dominant language of commerce for Sephardic communities across Italy and the eastern Mediterranean.[40] This standardization was further supported by practices such as hiring tutors to teach Castilian in Hebrew script, as noted in a 1600 deposition from Pisa. Additionally, itinerant rabbis who preached in the vernacular contributed to the spread and standardization of Judeo-Spanish among diverse Sephardic congregations, including those in Greek- and Arabic-speaking regions.[40]
The closeness and mutual comprehensibility between Judaeo-Spanish and Spanish favoured trade among Sephardim, often relatives, from the Ottoman Empire to the Netherlands and the conversos of the Iberian Peninsula.
Over time, a corpus of literature, both liturgical and secular, developed. Early literature was limited to translations from Hebrew. At the end of the 17th century, Hebrew was disappearing as the vehicle for rabbinic instruction. Thus, a literature appeared in the 18th century, such as Me'am Lo'ez and poetry collections. By the end of the 19th century, the Sephardim in the Ottoman Empire studied in schools of the Alliance Israélite Universelle. French became the language for foreign relations, as it did for Maronites, and Judaeo-Spanish drew from French for neologisms. New secular genres appeared, with more than 300 journals, history, theatre, and biographies.
Given the relative isolation of many communities, a number of regional dialects of Judaeo-Spanish appeared, many with only limited mutual comprehensibility, largely because of the adoption of large numbers of loanwords from the surrounding populations, including, depending on the location of the community, from Greek, Turkish, Arabic and, in the Balkans, Slavic languages, especially Serbo-Croatian and Bulgarian. The borrowing in many Judaeo-Spanish dialects is so heavy that up to 30% of their vocabulary is of non-Spanish origin. Some words also passed from Judaeo-Spanish into neighbouring languages. For example, the word palavra 'word' (Vulgar Latin parabola; Greek parabole), passed into Turkish, Greek and Romanian[41] with the meaning 'bunk, hokum, humbug, bullshit' in Turkish and Romanian and 'big talk, boastful talk' in Greek (compare the English word palaver).
The language was known as Yahudice (Jewish language) in the Ottoman Empire. In the late 18th century, Ottoman poet Enderunlu Fazıl (Fazyl bin Tahir Enderuni) wrote in his Zenanname: "Castilians speak the Jewish language but they are not Jews."

Judaeo-Spanish was the common language of Salonica during the Ottoman period. The city became part of Greece in 1912 and was subsequently renamed Thessaloniki. Despite the Great Fire of Thessaloniki and mass settlement of Christian refugees, the language remained widely spoken in Salonica until the deportation of 50,000 Salonican Jews in the Holocaust during the Second World War. According to the 1928 census, the language had 62,999 native speakers in Greece. The figure drops down to 53,094 native speakers in 1940, but 21,094 citizens "usually" spoke the language.[42] The language was so prominent in Salonica that the most prestigious monument of the city was known by its Judeo-Spanish name, Las Incantadas (meaning "the enchanted women").[43]
Judaeo-Spanish was also a language used in Donmeh rites (Dönme being a Turkish word for 'convert' to refer to adepts of Sabbatai Tsevi converting to Islam in the Ottoman Empire). An example is Sabbatai Tsevi esperamos a ti. Today, the religious practices and the ritual use of Judaeo-Spanish seems confined to elderly generations.
The Castilian colonisation of Northern Africa favoured the role of polyglot Sephards, who bridged between Spanish colonizers and Arab and Berber speakers.
From the 17th to the 19th centuries, Judaeo-Spanish was the predominant Jewish language in the Holy Land, but its dialect was different in some respects from the one in Greece and Turkey. Some families have lived in Jerusalem for centuries and preserve Judaeo-Spanish for cultural and folklore purposes although they now use Hebrew in everyday life.
An often-told Sephardic anecdote from Bosnia-Herzegovina has it that as a Spanish consulate was opened in Sarajevo in the interwar period, two Sephardic women passed by. Upon hearing a Catholic priest who was speaking Spanish, they thought that his language meant that he was Jewish.[7]
In the 20th century, the number of speakers declined sharply: entire communities were murdered in the Holocaust, and many of the remaining speakers, many of whom emigrated to Israel, adopted Hebrew. The government of the new nation-state encouraged instruction in Hebrew. Similarly in the US, Sephardic Jews were encouraged to speak English rather than Judaeo-Spanish, therefore, the language was not passed down to younger generations.[44] In Turkey, where there is a large community of Sephardic Jews, Judaeo-Spanish was considered a language of little prestige; additionally, parents refused to teach their children the language, fearing that their children would develop a "Jewish accent" and therefore face discrimination.[45] At the same time, Judaeo-Spanish aroused the interest of philologists, as it conserved language and literature from before the standardisation of Spanish.
Judaeo-Spanish is in serious danger of extinction. As of 2011, the majority of fluent speakers are over the age of 70; the descendants of these speakers exhibit little to no knowledge of the language.[44] Nevertheless, it is experiencing a minor revival among Sephardic communities, especially in music. In addition, Sephardic communities in several Latin American countries still use Judaeo-Spanish. There, the language is exposed to the different danger of assimilation to modern Spanish.
Kol Yisrael[46] and Radio Nacional de España[47] hold regular radio broadcasts in Judaeo-Spanish. Law & Order: Criminal Intent showed an episode, titled "A Murderer Among Us", with references to the language. Films partially or totally in Judaeo-Spanish include the Mexican film Novia que te vea (directed by Guita Schyfter), The House on Chelouche Street, and Every Time We Say Goodbye.
Efforts have been made to gather and publish modern Judaeo-Spanish fables and folktales. In 2001, the Jewish Publication Society published the first English translation of Judaeo-Spanish folktales, collected by Matilda Koen-Sarano, Folktales of Joha, Jewish Trickster: The Misadventures of the Guileful Sephardic Prankster. A survivor of Auschwitz, Moshe Ha-Elion, issued his translation into Judeo-Spanish of the ancient Greek epic Odyssey in 2012, in his 87th year,[48] and later completed a translation of the sister epic, the Iliad, into his mother tongue.
The language was initially spoken by the Sephardic Jewish community in India, but was later replaced with Judeo-Malayalam.
