List of active Royal Navy ships
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 17 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 17 min
 |
| His Majesty's Naval Service of the British Armed Forces |
|---|
| Components |
|
| History and future |
| Operations |
| Equipment |
| Personnel |
| Auxiliary services |
The Royal Navy is the principal naval warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Its assets include both commissioned warships and non-commissioned vessels. As of mid-2025, there are 63 commissioned and active ships in the Royal Navy.
Of the commissioned vessels, sixteen are major surface combatants (two aircraft carriers, six guided missile destroyers and eight frigates) and nine are nuclear-powered submarines (four ballistic missile submarines and five fleet submarines). In addition the Navy possesses eight mine countermeasures vessels, twenty-six patrol vessels, two survey vessels, one icebreaker and one historic warship, Victory. The total displacement of the Royal Navy's commissioned and active ships is approximately 399,000 tonnes.
The Royal Navy also includes a number of smaller non-commissioned assets. The naval training vessels Brecon and Hindostan can be found based at the Royal Navy stone frigates HMS Raleigh and the Britannia Royal Naval College, respectively. Non-commissioned Sea-class workboats, procured under Project Vahana, are operated by the Royal Navy in various support, survey and training roles, replacing previous P1000 Class Picket Boat vessels.[1][2][3] This class of vessel also incorporates an autonomous minehunting variant (known as the Arcims-class),[4] while another autonomous vessel, Madfox, is employed in varied roles including as a testbed for autonomous combat operations.[5] Madfox and other experimental vessels, including XV Patrick Blackett and APAC-24 (a crewless Pacific 24 rigid-hulled inflatable boat), are operated by the Fleet Experimentation Squadron within the Disruptive Capabilities and Technologies Office.[6][7][8] As of 2025, XV Excalibur, an Extra-Large Uncrewed Underwater Vehicle (XLUUV), was also operated by the Squadron[6] while other autonomous surface vessels, for minehunting, were in service and in the process of procurement from Thales Group.[9]
Besides the Royal Navy, the Royal Fleet Auxiliary (RFA) and the Royal Marines operate their own flotillas of vessels which complement the assets of the Royal Navy. These vessels are not included in this list or the above figures. Nevertheless, combined, the Royal Navy and RFA have 73 vessels with a total displacement of about 671,000 tonnes, with the principal landing craft of the Royal Marines having an additional combined displacement of about 2,200 tonnes.
As a supporting contingent of His Majesty's Naval Service, the civilian Marine Services operate nearly 100 auxiliary ships (including coastal logistics, tugs and research vessels) in support of Royal Navy and Royal Fleet Auxiliary operations.[10][11]
In the United Kingdom, the Royal Navy operates three main bases where commissioned ships are based: HMNB Portsmouth, HMNB Devonport and HMNB Clyde. A number of commissioned vessels, belonging to the University Royal Naval Units (URNU), are stationed at various other locations around the United Kingdom.
The Royal Navy's principal overseas base is HMS Jufair in Bahrain.[12] A general-purpose frigate and vessels belonging to the navy's 9th Mine Counter-Measures Squadron are forward-deployed there. Two fast patrol boats, together with a forward-deployed River-class offshore patrol vessel, normally form part of the Gibraltar Squadron and are permanently based there. Four other River-class vessels are also forward-deployed: one in the Falkland Islands, one in the Caribbean and two in the Indo-Pacific region. Additionally, the United Kingdom maintains a Joint Logistics Support Base in Duqm, Oman.[13]
All ships and submarines currently in commission with the Royal Navy were built in the United Kingdom, with the exceptions of icebreaker Protector which was built in Norway and survey vessel Magpie which was substantially built in Ireland. All commissioned vessels of the Royal Navy bear the ship prefix "HMS", for His Majesty's Ship or His Majesty's Submarine.
