New York State Police
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 12 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 12 min
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
| New York State Police | |
|---|---|
 Patch | |
 Seal | |
 Shield of New York State Police | |
 Flag of the State of New York | |
| Common name | New York State Troopers |
| Abbreviation | NYSP |
| Motto | Excellence Through Knowledge |
| Agency overview | |
| Formed | April 11, 1917 |
| Employees | 5,711 (as of 2018)[1] |
| Annual budget | $926,123,000 (2018) |
| Jurisdictional structure | |
| Operations jurisdiction | New York, U.S. |
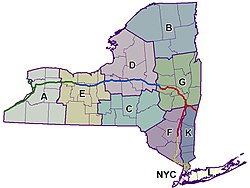 | |
| Troops of the New York State Police | |
| Size | 54,556 sq mi (141,300 km2) |
| Population | 19.4 million |
| Legal jurisdiction | State of New York |
| Governing body | New York State Executive Department |
| General nature | |
| Operational structure | |
| Headquarters | Building 22 W. Averell Harriman State Office Building Campus Albany, New York, United States |
| Troopers | 5,009[2] |
| Non-sworn members | 711 |
| Agency executive |
|
| Facilities | |
| Troops | 11 |
| Website | |
| Official Site | |
The New York State Police (NYSP) is the state police of the U.S. state of New York; it is part of the New York State Executive Department and employs over 5,000 sworn state troopers and 711 non-sworn members.
The New York State Police are responsible for patrolling state highways, rural communities, and providing law enforcement services across the state.
History
[edit]
Like most U.S. states, New York did not establish a state police force until the early twentieth century. In part this reflected the pattern of settlement across a wide frontier. A number of proposals to create such a force during the early 1900s, but faced considerable opposition from trade union interests. They feared the police would be used against union organizing, as was happening in several other states.[3]
Following the 1913 murder of Sam Howell, a construction foreman in Westchester County, and failure of the local police to arrest suspects he had named before his death, the New York State Legislature passed a bill to establish a state police force. The New York State Police was officially established on April 11, 1917.
The division's first superintendent was George Fletcher Chandler, who was appointed by Governor Charles S. Whitman. Chandler is credited with much of the division's early organization and development. Chandler coined the term "New York State Troopers." He was an early advocate of officers carrying their weapons exposed on a belt, which was not common practice at the time.[citation needed]
On January 1, 1980, the Long Island State Parkway Police merged with the state police; this resulted in the official establishment of Troop L. In October 1997, the New York State Capital Police was consolidated and absorbed into the state police.
Since February 1994, the agency has accepted DNA evidence for forensic investigation and analysis. The New York State Police Forensic Investigation Center (FIC) opened in November 1996. The Crime Laboratory performs DNA analysis for state investigations and for local law enforcement. It includes a new DNA Data Bank Section that compiles DNA records from violent felons sentenced to prison in New York State. These records can be searched and compared by computer to other evidence collected in unsolved crimes.[4]
In December 2019, Governor Andrew Cuomo announced that the New York State Park Police was to be merged with the New York State Police. The merger was expected to take about six months.[5] Cuomo resigned in August 2021, and by January 2022, New York officials announced that the two police forces would remain separate.[6]
Since the establishment of the New York State Police, 140 troopers have died while on duty.[7]
Structure and organization
[edit]

The NYSP divides New York state geographically into eleven "Troops," each comprising a specific geographic area, usually several counties. Each is supervised by a "Troop Commander" usually of the rank of Major.[8] NYSP Troops cover the following counties and regions as listed:
Each Troop encompasses 2–4 "Zones" which are referred to simply by a Zone number. There are up to several "sub-stations" located within each zone.
Ranks
[edit]Uniforms
[edit]
Trooper uniforms are made of grey wool, with the exception of the Gore-Tex jacket. Prior to 1958, uniforms (shirts, jackets and britches) were woven of equal parts white fiber and black fiber to symbolize the impartiality of justice.[citation needed] The NYSP do not wear a badge on their uniform shirts.[10][self-published source?]
Equipment
[edit]Current equipment
[edit]- Glock 47, chambered in 9×19mm Parabellum — equipped with Aimpoint Acro P2 & Streamlight TLR-7 HL-X weapon-mounted light.