Literature
[edit]
The first printed Judaeo-Spanish book was Me-'am lo'ez in 1730. It was a commentary on the Bible in the Judaeo-Spanish language. Most Jews in the Ottoman Empire knew the Hebrew alphabet but did not speak Hebrew. The printing of Me-'am lo'ez marked the emergence of large-scale printing activity in Judaeo-Spanish in the western Ottoman Empire and in Istanbul in particular.[49] The earliest Judaeo-Spanish books were religious in nature, mostly created to maintain religious knowledge for exiles who could not read Hebrew; the first of the known texts is Dinim de shehitah i bedikah [The Rules of Ritual Slaughter and Inspection of Animals]; (Istanbul, 1510).[50] Texts continued to be focussed on philosophical and religious themes, including a large body of rabbinic writings, until the first half of the 19th century. The largest output of secular Judaeo-Spanish literature occurred during the latter half of the 19th and the early 20th centuries in the Ottoman Empire. The earliest and most abundant form of secular text was the periodical press: between 1845 and 1939, Ottoman Sephardim published around 300 individual periodical titles.[51] The proliferation of periodicals gave rise to serialised novels: many of them were rewrites of existing foreign novels into Judaeo-Spanish. Unlike the previous scholarly literature, they were intended for a broader audience of educated men and less-educated women alike. They covered a wider range of less weighty content, at times censored to be appropriate for family readings.[52] Popular literature expanded to include love stories and adventure stories, both of which had been absent from Judaeo-Spanish literary canon.[53] The literary corpus meanwhile also expanded to include theatrical plays, poems and other minor genres.
Multiple documents made by the Ottoman government were translated into Judaeo-Spanish; usually translators used terms from Ottoman Turkish.[54]
Religious use
[edit]The Jewish communities of Sarajevo, Bosnia-Herzegovina, and Belgrade, Serbia, still chant part of the Sabbath Prayers (Mizmor David) in Judaeo-Spanish. The Sephardic Synagogue Ezra Bessaroth in Seattle, Washington, United States, was formed by Jews from Turkey and the Greek island of Rhodes, and it uses the language in some portions of its Shabbat services. The Siddur is called Zehut Yosef and was written by Hazzan Isaac Azose.
At Congregation Etz Ahaim of Highland Park, New Jersey,[55] a congregation founded by Sephardic Jews from Salonika, a reader chants the Aramaic prayer B'rikh Shemay in Judaeo-Spanish before he takes out the Torah on Shabbat. That is known as Bendichu su Nombre in Judaeo-Spanish. Additionally, at the end of Shabbat services, the entire congregation sings the well-known Hebrew hymn Ein Keloheinu, which is Non Como Muestro Dio in Judaeo-Spanish.
Non Como Muestro Dio is also included, alongside Ein Keloheinu, in Mishkan T'filah, the 2007 Reform prayerbook.[56]
El Dio Alto (El Dyo Alto) is a Sephardic hymn often sung during the Havdalah service, its currently popular tune arranged by Judy Frankel.[57] Hazzan Isaac Azose, cantor emeritus of Synagogue Ezra Bessaroth and second-generation Turkish immigrant, has performed an alternative Ottoman tune.[58]
Rabbi Aryeh Kaplan translated some scholarly religious texts, including Me'am Loez into Hebrew, English or both.[59][60]
Izmir's grand rabbis Haim Palachi, Abraham Palacci, and Rahamim Nissim Palacci all wrote in the language and in Hebrew.

Modern education and use
[edit]In 1967, linguist Haïm Vidal Séphiha of the University of Paris became the first professor of Judaeo-Spanish in the world; courses of Judaeo-Spanish have been introduced in universities since then in other European countries, along with research centers dedicated to the study of the language.[61] The National Authority of Ladino, dedicated to the study and promotion of Judaeo-Spanish was established in Jerusalem in 1997.[44]
As with Yiddish,[62][63] Judaeo-Spanish is seeing a minor resurgence in educational interest in colleges across the United States and in Israel.[64] Almost all American Jews are Ashkenazi, with a tradition based on Yiddish, rather than Judaeo-Spanish, and so institutions that offer Yiddish are more common. As of 2011[update] the University of Pennsylvania[65][66] and Tufts University[67] offered Judaeo-Spanish courses among colleges in the United States; INALCO in Paris, the University of the Basque Country and University of Granada in Spain were offering courses as well.[44][68] In Israel, Moshe David Gaon Center for Ladino Culture at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev is leading the way in education (language and literature courses, Community oriented activities) and research (a yearly scientific journal, international congresses and conferences etc.). Hebrew University also offers courses.[69] The Complutense University of Madrid also used to have courses.[70] Prof. David Bunis taught Judaeo-Spanish at the University of Washington, in Seattle during the 2013–14 academic year.[71] Bunis returned to the University of Washington for the Summer 2020 quarter.[72]
In Spain, the Spanish Royal Academy (RAE) in 2017 announced plans to create a Judaeo-Spanish branch in Israel in addition to 23 existing academies, in various Spanish-speaking countries, that are associated in the Association of Spanish Language Academies. Its stated purpose is to preserve Judaeo-Spanish. The move was seen as another step to make up for the Expulsion, following the offer of Spanish citizenship to Sephardim who had some connection with Spain.[5]
When French-medium schools operated by Alliance Israelite Universelle opened in the Ottoman Empire in the 1860s, the position of Judaeo-Spanish began to weaken in the Ottoman Empire areas. In time Judaeo-Spanish became perceived as a low status language,[73] and Sephardic people began losing connections to that language.[74] Esther Benbassa and Aron Rodrigue, authors of Sephardi Jewry: A History of the Judeo-Spanish Community, 14th-20th Centuries, wrote that the AIU institutions "gallicized" people who attended.[75] As time progressed, Judaeo-Spanish language and culture declined. Although Mary Altabev in 1994 observed limited use of Ladino at home among educated Turkish Jews, Melis Alphan wrote in Hürriyet in 2017 that the Judaeo-Spanish language in Turkey was heading to extinction.[44][73]
As of 2023[update] the Ladino supplement of Şalom is the sole monthly newspaper in Ladino.[76] El Amaneser is the sole all Ladino newspaper.[77]
Samples
[edit]Comparison with other languages
[edit]| Judaeo-Spanish | Aki Yerushalayim orthography | איל גﬞודיאו־איספאנײול איס לה לינגואה פﬞאבﬞלאדה די לוס גﬞודיוס ספﬞרדים ארונגﬞאדוס די לה איספאנײה איניל 1492. איס אונה לינגואה דיריבﬞאדה דיל איספאנײול או איל קאסטעייאנו אי פﬞאבﬞלאדה די 150,000 פירסונאס אין קומוניטאס אין ישראל, לה טורקײה, אנטיקה יוגוסלאבﬞײה, לה גריסײה, איל מארואיקוס, מאיורקה, לה אמעריקא, אינטרי מונגﬞוס אוטרוס לוגאריס.
