Neptune
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 53 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 53 min
 | |||||||||||||
| Discovery[2] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discovered by | |||||||||||||
| Discovery date | 23 September 1846 | ||||||||||||
| Designations | |||||||||||||
| Pronunciation | US: /ˈnɛptuːn/ ⓘ, UK: /-tjuːn/[3] | ||||||||||||
Named after | Latin Neptunus, via French Neptune | ||||||||||||
| Adjectives | Neptunian (/nɛpˈtjuːniən/),[4] Poseidean[5] | ||||||||||||
| Symbol | |||||||||||||
| Orbital characteristics[6][b] | |||||||||||||
| Epoch J2000 | |||||||||||||
| Aphelion | 30.33 AU (4.54 billion km) | ||||||||||||
| Perihelion | 29.81 AU (4.46 billion km) | ||||||||||||
| 30.07 AU (4.50 billion km) | |||||||||||||
| Eccentricity | 0.008678 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| 367.49 days[8] | |||||||||||||
Average orbital speed | 5.43 km/s[8] | ||||||||||||
| 259.883° | |||||||||||||
| Inclination | 1.770° to ecliptic 6.43° to Sun's equator 0.74° to invariable plane[9] | ||||||||||||
| 131.783° | |||||||||||||
| 2042-Sep-04[10] | |||||||||||||
| 273.187° | |||||||||||||
| Known satellites | 16 | ||||||||||||
| Physical characteristics | |||||||||||||
| 24,622±19 km[11][c] | |||||||||||||
Equatorial radius | 24,764±15 km[11][c] 3.883 Earths | ||||||||||||
Polar radius | 24,341±30 km[11][c] 3.829 Earths | ||||||||||||
| Flattening | 0.0171±0.0013 | ||||||||||||
| 7.6183×109 km2[12][c] 14.94 Earths | |||||||||||||
| Volume | 6.253×1013 km3[8][c] 57.74 Earths | ||||||||||||
| Mass | 1.02409×1026 kg[8] 17.147 Earths 5.15×10−5 Suns | ||||||||||||
Mean density | 1.638 g/cm3[8][d] | ||||||||||||
| 11.15 m/s2 (1.137 g0)[8][c] | |||||||||||||
| 0.23[13] (estimate) | |||||||||||||
| 23.5 km/s[8][c] | |||||||||||||
| 0.67125 d 16 h 6 m 36 s[7] | |||||||||||||
| 0.6713 day[8] 16 h 6 min 36 s | |||||||||||||
Equatorial rotation velocity | 2.68 km/s[14] | ||||||||||||
| 28.32° (to orbit)[8] | |||||||||||||
North pole right ascension | 19h 57m 20s[11] 299.36°[15] | ||||||||||||
North pole declination | 43.46°[15] | ||||||||||||
| Albedo | 0.290 (bond)[16] 0.442 (geom.)[17] | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| 7.67[18] to 8.00[18] | |||||||||||||
| −6.9[19] | |||||||||||||
| 2.2–2.4″[8][20] | |||||||||||||
| Atmosphere[8] | |||||||||||||
| 19.7±0.6 km | |||||||||||||
| Composition by volume | |||||||||||||
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet orbiting the Sun. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times the mass of Earth. Compared to Uranus, its neighbouring ice giant, Neptune is slightly smaller, but more massive and denser. Being composed primarily of gases and liquids,[21] it has no well-defined solid surface. Neptune orbits the Sun once every 164.8 years at an orbital distance of 30.1 astronomical units (4.5 billion kilometres; 2.8 billion miles). It is named after the Roman god of the sea and has the astronomical symbol ![]() , representing Neptune's trident.[e]
, representing Neptune's trident.[e]
Neptune is not visible to the unaided eye and is the only planet in the Solar System that was not initially observed by direct empirical observation. Rather, unexpected changes in the orbit of Uranus led Alexis Bouvard to hypothesise that its orbit was subject to gravitational perturbation by an unknown planet. After Bouvard's death, the position of Neptune was mathematically predicted from his observations, independently, by John Couch Adams and Urbain Le Verrier. Neptune was subsequently directly observed with a telescope on 23 September 1846[2] by Johann Gottfried Galle within a degree of the position predicted by Le Verrier. Its largest moon, Triton, was discovered shortly thereafter, though none of the planet's remaining moons were located telescopically until the 20th century.
The planet's distance from Earth gives it a small apparent size, and its distance from the Sun renders it very dim, making it challenging to study with Earth-based telescopes. Only the advent of the Hubble Space Telescope and of large ground-based telescopes with adaptive optics allowed for detailed observations. Neptune was visited by Voyager 2, which flew by the planet on 25 August 1989; Voyager 2 remains the only spacecraft to have visited it.[22][23] Like the gas giants (Jupiter and Saturn), Neptune's atmosphere is composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, along with traces of hydrocarbons and possibly nitrogen, but contains a higher proportion of ices such as water, ammonia and methane. Similar to Uranus, its interior is primarily composed of ices and rock;[24] both planets are normally considered "ice giants" to distinguish them.[25] Along with Rayleigh scattering, traces of methane in the outermost regions make Neptune appear faintly blue.[26][27]
In contrast to the strongly seasonal atmosphere of Uranus, which can be featureless for long periods of time, Neptune's atmosphere has active and consistently visible weather patterns. At the time of the Voyager 2 flyby in 1989, the planet's southern hemisphere had a Great Dark Spot comparable to the Great Red Spot on Jupiter. In 2018, a newer main dark spot and smaller dark spot were identified and studied.[28] These weather patterns are driven by the strongest sustained winds of any planet in the Solar System, as high as 2,100 km/h (580 m/s; 1,300 mph).[29] Because of its great distance from the Sun, Neptune's outer atmosphere is one of the coldest places in the Solar System, with temperatures at its cloud tops approaching 55 K (−218 °C; −361 °F). Temperatures at the planet's centre are approximately 5,400 K (5,100 °C; 9,300 °F).[30][31] Neptune has a faint and fragmented ring system (labelled "arcs"), discovered in 1984 and confirmed by Voyager 2.[32]
History
[edit]Discovery
[edit]Some of the earliest known telescopic observations ever, Galileo's drawings on 28 December 1612 and 27 January 1613 (New Style) contain plotted points that match what is now known to have been the positions of Neptune on those dates. Both times, Galileo seems to have mistaken Neptune for a fixed star when it appeared close—in conjunction—to Jupiter in the night sky.[33] Hence, he is not credited with Neptune's discovery. At his first observation in December 1612, Neptune was almost stationary in the sky because it had just turned retrograde that day. This apparent backward motion is created when Earth's orbit takes it past an outer planet. Because Neptune was only beginning its yearly retrograde cycle, the motion of the planet was far too slight to be detected with Galileo's small telescope.[34] In 2009, a study suggested that Galileo was at least aware that the "star" he had observed had moved relative to fixed stars.[35]
In 1821, Alexis Bouvard published astronomical tables of the orbit of Uranus.[36] Subsequent observations revealed substantial deviations from the tables, leading Bouvard to hypothesize that an unknown body was perturbing the orbit through gravitational interaction.[37] In 1843, John Couch Adams began work on the orbit of Uranus using the data he had. He requested extra data from Sir George Airy, the Astronomer Royal, who supplied it in February 1844. Adams continued to work in 1845–1846 and produced several different estimates for the position of an undiscovered planet beyond Uranus.[38][39]
Independently from Adams, Urbain Le Verrier developed his own calculations in 1845–1846 that pointed to an undiscovered planet, but aroused no enthusiasm among his compatriots. In June 1846, upon seeing Le Verrier's first published estimate of a suspected undiscovered planet's longitude and its similarity to Adams's estimate, Airy persuaded James Challis to search for it. Challis vainly scoured the sky throughout August and September.[37][40] Challis had, in fact, observed Neptune a year before the planet's subsequent discoverer, Johann Gottfried Galle, and on two occasions, 4 and 12 August 1845. However, his out-of-date star maps and poor observing techniques meant that he failed to recognize the observations as such until he carried out later analysis. Challis was full of remorse but blamed his neglect on his maps and the fact that he was distracted by his concurrent work on comet observations.[41][37][42]
Meanwhile, Le Verrier sent a letter and urged Berlin Observatory astronomer Galle to search with the observatory's refractor. Heinrich d'Arrest, a student at the observatory, suggested to Galle that they could compare a recently drawn chart of the sky in the region of Le Verrier's predicted location with the current sky to seek the displacement characteristic of a planet, as opposed to a fixed star. On the evening of 23 September 1846, the day Galle received the letter, he discovered Neptune just northeast of Iota Aquarii, 1° from the "five degrees east of Delta Capricorn" position Le Verrier had predicted it to be,[43][44] about 12° from Adams's prediction, and on the border of Aquarius and Capricornus according to the modern IAU constellation boundaries.

In the wake of the discovery, there was a nationalistic rivalry between the French and the British over who deserved credit for the discovery. Eventually, an international consensus emerged that Le Verrier and Adams deserved joint credit.[45] Since 1966, Dennis Rawlins has questioned the credibility of Adams's claim to co-discovery, and the issue was re-evaluated by historians with the return in 1998 of the "Neptune papers" (historical documents) to the Royal Observatory, Greenwich.[46][47]
Naming
[edit]Shortly after its discovery, Neptune was referred to simply as "the planet exterior to Uranus" or as "Le Verrier's planet". The first suggestion for a name came from Galle, who proposed the name Janus. In England, Challis put forward the name Oceanus.[48]
Claiming the right to name his discovery, Le Verrier quickly proposed the name Neptune for this new planet, though falsely stating that this had been officially approved by the French Bureau des Longitudes.[49] In October, he sought to name the planet Le Verrier, after himself, and he had loyal support in this from the observatory director, François Arago. This suggestion met with stiff resistance outside France.[50] French almanacs quickly reintroduced the name Herschel for Uranus, after that planet's discoverer Sir William Herschel, and Leverrier for the new planet.[51]
Struve came out in favour of the name Neptune on 29 December 1846, to the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences,[52] after the colour of the planet as viewed through a telescope.[53] Soon, Neptune became the internationally accepted name. In Roman mythology, Neptune was the god of the sea, identified with the Greek Poseidon. The demand for a mythological name seemed to be in keeping with the nomenclature of the other planets, all of which were named for deities in Greek and Roman mythology.[f][54]
Most languages today use some variant of the name "Neptune" for the planet. In Chinese, Vietnamese, Japanese, and Korean, the planet's name was translated as "sea king star" (海王星).[55][56] In Mongolian, Neptune is called Dalain van (Далайн ван), reflecting its namesake god's role as the ruler of the sea. In modern Greek, the planet is called Poseidon (Ποσειδώνας, Poseidonas), the Greek counterpart of Neptune.[57] In Hebrew, Rahab (רהב), from a Biblical sea monster mentioned in the Book of Psalms, was selected in a vote managed by the Academy of the Hebrew Language in 2009 as the official name for the planet, even though the existing Latin term Neptun (נפטון) is commonly used.[58][59] In Māori, the planet is called Tangaroa, named after the Māori god of the sea.[60] In Nahuatl, the planet is called Tlāloccītlalli, named after the rain god Tlāloc.[60] In Thai, Neptune is referred to by the Westernised name Dao Nepchun/Nepjun (ดาวเนปจูน) but is also called Dao Ket (ดาวเกตุ, lit. 'star of Ketu'), after Ketu (केतु), the descending lunar node, who plays a role in Hindu astrology. In Malay, the name Waruna, after the Hindu god of seas, is attested as far back as the 1970s,[61] but was eventually superseded by the Latinate equivalents Neptun (in Malaysian[62]) or Neptunus (in Indonesian[63]).