Ceremonial/Historic ship
[edit]| Flagship of the First Sea Lord | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classic first-rate | |||||||
| Class | Ship | No. | Commissioned | Displacement | Type | Homeport | Note |
| Ship of the line | HMS Victory | — | 1778[N 1] | 3,556 tonnes | First-rate ship of the line | Portsmouth | [14] |
Submarine service
[edit]| Submarine service | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic | |||||||
| Class | Boat | No. | Commissioned | Displacement | Type | Homeport | Note |
| Vanguard class | HMS Vanguard | S28 | 1993 | 15,900 tonnes | Ballistic missile submarine | Clyde | [15] |
| HMS Victorious | S29 | 1995 | [16] | ||||
| HMS Vigilant | S30 | 1996 | [17] | ||||
| HMS Vengeance | S31 | 1999 | [18] | ||||
| Fleet | |||||||
| Class | Boat | Pennant No. | Commissioned | Displacement | Type | Homeport | Note |
| Astute class | HMS Astute | S119 | 2010 | 7,400 tonnes | Fleet submarine | Clyde | [19] |
| HMS Ambush | S120 | 2013 | [20] | ||||
| HMS Artful | S121 | 2016 | [21] | ||||
| HMS Audacious | S122 | 2021 | [22][23] | ||||
| HMS Anson | S123 | 2022 | [24] | ||||
Surface fleet
[edit]Auxiliary vessels
[edit]See also: Ships of the Royal Fleet Auxiliary and vessels operated by Serco Marine Services
| RN auxiliary ships | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survey | |||||||
| Class | Ship | No. | Commissioned | Displacement | Type | Homeport | Note |
| — | HMS Scott | H131 | 1997 | 13,500 tonnes | Ocean survey | Devonport | [80] |
| — | HMS Protector | A173 | 2011 | 5,000 tonnes | Icebreaker & survey | [81][N 16] | |
| Sea class 18 m variant | HMS Magpie | H130 | 2018 | 37 tonnes | Survey motor launch | [83] | |
| Non-commissioned vessels | |||||||
| Class | Ship | No. | In service | Displacement | Type | Homeport | Note |
| — | XV Excalibur | N/A | 2025 | 19 tonnes | Extra-Large Uncrewed Underwater Vehicle (XLUUV) | Devonport | [6][84] |
| — | XV Patrick Blackett | X01 | 2022 | 270 tonnes | Experimental vessel | Portsmouth | [85] |
| — | Madfox | N/A | 2021 | c. 10 tonnes | Autonomous surface vessel | Portsmouth | [5][86] |
| Hunt class | Brecon | M29 | 1979 | 750 tonnes | Static Training Ship | HMS Raleigh | [87] |