El djudeo-espanyol es la lingua favlada de los djudios sefardim arondjados de la Espanya enel 1492. Es una lingua derivada del espanyol o el kasteyano i favlada de 150.000 personas en komunitas en Israel, la Turkia, antika Yugoslavia, la Gresia, el Maruekos, Mayorka, la Amerika, entre munchos otros lugares. |
|---|---|---|
| Castillian-inspired orthography | El judeoespañol es la lingua fablada de los judiós sefaradim arronjados de la España en el 1492. Es una lingua derivada del español/casteyano y fablada de 150.000 personas en comunitás en Israel, la Turquía, antica Yugoslavia, la Grecia, el Marruecos, Mayorca, (las) América(s), entre munchos otros lugares. | |
| Castillian | El judeoespañol es la lengua hablada por los judíos sefardíes expulsados[note 2] de España en 1492. Es una lengua derivada del español/castellano y hablada por 150.000 personas en comunidades en Israel, Turquía, la antigua Yugoslavia, Grecia, Marruecos, Mallorca, (las) América(s), entre muchos otros lugares. | |
| Asturian | El xudeoespañol ye la llingua falada polos xudíos sefardinos espulsaos d'España en 1492. Ye una llingua derivada del español/castellanu y falada por 150.000 persones en comunidaes n'Israel, Turquía, na antigua Yugoslavia, Grecia, Marruecos, Mallorca, América/nes Amériques, ente munchos otros llugares. | |
| Galician | Standard | O xudeo-español é a lingua falada polos xudeus sefardís expulsados de España en 1492. É unha lingua derivada do español/castelán e falada por 150.000 persoas en comunidades en Israel, Turquía, antiga Iugoslavia, Grecia, Marrocos, Maiorca, América(s), entre moitos outros lugares. |
| Reintegrationist | O judeu-espanhol é a língua falada polos judeus sefardis espulsados de Espanha em 1492. É uma língua derivada do espanhol/castelom e falada por 150.000 pessoas em comunidades em Israel, Turquia, antiga Iugoslávia, Grécia, Marrocos, Maiorca, América(s), entre muitos outros lugares. | |
| Portuguese | European | O judeu-espanhol é a língua falada pelos judeus sefardis/sefarditas expulsos de Espanha em 1492. É uma língua derivada do espanhol/castelhano e falada por 150.000 pessoas em comunidades em Israel, na Turquia, na antiga Jugoslávia, na Grécia, em Marrocos, em Maiorca, na(s) América(s), entre muitos outros lugares. |
| Brazilian | O judeu-espanhol é a língua falada pelos judeus sefardis/sefarditas expulsos da Espanha em 1492. É uma língua derivada do espanhol/castelhano e falada por 150.000 pessoas em comunidades em Israel, na Turquia, na ex-Iugoslávia, na Grécia, no/em Marrocos, em Maiorca, na(s) América(s), entre muitos outros lugares. | |
| Aragonese | O chodigo-espanyol ye la luenga parlata por os chodigos sefardís expulsats d'Espanya en 1492. Ye una luenga derivata de l'espanyol/del castellano i parlata por 150.000 personas en comunitatz en Israel, Turquía, l'antiga Yugoslavia, Grecia, Marruecos, Mallorca, (las) América(s), entre muitos atros lugares. | |
| Catalan | El judeoespanyol és la llengua parlada pels jueus sefardites expulsats d'Espanya al 1492. És una llengua derivada de l'espanyol/del castellà i parlada per 150.000 persones en comunitats a Israel, Turquia, l'antiga Iugoslàvia, Grècia, el Marroc, Mallorca, Amèrica/les Amèriques, entre molts altres llocs. | |
| Occitan | Languedocien dialect | Lo judeoespanhol es la lenga parlada pels jusieus sefarditas expulsats d'Espanha en 1492. Es una lenga venent de l'espanhòu/del castelhan que 150 000 personas la parlan dins de comunautats en Israèl, Turquia, èx-Iogoslavia, Grècia, Marròc, Malhòrca, (las) America(s), entre fòrça autres luòcs. |
| English | Judaeo-Spanish is the language spoken by Sephardic Jews expelled from Spain in 1492. It is a language derived from Spanish and spoken by 150,000 people in communities in Israel, Turkey, the former Yugoslavia, Greece, Morocco, Majorca, the Americas, among many other places. | |
Songs
[edit]A tradition dating back to at least the 16th century exists of translating piyyutim into Judaeo-Spanish. Fragments from kinnot in Judeo-Spanish from probably the 16th century have been found.[78]: 84 It is known that certain women, known as endechederas ("singers of dirges") would attend funerals to sing endechas (dirges), however, none of these endechas are known to have survived.[78]: 90
A tradition of ballads, or romansas, also exists in the Judeo-Spanish tradition, and were predominantly sung by women.[79] Their original purpose was to transmit news; later they became work songs as well as entertainment. They covered a wide range of topics, from childbirth to marriage to death; they could also cover secular topics, such as unhappily married women, incest, violence, and single mothers. In one ballad, a pregnant princess pretends to her mother that she is not pregnant, but rather has indigestion, then proceeds to give birth to her fourth child.[79]
Folklorists have been collecting romances and other folk songs, some dating from before the expulsion. Many religious songs in Judaeo-Spanish are translations of Hebrew, usually with a different tune.[citation needed] For example, here is Ein Keloheinu in Judaeo-Spanish:
Non komo muestro Dio,
Non komo muestro Sinyor,
Non komo muestro Rey,
Non komo muestro Salvador.
etc.