The usual adjectival form is Neptunian. The nonce form Poseidean (/pəˈsaɪdiən/), from Poseidon, has also been used,[5] though the usual adjectival form of Poseidon is Poseidonian (/ˌpɒsaɪˈdoʊniən/).[64]
Status
[edit]From its discovery in 1846 until the discovery of Pluto in 1930, Neptune was the farthest known planet. When Pluto was discovered, it was considered a planet, and Neptune thus became the second-farthest known planet, except for a 20-year period between 1979 and 1999 when Pluto's elliptical orbit brought it closer than Neptune to the Sun, making Neptune the ninth planet from the Sun during this period.[65][66] The increasingly accurate estimations of Pluto's mass from ten times that of Earth's to far less than that of the Moon[67] and the discovery of the Kuiper belt in 1992 led many astronomers to debate whether Pluto should be considered a planet or as part of the Kuiper belt.[68][69] In 2006, the International Astronomical Union defined the word "planet" for the first time, reclassifying Pluto as a "dwarf planet" and making Neptune once again the outermost-known planet in the Solar System.[70]
Physical characteristics
[edit]
Neptune's mass of 1.0243×1026 kg[8] is intermediate between Earth and the larger gas giants: it is 17.15 times that of Earth but just 1/19th that of Jupiter.[g] Its gravity at 1 bar is 11.15 m/s2, 1.14 times the surface gravity of Earth,[71] and surpassed only by Jupiter.[72] Neptune's equatorial radius of 24,764 km[11] is nearly four times that of Earth. Neptune, like Uranus, is an ice giant, a subclass of giant planet, because they are smaller and have higher concentrations of volatiles than Jupiter and Saturn.[73] In the search for exoplanets, Neptune has been used as a metonym: discovered bodies of similar mass are often referred to as "Neptunes",[74] just as scientists refer to various extrasolar bodies as "Jupiters".
Internal structure
[edit]Neptune's internal structure resembles that of Uranus. Its atmosphere forms about 5 to 10% of its mass and extends perhaps 10 to 20% of the way towards the core. Pressure in the atmosphere reaches about 10 GPa, or about 105 atmospheres. Increasing concentrations of methane, ammonia and water are found in the lower regions of the atmosphere.[30]

The mantle is equivalent to 10 to 15 Earth masses and is rich in water, ammonia and methane.[2] As is customary in planetary science, this mixture is called icy even though it is a hot, dense supercritical fluid. This fluid, which has a high electrical conductivity, is sometimes called a water–ammonia ocean.[75] The mantle may consist of a layer of ionic water in which the water molecules break down into a soup of hydrogen and oxygen ions, and deeper down superionic water in which the oxygen crystallizes but the hydrogen ions float around freely within the oxygen lattice.[76] At a depth of 7,000 km, the conditions may be such that methane decomposes into diamond crystals that rain downwards like hailstones.[77][78][79] Scientists believe that this kind of diamond rain occurs on Jupiter, Saturn, and Uranus.[80][78] Very-high-pressure experiments at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory suggest that the top of the mantle may be an ocean of liquid carbon with floating solid 'diamonds'.[81][82][83]
The core of Neptune is likely composed of iron, nickel and silicates, with an interior model giving a mass about 1.2x that of Earth.[24] The pressure at the centre is 7 Mbar (700 GPa), about twice as high as that at the centre of Earth, and the temperature may be 5,400 K (5,100 °C; 9,300 °F).[30][31]
Atmosphere
[edit]At high altitudes, Neptune's atmosphere is 80% hydrogen and 19% helium.[30] A trace amount of methane is present. Prominent absorption bands of methane exist at wavelengths above 600 nm, in the red and infrared portion of the spectrum. As with Uranus, this absorption of red light by atmospheric methane is part of what gives Neptune its faint blue hue,[85] which is more pronounced for Neptune's due to concentrated haze in Uranus's atmosphere.[86][87]
Neptune's atmosphere is subdivided into two main regions: the lower troposphere, where temperature decreases with altitude, and the stratosphere, where temperature increases with altitude. The boundary between the two, the tropopause, lies at a pressure of 0.1 bars (10 kPa).[25] The stratosphere then gives way to the thermosphere at a pressure lower than 10−5 to 10−4 bars (1 to 10 Pa).[25] The thermosphere gradually transitions to the exosphere.[88]
Models suggest that Neptune's troposphere is banded by clouds of varying compositions depending on altitude.[84] The upper-level clouds lie at pressures below one bar, where the temperature is suitable for methane to condense. For pressures between one and five bars (100 and 500 kPa), clouds of ammonia and hydrogen sulfide are thought to form. Above a pressure of five bars, the clouds may consist of ammonia, ammonium sulfide, hydrogen sulfide and water. Deeper clouds of water ice should be found at pressures of about 50 bars (5.0 MPa), where the temperature reaches 273 K (0 °C; 32 °F). Underneath, clouds of ammonia and hydrogen sulfide may be found.[89]
High-altitude clouds on Neptune have been observed casting shadows on the opaque cloud deck below. There are high-altitude cloud bands that wrap around the planet at constant latitudes. These circumferential bands have widths of 50–150 km and lie about 50–110 km above the cloud deck.[90] These altitudes are in the layer where weather occurs, the troposphere. Weather does not occur in the higher stratosphere or thermosphere. In August 2023, the high-altitude clouds of Neptune vanished, prompting a study spanning thirty years of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope and ground-based telescopes. The study found that Neptune's high-altitude cloud activity is bound to Solar cycles, and not to the planet's seasons.[84][91][92]
Neptune's spectra suggest that its lower stratosphere is hazy due to condensation of products of ultraviolet photolysis of methane, such as ethane and ethyne.[25][30] The stratosphere is home to trace amounts of carbon monoxide and hydrogen cyanide.[25][93] The stratosphere of Neptune is warmer than that of Uranus due to the elevated concentration of hydrocarbons.[25]
For reasons that remain obscure, the planet's thermosphere is at an anomalously high temperature of about 750 K (477 °C; 890 °F).[94][95] The planet is too far from the Sun for this heat to be generated by ultraviolet radiation. One candidate for a heating mechanism is atmospheric interaction with ions in the planet's magnetic field. Other candidates are gravity waves from the interior that dissipate in the atmosphere. The thermosphere contains traces of carbon dioxide and water, which may have been deposited from external sources such as meteorites and dust.[89][93]
Colour
[edit]Neptune's atmosphere is faintly blue in the optical spectrum, only slightly more saturated than the blue of Uranus's atmosphere. Early renderings of the two planets greatly exaggerated Neptune's colour contrast "to better reveal the clouds, bands and winds", making it seem deep blue compared to Uranus's off-white. The two planets had been imaged with different systems, making it hard to directly compare the resulting composite images. This was revisited with the colour normalised over time, most comprehensively in late 2023.[87][96]
-
Colour recalibrated in 2016 (Justin Cowart), preserving some enhancement for contrast[98]
-
Colour recalibrated in 2023 (Patrick Irwin), approximating the true colour[99]
Magnetosphere
[edit]Neptune's magnetosphere consists of a magnetic field that is strongly tilted relative to its rotational axis at 47° and offset of at least 0.55 radius (~13,500 km) from the planet's physical centre—resembling Uranus's magnetosphere. Before the arrival of Voyager 2 to Neptune, it was hypothesised that Uranus's sideways rotation caused its tilted magnetosphere. In comparing the magnetic fields of the two planets, scientists now think the extreme orientation may be characteristic of flows in the planets' interiors. This field may be generated by convective fluid motions in a thin spherical shell of electrically conducting liquids (probably a combination of ammonia, methane and water),[89] resulting in a dynamo action.[100]
The dipole component of the magnetic field at the magnetic equator of Neptune is about 14 microteslas (0.14 G).[101] The dipole magnetic moment of Neptune is about 2.2 × 1017 T·m3 (14 μT·RN3, where RN is the radius of Neptune). Neptune's magnetic field has a complex geometry that includes relatively large contributions from non-dipolar components, including a strong quadrupole moment that may exceed the dipole moment in strength. By contrast, Earth, Jupiter and Saturn have only relatively small quadrupole moments, and their fields are less tilted from the polar axis. The large quadrupole moment of Neptune may be the result of an offset from the planet's centre and geometrical constraints of the field's dynamo generator.[102][103]
Neptune's bow shock, where the magnetosphere begins to slow the solar wind, occurs at a distance of 34.9 times the radius of the planet. The magnetopause, where the pressure of the magnetosphere counterbalances the solar wind, lies at a distance of 23–26.5 times the radius of Neptune. The tail of the magnetosphere extends out to at least 72 times the radius of Neptune, and likely much farther.[102]

Measurements by Voyager 2 in extreme-ultraviolet and radio frequencies revealed that Neptune has faint and weak but complex and unique aurorae; however, these observations were limited in time and did not contain infrared. Subsequent astronomers using the Hubble Space Telescope have not glimpsed the aurorae, in contrast to the more well-defined aurorae of Uranus.[104][105] In March 2025, aurorae on Neptune were pictured for the first time by combining visible light images from the Hubble Space Telescope with near-infrared (NIR) images from the James Webb Space Telescope. The relevant data were taken in June 2023. The James Webb Space Telescope attempted to learn the spectrography of Neptune's atmosphere and it was able to find trihydrogen cations (H+
3) which is generated during an aurora and is considered as a clear indicator of auroral activity on both gas giants and ice giants. The nature of Neptune's aurorae is greatly influenced by the peculiar nature of its magnetic field. Unlike the Earth, Jupiter or Saturn, Neptune's magnetic poles are not aligned with the planet's rotational poles which is why Neptune's aurorae mostly occur around its mid-latitude areas instead of its poles like on Earth or Jupiter.[106]
Climate
[edit]
Neptune's weather is characterized by extremely dynamic storm systems, with winds reaching speeds of almost 600 m/s (2,200 km/h; 1,300 mph)—exceeding supersonic flow.[29] More typically, by tracking the motion of persistent clouds, wind speeds have been shown to vary from 20 m/s in the easterly direction to 325 m/s westward.[108] At the cloud tops, the prevailing winds range in speed from 400 m/s along the equator to 250 m/s at the poles.[89] Most of the winds on Neptune move in a direction opposite the planet's rotation.[109] The general pattern of winds showed prograde rotation at high latitudes vs. retrograde rotation at lower latitudes. The difference in flow direction is thought to be a "skin effect" and not due to any deeper atmospheric processes.[25] At 70°S latitude, a high-speed jet travels at a speed of 300 m/s.[25] Due to seasonal changes, the cloud bands in the southern hemisphere of Neptune have been observed to increase in size and albedo. This trend was first seen in 1980. The long orbital period of Neptune results in seasons lasting 40 Earth years.[110]
Neptune differs from Uranus in its typical level of meteorological activity. Voyager 2 observed weather phenomena on Neptune during its 1989 flyby,[111] but no comparable phenomena on Uranus during its 1986 flyby.
