Khanate
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 9 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 9 min
A khanate (/ˈxɑːneɪt, -ət/ KHAHN-ayt, -ət) or khaganate refers to historic polities ruled by a khan, khagan, khatun, or khanum.[1][2] Khanates were typically nomadic Mongol and Turkic or Tatar societies located on the Eurasian Steppe,[3][4][5] and politically equivalent in status to kinship-based chiefdoms and feudal monarchies. Khanates and khaganates were organised tribally, where leaders gained power on the support and loyalty of their warrior subjects,[3] gaining tribute from subordinates as realm funding.[6] In comparison to a khanate, a khaganate, the realm of a khagan, was a large nomadic state maintaining subjugation over numerous smaller khanates.[7] The title of khagan, translating as "Khan of the Khans", roughly corresponds in status to that of an emperor.[4]
Mongol khanates
[edit]Mongol Empire (1206–1368)
[edit]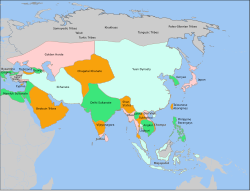
The Mongol Empire was the largest steppe nomadic Khaganate as well as second largest empire and the largest contiguous empire[8] in history. After Genghis Khan established appanages for his family in the Mongol Empire during his rule (1206–1227), his sons, daughters, and grandsons inherited separate sections of the empire. The Mongol Empire and Mongolian khanates that emerged from those appanages are listed below.
- List of Mongol khanates
- Chagatai Khanate (1226–1347), In 1226, the second son of Genghis Khan, Chagatai Khan established the Chagatai Khanate. At its height in the late 13th century, the khanate extended from the Amu Darya south of the Aral Sea to the Altai Mountains in the border of modern-day Mongolia and China, roughly corresponding to the defunct Qara Khitai Empire. Initially the rulers of the Chagatai Khanate recognized the supremacy of the Great Khan, but by the reign of Kublai Khan, Ghiyas-ud-din Baraq no longer obeyed the emperor's orders. By 1347 the khanate had split into the Moghulistan and West Chagatai Khanate.[9]
- Il-Khanate (1252–1335), In 1256, Il-Khanate was established by the grandson of Genghis Khan, Hulagu Khan. Its core territory lies in what is now part of the countries of Iran, Azerbaijan, and Turkey. At its greatest extent, the Ilkhanate also included parts of modern Iraq, Syria, Armenia, Georgia, Afghanistan, Turkmenistan, Pakistan, part of modern Dagestan, and part of modern Tajikistan. Later Ilkhanate rulers, beginning with Ghazan in 1295, converted to Islam. In the 1330s, the Ilkhanate was ravaged by the Black Death. Its last khan Abu Sa'id died in 1335, after which the khanate disintegrated. The Ilkhanid rulers, although of non-Iranian origin, tried to advertise their authority by tying themselves to the Iranian past, and they recruited historians in order to present the Mongols as heirs to the Sasanians (224–651 AD) of pre-Islamic Iran.

Turco-Mongol residual states and domains in the 15th century - Golden Horde
- Yuan dynasty
- Northern Yuan dynasty

Central Asia in 1636. The Dzungar Khanate was the last great nomadic empire in Central Asia.
- Northern Yuan dynasty
- Bogd Khanate (1911–1924), under rule of the Bogd Khan, the last Mongol khagan
- Dzungar Khanate, formed in 1634, covering Xinjiang region of China, Kyrgyzstan, eastern Kazakhstan and western Mongolia; 2 December 1717 – 1720, also styled Protector of Tibet; 1755 tributary to the Qing dynasty, 1758 annexed by Qing dynasty
- Kalmyk Khanate, established c.1630 by the Torghut branch of the Mongol Oirats, settled along the lower Volga River (in modern Russia and Kazakhstan), 1630-1771
- Kara Del
- Keraite Khanate
- Khamag Mongol Khanate
- Khoshut Khanate
- Khotgoid Khanate
- Mergid Khanate
- Naiman Khanate
- Tatar Khanate
- Moghul Khanate
- Kumul Khanate – a vassal state to Qing dynasty and Republic of China, abolished in 1930
Indefinite origin
[edit]
- Avar Khaganate
- Xiongnu, mentioned in Chinese sources, were possibly of Proto-Turkic, Turkic, Mongolic or else Iranic origin (disputed) and are proposed as the possible ancestors of the Huns (whose language remains unclassified).
- Xueyantuo, mentioned in Chinese sources, were a Tiele tribe, related to the earlier Dingling people, who emerged after the disintegration of the Xiongnu confederacy (they were at one point vassals of the Göktürks, later aligning with the Tang dynasty against the Eastern Göktürks).
Turkic khanates
[edit]Early and Late Medieval Turkic khaganates and khanates
[edit]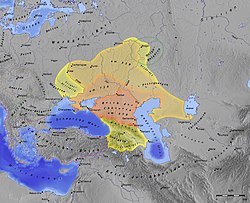
- First Turkic Khaganate
- Second Turkic Khaganate
- Uyghur Khaganate
- Yenisei Kyrgyz Khaganate
- Khazar Khaganate
- Turgesh Khaganate