Other songs relate to secular themes such as love:
| Adio, kerida | Goodbye, My Love (translation) |
|---|---|
Tu madre kuando te pario |
When your mother gave birth to you |
| Por una Ninya | For a Girl (translation) |
Por una ninya tan fermoza |
For a girl so beautiful |
No me mires ke'stó kantando |
Don't look at me; I am singing, |
No te lo kontengas tu, fijika, |
Don't hold your sorrows, young girl, for you are white like bread, there are dark girls in the world who set fire to Thessaloniki. |
| Quando el Rey Nimrod (Adaptation) | When King Nimrod (translation) |
Quando el Rey Nimrod al campo salía |
|
Avraham Avinu, Padre querido, |
Abraham Avinu [our Father], dear father |
Luego a las comadres encomendava |
Then he was telling all the midwives |
Avraham Avinu, Padre querido, |
Abraham Avinu, dear father |
La mujer de Terach quedó prenyada |
Terach's wife was pregnant |
Avraham Avinu, Padre querido, |
Abraham Avinu, dear father |
En fin de nueve meses parir quería |
After nine months she wanted to give birth |
Avraham Avinu, Padre querido, |
Abraham Avinu, dear father |
En aquella hora el nascido avlava |
In that hour the newborn was speaking |
Avraham Avinu, Padre querido, |
Abraham Avinu, dear father |
| Yo era ninya | I Was a Girl (translation) |
Yo era ninya de kaza alta |
I was a girl from an upper-class family |
Anachronistically, Abraham—who in the Bible is an Aramean and the very first Hebrew and the ancestor of all who followed, hence his appellation Avinu (Our Father)—is in the Judeo-Spanish song born already in the djudería (modern Spanish: judería), the Jewish quarter. This makes Terach and his wife into Hebrews, as are the parents of other babies killed by Nimrod. In essence, unlike its Biblical model, the song is about a Hebrew community persecuted by a cruel king and witnessing the birth of a miraculous saviour—a subject of obvious interest and attraction to the Jewish people who composed and sang it in medieval Spain.
The song attributes to Abraham elements that are from the story of Moses's birth, the cruel king killing innocent babies, with the midwives ordered to kill them, the 'holy light' in the Jewish area, as well as from the careers of Shadrach, Meshach, and Abednego who emerged unscathed from the fiery furnace, and Jesus of Nazareth. Nimrod is thus made to conflate the role and attributes of three archetypal cruel and persecuting kings: Nebuchadnezzar and Pharaoh and Herod
Another example is the Coplas de Purim, a folk song about Purim.
Dialectal differences
[edit]| Turkish (Istanbul) | Esto sta bueno. Importa voz soş las ratoneras, i los mansevos son los ratuneros. Dime tu a mi, stuvo kazado este Tolstoy? |
|---|---|
| Serbo-Croatian (Sarajevo) | Estu sta buenu. Importa vuoztras sos las ratoneras, i lus mansevus son lus ratunis. Dizmi tu a mi, stuvu kazadu esti Tolstoj? |
| Greek (Thessaloniki) | Esto sta bueno. Importa voz sos las ratoneras, i los mansevos son los ratuneros. Dime tu a mi, stuvo kasado este Tolstoi? |
| Macedonian (Bitola) | Estu sta buenu. Impurta vuoztras sos las ratoneras, i lus mansevus son lus ratunis. Dizmje tu a mi, stuvu kazadu isti Tolstoj? |
Selected words by origin
[edit]Words derived from Arabic:
- Alforría – 'liberty, freedom'
- Alhát – 'Sunday'
- Atemar – 'to terminate'
- Saraf – 'money changer'
- Shara – 'wood'
- Ziara – 'cemetery visit'
Words derived from Hebrew:
- Alefbet – 'alphabet' (from the Hebrew names of the first two letters of the alphabet)
- Anav – 'humble, obedient'
- Arón – 'grave'
- Atakanear – 'to arrange'
- Badkar – 'to reconsider'
- Beraxa – 'blessing'
- Din – 'religious law'
- Kal – 'community', 'synagogue'
- Kamma – 'how much?', 'how many?'
- Maaráv – 'west'
- Maasé – 'story, event'
- Maabe – 'deluge, downpour, torrent'
- Mazal – 'star', 'destiny'
- Met – 'dead'
- Niftar – 'dead'
- Purimlik – 'Purim present' (eerived from the Hebrew Purim + Turkic ending -lik)
- Sedaka – 'charity'
- Tefilá – 'prayer'
- Zahut – 'blessing'
Words derived from Persian:
- Chay – 'tea'
- Chini – 'plate'
- Paras – 'money'
- Shasheo – 'dizziness'
Words derived from Portuguese:
- Abastádo – 'almighty, omnipotent' (referring to God)
- Aínda – 'yet'
- Chapeo – 'hat'
- Preto – 'black' (in color)
- Trocar – 'to change'
Words derived from Turkish:
- Balta – 'axe'
- Biterear – 'to terminate'
- Boyadear – 'to paint, color'
- Innat – 'whim'
- Kolay – 'easy'
- Kushak – 'belt, girdle'
- Maalé – 'street, quarters, neighbourhood'; Maalé yahudí – 'Jewish quarters'
Words derived from Greek:
- meldar – 'read, learn'
- bora – 'storm, torrential rain, gust of wind'
- demet – 'bouquet'
- domate – 'tomato'
- fasaria – 'a fuss, to-do, agitation, bustle'
- fota – 'the moment when work, motion, traffic reaches its highest intensity'
- kuturu – 'a pile of mismatched objects, of overripe fruit, of mixed leftovers'
Modern singers
[edit]Jennifer Charles and Oren Bloedow from the New York-based band Elysian Fields released a CD in 2001 called La Mar Enfortuna, which featured modern versions of traditional Sephardic songs, many sung by Charles in Judeo-Spanish. The American singer Tanja Solnik has released several award-winning albums that feature songs in the languages: From Generation to Generation: A Legacy of Lullabies and Lullabies and Love Songs. There are a number of groups in Turkey that sing in Judeo-Spanish, notably Janet – Jak Esim Ensemble, Sefarad, Los Pasharos Sefaradis and the children's chorus Las Estreyikas d'Estambol. There is a Brazilian-born singer of Sephardic origins, Fortuna, who researches and plays Judeo-Spanish music.[81][82]
Israeli folk-duo Esther & Abi Ofarim recorded the song "Yo M'enamori d'un Aire" for their 1968 album Up To Date. Esther Ofarim recorded several Judaeo-Spanish songs as a solo artist. These included "Povereta Muchachica", "Noches Noches", "El Rey Nimrod", "Adio Querida" and "Pampaparapam". [83]
The Jewish Bosnian-American musician Flory Jagoda recorded two CDs of music taught to her by her grandmother, a Sephardic folk singer, among a larger discography.[84] Following her death in 2021, gentile musicians in Bosnia have recorded music in Judaeo-Spanish as well.[85]
The cantor Ramón Tasat, who learned Judeo-Spanish at his grandmother's knee in Buenos Aires, has recorded many songs in the language, with three of his CDs focusing primarily on that music.[86]
The Israeli singer Yasmin Levy has also brought a new interpretation to the traditional songs by incorporating more "modern" sounds of Andalusian Flamenco. Her work revitalising Sephardic music has earned Levy the Anna Lindh Euro-Mediterranean Foundation Award for promoting cross-cultural dialogue between musicians from three cultures:[87] In Yasmin Levy's own words:
I am proud to combine the two cultures of Ladino and flamenco, while mixing in Middle Eastern influences. I am embarking on a 500 years old musical journey, taking Ladino to Andalusia and mixing it with flamenco, the style that still bears the musical memories of the old Moorish and Jewish-Spanish world with the sound of the Arab world. In a way it is a 'musical reconciliation' of history.[88]
Notable music groups performing in Judeo-Spanish include Voice of the Turtle, Oren Bloedow and Jennifer Charles' La Mar Enfortuna and Vanya Green, who was awarded a Fulbright Fellowship for her research and performance of this music. She was recently selected as one of the top ten world music artists by the We are Listening International World of Music Awards for her interpretations of the music.