The abundance of methane, ethane and acetylene at Neptune's equator is 10–100 times greater than at the poles. This is interpreted as evidence for upwelling at the equator and subsidence near the poles, as photochemistry cannot account for the distribution without meridional circulation.[25]
In 2007, it was discovered that the upper troposphere of Neptune's south pole was about 10 K warmer than the rest of its atmosphere, which averages about 73 K (−200 °C). The temperature differential is enough to let methane, which elsewhere is frozen in the troposphere, escape into the stratosphere near the pole.[112] The relative "hot spot" is due to Neptune's axial tilt, which has exposed the south pole to the Sun for the last quarter of Neptune's year, or roughly 40 Earth years. As Neptune slowly moves towards the opposite side of the Sun, the south pole will be darkened and the north pole illuminated, causing the methane release to shift to the north pole.[113]
Storms
[edit]
In 1989, the Great Dark Spot, an anticyclonic storm system spanning 13,000 km × 6,600 km (8,100 mi × 4,100 mi),[111] was discovered by NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft. The storm resembled the Great Red Spot of Jupiter. Some five years later, on 2 November 1994, the Hubble Space Telescope did not see the Great Dark Spot on the planet. Instead, a new storm similar to the Great Dark Spot was found in Neptune's northern hemisphere.[114]
The Scooter is another storm, a white cloud group farther south than the Great Dark Spot. This nickname first arose during the months leading up to the Voyager 2 encounter in 1989, when they were observed moving at speeds faster than the Great Dark Spot (and images acquired later would subsequently reveal the presence of clouds moving even faster than those that had initially been detected by Voyager 2).[109] The Small Dark Spot is a southern cyclonic storm, the second-most-intense storm observed during the 1989 encounter. It was initially completely dark, but as Voyager 2 approached the planet, a bright core developed, which can be seen in most of the highest-resolution images.[115] In 2018, a newer main dark spot and smaller dark spot were identified and studied.[28] In 2023, the first ground-based observation of a dark spot on Neptune was announced.[116]
Neptune's dark spots are thought to occur in the troposphere at lower altitudes than the brighter cloud features,[118] so they appear as holes in the upper cloud decks. As they are stable features that can persist for several months, they are thought to be vortex structures.[90] Often associated with dark spots are brighter, persistent methane clouds that form around the tropopause layer.[119] The persistence of companion clouds shows that some former dark spots may continue to exist as cyclones even though they are no longer visible as a dark feature. Dark spots may dissipate when they migrate too close to the equator or possibly through some other, unknown mechanism.[120]

In 1989, Voyager 2's Planetary Radio Astronomy (PRA) experiment observed around 60 lightning flashes, or Neptunian electrostatic discharges emitting energies over 7×108 J.[122] A plasma wave system (PWS) detected 16 electromagnetic wave events with a frequency range of 50–12 kHz at magnetic latitudes 7–33˚.[123][124] These plasma wave detections were possibly triggered by lightning over 20 minutes in the ammonia clouds of the magnetosphere.[124]
During Voyager 2’s closest approach to Neptune, the PWS instrument provided Neptune's first plasma wave detections at a sample rate of 28,800 samples per second.[124] The measured plasma densities range from 10−3 – 10−1 cm3.[124][125] Neptunian lightning may occur in three cloud layers,[126] with microphysical modelling suggesting that most of these occurrences happen in the water clouds of the troposphere or the shallow ammonia clouds of the magnetosphere.[123][127] Neptune is predicted to have 1/19 the lightning flash rate of Jupiter and to display most of its lightning activity at high latitudes. However, lightning on Neptune seems to resemble lightning on Earth rather than Jovian lightning.[128]
Internal heating
[edit]Neptune's more varied weather when compared to Uranus is due in part to its higher internal heating. The upper regions of Neptune's troposphere reach a low temperature of 51.8 K (−221.3 °C). At a depth where the atmospheric pressure equals 1 bar (100 kPa), the temperature is 72.00 K (−201.15 °C).[129] Deeper inside the layers of gas, the temperature rises steadily. As with Uranus, the source of this heating is unknown, but the discrepancy is larger: Uranus only radiates 1.1 times as much energy as it receives from the Sun;[130] whereas Neptune radiates about 2.61 times as much energy as it receives from the Sun.[131]
Neptune is over 50% farther from the Sun than Uranus and receives only ~40% of Uranus's amount of sunlight;[25] however, its internal energy is still enough for the fastest planetary winds in the Solar System. Depending on the thermal properties of its interior, the heat left over from Neptune's formation may be sufficient to explain its current heat flow, though it is harder to explain Uranus's lack of internal heat while preserving the apparent similarity between the two planets.[132]
Orbit and rotation
[edit]
The average distance between Neptune and the Sun is 4.5 billion km (about 30.1 astronomical units (AU), the mean distance from the Earth to the Sun), and it completes an orbit on average every 164.79 years, subject to a variability of around ±0.1 years. The perihelion distance is 29.81 AU, and the aphelion distance is 30.33 AU.[h] Neptune's orbital eccentricity is only 0.008678, making it the planet in the Solar System with the second most circular orbit after Venus.[134] The orbit of Neptune is inclined 1.77° compared to that of Earth.
On 11 July 2011, Neptune completed its first full barycentric orbit since its discovery in 1846;[135] it did not appear at its exact discovery position in the sky because Earth was in a different location in its 365.26-day orbit. Because of the motion of the Sun in relation to the barycentre of the Solar System, on 11 July, Neptune was not at its exact discovery position in relation to the Sun—if the more common heliocentric coordinate system is used, the discovery longitude was reached on 12 July 2011.[12][136][137][138]
The axial tilt of Neptune is 28.32°,[139] which is similar to the tilts of Earth (23°) and Mars (25°). As a result, Neptune experiences seasonal changes similar to those on Earth. The long orbital period of Neptune means that the seasons last for forty Earth years.[110] Its sidereal rotation period (day) is roughly 16.11 hours.[12] Because its axial tilt is comparable to Earth's, the variation in the length of its day over the course of its long year is not any more extreme.
Because Neptune is not a solid body, its atmosphere undergoes differential rotation. The wide equatorial zone rotates with a period of about 18 hours, which is slower than the 16.1-hour rotation of the planet's magnetic field. By contrast, the reverse is true for the polar regions where the rotation period is 12 hours. This differential rotation is the most pronounced of any planet in the Solar System,[140] and it results in strong latitudinal wind shear.[90]
Formation and resonances
[edit]Formation
[edit]
The formation of the ice giants, Neptune and Uranus, has been difficult to model precisely. Current models suggest that the matter density in the outer regions of the Solar System was too low to account for the formation of such large bodies from the traditionally accepted method of core accretion, and various hypotheses have been advanced to explain their formation. One is that the ice giants were not formed by core accretion but from instabilities within the original protoplanetary disc and later had their atmospheres blasted away by radiation from a nearby massive OB star.[73]
An alternative concept is that they formed closer to the Sun, where the matter density was higher, and then subsequently migrated to their current orbits after the removal of the gaseous protoplanetary disc.[141] This hypothesis of migration after formation is favoured due to its ability to better explain the occupancy of the populations of small objects observed in the trans-Neptunian region.[142] The current most widely accepted[143][144][145] explanation of the details of this hypothesis is known as the Nice model, which is a dynamical evolution scenario that explores the potential effect of a migrating Neptune and the other giant planets on the structure of the Kuiper belt.
Orbital resonances
[edit]
Neptune's orbit has a profound impact on the region directly beyond it, known as the Kuiper belt. The Kuiper belt is a ring of small icy worlds, similar to the asteroid belt but far larger, extending from Neptune's orbit at 30 AU out to about 55 AU from the Sun.[146] Much in the same way that Jupiter's gravity dominates the asteroid belt, Neptune's gravity dominates the Kuiper belt. Over the age of the Solar System, certain regions of the Kuiper belt became destabilised by Neptune's gravity, creating gaps in its structure. The region between 40 and 42 AU is an example.[147]
There do exist orbits within these empty regions where objects can survive for the age of the Solar System. These resonances occur when Neptune's orbital period is a precise fraction of that of the object, such as 1:2, or 3:4. If, say, an object orbits the Sun once for every two Neptune orbits, it will only complete half an orbit by the time Neptune returns to its original position. The most heavily populated resonance in the Kuiper belt, with over 200 known objects,[148] is the 2:3 resonance. Objects in this resonance complete 2 orbits for every 3 of Neptune, and are known as plutinos because the largest of the known Kuiper belt objects, Pluto, is among them.[149] Although Pluto crosses Neptune's orbit regularly, the 2:3 resonance makes it so that they can never collide.[150] The 3:4, 3:5, 4:7 and 2:5 resonances are less populated.[151]
Neptune has a number of known trojan objects occupying both the Sun–Neptune L4 and L5 Lagrangian points—gravitationally stable regions leading and trailing Neptune in its orbit, respectively.[152] Neptune trojans can be viewed as being in a 1:1 resonance with Neptune. Some Neptune trojans are remarkably stable in their orbits, and are likely to have formed alongside Neptune rather than being captured. The first object identified as associated with Neptune's trailing L5 Lagrangian point was 2008 LC18.[153] Neptune has a temporary quasi-satellite, (309239) 2007 RW10.[154] The object has been a quasi-satellite of Neptune for about 12,500 years and it will remain in that dynamical state for another 12,500 years.[154]
Moons
[edit]
Neptune has 16 known moons.[155] Triton is the largest Neptunian moon, accounting for more than 99.5% of the mass in orbit around Neptune,[i] and is the only one massive enough to be spheroidal. Triton was discovered by William Lassell just 17 days after the discovery of Neptune itself. Unlike all other large planetary moons in the Solar System, Triton has a retrograde orbit, indicating that it was captured rather than forming in place; it was probably once a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt.[156] It is close enough to Neptune to be locked into a synchronous rotation, and it is slowly spiralling inward because of tidal acceleration. It will eventually be torn apart, in about 3.6 billion years, when it reaches the Roche limit.[157] In 1989, Triton was the coldest object that had yet been measured in the Solar System,[158] with estimated temperatures of 38 K (−235 °C).[159][160] This very low temperature is due to Triton's very high albedo which causes it to reflect a lot of sunlight instead of absorbing it.[161][162]
Neptune's second-known satellite (by order of discovery), the irregular moon Nereid, has one of the most eccentric orbits of any satellite in the Solar System. The eccentricity of 0.7512 gives it an apoapsis that is seven times its periapsis distance from Neptune.[j]
From July to September 1989, Voyager 2 discovered six moons of Neptune.[163] Of these, the irregularly shaped Proteus is notable for being as large as a body of its density can be without being pulled into a spherical shape by its own gravity.[164] Although the second-most-massive Neptunian moon, it is only 0.25% the mass of Triton. Neptune's innermost four moons—Naiad, Thalassa, Despina and Galatea—orbit close enough to be within Neptune's rings. The next-farthest out, Larissa, was originally discovered in 1981 when it had occulted a star. This occultation had been attributed to ring arcs, but when Voyager 2 observed Neptune in 1989, Larissa was found to have caused it. Five new irregular moons discovered between 2002 and 2003 were announced in 2004.[165][166] A new moon and the smallest yet, Hippocamp, was found in 2013 by combining multiple Hubble images.[167] Because Neptune was the Roman god of the sea, Neptune's moons have been named after lesser sea gods.[54]
Planetary rings
[edit]
Neptune has a planetary ring system, though one much less substantial than that of Saturn and Uranus.[168] The rings may consist of ice particles coated with silicates or carbon-based material, which most likely gives them a reddish hue.[169] The three main rings are the narrow Adams Ring, 63,000 km from the centre of Neptune, the Le Verrier Ring, at 53,000 km, and the broader, fainter Galle Ring, at 42,000 km. A faint outward extension to the Le Verrier Ring has been named Lassell; it is bounded at its outer edge by the Arago Ring at 57,000 km.[170]
The first of these planetary rings was detected in 1968 by a team led by Edward Guinan.[32][171] In the early 1980s, analysis of this data along with newer observations led to the hypothesis that this ring might be incomplete.[172] Evidence that the rings might have gaps first arose during a stellar occultation in 1984 when the rings obscured a star on immersion but not on emersion.[173] Images from Voyager 2 in 1989 settled the issue by showing several faint rings.