| Sandown class | Hindostan (ex-Cromer) | M103 | 1992 | 600 tonnes | Britannia Royal Naval College | [88] | |
| Sea class | 34 vessels:[89] * 8 x 15 m Officer Training Units; * 6 x 15 m Diver Training/Support Boats; * 4 x 15 m Survey/hydrographic Modules; * 3 x 13.8 m Passenger Transfer Boats (PTBs); * 10 x 11 m Standard Workboats; * 3 x 11 m Small Survey Modules |
— | 2018 to 2024 | 15 to 23 tonnes | Workboats | — | [N 17][90][1][91] |
| ALN-139 class | Sea Harrier Buccaneer Sea Vixen Swordfish |
— | 2017 | c. 15 - 20 tonnes | — | [N 18][92] | |
| Arcims class | RNMB Hussar | — | 2021 to 2023 | < 10 tonnes (six units); c.10+ tonnes (Hebe)[93][94] | Autonomous minehunting/sweeping | Clyde | [95][96][97][98][99] |
| RNMB Hazard | |||||||
| RNMB Hellcat [100] | |||||||
| RNMB Halcyon | |||||||
| RNMB Harrier | |||||||
| RNMB Hydra | |||||||
| RNMB Hebe | |||||||
| Thales Unmanned Surface Vessels (USVs) | RNMB Apollo | N/A | 2021 | < 10 tonnes[94] | N/A | [N 19][101][102][103][104] | |
| RNMB Abdiel | 2022 | ||||||
| RNMB Ariadne | 2025 | ||||||
Gallery
[edit]-
HMS Victory, Flagship of the First Sea Lord
-
Vanguard (Vanguard class)
-
Ambush (Astute class)
-
Queen Elizabeth
(Queen Elizabeth class) -
Daring (Type 45 destroyer)
-
St. Albans (Type 23 frigate)
-
Forth (River class)
-
Hurworth (Hunt class)
-
Ramsey (Sandown class)
-
Raider (Archer class)
-
Cutlass (Cutlass class)
-
Scott
-
Protector
-
Magpie (Sea class)
-
XV Patrick Blackett
-
RNMB Harrier (Arcims class)
-
Madfox
-
Stirling Castle
Silhouettes
[edit]Silhouettes of major fleet units:
Silhouettes of all Royal Navy and RFA units:
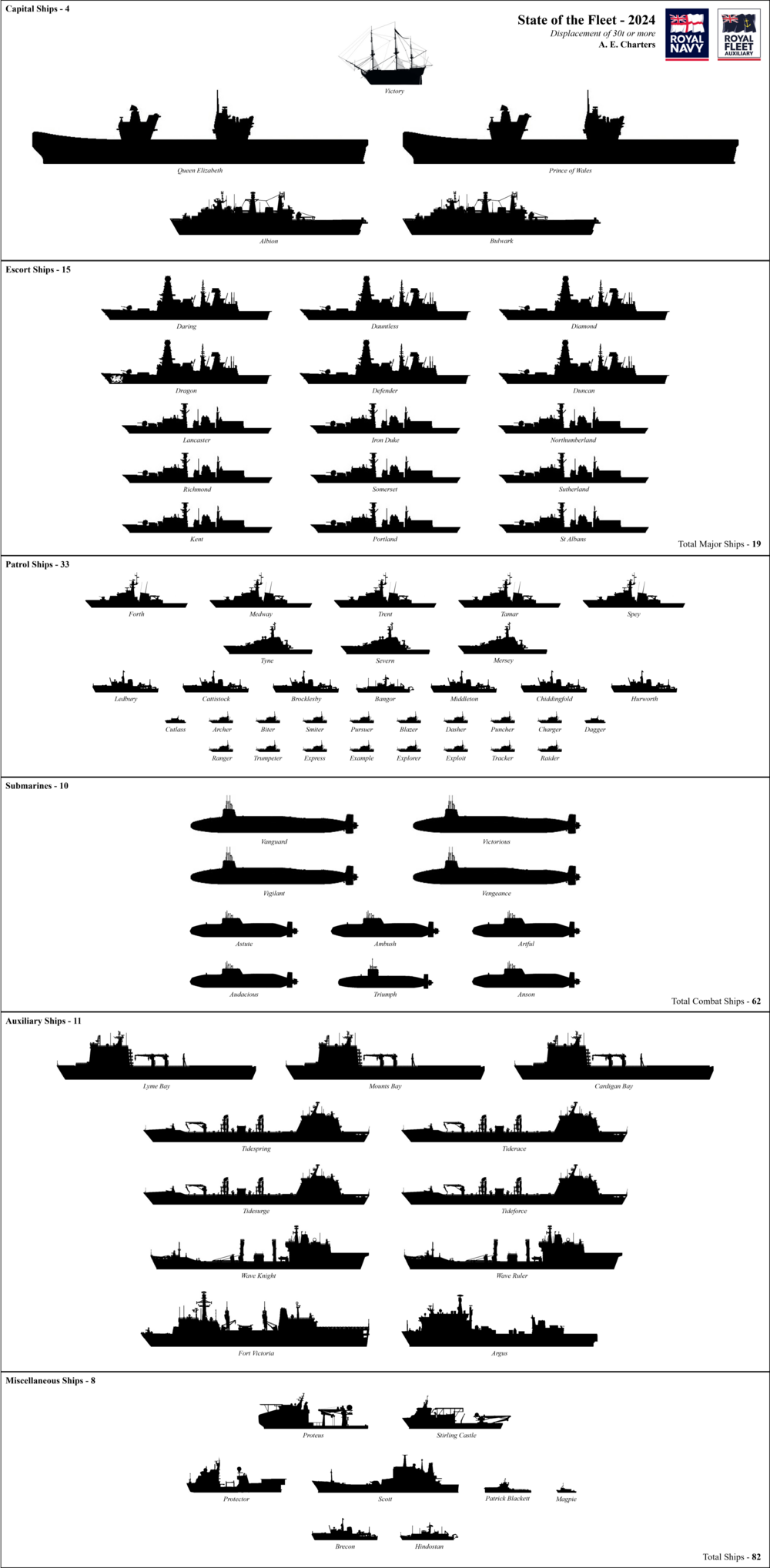
See also
[edit]- Lists of ships operated by or in support of His Majesty's Naval Service
- List of active Royal Fleet Auxiliary ships
- List of active Royal Marines military watercraft
- List of ships of Serco Marine Services
- Related articles
- List of Royal Navy shore establishments (the "stone frigates")
- List of ship names of the Royal Navy
- Active Royal Navy weapon systems
- Future of the Royal Navy
- Standing Royal Navy deployments
Footnotes
[edit]- ^ Launched in 1765 and commissioned in 1778, making Victory the world's oldest warship still in commission.