Robin Greenstein, a New York-based musician, received a federal CETA grant in the 1980s to collect and perform Sephardic Music under the guidance of the American Jewish Congress. Her mentor was Joe Elias, noted Sephardic singer from Brooklyn. She recorded residents of the Sephardic Home for the Aged, a nursing home in Coney Island, New York, singing songs from their childhood. The voices recorded included Victoria Hazan, a well known Sephardic singer who recorded many 78's in Judaeo-Spanish and Turkish from the 1930s and 1940s. Two Judaeo-Spanish songs can be found on her Songs of the Season holiday CD, released in 2010 on Windy Records.
German band In Extremo also recorded a version of the above-mentioned song Avram Avinu.
The Israeli-German folk band Baladino has released two albums that have songs with lyrics in Judaeo-Spanish.
See also
[edit]- Haketia
- Jewish languages
- Judaism
- Judeo-Gascon
- Judaeo-Portuguese
- Judaeo-Romance languages
- Judaeo-Spanish Wikipedia
- Knaanic language
- Mozarabic language
- Los Serenos Sefarad, Judaeo-Spanish hip-hop
- Laura Papo Bohoreta
- Matilda Koen-Sarano
- Sephardi Jews
- Tetuani
- Cicurel family
- Pallache family
- Şalom, a Turkish newspaper with a Judaeo-Spanish page[89]
- El Amaneser, a Turkish monthly newspaper in Judaeo-Spanish
- Aki Yerushalayim, an Israeli magazine in Judaeo-Spanish published 2–3 times a year
- Yiddish, language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews
- Judeo-Iranian languages, languages historically spoken by Mizrahi Jews in the former territories of the Persian Empire
References
[edit]Notes
- ^ Pronounced [dʒu-, ʒu-], [-ˈðeo-, -ˈdeo-, -ˈðeu-, -ˈdeu-], [-(e)spa-, -(e)ʃpa-], [-ˈɲol, -ˈɲoɫ, -ˈnjol, -ˈnjoɫ] in different dialects.
- ^ Speakers use different orthographical conventions depending on their social, educational, national and personal backgrounds, and there is no uniformity in spelling although some established conventions exist. The endonym Judeo-Espagnol is also spelled as Cudeo-Espanyol, Djudeo-Espagnol, Djudeo-Espanyol, Dschudeo-Espanjol, Dzhudeo-Espanyol, Džudeo-Espanjol, Dzsudeo-Eszpanyol (Hungary), Dżudeo-Espańol, Giudeo-Espagnol or Giudeo-Espaneol (Italy), Ġudeo-Espanjol, Ǧudéo-Españól, Judeo-Espaniol, Ĵudeo-Español and Judeo-Espanýol, Tzoudeo-Espaniol (Greece), Xhudeo-Espanjol. See the infobox for parallel spellings in scripts other than Latin.
- ^ The direct Spanish cognate of Judaeo-Spanish 'arondjado(s)' is 'arrojado(s)', which has the meaning of 'thrown' and 'kicked-out', but not 'exiled' like its Judaeo-Spanish counterpart.
Citations
- ^ a b Judaeo-Spanish at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ^ Quintana Rodríguez, Alidina (2006). Geografía lingüística del judeoespañol: estudio sincrónico y diacrónico (in Spanish). Peter Lang. ISBN 978-3-03910-846-6.
- ^ Koen, Hajim Mordehaj (1927). ЛЕКУТЕ ТЕФИЛОТ (ОРАСJОНИС ЕСКУЖИДАС) (in Ladino). Belgrade.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Peim, Benjamin (16 April 2009). "Ladino Lingers on in Brooklyn – Barely". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 12 August 2017.
- ^ a b Jones, Sam (1 August 2017). "Spain honours Ladino language of Jewish exiles". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 19 September 2017. Retrieved 1 August 2017.
- ^ Minervini, Laura (2006). "El desarollo histórico del judeoespañol" [The historical development of Judeo-Spanish]. Revista Internacional de Lingüística Iberoamericana (in Spanish).
- ^ a b Papo, Eliezer (2007). "Serbo-Croatian Influences on Bosnian Spoken Judeo-Spanish". European Journal of Jewish Studies. 1 (2): 343–363. doi:10.1163/187247107783876329. ISSN 1025-9996.
- ^ a b c Haim-Vidal Sephiha: Judeo-Spanish Archived 21 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine, on the former website of the Jewish Museum of Thessaloniki (Salonika). "The Jews Necropolis". Archived from the original on 15 February 2012. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link). Retrieved on 19 October 2011. - ^ "The Bosnians who speak medieval Spanish". www.bbc.com. Retrieved 3 September 2024.
- ^ "In memoriam DAVID KAMHI". University of Sarajevo. Retrieved 3 September 2024.
- ^ "Bosnian Jews mourn Moris Albahari, one of Sarajevo's last Ladino speakers". The Jerusalem Post | JPost.com. 22 November 2022. Retrieved 3 September 2024.
- ^ Nehama, Joseph (1977). Dictionnaire du judéo-espagnol (French Edition) (French).
- ^ "Cover". digitalcollections.lib.washington.edu.
- ^ "Cover". digitalcollections.lib.washington.edu. Archived from the original on 31 July 2021. Retrieved 14 April 2022.
- ^ Entry "judeoespañol, la", in the Diccionario de la Real Academia Española (DRAE). Retrieved on 1 June 2019.
- ^ "Ladino Today | My Jewish Learning". My Jewish Learning. Retrieved 5 October 2018.
- ^ Arnold, Rafael D. (28 August 2018). "Judeo-Romance varieties". Lexicographica. 33 (2017): 321–358. doi:10.1515/lex-2017-0016. Retrieved 29 July 2024.
- ^ Attig, Remy (September 2012). "Did the Sephardic Jews Speak Ladino?". Bulletin of Spanish Studies. 89 (6): 831–838. doi:10.1080/14753820.2012.712320. Retrieved 28 July 2024.