The outermost ring, Adams, contains five prominent arcs now named Courage, Liberté, Egalité 1, Egalité 2 and Fraternité (Courage, Liberty, Equality and Fraternity).[174] The existence of arcs was difficult to explain because the laws of motion would predict that arcs would spread out into a uniform ring over short timescales. Astronomers now estimate that the arcs are corralled into their current form by the gravitational effects of Galatea, a moon just inward from the ring.[175][176]
Earth-based observations announced in 2005 appeared to show that Neptune's rings were much more unstable than previously thought. Images taken from the W. M. Keck Observatory in 2002 and 2003 show considerable decay in the rings when compared to images by Voyager 2. In particular, it seems that the Liberté arc might disappear in as little as one century.[177]
Observation
[edit]
Neptune brightened about 10% between 1980 and 2000 mostly due to the changing of the seasons.[178] Neptune may continue to brighten as it approaches perihelion in 2042. The apparent magnitude currently ranges from 7.67 to 7.89 with a mean of 7.78 and a standard deviation of 0.06.[18] Prior to 1980, the planet was as faint as magnitude 8.0.[18] Neptune is too faint to be visible to the naked eye. It can be outshone by Jupiter's Galilean moons, the dwarf planet Ceres and the asteroids 4 Vesta, 2 Pallas, 7 Iris, 3 Juno, and 6 Hebe.[179] A telescope or strong binoculars will resolve Neptune as a small blue disk, similar in appearance to Uranus.[180]
Because of the distance of Neptune from Earth, its angular diameter only ranges from 2.2 to 2.4 arcseconds,[8][20] the smallest of the Solar System planets. Its small apparent size makes it challenging to study visually. Most telescopic data was fairly limited until the advent of the Hubble Space Telescope and large ground-based telescopes with adaptive optics (AO).[181][182][183] The first scientifically useful observation of Neptune from ground-based telescopes using adaptive optics was commenced in 1997 from Hawaii.[184] Neptune is currently approaching perihelion (closest approach to the Sun) and has been shown to be heating up, with increased atmospheric activity and brightness as a consequence. Combined with technological advancements, ground-based telescopes with adaptive optics are recording increasingly more detailed images of it. Both Hubble and the adaptive-optics telescopes on Earth have made many new discoveries within the Solar System since the mid-1990s, with a large increase in the number of known satellites and moons around the outer planet, among others. In 2004 and 2005, five new small satellites of Neptune with diameters between 38 and 61 kilometres were discovered.[185]
From Earth, Neptune goes through apparent retrograde motion every 367 days, resulting in a looping motion against the background stars during each opposition. These loops carried it close to the 1846 discovery coordinates in April and July 2010 and again in October and November 2011.[138]
Neptune's 164-year orbital period means that the planet takes an average of 13 years to move through each constellation of the zodiac. In 2011, it completed its first full orbit of the Sun since being discovered and returned to where it was first spotted northeast of Iota Aquarii.[43]
Observation of Neptune in the radio-frequency band shows that it is a source of both continuous emission and irregular bursts. Both sources are thought to originate from its rotating magnetic field.[89] In the infrared part of the spectrum, Neptune's storms appear bright against the cooler background, allowing the size and shape of these features to be readily tracked.[186]
Exploration
[edit]
Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft that has visited Neptune. The spacecraft's closest approach to the planet occurred on 25 August 1989. Because this was the last major planet the spacecraft could visit, it was decided to make a close flyby of the moon Triton, regardless of the consequences to the trajectory, similarly to what was done for Voyager 1's encounter with Saturn and its moon Titan. The images relayed back to Earth from Voyager 2 became the basis of a 1989 PBS all-night program, Neptune All Night.[187]
During the encounter, signals from the spacecraft required 246 minutes to reach Earth. Hence, for the most part, Voyager 2's mission relied on preloaded commands for the Neptune encounter. The spacecraft performed a near-encounter with the moon Nereid before it came within 4,400 km of Neptune's atmosphere on 25 August, then passed close to the planet's largest moon Triton later the same day.[188]
The spacecraft verified the existence of a magnetic field surrounding the planet and discovered that the field was offset from the centre and tilted in a manner similar to the field around Uranus. Neptune's rotation period was determined using measurements of radio emissions and Voyager 2 showed that Neptune had a surprisingly active weather system. Six new moons were discovered, and the planet was shown to have more than one ring.[163][188] The flyby provided the first accurate measurement of Neptune's mass which was found to be 0.5 per cent less than previously calculated. The new figure disproved the hypothesis that an undiscovered Planet X acted upon the orbits of Neptune and Uranus.[189][190]
Since 2018, the China National Space Administration has been studying a concept for a pair of Voyager-like interstellar probes tentatively known as Shensuo.[191] Both probes would be launched in the 2020s and take differing paths to explore opposing ends of the heliosphere; the second probe, IHP-2, would fly by Neptune in January 2038, passing only 1,000 km above the cloud tops, and potentially carry an atmospheric impactor to be released during its approach.[192] Afterward, it will continue its mission throughout the Kuiper belt toward the heliosphere tail, which is so far unexplored.
After Voyager 2 and IHP-2's flybys, the next step in scientific exploration of the Neptunian system is considered to be an orbital mission; most proposals have been by NASA, most often for a Flagship orbiter.[193] In 2003, there was a proposal in NASA's "Vision Missions Studies" for a "Neptune Orbiter with Probes" mission that does Cassini-level science.[194] A subsequent proposal, that was not selected, was for Argo, a flyby spacecraft to be launched in 2019, that would visit Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune, and a Kuiper belt object. The focus would have been on Neptune and its largest moon Triton to be investigated around 2029.[195] The proposed New Horizons 2 mission might have done a close flyby of the Neptunian system, but it was later scrapped. Currently a pending proposal for the Discovery Program, the Trident spacecraft would conduct a flyby of Neptune and Triton;[196] however, the mission was not selected for Discovery 15 or 16. Neptune Odyssey is another concept for a Neptune orbiter and atmospheric probe that was studied as a possible large strategic science mission by NASA; it would have launched between 2031 and 2033, and arrive at Neptune by 2049.[197] However, for logistical reasons the Uranus Orbiter and Probe mission was selected as the ice giant orbiter mission recommendation, with top priority ahead of the Enceladus Orbilander.[198] Two notable proposals for a Triton-focused Neptune orbiter mission that would be costed right between the Trident and Odyssey missions (under the New Frontiers program) are Triton Ocean World Surveyor and Nautilus, with cruise stages taking place in the 2031–47 and 2041–56 time periods, respectively.[199][200] Neptune is a potential target for China's Tianwen-5, which could arrive in 2058.[201]
See also
[edit]- Outline of Neptune
- Hot Neptune
- Neptune in astrology
- Neptune in fiction
- Neptunium
- Neptune, the Mystic – one of the seven movements in Gustav Holst's Planets suite
- Timeline of the far future
- Stats of planets in the Solar System
Notes
[edit]- ^ Neptune's dark spots are not permanent features; the large dark spot observed by Voyager 2 was designated GDS-89 for "Great Dark Spot 1989".
- ^ Orbital elements refer to the Neptune barycentre and Solar System barycentre. These are the instantaneous osculating values at the precise J2000 epoch. Barycentre quantities are given because, in contrast to the planetary centre, they do not experience appreciable changes on a day-to-day basis from the motion of the moons.
- ^ a b c d e f g Refers to the level of 1 bar (100 kPa) atmospheric pressure
- ^ Based on the volume within the level of 1 bar atmospheric pressure
- ^ A second symbol, an ‘LV’ monogram
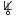 for 'Le Verrier', analogous to the ‘H’ monogram
for 'Le Verrier', analogous to the ‘H’ monogram 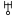 for Uranus. It was never much used outside of France and is now archaic.
for Uranus. It was never much used outside of France and is now archaic.
- ^ One could argue that it is true except for the 'Earth', which in the English language is the name of a Germanic deity, Erda. The IAU policy is that one may call the Earth and the Moon by any name commonly used in the language. According to the IAU, 'Terra' and 'Luna' are not the official names of planet Earth and its moon: "Naming of Astronomical Objects". International Astronomical Union. Archived from the original on 21 March 2024. Retrieved 27 April 2024.
- ^ The mass of Earth is 5.9722×1024 kg, giving a mass ratio
- ^ The last three aphelia were 30.33 AU, the next is 30.34 AU. The perihelia are even more stable at 29.81 AU.[133]
- ^ Mass of Triton: 2.14×1022 kg. Combined mass of 12 other known moons of Neptune: 7.53×1019 kg, or 0.35%. The mass of the rings is negligible.
- ^
References
[edit]- ^ Irwin, Patrick G. J.; Dobinson, Jack; James, Arjuna; Teanby, Nicholas A.; Simon, Amy A.; Fletcher, Leigh N.; Roman, Michael T.; Orton, Glenn S.; Wong, Michael H.; Toledo, Daniel; Pérez-Hoyos, Santiago; Beck, Julie (23 December 2023). "Modelling the seasonal cycle of Uranus's colour and magnitude, and comparison with Neptune". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 527 (4): 11521–11538. doi:10.1093/mnras/stad3761. hdl:20.500.11850/657542.
- ^ a b c Hamilton, Calvin J. (4 August 2001). "Neptune". Views of the Solar System. Archived from the original on 15 July 2007. Retrieved 13 August 2007.
- ^ Walter, Elizabeth (21 April 2003). "Neptune". Cambridge Advanced Learner's Dictionary (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-53106-1.
- ^ "Neptunian". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- ^ a b "Enabling Exploration with Small Radioisotope Power Systems" (PDF). NASA. September 2004. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 December 2016. Retrieved 26 January 2016.
- ^ Yeomans, Donald K. "HORIZONS Web-Interface for Neptune Barycenter (Major Body=8)". JPL Horizons On-Line Ephemeris System. Archived from the original on 7 September 2021. Retrieved 18 July 2014.—Select "Ephemeris Type: Orbital Elements", "Time Span: 2000-01-01 12:00 to 2000-01-02". ("Target Body: Neptune Barycenter" and "Center: Solar System Barycenter (@0)".)
- ^ a b Seligman, Courtney. "Rotation Period and Day Length". Archived from the original on 28 July 2011. Retrieved 13 August 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Williams, David R. (1 September 2004). "Neptune Fact Sheet". NASA. Archived from the original on 1 July 2010. Retrieved 14 August 2007.
- ^ Souami, D.; Souchay, J. (July 2012). "The solar system's invariable plane". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 543: 11. Bibcode:2012A&A...543A.133S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201219011. A133.
- ^ "HORIZONS Planet-center Batch call for September 2042 Perihelion". ssd.jpl.nasa.gov (Perihelion for Neptune's planet-center (899) occurs on 2042-Sep-04 at 29.80647406au during a rdot flip from negative to positive). NASA/JPL. Archived from the original on 7 September 2021. Retrieved 7 September 2021.
- ^ a b c d e Seidelmann, P. Kenneth; Archinal, Brent A.; A'Hearn, Michael F.; Conrad, Albert R.; Consolmagno, Guy J.; Hestroffer, Daniel; et al. (2007). "Report of the IAU/IAG Working Group on cartographic coordinates and rotational elements: 2006". Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy. 98 (3): 155–180. Bibcode:2007CeMDA..98..155S. doi:10.1007/s10569-007-9072-y.
- ^ a b c Munsell, K.; Smith, H.; Harvey, S. (13 November 2007). "Neptune: Facts & Figures". NASA. Archived from the original on 9 April 2014. Retrieved 14 August 2007.
- ^ de Pater, Imke; Lissauer, Jack J. (2015). Planetary Sciences (2nd updated ed.). New York: Cambridge University Press. p. 250. ISBN 978-0-521-85371-2. Archived from the original on 26 November 2016. Retrieved 17 August 2016.
- ^ Kennett, Carolyn (2022). Uranus and Neptune. Reaktion Books. p. 185. ISBN 978-1-78914-642-4.
- ^ a b Archinal, B. A.; Acton, C. H.; A'Hearn, M. F.; Conrad, A.; Consolmagno, G. J.; Duxbury, T.; Hestroffer, D.; Hilton, J. L.; Kirk, R. L.; Klioner, S. A.; McCarthy, D.; Meech, K.; Oberst, J.; Ping, J.; Seidelmann, P. K. (2018). "Report of the IAU Working Group on Cartographic Coordinates and Rotational Elements: 2015". Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy. 130 (3): 22. Bibcode:2018CeMDA.130...22A. doi:10.1007/s10569-017-9805-5.
