Outline of Arunachal Pradesh
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 10 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 10 min
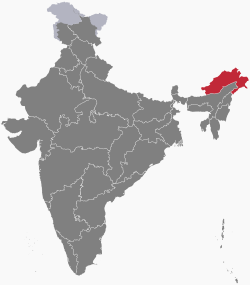
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Arunachal Pradesh:
Arunachal Pradesh – northeasternmost state of the Republic of India. Geographically, it is the largest among the North-east Indian states commonly known as the Seven Sister States. As in other parts of Northeast India, the people native to the state trace their origins to the Tibeto-Burman people. Arunachal Pradesh has close to 61,000 square kilometres of forests, and forest products are the next most significant sector of the economy. Among the crops grown here are rice, maize, millet, wheat, pulses, sugarcane, ginger, and oilseeds. Arunachal is also ideal for horticulture and fruit orchards. Its major industries are rice mills, fruit preservation and processing units, and handloom handicrafts. Sawmills and plywood trades are prohibited under law.[1]
General reference
[edit]Names
[edit]- Common name: Arunachal Pradesh
- Previously known as:
- North-East Frontier Agency
- Union Territory of Arunachal Pradesh (20 January 1972 to 20 February 1987.)
- Official name: Arunachal Pradesh
- Adjectival(s): Arunachali
- Demonym(s): Arunachalis
- Abbreviations and name codes
Rankings (amongst India's states and union territories)
[edit]- by population: 31st
- by area (2011 census): 15th
- by crime rate (2016): 17th
- by gross domestic product (GDP) (2014): 27th
- by Human Development Index (HDI)(2017): 24th
- by life expectancy at birth:
- by literacy rate (2011 census): 34th
Geography of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]Geography of Arunachal Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh is: an Indian state, one of the Seven Sister States
- Population of Arunachal Pradesh: 1,382,611
- Area of Arunachal Pradesh: 83,743 km2 (32,333 sq mi)
- Atlas of Arunachal Pradesh
Location of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]- Arunachal Pradesh is situated within the following regions:
- Time zone(s): Indian Standard Time (IST) (UTC+05:30)
Environment of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]- Climate of Arunachal Pradesh
- Topography of Arunachal Pradesh
- Biome types in Arunachal Pradesh
- Wildlife of Arunachal Pradesh
- Flora of Arunachal Pradesh
Natural geographic features of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]- Hills in Arunachal Pradesh
- Mountains in Arunachal Pradesh
- Rivers in Arunachal Pradesh
Protected areas of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]- Dibang Wildlife Sanctuary
- Dihang-Dibang Biosphere Reserve
- Eaglenest Wildlife Sanctuary
- Kameng Elephant Reserve
- Kamlang Wildlife Sanctuary
- Mehao Wildlife Sanctuary
- Mouling National Park
- Namdapha National Park
- Sessa Orchid Sanctuary
- Talley Valley Wildlife Sanctuary
Regions of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]Ecoregions of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]- Brahmaputra Valley semi-evergreen forests
- Eastern Himalayan broadleaf forests
- Eastern Himalaya subalpine conifer forests
- Northeastern Himalayan subalpine conifer forests
- Eastern Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows
Administrative divisions of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]Districts of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]- Districts of Arunachal Pradesh
- Tawang district
- West Kameng district
- East Kameng district
- Pakke-Kessang district
- Papum Pare district
- Kurung Kumey district
- Kra Daadi district
- Lower Subansiri district
- Upper Subansiri district
- West Siang district
- Siang district
- Upper Siang district
- Lower Siang district
- Lepa-Rada district
- Shi-Yomi district
- East Siang district
- Lower Dibang Valley district
- Upper Dibang Valley district
- Lohit district
- Anjaw district
- Namsai district
- Changlang district
- Tirap district
- Longding district
- Kamle district
Municipalities of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]Cities and towns in Arunachal Pradesh
- Capital of Arunachal Pradesh: Itanagar
- Along
- Bomdila
- Daporijo
- Naharlagun
- Pasighat
- Seppa
- Tawang
- Tezu
- Ziro
Demographics of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1961 | 337,000 | — |
| 1971 | 468,000 | +38.9% |
| 1981 | 632,000 | +35.0% |
| 1991 | 865,000 | +36.9% |
| 2001 | 1,098,000 | +26.9% |
| 2011 | 1,382,611 | +25.9% |
| Source:Census of India[2] First ever census was carried out in 1961. | ||
Demographics of Arunachal Pradesh – according to the 2011 census of India, the total population of Arunachal Pradesh is 13,82,611, of which 21,201,678 (50.54%) are male and 20,745,680 (49.46%) are female, or 978 females per 1000 males.