- ^ a b Guillermo Angel R. José (2006). "Sobre el Ladino: Yo havlo, meldo i eskrivo Djudio". In Díaz-Mas, Paloma; den Boer, Harm (eds.). Fronteras e interculturalidad entre los sefardíes occidentales. Foro Hispánico. Vol. 28. Brill. pp. 97–110. doi:10.1163/9789401202503_010. ISBN 9789401202503.
- ^ Harris, Tracy (1994). Death of a language: The history of Judeo-Spanish. Newark, DE: University of Delaware Press.
- ^ Wexler, Paul (1977). "Ascertaining the Position of Judezmo within Ibero-Romance". Vox Romanica: 163.
- ^ (in Spanish) Entry "ladino, na", in the Diccionario de la Real Academia Española (DRAE). Retrieved on 1 June 2019.
- ^ "Clearing up Ladino, Judeo-Spanish, Sephardic Music" Judith Cohen, HaLapid, winter 2001; Sephardic Song at the Wayback Machine (archived 16 April 2008), Judith Cohen, Midstream July/August 2003
- ^ Attig, Remy (September 2012). "Did the Sephardic Jews Speak Ladino?". Bulletin of Spanish Studies. 89 (6): 831–838. doi:10.1080/14753820.2012.712320. ISSN 1475-3820. S2CID 162360656.
- ^ a b c d Kohen, Elli; Kohen-Gordon, Dahlia (2000). Ladino-English/English-Ladino Concise Encyclopedic Dictionary (Judeo-Spanish). New York: Hippocene Books. ISBN 0-7818-0658-5.
- ^ Pulido, Ángel (2016). Sephardic Jews and the Spanish language. New York: Ateven Capsuto Books & Translation Services. ISBN 978-0997825404.
- ^ "EL JUDEOESPAÑOL O LADINO | Sefardiweb". www.proyectos.cchs.csic.es. Retrieved 25 April 2023.
- ^ "Judeo-Spanish (Ladino) and Its Deal with Dialects". Lynn Chenel. Retrieved 25 April 2023.
- ^ Quintana, Aldina (January 2006). Geografía lingüística del judeoespañol. Estudio sincrónico y diacrónico. ISBN 978-3-0351-0275-8.
- ^ Angel, Marc D. (1978). The Jews of Rhodes (2nd ed.). p. 135. ISBN 0-87203-072-5.
- ^ Hualde, José Ignacio; Şaul, Mahir (2011). "Istanbul Judeo-Spanish". Journal of the International Phonetic Association. 41 (1): 89–110. doi:10.1017/S0025100310000277. ISSN 0025-1003. S2CID 145143546.
- ^ "Ladino". archive.phonetics.ucla.edu.
- ^ a b c d e Penny, Ralph (2000). Variation and Change in Spanish. Cambridge University Press. pp. 179–189. ISBN 0-521-60450-8.
- ^ Travis G. Bradley and Ann Marie Delforge, Phonological Retention and Innovation in the Judeo-Spanish of Istanbul in Selected Proceedings of the 8th Hispanic Linguistics Symposium, ed. Timothy L. Face and Carol A. Klee, 73–88. 2006. Somerville, MA: Cascadilla Proceedings Project.
- ^ Batzarov, Zdravko. "Judeo-Spanish: Noun". orbilat.com. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- ^ Sevi, Aldo et. al. (ed.), "Grafía del Djudeo-Espanyol Sigún el Método de Akí Yerushaláyim." Akí Yerushaláyim, no. 113, October 2024, pp. 117-120
- ^ Verba Hispanica X: Los problemas del estudio de la lengua sefardí Archived 7 April 2008 at the Wayback Machine, Katja Šmid, Ljubljana, pages 113–124: Es interesante el hecho que en Bulgaria se imprimieron unas pocas publicaciones en alfabeto cirílico búlgaro y en Grecia en alfabeto griego. [...] Nezirović (1992: 128) anota que también en Bosnia se ha encontrado un documento en que la lengua sefardí está escrita en alfabeto cirilico. The Nezirović reference is: Nezirović, M., Jevrejsko-Španjolska književnost. Institut za književnost, Svjetlost, Sarajevo, Bosnia 1992.
- ^ See preface by Iacob M. Hassán to Romero, Coplas Sefardíes, Cordoba, pp. 23–24.
- ^ "Ladinoikonunita: A quick explanation of Ladino (Judaeo-Spanish) Archived 2 April 2010 at the Wayback Machine. Sephardicstudies.org. Retrieved on 19 October 2011.
- ^ a b Ray, Jonathan Stewart (2013). After expulsion: 1492 and the making of Sephardic Jewry. New York: New York University Press. pp. 137–138. ISBN 978-0-8147-2911-3.
- ^ palavră in the Dicționarul etimologic român, Alexandru Ciorănescu, Universidad de la Laguna, Tenerife, 1958–1966: Cuvînt introdus probabil prin. iud. sp: "Word introduced probably through Judaeo-Spanish.
- ^ Συγκριτικός πίνακας των στοιχείων των απογραφών του 1928, 1940 ΚΑΙ 1951 σχετικά με τις ομιλούμενες γλώσσες στην Ελλάδα. – Μεινοτικές γλώσσες στην Ελλάδα, Κωνσταντίνος Τσιτσελίκης (2001), Πύλη για την Ελληνική Γλώσσα
- ^ Marovitz, Sanford E.; Christodoulou, Athanasios C. (2001). Melville "Among the Nations": Proceedings of an International Conference, Volos, Greece, July 2-6, 1997. Kent State University Press. p. 101. ISBN 978-0-87338-696-8.
- ^ a b c d e Harris, Tracy K. (2011). "The State of Ladino Today". European Judaism: A Journal for the New Europe. 44 (1): 51–61. doi:10.3167/ej.2011.44.01.07. ISSN 0014-3006. JSTOR 41444099. Retrieved 28 July 2024.
- ^ Gerson Şarhon, Karen (2011). "Ladino in Turkey: The Situation Today as Reflected by the Ladino Database Project". European Judaism: A Journal for the New Europe. 44 (1): 62–71. doi:10.3167/ej.2011.44.01.08. ISSN 0014-3006. JSTOR 41444100. Retrieved 28 July 2024.
- ^ Reka Network: Kol Israel International Archived 23 March 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Radio Exterior de España: Emisión en sefardí
- ^ Nir Hasson, Holocaust survivor revives Jewish dialect by translating Greek epic, at Haaretz, 9 March 2012.