- ^ Prince of Wales is the current Fleet Flagship as of late 2024.
- ^ HMS Lancaster is forward deployed, operating from HMS Jufair in Bahrain.
- ^ HMS Forth is forward deployed, operating from Mare Harbour as guardship in the Falkland Islands.
- ^ HMS Medway is forward deployed as Atlantic Patrol Tasking (North) guardship in the Caribbean.
- ^ HMS Trent is forward deployed to Gibraltar for regional operations in the Mediterranean and Gulf of Guinea.
- ^ HMS Tamar is forward deployed to the Indo-Pacific region with her primary logistics hub at the British Defence Singapore Support Unit in Singapore[51]
- ^ HMS Spey is forward deployed to the Indo-Pacific region with her primary logistics hub at the British Defence Singapore Support Unit in Singapore[51]
- ^ HMS Middleton is forward deployed as part of 9 Mine Countermeasures Squadron, operating from HMS Jufair in Bahrain.
- ^ HMS Bangor is forward deployed as part of 9 Mine Countermeasures Squadron, operating from HMS Jufair in Bahrain.
- ^ Former vessel of the Royal Fleet Auxiliary serving as mothership for Royal Navy autonomous minehunting/sweeping systems.
- ^ Forms part of the Faslane Patrol Boat Squadron providing security to nuclear submarines entering and leaving the waters in and around HMNB Clyde.
- ^ Forms part of the Faslane Patrol Boat Squadron providing security to nuclear submarines entering and leaving the waters in and around HMNB Clyde.
- ^ Permanently based in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. Forms part of the Gibraltar Squadron.
- ^ Permanently based in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. Forms part of the Gibraltar Squadron.
- ^ Deployed in Antarctic waters during the regional summer. Official role to: "patrol and survey in the Antarctic and South Atlantic, maintaining UK sovereign presence with wider regional engagement".[82]
- ^ Officer training units assigned to Britannia Royal Naval College; Diver support boats at HMNB Portsmouth (three units), Devonport, Clyde and Gibraltar (one unit each); Passenger Transfer units to HMS Prince of Wales; and two or more small survey modules to HMS Protector and HMS Scott.
- ^ Three assigned as passenger transfer vessels to HMS Queen Elizabeth
- ^ Apollo and Abdiel are pre-production units within joint UK-France MCM programme; Ariadne first production USV within a complete Maritime Mine Counter Measures (MMCM) system also consisting of Portable Operation Centre (POC), Synthetic Aperture & Mine Detection Imaging Sonar and Multi-Shot Mine Neutralisation System; three additional USVs to be delivered in 2025 within larger MMCM systems
References
[edit]- ^ a b "In focus: the versatile new workboats being built for the Royal Navy". Navy Lookout. 6 August 2018. Retrieved 11 March 2023.
- ^ Bush, Steve (2014). British Warships and Auxiliaries. Maritime Books. p. 119. ISBN 978-1-904459552.
- ^ "New lease of life for BRNC boats". Royal Navy. 29 June 2017. Retrieved 11 July 2017.
- ^ "Autonomous systems - the future of royal navy mine warfare". NavyLookout. 26 May 2021.
