Outline of the Byzantine Empire
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 10 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 10 min
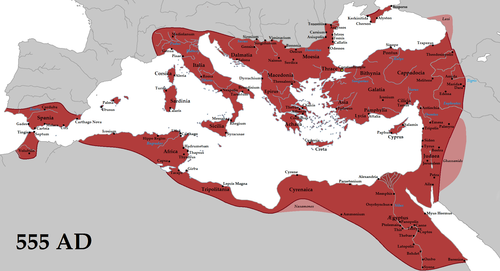
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Byzantine Empire:
Byzantine Empire (or Byzantium) – the Constantinople-centred Roman Empire of the Middle Ages. It is also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire, primarily in the context of Late Antiquity, while the Roman Empire was still administered with separate eastern and western political centres. In its own time, there was no such thing as "the Byzantine Empire," there was just the ongoing Roman Empire; "Byzantine Empire" is a scholarly term of convenience to differentiate the empire from its earlier existence during classical antiquity before the western half collapsed (see decline of the Roman Empire). Its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire (Ancient Greek: Βασιλεία Ῥωμαίων, Basileia Rhōmaiōn;[1] Latin: Imperium Romanum) or Romania (Ῥωμανία).[2] After the Western Roman Empire fragmented and collapsed in the 5th century, the eastern half continued to thrive, existing for an additional thousand years until it fell to the Ottoman Turks in 1453. During much of its existence, the empire was the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe.
Geography of the Byzantine Empire
[edit]Regions of the Byzantine Empire
[edit]- Albania under the Byzantine Empire
- Byzantine Armenia
- Byzantine Crete
- Byzantine Egypt
- Byzantine Greece
Administrative divisions of the Byzantine Empire
[edit]Provinces of the Byzantine Empire
[edit]- Bithynia
- Byzacena
- Byzantine Crete
- Catepanate of Italy
- Catepanate of Serbia
- Drougoubiteia
- Duchy of Perugia
- Duchy of Rome
- Duchy of the Pentapolis
- Duchy of Venetia
- Egypt (Roman province)
- Europa (Roman province)
- Duchy of Gaeta
- Galatia (Roman province)
- Haemimontus
- Helenopontus
- Honorias
- Isauria
- Mauretania Caesariensis
- Mauretania Tingitana
- Mesopotamia (Roman province)
- Moesia Secunda
- Duchy of Naples
- Palaestina Prima
- Paphlagonia
- Paristrion
- Phrygia Pacatiana
- Phrygia Salutaris
- Pontus Polemoniacus
- Rhodope (Roman province)
- Scythia Minor
- Spania
- Theodorias (province)
- Thessaly
Themes of the Byzantine Empire
[edit]Cities of the Byzantine Empire
[edit]- Constantinople (capital)
- Thessalonika
Affiliated polities
[edit]- Republic of Venice
- Frankokratia
- Despotate of Epirus
- Empire of Trebizond
- Bulgarian Empire
- Serbian Empire
Demography of the Byzantine Empire
[edit]Government and politics of the Byzantine Empire
[edit]Political institutions of the Byzantine Empire
[edit]Political institutions of the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine law
[edit]Military of the Byzantine Empire
[edit]Military of the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine armed forces
[edit]Military conflicts
[edit]General history of the Byzantine Empire
[edit]History of the Byzantine Empire
- Byzantine civilisation in the twelfth century
- Byzantine Empire under the Amorian dynasty
- Byzantine Empire under the Angelos dynasty
- Byzantine Empire under the Doukas dynasty
- Byzantine Empire under the Heraclian dynasty
- Byzantine Empire under the Isaurian dynasty
- Byzantine Empire under the Komnenos dynasty
- Byzantine Empire under the Leonid dynasty
- Byzantine Empire under the Macedonian dynasty
- Byzantine Empire under the Nikephorian dynasty
- Byzantine Empire under the Palaiologos dynasty
- Byzantine Empire under the Theodosian dynasty
- Byzantine Iconoclasm
- History of Lebanon under Byzantine rule
- History of the Jews in the Byzantine Empire
- Decline of the Byzantine Empire
Military history of the Byzantine Empire
[edit]- List of Byzantine wars
- List of sieges of Constantinople
- Byzantine–Sassanid Wars