- ^ Pearl, J.C.; et al. (1991). "The albedo, effective temperature, and energy balance of Neptune, as determined from Voyager data". Journal of Geophysical Research. 96: 18, 921–930. Bibcode:1991JGR....9618921P. doi:10.1029/91JA01087.
- ^ Mallama, Anthony; Krobusek, Bruce; Pavlov, Hristo (2017). "Comprehensive wide-band magnitudes and albedos for the planets, with applications to exo-planets and Planet Nine". Icarus. 282: 19–33. arXiv:1609.05048. Bibcode:2017Icar..282...19M. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2016.09.023. S2CID 119307693.
- ^ a b c d Mallama, A.; Hilton, J.L. (2018). "Computing apparent planetary magnitudes for The Astronomical Almanac". Astronomy and Computing. 25: 10–24. arXiv:1808.01973. Bibcode:2018A&C....25...10M. doi:10.1016/j.ascom.2018.08.002. S2CID 69912809.
- ^ "Encyclopedia - the brightest bodies". IMCCE. Archived from the original on 24 July 2023. Retrieved 29 May 2023.
- ^ a b Espenak, Fred (20 July 2005). "Twelve Year Planetary Ephemeris: 1995–2006". NASA. Archived from the original on 5 December 2012. Retrieved 1 March 2008.
- ^ "Neptune". NASA Science. 10 November 2017. Retrieved 19 July 2024.
- ^ Chang, Kenneth (18 October 2014). "Dark Spots in Our Knowledge of Neptune". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 28 October 2014. Retrieved 21 October 2014.
- ^ "Exploration | Neptune". NASA Solar System Exploration. 10 November 2017. Archived from the original on 17 July 2020. Retrieved 3 February 2020.
In 1989, NASA's Voyager 2 became the first-and only-spacecraft to study Neptune up close.
- ^ a b Podolak, M.; Weizman, A.; Marley, M. (December 1995). "Comparative models of Uranus and Neptune". Planetary and Space Science. 43 (12): 1517–1522. Bibcode:1995P&SS...43.1517P. doi:10.1016/0032-0633(95)00061-5.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Lunine, Jonathan I. (September 1993). "The atmospheres of Uranus and Neptune". Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics. 31: 217–263. Bibcode:1993ARA&A..31..217L. doi:10.1146/annurev.aa.31.090193.001245.
- ^ Munsell, Kirk; Smith, Harman; Harvey, Samantha (13 November 2007). "Neptune overview". Solar System Exploration. NASA. Archived from the original on 3 March 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Gemini North Telescope Helps Explain Why Uranus and Neptune Are Different Colors - Observations from Gemini Observatory, a Program of NSF's NOIRLab, and other telescopes reveal that excess haze on Uranus makes it paler than Neptune". noirlab.edu. 31 May 2022. Archived from the original on 30 July 2022. Retrieved 30 July 2022.
- ^ a b Stirone, Shannon (22 December 2020). "Neptune's Weird Dark Spot Just Got Weirder – While observing the planet's large inky storm, astronomers spotted a smaller vortex they named Dark Spot Jr". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 22 December 2020. Retrieved 22 December 2020.
- ^ a b Suomi, V. E.; Limaye, S. S.; Johnson, D. R. (22 February 1991). "High Winds of Neptune: A Possible Mechanism". Science. 251 (4996): 929–932. Bibcode:1991Sci...251..929S. doi:10.1126/science.251.4996.929. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 17847386. S2CID 46419483.
- ^ a b c d e Hubbard, W.B. (1997). "Neptune's Deep Chemistry". Science. 275 (5304): 1279–80. doi:10.1126/science.275.5304.1279. PMID 9064785. S2CID 36248590.
- ^ a b Nettelmann, N.; French, M.; Holst, B.; Redmer, R. "Interior Models of Jupiter, Saturn and Neptune" (PDF). University of Rostock. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 July 2011. Retrieved 25 February 2008.
- ^ a b Wilford, John N. (10 June 1982). "Data Shows 2 Rings Circling Neptune". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 10 December 2008. Retrieved 29 February 2008.
- ^ Hirschfeld, Alan (2001). Parallax: The Race to Measure the Cosmos. New York, New York: Henry Holt. ISBN 978-0-8050-7133-7.
- ^ Littmann, Mark (2004). Planets Beyond: Discovering the Outer Solar System. Mineola, New York: Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0-486-43602-9.
- ^ Britt, Robert Roy (2009). "Galileo discovered Neptune, new theory claims". NBC News. Archived from the original on 4 November 2013. Retrieved 10 July 2009.
- ^ Bouvard, A. (1821). Tables astronomiques publiées par le Bureau des Longitudes de France (in French). Paris: Bachelier.
- ^ a b c Airy, G.B. (13 November 1846). "Account of some circumstances historically connected with the discovery of the planet exterior to Uranus". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 7 (10): 121–144. Bibcode:1846MNRAS...7..121A. doi:10.1093/mnras/7.9.121.
- ^ O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F. (2006). "John Couch Adams' account of the discovery of Neptune". University of St Andrews. Archived from the original on 26 January 2008. Retrieved 18 February 2008.
- ^ Adams, J. C. (13 November 1846). "Explanation of the observed irregularities in the motion of Uranus, on the hypothesis of disturbance by a more distant planet". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 7 (9): 149–152. Bibcode:1846MNRAS...7..149A. doi:10.1093/mnras/7.9.149. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 25 August 2019.
- ^ Challis, J. (13 November 1846). "Account of observations at the Cambridge observatory for detecting the planet exterior to Uranus". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 7 (9): 145–149. Bibcode:1846MNRAS...7..145C. doi:10.1093/mnras/7.9.145. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 May 2019. Retrieved 25 August 2019.
- ^ Sack, Harald (12 December 2017). "James Challis and his failure to discover the planet Neptune". scihi.org. Archived from the original on 15 November 2021. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ^ Galle, J. G. (13 November 1846). "Account of the discovery of the planet of Le Verrier at Berlin". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 7 (9): 153. Bibcode:1846MNRAS...7..153G. doi:10.1093/mnras/7.9.153.
- ^ a b Gaherty, Geoff (12 July 2011). "Neptune Completes First Orbit Since Its Discovery in 1846". space.com. Archived from the original on 25 August 2019. Retrieved 3 September 2019.
- ^ Levenson, Thomas (2015). The Hunt for Vulcan ... and how Albert Einstein Destroyed a Planet, Discovered Relativity, and Deciphered the Universe. Random House. p. 38.
- ^ Williams, Matt (14 September 2015). "The gas (and ice) giant Neptune". Universe Today. Archived from the original on 27 September 2023. Retrieved 26 April 2024.
- ^ Kollerstrom, Nick (2001). "Neptune's Discovery. The British Case for Co-Prediction". University College London. Archived from the original on 11 November 2005. Retrieved 19 March 2007.
- ^ Sheehan, William; Kollerstrom, Nicholas; Waff, Craig B. (December 2004). "The case of the pilfered planet – did the British steal Neptune?". Scientific American. JSTOR 26060804. Archived from the original on 19 March 2011. Retrieved 20 January 2011.
- ^ Moore (2000):206
- ^ Littmann, Mark (2004). Planets Beyond, Exploring the Outer Solar System. Mineola, New York: Dover Publications. p. 50. ISBN 978-0-486-43602-9.
- ^ Baum, Richard; Sheehan, William (2003). In Search of Planet Vulcan: The ghost in Newton's clockwork universe. Basic Books. pp. 109–10. ISBN 978-0-7382-0889-3.
- ^ Gingerich, Owen (October 1958). "The naming of Uranus and Neptune". Astronomical Society of the Pacific Leaflets. 8 (352): 9–15. Bibcode:1958ASPL....8....9G.
- ^ Hind, J. R. (1847). "Second report of proceedings in the Cambridge Observatory relating to the new Planet (Neptune)". Astronomische Nachrichten. 25 (21): 309–314. Bibcode:1847AN.....25..309.. doi:10.1002/asna.18470252102. Archived from the original on 29 September 2021. Retrieved 12 June 2019.
- ^ Faure, Gunter; Mensing, Teresa M. (2007). "Neptune: More Surprises". Introduction to Planetary Science. Dordrecht: Springer. pp. 385–399. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-5544-7_19. ISBN 978-1-4020-5544-7.
- ^ a b "Planet and Satellite Names and Discoverers". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. U.S. Geological Survey. 17 December 2008. Archived from the original on 9 August 2018. Retrieved 26 March 2012.
- ^ "Planetary linguistics". nineplanets.org. Archived from the original on 7 April 2010. Retrieved 8 April 2010.
- ^ "Sao Hải Vương – 'Cục băng' khổng lồ xa tít tắp". Kenh14 (in Vietnamese). 31 October 2010. Archived from the original on 30 July 2018. Retrieved 30 July 2018.
- ^ "Greek Names of the Planets". 25 April 2010. Archived from the original on 9 May 2010. Retrieved 14 July 2012.
Neptune or Poseidon as is its Greek name, was the God of the Seas. It is the eight planet from the sun ...
- ^ Ettinger, Yair (31 December 2009). "Uranus and Neptune get Hebrew names at last". Haaretz. Archived from the original on 25 June 2018. Retrieved 16 August 2018.
- ^ Belizovsky, Avi (31 December 2009). "אוראנוס הוא מהיום אורון ונפטון מעתה רהב" [Uranus is now Oron and Neptune is now Rahav]. Hayadan (in Hebrew). Archived from the original on 24 June 2018. Retrieved 16 August 2018.
- ^ a b Ian (25 September 2019). "Planetary Linguistics | Latin, Greek, Sanskrit & Different Languages". The Nine Planets. Archived from the original on 2 February 2019. Retrieved 1 February 2024.
- ^ Mohamed, Kadir (1975). "Waruna". Kamus Kebangsaan Ejaan Baru, Inggeris-bahasa Malaysia, Bahasa Malaysia-Inggeris. Titiwangsa. pp. 299, 857. Archived from the original on 29 September 2021. Retrieved 29 May 2021.
- ^ "Neptun". Kamus Dewan (4th ed.). Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka Malaysia. 2017. Archived from the original on 7 May 2021. Retrieved 5 May 2021.
- ^ "Neptunus". Kamus Besar Bahasa Indonesia (3rd ed.). Badan Pengembangan dan Pembinaan Bahasa Indonesia. 2016. Archived from the original on 29 September 2021. Retrieved 5 May 2021.
- ^ The Century Dictionary (1914)
- ^ Long, Tony (21 January 2008). "Jan. 21, 1979: Neptune Moves Outside Pluto's Wacky Orbit". Wired. Archived from the original on 27 March 2008. Retrieved 13 March 2008.
- ^ "Neptune Data Sheet". Space.com. 17 November 2006. Archived from the original on 11 February 2023. Retrieved 11 February 2023.
- ^ Stern, Alan; Tholen, David James (1997). Pluto and Charon. University of Arizona Press. pp. 206–208. ISBN 978-0-8165-1840-1.
- ^ Weissman, Paul R. (September 1995). "The Kuiper Belt". Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics. 33 (1): 327–357. Bibcode:1995ARA&A..33..327W. doi:10.1146/annurev.aa.33.090195.001551. ISSN 0066-4146.
- ^ "The Status of Pluto:A clarification". International Astronomical Union, Press release. 1999. Archived from the original on 15 June 2006. Retrieved 25 May 2006.
- ^ "IAU 2006 General Assembly: Resolutions 5 and 6" (PDF). IAU. 24 August 2006. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 June 2008. Retrieved 22 July 2008.
- ^ "Neptune Fact Sheet". NASA. Archived from the original on 1 July 2010. Retrieved 22 September 2005.
