Maguindanao del Norte
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 14 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 14 min
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
Maguindanao del Norte
Utara Magindanaw اُوْتَرَ مَڬِنْدَنَوْ | |
|---|---|
 Polloc Port in Parang | |
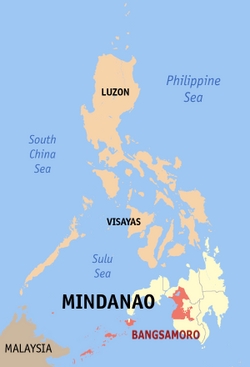
 Location in the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 07°08′N 124°16′E / 7.133°N 124.267°E | |
| Country | |
| Region | |
| Plebiscite | September 17, 2022 |
| Transition period | September 18, 2022 - January 9, 2023 |
| Capital | Datu Odin Sinsuat |
| Largest city | Cotabato City |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Tucao Mastura |
| • Vice Governor | Marshall Sinsuat |
| • Representative | Sittie Shahara I. Mastura |
| Area | |
• Total | 3,988.82 km2 (1,540.09 sq mi) |
| Population (2025) | |
• Total | 1,105,061 |
| • Rank | 52nd out of 82 |
| • Density | 280/km2 (720/sq mi) |
| • Rank | 24th out of 82 |
| Demonym | North Magindanawon |
| Divisions | |
| • Independent cities | 1
|
| • Component cities | 0 |
| • Municipalities | |
| • Districts | Legislative districts of Maguindanao del Norte |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PHT) |
| ISO 3166 code | PH-MGN |
| Spoken languages | |
| Income classification | 4th class |
Maguindanao del Norte, officially the Province of Maguindanao del Norte (Maguindanaon: Dairat nu Utara Magindanaw, Jawi: دَاِيْرَتْ نُوْ اُوْتَرَ مَڬِنْدَنَوْ; Iranun: Perobinsia a Pangutaran Magindanao, ڤروبنسيا ا ڤڠوترن مڬیندانو Filipino: Hilagang Maguindanao), is a province in the Philippines located in the Bangsamoro region in Mindanao. Its capital is the municipality of Datu Odin Sinsuat. It borders Cotabato province to the east, Lanao del Sur to the north, Maguindanao del Sur to the south-east, and Sultan Kudarat to the south.
The province's largest city, Cotabato City, is administratively independent from the province but is grouped for congressional representation.
History
[edit]
Spain 1521–1898
United States of America 1898–1942
Japan 1942–1945
United States of America 1945–1946
Philippines 1946–present
Foundation
[edit]The idea of creating a province in the present territory of Maguindanao del Norte dates back to 2006 when the province of Shariff Kabunsuan briefly existed for two years before being reverted as part of Maguindanao.[1]
Maguindanao del Norte was formed when Maguindanao province was split into two provinces; the other province being Maguindanao del Sur. The division occurred following a plebiscite on September 17, 2022 which ratified Republic Act 11550 wherein it proposed the partitioning of the province. Former Maguindanao Vice Governor Ainee Sinsuat was expected to become the acting governor of the newly formed Maguindanao del Norte province.[2] However an issue arose since the determination of the first set of officials of the province presumes that the plebiscite was held prior to the 2022 national and local elections. However the plebiscite was postponed to a date after the elections.[3] This led to the Commission on Elections to come up with a legal opinion.[4][5] The position was issued on September 28, 2022, where the election body conclude that only the Department of the Interior and Local Government could appoint the first officials of the province.[3]
Sinsuat took oath as the first governor of the province on October 13, 2022 with former Maguindanao Provincial Board member Sharifudin Mastura as her vice governor.[6] A transition period would take place until January 9, 2023.[7] On April 28, 2023, President Bongbong Marcos appointed Abdulraof Macacua as the full pledged governor of the province while Sinsuat was appointed as the vice governor. On August 14, 2023, Sinsuat vacated her position as vice governor and revived her claim as the legitimate governor. Both the national and Bangsamoro regional government does not recognize Sinsuat's claim.
Geography
[edit]
Maguindanao del Norte has a total area of 3,988.82 square kilometers (1,540.09 sq mi). The province is bordered to the north by Lanao del Sur, to the east by Cotabato, to the southwest by Maguindanao del Sur, and to the south by Sultan Kudarat. It has an outlying island near the mainland called Bongo Island, which falls under its jurisdiction.
Administrative divisions
[edit]Maguindanao del Norte is composed of 1 independent city, 12 municipalities, and 3 legislative districts.