- Byzantine–Arab Wars
- Rus'–Byzantine Treaty
- Rus'–Byzantine War
- Byzantine–Venetian Treaty of 1082
- Byzantine–Venetian War (1294–1302)
- Byzantine civil war of 1321–1328
- Byzantine civil war of 1341–1347
- Byzantine civil war of 1373–1379
- Byzantine–Genoese War (1348–1349)
- Byzantine–Bulgarian Wars
- Byzantine–Norman wars
- Byzantine–Seljuq Wars
- Byzantine–Georgian wars
- Byzantine–Mongol alliance
- Byzantine–Ottoman Wars
Works on Byzantine history
[edit]Byzantine historiography and scholars
[edit]18th century
[edit]19th century
[edit]20th century
[edit]Culture of the Byzantine Empire
[edit]- Byzantine architecture
- Byzantine art
- Byzantine calendar
- Byzantine cuisine
- Byzantine dress
- Byzantine gardens
- Byzantine Greeks
- Byzantine philosophy
Religion in the Byzantine Empire
[edit]Byzantine language
[edit]Byzantine economy
[edit]- Byzantine economy
- Byzantine agriculture
- Byzantine currency
- Byzantine coinage
- Byzantine mints
- Byzantine silk
- Slavery in the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine education
[edit]Byzantine science and technology
[edit]See also
[edit]- Outline of classical studies
- Agnes of France, Byzantine Empress
- Albanian Greek Catholic Church
- Alexander (Byzantine emperor)
- Argyros (Byzantine family)
- Bandon (Byzantine Empire)
- Book of Job in Byzantine illuminated manuscripts
- Bristol Byzantine
- Byzantine & Christian Museum
- Byzantine Catholic World
- Byzantine Chain
- Byzantine Church, Lin
- Byzantine Discalced Carmelites
- Byzantine Fresco Chapel
- Byzantine Institute of America
- Byzantine Master of the Crucifix of Pisa
- Byzantine Museum of Antivouniotissa
- Byzantine Museum of Ioannina
- Byzantine Museum of Kastoria
- Byzantine Revival architecture
- Byzantine Rite Christianity in Canada
- Byzantine Rite Lutheranism
- Byzantine and Modern Greek Studies
- Byzantine and Post-Byzantine Collection of Chania
- Byzantine commonwealth
- Byzantine fault tolerance
- Byzantine heraldry
- Byzantine lyra
- Byzantine text-type
- Cathedral of St. Mary Byzantine Catholic Church
- Chios Byzantine Museum
- Constantine III (Byzantine emperor)
- Cours (Byzantine general)
- Early Byzantine mosaics in the Middle East
- Eastern (Byzantine) Catholic Martyrology for February
- Eastern (Byzantine) Catholic Martyrology for January
- Georgian Byzantine-Rite Catholics
- Greek Byzantine Catholic Church
- Holy Ghost Byzantine Catholic Church (Pittsburgh)
- Immortals (Byzantine)
- Index of Byzantine Empire-related articles
- Irene Palaiologina (Byzantine empress)
- John the Deacon (Byzantine writer)
- Julian Byzantine
- Kephale (Byzantine Empire)
- Kleisoura (Byzantine district)
- Komnenian Byzantine army
- List of Byzantine foreign treaties
- List of Byzantine monuments in Istanbul
- List of Byzantine revolts and civil wars
- List of Byzantine scholars
- List of Byzantine usurpers
- List of Roman and Byzantine Empresses
- List of exiled and pretending Byzantine Empresses
- List of leaders during the Byzantine Papacy
- Museum of Ancient Greek, Byzantine and Post-Byzantine Musical Instruments
- Museum of Byzantine Culture
- Neo-Byzantine architecture in the Russian Empire
- Norman-Arab-Byzantine culture
- Palaiologan Byzantine army
- Pannonia, Byzantine Empire
- Papias (Byzantine office)
- Phokas (Byzantine family)
- Political mutilation in Byzantine culture
- Prosopography of the Byzantine World
- Quantum Byzantine agreement
- Raoul (Byzantine family)
- Saint Anne Catholic Church of the Byzantine Rite
- Serbo-Byzantine architecture
- St. John Chrysostom Byzantine Catholic Church (Pittsburgh)
- St. John the Baptist Byzantine Catholic Cathedral (Pittsburgh)
- St. John the Baptist Byzantine Catholic Cemetery
- St. Michael Byzantine Catholic Church Toledo
- St. Nicholas Byzantine Catholic Church
References
[edit]- ^ Kazhdan & Epstein 1985, p. 1.