Religion demographics of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]Religion demographics of Arunachal Pradesh – according to the 2011 Indian Census, the religions of Arunachal Pradesh break down as follows:[6]
- Christian: 418,732 (30.26%)
- Hindu: 401,876 (29.04%)
- Others (mostly Donyi-Polo): 362,553 (26.2%)
- Buddhist: 162,815 (11.76%)
- Muslim: 27,045 (1.9%)
- Sikh: 1,865 (0.1%)
- Jain: 216 (<0.1%)
Language demographics of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]Language demographics of Arunachal Pradesh – Arunachal Pradesh is one of the linguistically richest and most diverse regions in all of Asia, being home to at least 30 and possibly as many as 50 distinct languages in addition to innumerable dialects and subdialects thereof.
Government and politics of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]- Form of government: Indian state government (parliamentary system of representative democracy)
- Capital of Arunachal Pradesh: Itanagar
- Elections in Arunachal Pradesh
Union government in Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]- Indian general election, 2009 (Arunachal Pradesh)
- Indian general election, 2014 (Arunachal Pradesh)
- Congressional representation of Arunachal Pradesh
Indian military in Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]Branches of the government of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]Government of Arunachal Pradesh
Executive branch of the government of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]- Head of state: Governor of Arunachal Pradesh,
- Raj Bhavan – official residence of the Governor
- Head of government: Chief Minister of Arunachal Pradesh,
- Departments and agencies of Arunachal Pradesh
Legislative branch of the government of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]Arunachal Pradesh Legislative Assembly
Judicial branch of the government of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]Law and order in Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]History of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]History of Arunachal Pradesh, by period
[edit]Prehistoric Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]Ancient Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]Medieval Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]History of Arunachal Pradesh[edit] History of Arunachal Pradesh
History of Arunachal Pradesh, by period[edit] Prehistoric Arunachal Pradesh[edit] Ancient Arunachal Pradesh[edit] Medieval Arunachal Pradesh[edit] Colonial Arunachal Pradesh[edit] Contemporary Arunachal Pradesh[edit] North-East Frontier Agency (1951 to 20 January 1972) – part of Assam Union Territory of Arunachal Pradesh (20 January 1972 to 20 February 1987.) History of Arunachal Pradesh, by region[edit] Historical places in Arunachal Pradesh[edit] Gomsi Ita Fort
Colonial Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]Contemporary Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]- North-East Frontier Agency (1951 to 20 January 1972) – part of Assam
- Union Territory of Arunachal Pradesh (20 January 1972 to 20 February 1987.)
History of Arunachal Pradesh, by region
[edit]Historical places in Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]History of Arunachal Pradesh, by subject
[edit]Culture of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]- Architecture of Arunachal Pradesh
- Cuisine of Arunachal Pradesh
- Languages of Arunachal Pradesh
- Monuments in Arunachal Pradesh
- World Heritage Sites in Arunachal Pradesh
Art in Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]People of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]Religion in Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]Sports in Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]Symbols of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]- State Bird: Hornbill
- State Flower: Foxtail Orchid
- State Animal: Gayal (AKA mithun)
- State Tree: Hollong
Economy and infrastructure of Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]- Tourism in Arunachal Pradesh
- Transport in Arunachal Pradesh
- Roads in Arunachal Pradesh
- Highways in Arunachal Pradesh
- Proposed roads
- Roads in Arunachal Pradesh
Education in Arunachal Pradesh
[edit]Education in Arunachal Pradesh
See also
[edit]- Outline of India
- Fact about Arunachal Pradesh
References
[edit]- ^ Arunachal Pradesh Economy, This Is My India
- ^ "Census Population" (PDF). Census of India. Ministry of Finance India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 December 2008. Retrieved 18 December 2008.
- ^ "Distribution of the 22 Scheduled Languages". Census of India. Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. 2001. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- ^ "Census Reference Tables, A-Series - Total Population". Census of India. Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. 2001. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- ^ [1] Census 2011 Non scheduled languages
- ^ "Census of India – Religious Composition". Government of India, Ministry of Home Affairs. Retrieved 27 August 2015.
External links
[edit]![]() Wikimedia Atlas of Arunachal Pradesh
Wikimedia Atlas of Arunachal Pradesh
- Official website
- Tourism in Arunachal Pradesh (Official)
- Arunachal Pradesh Territorial Dispute between India and China, Inventory of Conflict and Environment
- reviewNE – all things North East India
- STD Codes of Arunachal Pradesh Archived 31 May 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- Languages of Arunachal Pradesh (Roger Blench)
 KSF
KSF