Order of Saint Louis
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 9 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 9 min
| Order of Saint Louis Ordre de Saint-Louis | |
|---|---|
 Cross of the Order of Saint Louis | |
| Awarded by the | |
| Type | Dynastic order |
| Established | 5 April 1693 |
| Royal house | House of France |
| Religious affiliation | Roman Catholicism |
| Ribbon | Bright red |
| Motto | Bellicæ Virtutis Præmium ('The Reward of Warring Valor') |
| Eligibility | Military officers of Catholic faith with over 10 years of service, including non-nobles |
| Awarded for | Exceptional merit |
| Status |
|
| Founder | Louis XIV of France |
| Precedence | |
| Next (higher) | Order of Saint Michael |
| Equivalent | Order of Military Merit awarded to non-Catholics |
Ribbon of the order | |
The Royal and Military Order of Saint Louis (French: Ordre Royal et Militaire de Saint-Louis) is a dynastic order of chivalry founded 5 April 1693[1][2] by King Louis XIV, named after Saint Louis (King Louis IX of France). It was intended as a reward for exceptional officers, notable as the first decoration that could be granted to non-nobles. By the authorities of the French Republic, it is considered a predecessor of the Legion of Honour, with which it shares the red ribbon (though the Legion of Honour is awarded to military personnel and civilians alike).
Although officially abolished by the government authorities of the July Revolution in 1830 following the French Revolution, its activities carried on as a dynastic order of the formerly sovereign royal family. As such, it is still recognised by the International Commission on Orders of Chivalry.[3]
Members
[edit]
The King was the Grand Master of the order, and the Dauphin was automatically a member as well. The Order had three classes:
- Grand-Croix (Grand Cross)
- Commandeur (Commander)
- Chevalier (Knight)
The entire order included 8 Grand Crosses, 28 Commanders and a variable number of Knights. Officers of the Order included, after the Grand Master, a Trésorier (Treasurer), a Greffier (Registrar) and a Huissier (Gentleman Usher).
The badge of the order consisted of a portrait of Saint Louis surrounded by the motto « LUD(OVICUS) M(AGNUS) IN(STITUIT) 1693 » ("Louis the Great instituted it in 1693"). The reverse features a sword interlaced with a laurel crown and a white sash, with the inscription « BELL(ICAE) VIRTUTIS PRAEM(IUM) » ("Reward of wartime valour"). Knights wore the badge suspended from a ribbon on the breast, Commanders wore a red ribband (sash) over the right shoulder, and recipients of the Grand Cross wore the ribband as well as a star on the left breast. The general assembly of the Order was held annually on 25 August, the feast day of Saint Louis, in the residence of the King.
Conditions for being inducted did not include nobility; however, Catholic faith was mandatory, as well as at least ten years' service as a commissioned officer in the Army or the Navy. Members of the Order received a pension. Hereditary nobility was granted to a knight's son and grandsons. Another decoration, the Institution of Military Merit (fr:Institution du mérite militaire) was created for the Protestant officers in service of the French king (mainly foreign mercenaries, as French Protestants were not tolerated at the time).
Until the death of Louis XIV, the medal was awarded to outstanding officers only, but it gradually came to be an award that most officers would receive during their career. On 1 January 1791, during the French Revolution, a decree changed the name to décoration militaire ("military decoration"). It was subsequently withdrawn on 15 October 1792.
One of the first acts of Louis XVIII was to reinstate the Order of Saint Louis, using it to award officers of the Royal and Imperial armies alike. In 1830 the new king Louis-Philippe abolished the order, which was never reinstated.
-
Comte d'Angiviller depicted wearing the insignia of the Order of Saint Louis with a rosette.
-
Jean-Baptiste Symon de Solémy wearing the insigna of Chevalier of the order of Saint Louis.
-
Rochambeau wearing the sash of Commandeur of the Order of Saint Louis
-
Count d'Argenson wearing the insignia of the Order of Saint Louis around his neck, by Hyacinthe Rigaud
-
Pierre Victor, Baron de Besenval de Brunstatt in armour, portrayed by Jean-Marc Nattier in 1766, wearing the insignia of Chevalier of the order of Saint Louis
-
Painting by Charles Wilson Peale showing a young French dragoon officer having fought in the American Revolution; his father holds the Order of Saint Louis,
Decree by His Majesty the King Louis XIV of France
[edit]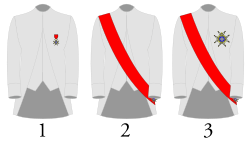
- Louis, by the grace of God King of France and Navarre, to all present and yet to come, hail.
- The officers of our troops have distinguished themselves by so many actions of considerable virtue and courage, in the conquest which it pleased God to bless the justice of our arms, that, ordinary awards becoming insufficient to the affection and the thankfulness which we have for them, we have deemed it necessary to seek new ways to reward their zeal and fidelity.
- In this view have we decided to establish a purely military Order to which, in addition to the external marks of honour which are associated to it, we shall guarantee revenues and pensions which shall rise in proportion to them growing more and more worthy through their behaviour.
- We have decided that only officers still serving in our troops shall be introduced and that virtue, merit and distinguished service in our armies shall be the only criteria to enter. We shall also in the future give a particular attention to increase the advantages of this order, so that we shall ever have the satisfaction to always be able to grant graces to the officers, and on the other hand, seeing rewards guaranteed by valour, they would every day bear renewed ardour in deserving them by their actions.
- In these causes, with the advice of our council, and our certain science, full power and royal authority, we have created, instituted and built, by the present, our military Order with the name of Saint Louis, and with the forms, statutes, ordinances and rules as follow: (...)
References
[edit]- ^ Hamilton, Walter. "Dated Book-plates (Ex Libris) with a Treatise on Their Origin", P37. Published 1895. A.C. Black.
- ^ Edmunds, Martha. "Piety and Politics", P274. Published 2002. University of Delaware Press. ISBN 0-87413-693-8
- ^ Icoregister (PDF)
External links
[edit]- (in French) Ordre Royal et Militaire de Saint-Louis—includes photographs, explanations and a 20,000 name list of recipients
- (in French) Histoire de l'Ordre royal & militaire de Saint-Louis Archived 2017-07-07 at the Wayback Machine—History of the Order
 KSF
KSF