Previously issued equipment
[edit]- Glock 21 Gen 4 .45 ACP (2018–2024)
- Glock 37 .45 GAP (2007–2018)[11]
- Glock 17 9mm (1990–2007)[12]
- Smith & Wesson Model 681 .357 Magnum
- Smith & Wesson Model 13 .357 Magnum
- Smith & Wesson Model 10 .38 Special
Cameras
[edit]The New York State Police is one of only five state police agencies in the United States that does not equip its state police vehicles with dashboard cameras. New York State Troopers, as of April 5, 2021, have been receiving body-worn cameras.[13]
Aviation
[edit]
The New York State Police has three Bell 407 single engine utility helicopters, six Bell 430 twin engine helicopters, three Bell UH-1 “HUEY 2” Single engine utility helicopters and one UH-1H “HUEY 1” Single engine utility helicopter. Their other aircraft are two Cessna 206 Stationair Single engine airplanes, one Cessna 172 Single engine airplane, one Partenavia 68 Twin engine observation airplane, one Sikorsky S-76 (used for transporting the governor), and two Beech King Air twin engine turboprop airplanes. All of these aircraft operate under the call sign “GrayRider”.[14] In 2025, New York State Police put an order for a Airbus H160 and three Airbus H145[15]
Line of duty deaths
[edit]Since its establishment, a total of 162 officers and 2 K9s have died in the line of duty.[16]
See also
[edit]- New York State Police Troop C scandal
- List of law enforcement agencies in New York
- New York State University Police
- State Police (United States)
- Highway Patrol
Notes
[edit]- ^ NYSP Troop T was responsible for protecting Interstate 84 from 1991 to 2010 because the New York State Thruway Authority (NYSTA) maintained Interstate 84. However, due to the transfer of maintenance from NYSTA back to the NYSDOT in October 2010, NYSP Troop T no longer patrols Interstate 84 as patrolling duties were reassigned to Troop F and Troop K.
References
[edit]- ^ "NYS DOB: FY 2018 Executive Budget | Agency Appropriations | State Police, Division of". www.budget.ny.gov. Retrieved 2018-06-10.
- ^ "208 troopers graduate from NY State Police Academy".
- ^ Van de Water, Frederic Franklyn (1922). Grey Riders: The Story of the New York State Troopers. Putnam's Sons.
- ^ [1], Troopers, NY
- ^ Slattery, Denis (3 December 2019). "Gov. Cuomo says New York State Police will absorb State Park Police Officers in union-backed move". nydailynews.com.
- ^ "Officials: New York State park police, troopers to stay separate". Newsday. 25 January 2022. Retrieved 2022-05-20.
- ^ Down Memorial Page
- ^ NYSP site http://www.troopers.ny.gov/Contact_Us/Troop_Information/
- ^ Rife, Judy (October 11, 2010). "DOT takes over maintenance on I-84". Times Herald-Record. Middletown, NY. Retrieved October 13, 2010.
- ^ Kidd, R. Spencer (2012). Uniforms of the U.S. State Police & Highway Patrols. lulu.com. p. 11. ISBN 978-1-4717-7729-5. OCLC 929822564.[self-published source]
- ^ "Glock 37". New York State Police.
- ^ "Switch to Semi-Automatic Pistol". New York State Police.
- ^ "N.Y. State Police lag behind agencies nationwide". Sentinel and Enterprise. Associated Press. 23 July 2019. Retrieved 19 September 2019.
- ^ "Current Equipment". New York State Police. Retrieved 15 February 2019.
- ^ "New York State Police orders Airbus H160 and three H145 helicopters | Airbus". www.airbus.com. 2025-03-12. Retrieved 2025-03-13.
- ^ "New York State Police, NY". The Officer Down Memorial Page (ODMP). Retrieved 2025-04-12.
External links
[edit]- New York State Police website
- New York State Police in the New York Codes, Rules and Regulations
- NYSP Recruitment Center website
- Union representing Troopers and Supervisors
- Union representing Investigators
- New York State Police collected news and commentary at The New York Times
 KSF
KSF