- ^ a b "Royal Navy launches missile from autonomous vessel in NATO exercise". Royal Navy. 14 October 2021. Retrieved 27 May 2023.
- ^ "Royal Navy establishes new Disruptive Capabilities and Technologies Office". Navy Lookout. 30 April 2025. Retrieved 15 May 2025.
- ^ "Royal Navy Launched Its First 'Crewless Pacific 24 Boat' USV". Naval News. 24 June 2020. Retrieved 28 May 2023.
- ^ "Autonomous minehunter RNMB Apollo passes trials". 15 June 2023.
- ^ "Outsourcing giant Serco marks 25 years working with Royal Navy". BusinessLive. 12 August 2021. Retrieved 30 April 2023.
- ^ "Vessel Management". Serco Marine Services. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 20 June 2014.
- ^ "Navy's new Gulf home almost ready for first sailors". Royal Navy. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ Allison, George (30 July 2021). "British Littoral Response Group ships to be based in Oman". UK Defence Journal. Retrieved 23 September 2021.
- ^ Farmer, Ben (7 December 2017). "The Queen commissions the Royal Navy's newest aircraft carrier - HMS Queen Elizabeth". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- ^ "HMS Vanguard". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Victorious". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Vigilant". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Vengeance". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Astute". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Ambush". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Artful". Royal Navy. Retrieved 18 March 2016.
- ^ "HMS Audacious". UK Parliament. Retrieved 11 May 2020.
- ^ Navy Lookout [@NavyLookout] (23 September 2021). "HMS Audacious commissioned in Faslane today. https://t.co/CiEgVDE7Er" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 24 September 2021. Retrieved 14 November 2021 – via Twitter.
- ^ Edwards, Lucy (31 August 2022). "Boris Johnson visits BAE Systems in Barrow". CumbriaCrack.
- ^ "Aircraft Carriers - Future Flagships". Royal Navy. Retrieved 7 December 2017.
- ^ "HMS Queen Elizabeth". Royal Navy. Retrieved 12 January 2018.
- ^ "Commissioning day for HMS Prince of Wales". Royal Navy. Portsmouth. 10 December 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ "HMS Daring". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "A return to the old routine for 14 dock". Royal Navy. 24 June 2020.
- ^ "HMS Dauntless". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Diamond". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Dragon". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Defender". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Duncan". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Lancaster". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Iron Duke". Royal Navy. Archived from the original on 28 April 2015. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Richmond". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Somerset". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Sutherland". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Kent". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "FOI(A) regarding the Royal Navy" (PDF). What do they know?. 27 April 2021. Retrieved 1 June 2023.
- ^ "HMS Portland". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS St Albans". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Tyne". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Severn Re-Commissioned Into Royal Navy After Nearly Three Years". Forces News. 1 July 2020. Retrieved 7 July 2020.
- ^ "HMS Tyne returns to service after being paid off in May". Save the Royal Navy. 31 July 2018. Retrieved 1 August 2018.
- ^ "HMS Forth". Royal Navy. Retrieved 6 April 2018.
- ^ "HMS Medway". Royal Navy. Retrieved 19 September 2019.
- ^ "HMS Trent Commissioned Into Royal Navy In Portsmouth". Forces News. Portsmouth. 3 August 2020. Retrieved 3 August 2020.
- ^ "HMS Tamar Raises Her Flag On Her Own River". Royal Navy. River Tamar. 4 June 2020. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- ^ a b Graham, Euan (19 October 2021). "Reflections on the Royal Navy's Indo-Pacific engagement". International Institute for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 20 October 2021.
- ^ "@HMS_Spey" on Twitter
- ^ "HMS Ledbury". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Cattistock". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Brocklesby". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Middleton". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Chiddingfold". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Hurworth". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Bangor". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "Specialist mine hunting ship formally becomes Royal Navy warship". Royal Navy. 21 July 2025. Retrieved 21 July 2025.
- ^ "HMS Archer". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Biter". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Smiter". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Pursuer (P273) | Royal Navy".
- ^ "HMS Blazer". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Dasher (P280) | Royal Navy".