- Old Great Bulgaria
- Volga Bulgaria
- First Bulgarian Empire, which started as a Turkic state, also known as Danube Bulgaria (in contrast to Volga Bulgaria, as both were established by members of the same Bulgar Turkic Dulo clan), but later became fully Slavicized and a Tsardom.
- Golden Horde
- Khanate of Kazan
- Crimean Khanate
Central Asian Turkic khanates
[edit]- Kara-Khanid Khanate
- Kimek Khanate
- Keraite Khanate
- Naiman Khanate
- Tatar Khanate
- Merkit Khanate
- Nogai Khanate
- Astrakhan Khanate
- Besh Tau El
- Khanate of Bukhara
- Khanate of Khiva
- Kyrgyz Khaganate
- Kara-Kyrgyz Khanate
- Karluk Khanate
- Khanate of Kashgaria – Kashgaria was founded in 1514 as part of Chagatai Khanate; in the 17th century it was divided into several minor khanates without importance, with real power going to the so-called Khwaja, Arabic Islamic religious leaders. It became the Yarkent Khanate which was annexed by the Dzungar Khanate in the Dzungar conquest of Altishahr in 1680.
- Kazakh Khanate
- Senior zhuz
- Middle zhuz
- Junior zhuz
- Bukey Horde, Bokei or Buqei; also known as the Inner or Interior Horde – This state founded in 1801 by Sultan Bukey under Russian suzerainty, and restyled as the khanate of the Inner Horde in 1812. 5,000–7,500 families of Kazakhs from the Younger Kazakh Zhuz tribe settled between the Volga and Yaik (Ural) rivers. In 1845 the post of khan was abolished, and Russia took over the region.
- Kokand Khanate
- Kumul Khanate – a vassal state to Qing dynasty and Republic of China, abolished in 1930
- Kunduz Khanate
- Maimana Khanate
- Oghuz Yabgu State
- Qasim Khanate (hence modern Kasimov) – named after its founder, a vassal of Moscow and Russia
- Khanate of Sibir – source of the name Siberia, as the first significant conquest during Russia's great eastern expansion across the Urals
- The Khanate of Tuva near Outer Mongolia
- Uzbek Khanate
- Yarkent Khanate
- Turpan Khanate
Khanates of Azerbaijan
[edit]- Ardabil Khanate
- Karadagh khanate
- Khalkhal Khanate
- Maku Khanate
- Maragheh Khanate
- Sarab Khanate
- Tabriz Khanate
- Urmia Khanate
Khanates of the Caucasus
[edit]- Khundzakh Khanate
- Baku Khanate
- Derbent Khanate
- Erivan Khanate
- Ganja Khanate
- Gazikumukh Khanate
- Javad Khanate
- Karabakh Khanate
- Khoy Khanate
- Kura Khanate
- Marand Khanate
- Mehtuli Khanate
- Nakhchivan Khanate
- Quba Khanate
- Shaki Khanate
- Shamakhy Khanate
- Shirvan Khanate
- Talysh Khanate
Other khanates
[edit]- Nishapur Khanate
- Rouran Khaganate
- Later Jin dynasty – Later evolved into the Qing dynasty
- Khanate of Kalat – Brahui/Baloch Khanate
- Khazar Khaganate – Turkic nomads who later converted to Rabbinic Judaism
See also
[edit]- Rus Khaganate (not an actual Khanate but so named retroactively)
- Afsharid dynasty
- Beg Khan
- Orda (organization)
- Safavid dynasty
- Timurid dynasty
References
[edit]- ^ "Definition of KHANATE". merriam-webster.com. Retrieved 21 April 2023.
- ^ "khagan in Old Turkish – English-Old Turkish Dictionary | Glosbe". glosbe.com. Retrieved 21 April 2023.
- ^ a b "khanate". Oxford Reference. Retrieved 21 April 2023.
- ^ a b "What Is a Khan?". ThoughtCo. Retrieved 21 April 2023.
- ^ "The Mongol Khans". education.nationalgeographic.org. Retrieved 21 April 2023.
- ^ Cartwright, Mark. "Genghis Khan". World History Encyclopedia. Retrieved 21 April 2023.
- ^ Królikowska-Jedlińska, Natalia. Law and Division of Power in the Crimean Khanate (1532–1774).
- ^ Morgan. The Mongols. p. 5.
- ^ The Yenching Journal of Social Studies, Volumes 4-5. 1948. p. 68.
External links
[edit] Media related to Khanates at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Khanates at Wikimedia Commons
 KSF
KSF