- ^ Simon, Rachel (2011). "The Contribution of Hebrew Printing Houses and Printers in Istanbul to Ladino Culture and Scholarship". Judaica Librarianship. 16/17: 125–135. doi:10.14263/2330-2976.1008.
- ^ Borovaya, Olga (2012). Modern Ladino Culture: Press, Belles Lettres, and Theater in the Late Ottoman Empire. Indiana University Press. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-253-35672-7.
- ^ Borovaya, Olga (2012). Modern Ladino Culture: Press, Belles Lettres, and Theater in the Late Ottoman Empire. Indiana University Press. p. 24. ISBN 978-0-253-35672-7.
- ^ Borovaya, Olga (2012). Modern Ladino Culture: Press, Belles Lettres, and Theater in the Late Ottoman Empire. Indiana University Press. p. 144. ISBN 978-0-253-35672-7.
- ^ Borovaya, Olga (2012). Modern Ladino Culture: Press, Belles Lettres, and Theater in the Late Ottoman Empire. Indiana University Press. p. 191. ISBN 978-0-253-35672-7.
- ^ Strauss, Johann (2010). "A Constitution for a Multilingual Empire: Translations of the Kanun-ı Esasi and Other Official Texts into Minority Languages". In Herzog, Christoph; Malek Sharif (eds.). The First Ottoman Experiment in Democracy. Würzburg: Orient-Institut Istanbul. pp. 21–51. Archived from the original on 11 October 2019. Retrieved 15 September 2019. (info page on book Archived 20 September 2019 at the Wayback Machine at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338). "This seems surprising insofar as Judaeo-Spanish translators do not generally shun Turkish terms."
- ^ "Congregation Etz Ahaim – Sephardic". Congregation Etz Ahaim – Sephardic.
- ^ Frishman, Elyse D., ed. (2007). Mishkan T'filah: a Reform siddur: services for Shabbat. New York: Central Conference of American Rabbis. p. 327. ISBN 978-0-88123-104-5.
- ^ ben Or, David (2016). "El Dio Alto". sefaradizo.org. Archived from the original on 17 September 2021. Retrieved 17 September 2021.
- ^ Guo, Ke (30 December 2020). "Listen to Hazzan Isaac Azose sing a popular Ladino song with an Ottoman melody". UW Stroum Center for Jewish Studies. Retrieved 17 September 2021.
- ^ > Events > Exhibitions > Rare Book Library Collection Restoration Project – Ladino[usurped]. American Sephardi Federation (23 April 1918). Retrieved on 19 October 2011.
- ^ Yalkut May'Am Loez, Jerusalem 5736 Hebrew translation from Ladino language.
- ^ Sephiha, Haim Vidal; Mitchell, Bruce (2001). "The Instruction of Judeo-Spanish in Europe". Shofar. 19 (4): 58–70. ISSN 0882-8539. JSTOR 42943398. Retrieved 27 July 2024.
- ^ Price, Sarah. (25 August 2005) Schools to Teach Ein Bisel Yiddish | Education. Jewish Journal. Retrieved on 19 October 2011.
- ^ The Mendele Review: Yiddish Literature and Language, Volume 11, No. 10 Archived 5 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Yiddish.haifa.ac.il (30 September 2007). Retrieved on 19 October 2011.
- ^ EJP | News | Western Europe | Judaeo-Spanish language revived Archived 29 May 2009 at the Wayback Machine. Ejpress.org (19 September 2005). Retrieved on 19 October 2011.
- ^ Jewish Studies Program Archived 17 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Ccat.sas.upenn.edu. Retrieved on 19 October 2011.
- ^ Ladino Class at Penn Tries to Resuscitate Dormant Language Archived 23 March 2011 at the Wayback Machine. The Jewish Exponent (1 February 2007). Retrieved on 19 October 2011.
- ^ Department of German, Russian & Asian Languages and Literature – Tufts University. Ase.tufts.edu. Retrieved on 19 October 2011.
- ^ "For love of Ladino". The Jewish Standard. Archived from the original on 24 January 2016. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
- ^ "Courses – Ladino Studies At The Hebrew University of Jerusalem". Hebrew University of Jerusalem. 30 July 2010. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
- ^ "Hebrew Philology courses (in Spanish)". UCM. Archived from the original on 12 December 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ "Why I'm teaching a new generation to read and write Ladino". Jewish Studies. 23 February 2014.
- ^ "The Legacy of Ladino". College of Arts and Sciences – University of Washington. 17 August 2020. Retrieved 13 May 2021.
- ^ a b Alphan, Melis (9 December 2017). "Ladino: A Judeo-Ottoman language that is dying in Turkey". Hürriyet. Retrieved 14 June 2019.
- ^ Austin, Dana. "World War II and the Decline of the Ladino Language" (PDF). USC Shoah Foundation. p. 2/6. Retrieved 3 February 2004.
- ^ Benbassa, Esther; Rodrigue, Aron (13 April 2000). Sephardi Jewry: A History of the Judeo-Spanish Community, 14th-20th Centuries. University of California Press. p. 93.
- ^ Dubov, Gail P. (2 March 2023). "Ladino in Turkey: Rescuing an Endangered Language". Moment. Retrieved 27 June 2025.
- ^ "Newspaper brings hope for dying language of Sephardic Jewish community in Turkey". Media Diversity Institute. 27 January 2022. Retrieved 27 June 2025.
- ^ a b Díaz-Mas, Paloma (2011). "Sephardic Songs of Mourning and Dirges". European Judaism: A Journal for the New Europe. 44 (1): 84–97. ISSN 0014-3006. Retrieved 29 April 2025.
- ^ a b Pomeroy, Hilary (2011). "The Sephardi Ballad: Past and Present". European Judaism: A Journal for the New Europe. 44 (1): 107–120. ISSN 0014-3006. Retrieved 29 April 2025.
- ^ meara=מערה=Heb. cave
- ^ "Conference News". Shofar. 28 (1): 131. 2009. ISSN 0882-8539. JSTOR 10.5703/shofar.28.1.127.
- ^ "BIOGRAPHY". Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ^ "Esther Ofarim web site". Esther Ofarim. Archived from the original on 9 May 2018. Retrieved 4 December 2018.
- ^ "Flory Jagoda". Jewish Women's Archive. 23 June 2021. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ^ Klein, David I. (20 November 2023). "In Bosnia, gentile musicians work to preserve the country's Sephardic Jewish tradition". Religion News Service. Retrieved 28 July 2024.