- ^ Unsöld, Albrecht; Baschek, Bodo (2001). The New Cosmos: An introduction to astronomy and astrophysics (5th ed.). Springer. Table 3.1, page 47. Bibcode:2001ncia.book.....U. ISBN 978-3-540-67877-9.
- ^ a b Boss, Alan P. (2002). "Formation of gas and ice giant planets". Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 202 (3–4): 513–23. Bibcode:2002E&PSL.202..513B. doi:10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00808-7.
- ^ Lovis, C.; Mayor, M.; Alibert, Y.; Benz, W. (18 May 2006). "Trio of Neptunes and their Belt". ESO. Archived from the original on 13 January 2010. Retrieved 25 February 2008.
- ^ Atreya, S.; Egeler, P.; Baines, K. (2006). "Water-ammonia ionic ocean on Uranus and Neptune?" (PDF). Geophysical Research Abstracts. 8. 05179. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 February 2012. Retrieved 7 November 2007.
- ^ Shiga, David (1 September 2010). "Weird water lurking inside giant planets". New Scientist. No. 2776. Archived from the original on 12 February 2018. Retrieved 11 February 2018.
- ^ Kerr, Richard A. (October 1999). "Neptune May Crush Methane into Diamonds". Science. 286 (5437): 25a–25. doi:10.1126/science.286.5437.25a. PMID 10532884. S2CID 42814647.
- ^ a b Kaplan, Sarah (25 August 2017). "It rains solid diamonds on Uranus and Neptune". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 27 August 2017. Retrieved 27 August 2017.
- ^ Kraus, D.; et al. (September 2017). "Formation of diamonds in laser-compressed hydrocarbons at planetary interior conditions" (PDF). Nature Astronomy. 1 (9): 606–11. Bibcode:2017NatAs...1..606K. doi:10.1038/s41550-017-0219-9. OSTI 1393331. S2CID 46945778. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 July 2018. Retrieved 25 August 2018.
- ^ Kane, Sean (29 April 2016). "Lightning storms make it rain diamonds on Saturn and Jupiter". Business Insider. Archived from the original on 26 June 2019. Retrieved 22 May 2019.
- ^ Baldwin, Emily (21 January 2010). "Oceans of diamond possible on Uranus and Neptune". Astronomy Now. Archived from the original on 3 December 2013.
- ^ Bradley, D.K.; Eggert, J.H.; Hicks, D.G.; Celliers, P.M. (30 July 2004). "Shock Compressing Diamond to a Conducting Fluid" (PDF). Physical Review Letters. 93 (19): 195506. Bibcode:2004PhRvL..93s5506B. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.93.195506. hdl:1959.3/380076. PMID 15600850. S2CID 6203103. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 December 2016. Retrieved 16 March 2016.
- ^ Eggert, J.H.; Hicks, D.G.; Celliers, P.M.; Bradley, D.K.; et al. (8 November 2009). "Melting temperature of diamond at ultrahigh pressure". Nature Physics. 6 (40): 40–43. Bibcode:2010NatPh...6...40E. doi:10.1038/nphys1438.
- ^ a b c Andrews, Robin George (18 August 2023). "Neptune's Clouds Have Vanished, and Scientists Think They Know Why - A recent study suggests a relationship between solar cycles and the atmosphere of the solar system's eighth planet". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 18 August 2023. Retrieved 21 August 2023.
- ^ Crisp, D.; Hammel, H.B. (14 June 1995). "Hubble Space Telescope Observations of Neptune". Hubble News Center. Archived from the original on 2 August 2007. Retrieved 22 April 2007.
- ^ Ferreira, Becky (4 January 2024). "Uranus and Neptune Reveal Their True Colors - Neptune is not as blue as you've been led to believe, and Uranus's shifting colors are better explained, in new research". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 5 January 2024. Retrieved 5 January 2024.
- ^ a b NASA Science Editorial Team (31 May 2022). "Why Uranus and Neptune Are Different Colors". NASA. Archived from the original on 31 October 2023. Retrieved 30 October 2023.
- ^ Williams, Matt (14 September 2015). "The gas (and ice) giant Neptune". Phys.org. Retrieved 27 August 2024.
- ^ a b c d e Elkins-Tanton, Linda T. (2006). Uranus, Neptune, Pluto, and the Outer Solar System. New York: Chelsea House. pp. 79–83. ISBN 978-0-8160-5197-7.
- ^ a b c Max, C. E.; Macintosh, B. A.; Gibbard, S. G.; Gavel, D. T.; et al. (January 2003). "Cloud Structures on Neptune Observed with Keck Telescope Adaptive Optics". The Astronomical Journal. 125 (1): 364–375. Bibcode:2003AJ....125..364M. doi:10.1086/344943.
- ^ Gianopoulos, Andrea (16 August 2023). "Neptune's Disappearing Clouds Linked to the Solar Cycle". NASA. Archived from the original on 24 August 2023. Retrieved 24 August 2023.
- ^ Chavez, Erandi; de Pater, Imke; Redwing, Erin; Molter, Edward M.; Roman, Michael T.; Zorzi, Andrea; Alvarez, Carlos; Campbell, Randy; de Kleer, Katherine; Hueso, Ricardo; Wong, Michael H.; Gates, Elinor; Lynam, Paul David; Davies, Ashley G.; Aycock, Joel; Mcilroy, Jason; Pelletier, John; Ridenour, Anthony; Stickel, Terry (1 November 2023). "Evolution of Neptune at near-infrared wavelengths from 1994 through 2022". Icarus. 404 115667. arXiv:2307.08157. Bibcode:2023Icar..40415667C. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2023.115667. S2CID 259515455. Archived from the original on 24 August 2023. Retrieved 24 August 2023.
The clear positive correlation we find between cloud activity and Solar Lyman-Alpha (121.56 nm) irradiance lends support to the theory that the periodicity in Neptune's cloud activity results from photochemical cloud/haze production triggered by Solar ultraviolet emissions.
- ^ a b Encrenaz, Thérèse (February 2003). "ISO observations of the giant planets and Titan: What have we learnt?". Planetary and Space Science. 51 (2): 89–103. Bibcode:2003P&SS...51...89E. doi:10.1016/S0032-0633(02)00145-9.
- ^ Broadfoot, A.L.; Atreya, S.K.; Bertaux, J.L.; et al. (1999). "Ultraviolet Spectrometer Observations of Neptune and Triton" (PDF). Science. 246 (4936): 1459–66. Bibcode:1989Sci...246.1459B. doi:10.1126/science.246.4936.1459. PMID 17756000. S2CID 21809358. Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 May 2008. Retrieved 12 March 2008.
- ^ Herbert, Floyd; Sandel, Bill R. (August–September 1999). "Ultraviolet observations of Uranus and Neptune". Planetary and Space Science. 47 (8–9): 1, 119–139. Bibcode:1999P&SS...47.1119H. doi:10.1016/S0032-0633(98)00142-1.
- ^ Irwin, Patrick G. J.; Dobinson, Jack; James, Arjuna; Teanby, Nicholas A.; Simon, Amy A.; Fletcher, Leigh N.; Roman, Michael T.; Orton, Glenn S.; Wong, Michael H.; Toledo, Daniel; Pérez-Hoyos, Santiago; Beck, Julie (February 2024). "Modelling the seasonal cycle of Uranus's colour and magnitude, and comparison with Neptune". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 527 (4): 11521–11538. doi:10.1093/mnras/stad3761. hdl:20.500.11850/657542.
- ^ "Catalog Page for PIA01492". photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov. Archived from the original on 22 July 2023. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- ^ "The subtle color difference between Uranus and Neptune". The Planetary Society. Archived from the original on 5 February 2024. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- ^ Oxford, University of. "New images reveal what Neptune and Uranus really look like". phys.org. Archived from the original on 5 February 2024. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- ^ Stanley, Sabine; Bloxham, Jeremy (March 2004). "Convective-region geometry as the cause of Uranus' and Neptune's unusual magnetic fields". Nature. 428 (6979): 151–153. Bibcode:2004Natur.428..151S. doi:10.1038/nature02376. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 15014493. S2CID 33352017.
- ^ Connerney, J.E.P.; Acuña, Mario H.; Ness, Norman F. (1991). "The magnetic field of Neptune". Journal of Geophysical Research. 96: 19, 023–42. Bibcode:1991JGR....9619023C. doi:10.1029/91JA01165.
- ^ a b Ness, Norman F.; Acuña, Mario H.; Burlaga, Leonard F.; Connerney, John E. P.; Lepping, Ronald P.; Neubauer, Fritz M. (15 December 1989). "Magnetic Fields at Neptune". Science. 246 (4936): 1473–1478. Bibcode:1989Sci...246.1473N. doi:10.1126/science.246.4936.1473. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 17756002. S2CID 20274953. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 July 2019. Retrieved 25 August 2019.
- ^ Russell, C.T.; Luhmann, J.G. (1997). "Neptune: Magnetic Field and Magnetosphere". University of California, Los Angeles. Archived from the original on 29 June 2019. Retrieved 10 August 2006.
- ^ Lamy, L. (9 November 2020). "Auroral emissions from Uranus and Neptune". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 378 (2187). The Royal Society: 20190481. Bibcode:2020RSPTA.37890481L. doi:10.1098/rsta.2019.0481. PMC 7658782. PMID 33161867.
- ^ "ESA Portal – Mars Express discovers auroras on Mars". European Space Agency. 11 August 2004. Archived from the original on 19 October 2012. Retrieved 5 August 2010.
- ^ "NASA's Webb Captures Neptune's Auroras For First Time". NASA Webb Mission Team. 26 March 2025. Retrieved 26 March 2025.
- ^ Lavoie, Sue (8 January 1998). "PIA01142: Neptune Scooter". NASA. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 26 March 2006.
- ^ Hammel, H. B.; Beebe, R. F.; De Jong, E. M.; Hansen, C. J.; et al. (22 September 1989). "Neptune's Wind Speeds Obtained by Tracking Clouds in Voyager Images". Science. 245 (4924): 1367–1369. Bibcode:1989Sci...245.1367H. doi:10.1126/science.245.4924.1367. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 17798743. S2CID 206573894.
- ^ a b Burgess (1991):64–70.
- ^ a b Villard, Ray; Devitt, Terry (15 May 2003). "Brighter Neptune Suggests A Planetary Change of Seasons". Hubble News Center. Archived from the original on 28 February 2008. Retrieved 26 February 2008.
- ^ a b Lavoie, Sue (16 February 2000). "PIA02245: Neptune's blue-green atmosphere". NASA JPL. Archived from the original on 5 August 2013. Retrieved 28 February 2008.
- ^ Orton, G. S.; Encrenaz, T.; Leyrat, C.; Puetter, R.; et al. (October 2007). "Evidence for methane escape and strong seasonal and dynamical perturbations of Neptune's atmospheric temperatures" (PDF). Astronomy & Astrophysics. 473 (1): L5 – L8. Bibcode:2007A&A...473L...5O. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078277. ISSN 0004-6361. S2CID 54996279. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 February 2024. Retrieved 1 February 2024.
- ^ Orton, Glenn; Encrenaz, Thérèse (18 September 2007). "A Warm South Pole? Yes, On Neptune!". ESO. Archived from the original on 23 March 2010. Retrieved 20 September 2007.
- ^ Hammel, H. B.; Lockwood, G. W.; Mills, J. R.; Barnet, C. D. (1995). "Hubble Space Telescope Imaging of Neptune's Cloud Structure in 1994". Science. 268 (5218): 1740–42. Bibcode:1995Sci...268.1740H. doi:10.1126/science.268.5218.1740. PMID 17834994. S2CID 11688794.
- ^ Lavoie, Sue (29 January 1996). "PIA00064: Neptune's Dark Spot (D2) at High Resolution". NASA JPL. Archived from the original on 27 September 2013. Retrieved 28 February 2008.