- ^ Millar 2006, pp. 2, 15; James 2010, p. 5; Freeman 1999, pp. 431, 435–437, 459–462; Baynes & Moss 1948, p. xx; Ostrogorsky 1969, p. 27; Kaldellis 2007, pp. 2–3; Kazhdan & Constable 1982, p. 12; Norwich 1998, p. 383.
Sources
[edit]- Baynes, Norman Hepburn; Moss, Henry St. Lawrence Beaufort, eds. (1948). Byzantium: An Introduction to East Roman Civilization. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- Freeman, Charles (1999). The Greek Achievement – The Foundation of the Western World. New York: Penguin. ISBN 0-670-88515-0.
- James, Liz (2010). A Companion to Byzantium. Chichester: John Wiley. ISBN 978-1-4051-2654-0.
- Kaldellis, Anthony (2007). Hellenism in Byzantium: The Transformations of Greek Identity and the Reception of the Classical Tradition. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-87688-9.
- Kazhdan, Alexander Petrovich; Constable, Giles (1982). People and Power in Byzantium: An Introduction to Modern Byzantine Studies. Washington, DC: Dumbarton Oaks. ISBN 0-88402-103-3.
- Kazhdan, A. P.; Epstein, Ann Wharton (1985). Change in Byzantine Culture in the Eleventh and Twelfth Centuries. Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-05129-7.
- Millar, Fergus (2006). A Greek Roman Empire: Power and Belief under Theodosius II (408–450). Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-24703-5.
- Norwich, John Julius (1998). A Short History of Byzantium. Ringwood, Vic.: Penguin. ISBN 978-0-14-025960-5.
- Ostrogorsky, George (1969). History of the Byzantine State. New Brunswick: Rutgers University Press. ISBN 978-0-8135-1198-6.
External links
[edit]- Byzantine studies, resources and bibliography
- Adena, L. "The Enduring Legacy of Byzantium Archived 2020-04-13 at the Wayback Machine", Clio History Journal, 2008.
- Ciesniewski, C. "The Byzantine Achievement", Clio History Journal, 2006.
- Fox, Clinton R. What, If Anything, Is a Byzantine? (Online Encyclopedia of Roman Emperors)
- The Cambridge Medieval History (IV) The Eastern Roman Empire (717–1453)[usurped].
- Byzantine studies homepage at Dumbarton Oaks. Includes links to numerous electronic texts.
- Byzantium: Byzantine studies on the Internet. Links to various online resources.
- Translations from Byzantine Sources: The Imperial Centuries, c. 700–1204. Online sourcebook.
- De Re Militari. Resources for medieval history, including numerous translated sources on the Byzantine wars.
- Medieval Sourcebook: Byzantium. Numerous primary sources on Byzantine history.
- Bibliography on Byzantine Material Culture and Daily Life. Hosted by the University of Vienna; in English.
- Constantinople Home Page. Links to texts, images and videos on Byzantium.
- Byzantium in Crimea: Political History, Art and Culture.
- Institute for Byzantine Studies of the Austrian Academy of Sciences (with further resources and a repository with papers on various aspects of the Byzantine Empire)
- Miscellaneous
- Byzantine Empire on In Our Time at the BBC
- De Imperatoribus Romanis. Scholarly biographies of many Byzantine emperors.
- The Fall of the Empire. Byzantine Lesson (2007). (Russian: Гибель империи. Византийский урок) A film explaining the political and economical reasons for the fall of the Empire, filmed by the Russian Orthodox Church.
- 12 Byzantine Rulers by Lars Brownworth of The Stony Brook School; audio lectures. NYTimes review.
- 18 centuries of Roman Empire by Howard Wiseman (Maps of the Roman/Byzantine Empire throughout its lifetime)
 KSF
KSF