- ^ "HMS Puncher". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Charger". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Ranger". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Trumpeter". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Express". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Example". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Explorer". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Exploit". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Tracker". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Raider". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ @MODGibraltar (4 May 2022). "Today HMS Cutlass was officially commissioned at @RNGibSqn" (Tweet). Retrieved 7 May 2022 – via Twitter.
- ^ Navy Lookout [@NavyLookout] (13 June 2022). "Newly commissioned HMS Dagger keeps an eye on Spanish frigate Blas de Lezo..." (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ "UK Royal Navy receives patrol boat HMS Dagger". Naval Technology.com. 4 April 2022.
- ^ "HMS Scott". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "HMS Protector". Royal Navy. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ "In focus: HMS Protector – the Royal Navy's Antarctic patrol ship". Navy Lookout. 7 May 2019.
- ^ "HMS Magpie". Royal Navy. Retrieved 29 June 2018.
- ^ "Royal Navy unveil 12 metre uncrewed submarine named after Excalibur". Royal Navy. 15 May 2025. Retrieved 16 May 2025.
- ^ "Debut for UK Royal Navy's new experimental vessel". Jane's Information Group. 29 July 2022. Retrieved 1 August 2022.
- ^ "Maritime Demonstrator for Operational eXperimentation (MADFOX) Uncrewed Surface Vessel, UK". Naval Technology. 21 October 2021. Retrieved 27 May 2023.
- ^ "HMS Raleigh Training Establishment". Royal Navy. Retrieved 7 June 2014.
- ^ "Future of minehunting sails into Dartmouth | Royal Navy".
- ^ "Final Vahana Workboats delivered to complete Royal Navy fleet". Ministry of Defence. 19 July 2024.
- ^ "ATLAS ELEKTRONIK UK SEA Class – Delivering an Innovative, Flexible, Cost-effective Solution to the UK MOD". thyssenkrupp-marinesystems.com. Retrieved 11 March 2023.
- ^ "The final of six new boats to improve support to Royal Navy divers has been delivered". Royal Navy. 23 February 2023. Retrieved 3 July 2023.
- ^ "Passenger Transfer Boats for HMS Prince of Wales to be delivered this year". Navy Lookout. 15 July 2021.
- ^ "Royal Navy Fleet Poster p.21" (PDF). Navy News. February 2023. Retrieved 13 June 2023.
- ^ a b "Up close with RFA Stirling Castle – first of the navy's new motherships". Navy Lookout. 4 July 2023.
- ^ "Autonomous systems – the future of Royal Navy mine warfare | Navy Lookout". www.navylookout.com. 26 May 2021.
- ^ "Future mine hunting system comes to Clyde | Royal Navy".
- ^ "ATLAS ELEKTRONIK UK TO DELIVER A FURTHER AUTONOMOUS MINEHUNTING SYSTEM TO THE ROYAL NAVY". Atlas Elektronik. 1 February 2022.
- ^ "Royal Navy autonomous mine hunting at the sharp end". Navy Lookout. 30 March 2023.
- ^ "Royal Navy accepts new autonomous mine hunting system into service". Naval News. 7 July 2025.
- ^ Molinelli, Gabriele (16 July 2025). "TKMS Atlas completes deliveries of 3 SWEEP systems for the Royal Navy Mine CounterMeasures capability". Future Warfare Magazine.
- ^ "Thales' Uncrewed Surface Vessel passes a significant milestone in Automomous minehunting trials". Thales. 14 June 2023.
- ^ Felstead, Peter (15 June 2023). "Thales-Supplied USV Successfully Completes RN Assurance Trials". European Security and Defence.
- ^ Fish, Tim (December 2022). "Beating the Minefield with Autonomous Countermeasures". issuu.com.
- ^ "Royal Navy receives first fully autonomous end-to-end mine warfare system". Navy Lookout. 3 March 2025.
External links
[edit]- Royal Navy (royalnavy.mod.uk)
- Royal Navy — The Equipment — Ships (royalnavy.mod.uk)
 KSF
KSF





