- ^ "Mysterious Neptune dark spot detected from Earth for the first time". ESO. Archived from the original on 26 August 2023. Retrieved 26 August 2023.
- ^ SDS-2015 meant that it was a Southern Dark Spot that was discovered in 2015.
H. Wong, Michael; Tollefson, Joshua; I. Hsu, Andrew; de Pater, Imke; A. Simon, Amy; Hueso, Ricardo; Sánchez-Lavega, Agustín; Sromovsky, Lawrence; Fry, Patrick; Luszcz-Cook, Statia (15 February 2018). "A New Dark Vortex on Neptune". The American Astronomical Society. 155 (3). Abstract section. doi:10.3847/1538-3881 (inactive 1 July 2025).{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of July 2025 (link) - ^ S.G., Gibbard; de Pater, I.; Roe, H. G.; Martin, S.; et al. (2003). "The altitude of Neptune cloud features from high-spatial-resolution near-infrared spectra" (PDF). Icarus. 166 (2): 359–74. Bibcode:2003Icar..166..359G. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2003.07.006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 February 2012. Retrieved 26 February 2008.
- ^ Stratman, P.W.; Showman, A.P.; Dowling, T.E.; Sromovsky, L.A. (2001). "EPIC Simulations of Bright Companions to Neptune's Great Dark Spots" (PDF). Icarus. 151 (2): 275–85. Bibcode:1998Icar..132..239L. doi:10.1006/icar.1998.5918. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 February 2008. Retrieved 26 February 2008.
- ^ Sromovsky, L.A.; Fry, P.M.; Dowling, T.E.; Baines, K.H. (2000). "The unusual dynamics of new dark spots on Neptune". Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society. 32: 1005. Bibcode:2000DPS....32.0903S.
- ^ "Happy birthday Neptune". ESA/Hubble. Archived from the original on 15 July 2011. Retrieved 13 July 2011.
- ^ Borucki, W.J. (1989). "Predictions of lightning activity at Neptune". Geophysical Research Letters. 16 (8): 937–939. Bibcode:1989GeoRL..16..937B. doi:10.1029/gl016i008p00937.
- ^ a b Aplin, K.L.; Fischer, G.; Nordheim, T.A.; Konovalenko, A.; Zakharenko, V.; Zarka, P. (2020). "Atmospheric Electricity at the Ice Giants". Space Science Reviews. 216 (2): 26. arXiv:1907.07151. Bibcode:2020SSRv..216...26A. doi:10.1007/s11214-020-00647-0.
- ^ a b c d Gurnett, D. A.; Kurth, W. S.; Cairns, I. H.; Granroth, L. J. (1990). "Whistlers in Neptune's magnetosphere: Evidence of atmospheric lightning". Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics. 95 (A12): 20967–20976. Bibcode:1990JGR....9520967G. doi:10.1029/ja095ia12p20967. hdl:2060/19910002329.
- ^ Belcher, J.W.; Bridge, H.S.; Bagenal, F.; Coppi, B.; Divers, O.; Eviatar, A.; Gordon, G.S.; Lazarus, A.J.; McNutt, R.L.; Ogilvie, K.W.; Richardson, J.D.; Siscoe, G.L.; Sittler, E.C.; Steinberg, J.T.; Sullivan, J.D.; Szabo, A.; Villanueva, L.; Vasyliunas, V.M.; Zhang, M. (1989). "Plasma observations near Neptune: Initial results from Voyager 2". Science. 246 (4936): 1478–1483. Bibcode:1989Sci...246.1478B. doi:10.1126/science.246.4936.1478. PMID 17756003.
- ^ Gibbard, S.G.; Levy, E.H.; Lunine, J.I.; de Pater, I. (1999). "Lightning on Neptune". Icarus. 139 (2): 227–234. Bibcode:1999Icar..139..227G. doi:10.1006/icar.1999.6101.
- ^ Aglyamov, Y.S.; Lunine, J.; Atreya, S.; Guillot, T.; Becker, H.N.; Levin, S.; Bolton, S.J. (2020). "Atmospheric Electricity at the Ice Giants". Space Science Reviews. 216 (2) 26. arXiv:1907.07151. Bibcode:2020SSRv..216...26A. doi:10.1007/s11214-020-00647-0.
- ^ Borucki, W.J. (1989). "Predictions of lightning activity at Neptune". Geophysical Research Letters. 16 (8): 937–939. Bibcode:1989GeoRL..16..937B. doi:10.1029/gl016i008p00937.
- ^ Lindal, Gunnar F. (1992). "The atmosphere of Neptune – an analysis of radio occultation data acquired with Voyager 2". Astronomical Journal. 103: 967–82. Bibcode:1992AJ....103..967L. doi:10.1086/116119.
- ^ "Class 12 – Giant Planets – Heat and Formation". 3750 – Planets, Moons & Rings. Colorado University, Boulder. 2004. Archived from the original on 21 June 2008. Retrieved 13 March 2008.
- ^ Pearl, J.C.; Conrath, B.J. (1991). "The albedo, effective temperature, and energy balance of Neptune, as determined from Voyager data". Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics. 96: 18, 921–30. Bibcode:1991JGR....9618921P. doi:10.1029/91ja01087.
- ^ Pater, Imke de; Lissauer, Jack J. (6 December 2001). Planetary Sciences. Cambridge University Press. p. 224. ISBN 978-0-521-48219-6. Archived from the original on 29 September 2021. Retrieved 15 March 2023.
- ^ Meeus, Jean (1998). Astronomical Algorithms. Richmond, VA: Willmann-Bell. p. 273. Supplemented by further use of VSOP87.
- ^ "Planetary Fact Sheet". Archived from the original on 2 February 2024. Retrieved 2 January 2024.
- ^ McKie, Robin (9 July 2011). "Neptune's first orbit: a turning point in astronomy". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 23 August 2016. Retrieved 15 December 2016.
- ^ Atkinson, Nancy (26 August 2010). "Clearing the Confusion on Neptune's Orbit". Universe Today. Archived from the original on 29 September 2023. Retrieved 1 February 2024.
- ^ Lakdawalla, Emily [@elakdawalla] (19 August 2010). "Doh! RT @lukedones: From Bill Folkner at JPL: Neptune will reach the same ecliptic longitude it had on Sep. 23, 1846, on July 12, 2011" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ a b "Horizons Output for Neptune 2010–2011". 16 November 2007. Archived from the original on 2 May 2013. Retrieved 25 February 2008.—Numbers generated using the Solar System Dynamics Group, Horizons On-Line Ephemeris System.
- ^ Williams, David R. (6 January 2005). "Planetary Fact Sheets". NASA. Archived from the original on 25 September 2008. Retrieved 28 February 2008.
- ^ Hubbard, W. B.; Nellis, W. J.; Mitchell, A. C.; Holmes, N. C.; et al. (9 August 1991). "Interior Structure of Neptune: Comparison with Uranus". Science. 253 (5020): 648–651. Bibcode:1991Sci...253..648H. doi:10.1126/science.253.5020.648. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 17772369. S2CID 20752830. Archived from the original on 23 October 2018. Retrieved 12 June 2019.
- ^ Thommes, E. W.; Duncan, M. J.; Levison, H. F. (May 2002). "The Formation of Uranus and Neptune among Jupiter and Saturn". The Astronomical Journal. 123 (5): 2862–2883. arXiv:astro-ph/0111290. Bibcode:2002AJ....123.2862T. doi:10.1086/339975. S2CID 17510705.
- ^ Hansen, Kathryn (7 June 2005). "Orbital shuffle for early solar system". Geotimes. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 26 August 2007.
- ^ Crida, A. (2009). "Solar System Formation". Reviews in Modern Astronomy. Vol. 21. p. 3008. arXiv:0903.3008. Bibcode:2009RvMA...21..215C. doi:10.1002/9783527629190.ch12. ISBN 978-3-527-62919-0. S2CID 118414100.
- ^ Desch, S.J. (2007). "Mass Distribution and Planet Formation in the Solar Nebula" (PDF). The Astrophysical Journal. 671 (1): 878–93. Bibcode:2007ApJ...671..878D. doi:10.1086/522825. S2CID 120903003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 February 2020.
- ^ Smith, R.; Churcher, L. J.; Wyatt, M. C.; Moerchen, M. M.; et al. (January 2009). "Resolved debris disc emission around η Telescopii: a young solar system or ongoing planet formation?". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 493 (1): 299–308. arXiv:0810.5087. Bibcode:2009A&A...493..299S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200810706. ISSN 0004-6361. S2CID 6588381.
- ^ Stern, S. Alan; Colwell, Joshua E. (1997). "Collisional Erosion in the Primordial Edgeworth-Kuiper Belt and the Generation of the 30–50 AU Kuiper Gap". The Astrophysical Journal. 490 (2): 879–82. Bibcode:1997ApJ...490..879S. doi:10.1086/304912.
- ^ Petit, Jean-Marc; Morbidelli, Alessandro; Valsecchi, Giovanni B. (1999). "Large Scattered Planetesimals and the Excitation of the Small Body Belts" (PDF). Icarus. 141 (2): 367–87. Bibcode:1999Icar..141..367P. doi:10.1006/icar.1999.6166. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 December 2007. Retrieved 23 June 2007.
- ^ "List of Transneptunian Objects". Minor Planet Center. Archived from the original on 27 October 2010. Retrieved 25 October 2010.
- ^ Jewitt, David (2004). "The Plutinos". UCLA. Archived from the original on 19 April 2007. Retrieved 28 February 2008.
- ^ Varadi, F. (1999). "Periodic Orbits in the 3:2 Orbital Resonance and Their Stability". The Astronomical Journal. 118 (5): 2526–31. Bibcode:1999AJ....118.2526V. doi:10.1086/301088.
- ^ Davies, John (2001). Beyond Pluto: Exploring the outer limits of the solar system. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 104. ISBN 978-0-521-80019-8.
- ^ Chiang, E. I.; Jordan, A. B.; Millis, R. L.; Buie, M. W.; et al. (July 2003). "Resonance Occupation in the Kuiper Belt: Case Examples of the 5:2 and Trojan Resonances". The Astronomical Journal. 126 (1): 430–443. arXiv:astro-ph/0301458. Bibcode:2003AJ....126..430C. doi:10.1086/375207. ISSN 0004-6256. S2CID 54079935.
- ^ Sheppard, Scott S.; Trujillo, Chadwick A. (10 September 2010). "Detection of a Trailing (L5) Neptune Trojan". Science. 329 (5997): 1304. Bibcode:2010Sci...329.1304S. doi:10.1126/science.1189666. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 20705814. S2CID 7657932.
- ^ a b De La Fuente Marcos, C. & De La Fuente Marcos, R. (2012). "(309239) 2007 RW10: a large temporary quasi-satellite of Neptune". Astronomy and Astrophysics Letters. 545 (2012): L9. arXiv:1209.1577. Bibcode:2012A&A...545L...9D. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201219931. S2CID 118374080.
- ^ "New Uranus and Neptune Moons". Earth & Planetary Laboratory. Carnegie Institution for Science. 23 February 2024. Archived from the original on 23 February 2024. Retrieved 23 February 2024.
- ^ Agnor, Craig B.; Hamilton, Douglas P. (May 2006). "Neptune's capture of its moon Triton in a binary–planet gravitational encounter". Nature. 441 (7090): 192–194. Bibcode:2006Natur.441..192A. doi:10.1038/nature04792. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 16688170. S2CID 4420518.
- ^ Chyba, Christopher F.; Jankowski, D.G.; Nicholson, P.D. (1989). "Tidal evolution in the Neptune-Triton system". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 219 (1–2): L23 – L26. Bibcode:1989A&A...219L..23C.
- ^ Wilford, John N. (29 August 1989). "Triton May Be Coldest Spot in Solar System". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 10 December 2008. Retrieved 29 February 2008.