- ^ "Ramón Tasat". Maryland State Arts Council. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ^ "2008 Event Media Release – Yasmin Levy". Sydney Opera House. Archived from the original on 28 August 2008. Retrieved 19 August 2008.
- ^ "BBC – Awards for World Music 2007 – Yasmin Levy". BBC. Archived from the original on 19 October 2017. Retrieved 19 August 2008.
- ^ Åžalom Gazetesi – 12.10.2011 – Judeo-Espanyol İçerikleri Archived 11 December 2008 at the Wayback Machine. Salom.com.tr. Retrieved on 19 October 2011.
Bibliography
- Arias, Álvaro (2024). "La abertura /e/ > /a/ condicionada por /r/ y /l/ en judeoespañol". Revista de Filología Española. 104 (1) 1420. doi:10.3989/rfe.2024.1420.
- Barton, Thomas Immanuel (Toivi Cook) (2010). Judezmo Expressions. New Century Press. ISBN 1890035750.
- Barton, Thomas Immanuel (Toivi Cook) (2008). Judezmo (Judeo-Castilian) Dictionary. ISBN 978-1-890035-73-0.
- Bunis, David M. (1999). Judezmo: an introduction to the language of the Sephardic Jews of the Ottoman Empire. Jerusalem: The Magnes Press. ISBN 978-965-493-024-6.
- Bunis, David M. (2015). "Judezmo (Ladino)". In Kahn, Lily; Rubin, Aaron D. (eds.). Handbook of Jewish languages. Leiden: Brill. pp. 366–451.
- Gabinsky, Mark A. (1992). Сефардский (еврейской-испанский) язык [Sephardic (Judeo-Spanish) language] (in Russian). Chişinău: Ştiinţa.
- Harris, Tracy (1994). Death of a language: The history of Judeo-Spanish. Newark, DE: University of Delaware Press.
- Hemsi, Alberto (1995). Seroussi, Edwin (ed.). Cancionero Sefardí. Yuval Music Series. Vol. 4. Jerusaelem: The Jewish Music Research Centre, the Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
- Hualde, José Ignacio (2013). "Intervocalic lenition and word-boundary effects: Evidence from Judeo-Spanish". Diachronica. 30 (2): 232–226. doi:10.1075/dia.30.2.04hua.
- Kohen, Elli; Kohen-Gordon, Dahlia (2000). Ladino-English, English-Ladino: concise encyclopedic dictionary. New York: Hippocrene Books.
- Markova, Alla (2008). Beginner's Ladino with 2 Audio CDs. New York: Hippocrene Books. ISBN 0-7818-1225-9.
- Markus, Shimon (1965). השפה הספרדית יהודית [The Judeo-Spanish language] (in Hebrew). Jerusalem.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Minervini, Laura (1999). "The Formation of the Judeo-Spanish koiné: Dialect Convergence in the Sixteenth Century". In Benaim, Annete (ed.). Proceedings of the Tenth British Conference on Judeo-Spanish Studies. London: Queen Mary and Westfield College. pp. 41–52.
- Minervini, Laura (2006). "El desarollo histórico del judeoespañol". Revista Internacional de Lingüística Iberoamericana (in Spanish). 4 (2): 13–34. JSTOR 41678238.
- Molho, Michael (1950). Usos y costumbres de los judíos de Salónica. Biblioteca Hebraicoespañola (in Spanish). Vol. 3. Translated by Perez Castro, F. Madrid: Instituto Arias Montano.
- Quintana Rodriguez, Aldina (2001). "Concomitancias lingüisticas entre el aragones y el ladino (judeoespañol)". Archivo de Filología Aragonesa (in Spanish). 57–58: 163–192.
- Quintana Rodriguez, Aldina (2006). Geografía lingüistica del judeoespañol: Estudio sincrónico y diacrónico (in Spanish). Bern: Peter Lang.
- Sephiha, Haïm-Vidal (1997). "Judeo-Spanish". In Weinstock, Nathan; Sephiha, Haïm-Vidal; Barrera-Schoonheere, Anita (eds.). Yiddish and Judeo-Spanish: a European Heritage. European Languages. Vol. 6. Brussels: European Bureau for Lesser-Used Languages. pp. 23–39.
- Varol-Bornes, Marie-Christine (2008). Manual of Judeo-Spanish: language and culture. Translated by Tarica, Ralph. Bethesda, Md.: University Press of Maryland. ISBN 978-2-915255-75-1.
Further reading
[edit]- Lleal, Coloma (1992). "A propósito de una denominación: el judeoespañol". Actas del II Congreso Internacional de Historia de la Lengua Española (in Spanish). Vol. 2. Madrid: Pabellón de España. pp. 200–205 – via Centro Virtual Cervantes.
- Saporta y Beja, Enrique (1978). Refranes de los judíos sefardíes y otras locuciones típicas de Salónica y otros sitios de Oriente (in Spanish). Barcelona: Ameller.
External links
[edit]- Autoridad Nasionala del Ladino (in Ladino)
- Jewish Museum of Thessaloniki
- Ladino Center
- Ladinokomunita, an email list in Ladino
- La pajina djudeo-espanyola de Aki Yerushalayim
- The Ladino Alphabet
- Judeo-Spanish (Ladino) at Orbis Latinus
- Ladino music by Suzy and Margalit Matitiahu
- Socolovsky, Jerome. "Lost Language of Ladino Revived in Spain", Morning Edition, National Public Radio, 19 March 2007.
- A randomly selected example of use of ladino on the Worldwide Web: La komponente kulinaria i linguístika turka en la kuzina djudeo-espanyola
- Israeli Ladino Language Forum (Hebrew)
- LadinoType – A Ladino Transliteration System for Solitreo, Meruba, and Rashi
- Habla Ladino? Sephardim meet to preserve language Friday 9 January 1998
- Edición SEFARAD, Radio programme in Ladino from Radio Nacional de España
- Etext of Nebrija's Gramática de la lengua castellana, showing orthography of Old Spanish Archived 10 May 2010 at the Wayback Machine.
- Sefarad, Revista de Estudios Hebraicos, Sefardíes y de Oriente Próximo, ILC, CSIC
- Judæo-Spanish Language (Ladino) and Literature, Jewish Encyclopedia
- Yitshak (Itzik) Levy An authentic documentation of Ladino heritage and culture
- Sephardic Studies Digital Library & Museum – UW Stroum Jewish Studies
- An inside look into the Portuguese corpus of words in Nehama's Dictionnaire du Judeo-Espagnol Yossi Gur, 2003.
- Ladino romanization standard used by the Library of Congress
 KSF
KSF