- † Capital municipality
- Municipality
- ∗∗ Independent component city (only geographically grouped with the province)
- ∞ Largest settlement
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Demographics
[edit]| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1903 | 1,706 | — |
| 1918 | 25,719 | +19.83% |
| 1939 | 52,766 | +3.48% |
| 1948 | 105,386 | +7.99% |
| 1960 | 190,201 | +5.04% |
| 1970 | 241,796 | +2.43% |
| 1975 | 265,383 | +1.88% |
| 1980 | 297,597 | +2.32% |
| 1990 | 424,267 | +3.61% |
| 1995 | 456,208 | +1.37% |
| 2000 | 529,697 | +3.25% |
| 2010 | 695,622 | +2.76% |
| 2015 | 821,475 | +3.22% |
| 2020 | 926,037 | +2.55% |
| 2024 | 1,105,061 | +4.33% |
| a No census was held in 1985 due to a political and economic crisis b Census was delayed from the original 2005 due to the reenacted budget that lasted until 2006 Source: National Census and Statistics Office (1975,[10] 1980,[11] and 1990[12] census), National Statistics Office (1995,[13] 2000,[14] 2007,[15] and 2010[16] census) and Philippine Statistics Authority (2015 and 2020 census)[17] | ||
According to the 2020 census conducted before the province's creation, Maguindanao del Norte has a population of 926,037 people, with a population density of 230 inhabitants per square kilometer or 600 inhabitants per square mile.[18] The predominant ethnic group is the Maguindanaon.
| Population percentage (2020 Census)[19] |
|---|
|
| Total population: 994,182 |
Government
[edit]GOVERNORS OF MAGUINDANAO DEL NORTE
- Bai Fatimah Aimee L. Sinsuat
- Abdulraof A. Macacua
- Datu Shariffudin Tucao P. Mastura
- Datu Tucao O. Mastura
VICE GOVERNORS OF MAGUINDANAO DEL NORTE
- Datu Shariffudin Tucao P. Mastura
- Bai Fatimah Aimee L. Sinsuat
- Abdulnasser A. Abas
- Datu Marshall I. Sinsuat
Economy
[edit]Transportation and storage, other non-agricultural services, food and accommodation services is becoming the fastest growing sector in the province. Agricultural activities include forestry and fishing.[20]
According to the Philippine Statistics Authority, Maguindanao del Norte had improved its economic growth from 7.8 percent in 2021 (before its establishment) to 8.8 percent in 2022. The province had a Gross Domestic Product of 78.01 billion Philippine pesos in 2022.[20]
Notable people
[edit]- Orlando Quevedo – Cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church
- Elias Lumayog Ayuban Jr. – second bishop of Roman Catholic Diocese of Cubao.
- Noel Felongco – Lead Convenor of National Anti-Poverty Commission
- Imah Dumagay – Stand-up comedian based in Dubai
- Romero Duno – Professional Boxer
- Jay Jaboneta – Blogger, Philanthropist, Media Advocate, and Online Community Organizer
- Kublai Millan – Prolific Artist
- Ben Farrales – Fashion Designer, known for his muslim inspired terno designs
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Unson, John (January 11, 2009). "Shariff Kabunsuan province abolished". The Philippine Star. Retrieved September 19, 2022.
- ^ "With Maguindanao split into 2, Mindanao now has 28 provinces and BARMM has 6". MindaNews. September 18, 2022. Retrieved September 18, 2022.
- ^ a b Villegas, Gab Humilde (September 27, 2022). "DILG urged: Appoint Maguindanao official". Daily Tribune.
- ^ Patinio, Ferdinand (September 19, 2022). "Comelec legal opinion on Maguindanao leadership 'row' out soon". Philippine News Agency. Retrieved September 19, 2022.
- ^ "Who will lead two Maguindanao provinces? Comelec to issue legal opinion soon". CNN Philippines. September 19, 2022. Archived from the original on September 19, 2022. Retrieved September 19, 2022.
- ^ "Governors, vice govs of split Maguindanao provinces assume posts". ABS-CBN News. October 22, 2022. Retrieved October 23, 2022.
- ^ "End of an era: Maguindanao holds final flag-raising ceremony". Rappler. January 10, 2023. Retrieved January 11, 2023.
- ^ Census of Population (2020). Table B - Population and Annual Growth Rates by Province, City, and Municipality - By Region. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ^ Census of Population (2015). Highlights of the Philippine Population 2015 Census of Population. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved June 20, 2016.
- ^ "1975 Integrated Census of the Population and Its Economic Activities – Population Rizal" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. p. 13. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 12, 2024. Retrieved June 28, 2024.
- ^ "1980 Population Count" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. p. 51. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 27, 2023. Retrieved June 28, 2024.
- ^ "1990 Census of Population and Housing" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 12, 2024. Retrieved June 28, 2024.
- ^ "Population Census". National Statistics Office. Archived from the original on February 11, 1998. Retrieved June 28, 2024.
- ^ "Census 2000". National Statistics Office. Archived from the original on April 5, 2002. Retrieved June 28, 2024.
- ^ "2007 Census of Population". National Statistics Office. Archived from the original on February 9, 2010. Retrieved June 28, 2024.
- ^ "Population Counts - Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao" (PDF). National Statistics Office. p. 43. Archived (PDF) from the original on November 27, 2023. Retrieved December 13, 2024.
- ^ "2020 Census of Population and Housing" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. p. 70. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 9, 2024. Retrieved June 27, 2024.
- ^ Census of Population (2020). Table B - Population and Annual Growth Rates by Province, City, and Municipality - By Region. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ^ Census of Population (2020). "Region V (Bicol Region)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ^ a b "2022 Economic Performance of Maguindanao del Norte | Philippine Statistics Authority". rssobarmm.psa.gov.ph. Retrieved October 26, 2024.
 KSF
KSF