- ^ "Triton - NASA Science". 21 November 2017. Archived from the original on 7 January 2024. Retrieved 7 January 2024.
- ^ Nelson, Robert M.; Smythe, William D.; Wallis, Brad D.; Horn, Linda J.; et al. (19 October 1990). "Temperature and Thermal Emissivity of the Surface of Neptune's Satellite Triton". Science. 250 (4979): 429–431. Bibcode:1990Sci...250..429N. doi:10.1126/science.250.4979.429. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 17793020. S2CID 20022185.
- ^ "12.3: Titan and Triton". 7 October 2016. Archived from the original on 7 January 2024. Retrieved 7 January 2024.
- ^ "Triton: Neptune's Moon". January 2010. Archived from the original on 7 January 2024. Retrieved 7 January 2024.
- ^ a b Stone, E. C.; Miner, E. D. (15 November 1989). "The Voyager 2 Encounter with the Neptunian System". Science. 246 (4936): 1417–1421. Bibcode:1989Sci...246.1417S. doi:10.1126/science.246.4936.1417. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 17755996. S2CID 9367553.
- ^ Brown, Michael E. "The Dwarf Planets". California Institute of Technology, Department of Geological Sciences. Archived from the original on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 9 February 2008.
- ^ Holman, M.J.; Kavelaars, J.J.; Grav, T.; et al. (2004). "Discovery of five irregular moons of Neptune" (PDF). Nature. 430 (7002): 865–67. Bibcode:2004Natur.430..865H. doi:10.1038/nature02832. PMID 15318214. S2CID 4412380. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 November 2013. Retrieved 24 October 2011.
- ^ "Five new moons for planet Neptune". BBC News. 18 August 2004. Archived from the original on 8 August 2007. Retrieved 6 August 2007.
- ^ Grush, Loren (20 February 2019). "Neptune's newly discovered moon may be the survivor of an ancient collision". The Verge. Archived from the original on 21 February 2019. Retrieved 22 February 2019.
- ^ O"Callaghan, Jonathan (21 September 2022). "Neptune and Its Rings Come Into Focus With Webb Telescope - New images from the space-based observatory offer a novel view of the planet in infrared". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 22 September 2022. Retrieved 23 September 2022.
- ^ Cruikshank, Dale P. (1996). Neptune and Triton. University of Arizona Press. pp. 703–804. ISBN 978-0-8165-1525-7.
- ^ Blue, Jennifer (8 December 2004). "Nomenclature Ring and Ring Gap Nomenclature". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS. Archived from the original on 5 July 2010. Retrieved 28 February 2008.
- ^ Guinan, E.F.; Harris, C.C.; Maloney, F.P. (1982). "Evidence for a Ring System of Neptune". Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society. 14: 658. Bibcode:1982BAAS...14..658G.
- ^ Goldreich, P.; Tremaine, S.; Borderies, N. (August 1986). "Towards a theory for Neptune's arc rings" (PDF). The Astronomical Journal. 92: 490. Bibcode:1986AJ.....92..490G. doi:10.1086/114178. Archived from the original on 29 September 2021. Retrieved 12 June 2019.
- ^ Nicholson, Philip D.; Cooke, Maren L.; Matthews, Keith; Elias, Jonathan H.; Gilmore, Gerard; et al. (September 1990). "Five stellar occultations by Neptune: Further observations of ring arcs". Icarus. 87 (1): 1–39. Bibcode:1990Icar...87....1N. doi:10.1016/0019-1035(90)90020-A.
- ^ Cox, Arthur N. (2001). Allen's Astrophysical Quantities. Springer. ISBN 978-0-387-98746-0.
- ^ Munsell, Kirk; Smith, Harman; Harvey, Samantha (13 November 2007). "Planets: Neptune: Rings". Solar System Exploration. NASA. Archived from the original on 4 July 2012. Retrieved 29 February 2008.
- ^ Salo, Heikki; Hänninen, Jyrki (1998). "Neptune's Partial Rings: Action of Galatea on Self-Gravitating Arc Particles". Science. 282 (5391): 1102–04. Bibcode:1998Sci...282.1102S. doi:10.1126/science.282.5391.1102. PMID 9804544.
- ^ "Neptune's rings are fading away". New Scientist. 26 March 2005. Archived from the original on 10 December 2008. Retrieved 6 August 2007.
- ^ Schmude, R.W. Jr.; Baker, R.E.; Fox, J.; Krobusek, B.A.; Pavlov, H.; Mallama, A. (29 March 2016). The secular and rotational brightness variations of Neptune (unpublished manuscript). arXiv:1604.00518.
- ^ See the respective articles for magnitude data.
- ^ Moore (2000):207.
- ^ In 1977, for example, even the rotation period of Neptune remained uncertain. Cruikshank, D.P. (1 March 1978). "On the rotation period of Neptune". Astrophysical Journal Letters. 220: L57 – L59. Bibcode:1978ApJ...220L..57C. doi:10.1086/182636.
- ^ Max, C.; MacIntosh, B.; Gibbard, S.; Roe, H.; et al. (1999). "Adaptive Optics Imaging of Neptune and Titan with the W.M. Keck Telescope". Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society. 31: 1512. Bibcode:1999AAS...195.9302M.
- ^ Nemiroff, R.; Bonnell, J., eds. (18 February 2000). "Neptune through Adaptive Optics". Astronomy Picture of the Day. NASA.
- ^ Roddier, F.; Roddier, C.; Brahic, A.; Dumas, C.; Graves, J. E.; Northcott, M. J.; Owen, T. (1 August 1997). "First ground-based adaptive optics observations of Neptune and Proteus". Planetary and Space Science. 45 (8): 1031–1036. Bibcode:1997P&SS...45.1031R. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.66.7754. doi:10.1016/S0032-0633(97)00026-3. Archived from the original on 1 February 2024. Retrieved 1 February 2024.
- ^ Engvold, Oddbjorn (10 May 2007). Reports on Astronomy 2003-2005 (IAU XXVIA): IAU Transactions XXVIA. Cambridge University Press. pp. 147f. ISBN 978-0-521-85604-1. Archived from the original on 11 May 2023. Retrieved 15 March 2023.
- ^ Gibbard, S. G.; Roe, H.; de Pater, I.; Macintosh, B.; et al. (March 2002). "High-Resolution Infrared Imaging of Neptune from the Keck Telescope". Icarus. 156 (1): 1–15. Bibcode:2002Icar..156....1G. doi:10.1006/icar.2001.6766. ISSN 0019-1035. Archived from the original on 23 October 2018. Retrieved 12 June 2019.
- ^ Phillips, Cynthia (5 August 2003). "Fascination with Distant Worlds". SETI Institute. Archived from the original on 3 November 2007. Retrieved 3 October 2007.
- ^ a b Burgess (1991):46–55.
- ^ Standage 2000, p. 188
- ^ Gebhardt, Chris; Goldader, Jeff (20 August 2011). "Thirty-four years after launch, Voyager 2 continues to explore". NASASpaceflight. Archived from the original on 19 February 2016. Retrieved 22 January 2016.
- ^ Wu, Weiren; Yu, Dengyun; Huang, Jiangchuan; Zong, Qiugang; Wang, Chi; Yu, Guobin; He, Rongwei; Wang, Qian; Kang, Yan; Meng, Linzhi; Wu, Ke; He, Jiansen; Li, Hui (9 January 2019). "Exploring the solar system boundary". Scientia Sinica Informationis. 49 (1): 1. doi:10.1360/N112018-00273.
- ^ Jones, Andrew (16 April 2021). "China to launch a pair of spacecraft towards the edge of the solar system". SpaceNews. Archived from the original on 15 May 2021. Retrieved 29 April 2021.
- ^ Clark, Stephen (25 August 2015). "Uranus, Neptune in NASA's sights for new robotic mission". Spaceflight Now. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 7 September 2015.
- ^ Spilker, T.R.; Ingersoll, A.P. (2004). "Outstanding Science in the Neptune System From an Aerocaptured Vision Mission". Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society. 36: 1094. Bibcode:2004DPS....36.1412S.
- ^ Hansen, Candice; et al. "Argo – A Voyage Through the Outer Solar System" (PDF). SpacePolicyOnline.com. Space and Technology Policy Group, LLC. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 5 August 2015.
- ^ "Exploring Triton With Trident: A Discovery-Class Mission" (PDF). Universities Space Research Association. 23 March 2019. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 August 2020. Retrieved 26 March 2019.
- ^ Rymer, Abigail; Clyde, Brenda; Runyon, Kirby (August 2020). "Neptune Odyssey: Mission to the Neptune-Triton System" (PDF). NASA Science. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 December 2020. Retrieved 18 April 2021.
- ^ Origins, Worlds, and Life: A Decadal Strategy for Planetary Science and Astrobiology 2023-2032 (Prepublication ed.). National Academies Press. 19 January 2023. p. 800. Bibcode:2023owld.book.....N. doi:10.17226/26522. ISBN 978-0-309-47578-5. S2CID 248283239. Retrieved 30 April 2022.
- ^ Hansen-Koharcheck, Candice; Fielhauer, Karl (7 June 2021). "Triton Ocean Worlds Surveyor concept study" (PDF). NASA. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 November 2023. Retrieved 11 January 2024.
- ^ Steckel, Amanda; Conrad, Jack William; Dekarske, Jason; Dolan, Sydney; Downey, Brynna Grace; Felton, Ryan; Hanson, Lavender Elle; Giesche, Alena; Horvath, Tyler; Maxwell, Rachel; Shumway, Andrew O; Siddique, Anamika; Strom, Caleb; Teece, Bronwyn; Todd, Jessica; Trinh, Kevin T; Velez, Michael A; Walter, Callum Andrew; Lowes, Leslie L; Hudson, Troy; Scully, Jennifer E. C. (12 December 2023). "The Science Case for Nautilus: A Multi-Flyby Mission Concept to Triton". AGU - Agu23 (3089). AGU. Bibcode:2023AGUFM.P23D3089S. Archived from the original on 11 January 2024. Retrieved 11 January 2024.
- ^ "China's plans for outer Solar System exploration". The Planetary Society. 21 December 2023. Retrieved 18 April 2024.
Bibliography
[edit]- Burgess, Eric (1991). Far Encounter: The Neptune System. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-07412-4.
- Moore, Patrick (2000). The Data Book of Astronomy. Baton Rouge: Taylor & Francis Group. ISBN 978-0-7503-0620-1.
Further reading
[edit]- Miner, Ellis D.; Wessen, Randii R. (2002). Neptune: The Planet, Rings, and Satellites. Springer-Praxis books in astronomy and space sciences. London; New York: Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-216-7.
- Standage, Tom (2000). The Neptune File: A Story of Astronomical Rivalry and the Pioneers of Planet Hunting. New York: Walker. ISBN 978-0-8027-1363-6.
External links
[edit]- NASA's Neptune fact sheet
- Neptune from Bill Arnett's nineplanets.org
- Neptune Astronomy Cast episode No. 63, includes full transcript.
- Neptune Profile (archived 15 November 2002) at NASA's Solar System Exploration site
- Interactive 3D gravity simulation of Neptune and its inner moons Archived 22 September 2020 at the Wayback Machine
 KSF
KSF





![Original 2-colour (orange-green) NASA/JPL image from Voyager 2, with exaggerated colour[97]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/56/Neptune_Full.jpg/250px-Neptune_Full.jpg)
![Colour recalibrated in 2016 (Justin Cowart), preserving some enhancement for contrast[98]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/63/Neptune_-_Voyager_2_%2829347980845%29_flatten_crop.jpg/250px-Neptune_-_Voyager_2_%2829347980845%29_flatten_crop.jpg)
![Colour recalibrated in 2023 (Patrick Irwin), approximating the true colour[99]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b9/Neptune_Voyager2_color_calibrated.png/250px-Neptune_Voyager2_color_calibrated.png)









