Pannonia Inferior
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 8 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 8 min
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2008) |
| Pannonia Inferior | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Province of the Roman Empire | |||||||||||
| 103–3rd century | |||||||||||
 Pannonia Inferior (125 AD) | |||||||||||
| Capital | Aquincum and Sirmium[1] | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Established | 103 | ||||||||||
• Reorganized | 3rd century | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | Bosnia and Herzegovina Croatia Hungary Serbia | ||||||||||
Pannonia Inferior, lit. Lower Pannonia, was a province of the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sirmium. It was one of the border provinces on the Danube. It was formed in the year 103 AD by Emperor Trajan who divided the former province of Pannonia into two parts: Pannonia Superior and Pannonia Inferior. The province included parts of present-day states of Hungary, Serbia, Croatia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina. The province was bordered to the east (across the Danube) by a Sarmatian tribe—the Iazyges. Later, the Vandals appeared to the north-east.
Settlements
[edit]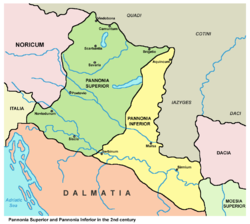
Major settlements in Pannonia Inferior included:
- Sirmium (Sremska Mitrovica) which several times served as an imperial residence for several emperors.
- Aquincum (Buda), the provincial capital.
- Cuccium (Ilok)
- Cibalae (Vinkovci)
- Mursa (Osijek)
- Certissa (Đakovo)
- Marsonia (Slavonski Brod)
- Sopianae (Pécs)
Aftermath and legacy
[edit]The province was yet again split during the reign of the tetrarchs into two more provinces, Pannonia Valeria in the north, with the new provincial capital at Sopianae, and Pannonia Secunda in the south with Sirmium as the provincial capital. During the Frankish period, in the 9th century, the term Lower Pannonia was used to designate eastern and southern regions of Pannonia, including the Slavic Principality of Lower Pannonia, particularly Posavina.
List of Roman governors
[edit]- Publius Aelius Hadrianus 106-108[2]
- Titus Julius Maximus Manlianus 108-110/111
- Publius Afranius Flavianus 111/112-114/115
- Quintus Marcius Turbo 117/118-118/119
- Lucius Cornelius Latinianus 119-121?[3]
- Lucius Attius Macro 130/131-133/134
- Nonius Mucianus 135[4]
- Lucius Aelius Caesar 136-137
- Claudius Maximus 137-c. 141[5]
- Marcus Pontius Laelianus Larcius Sabinus c. 141-c. 144
- Quintus Fuficius Cornutus c. 144-147
- Marcus Cominius Secundus 147-c. 150
- Marcus Nonius Macrinus c. 150-c. 153
- Marcus Iallius Bassus Fabius Valerianus c. 156-c. 159
- Gaius Julius Geminius Capellianus c. 159-c. 161
- Tiberius Haterius Saturninus c. 161-164
- Tiberius Claudius Pompeianus c. 167
- Lucius Ulpius Marcellus before 173
- Gaius Vettius Sabinianus Julius Hospes c. 173-175
- Sextus Quintilius Condianus c. 175-c. 179
- Lucius Septimius Flaccus c. 179-c. 183
- Lucius Cornelius Felix Plotianus c. 183-185[6]
- Gaius Pomponius Bassus Terentianus 192[7]
- Gaius Valerius Pudens c. 192-c. 194
- Tiberius Claudius Claudianus c. 197/198
- Lucius Baebius Caecilianus 199-202
- Lucius Cassius Marcellinus between 202 and 204
- Gaius Julius Septimius Castinus c. 211/212
- Gaius Octavius Appius Suetonius Sabinus c. 215/216[8]
- Lucius Alfenus Avitianus between 218 and 222
- Marcius Claudius Agrippa c. 217
- Triccianus 217-218[9]
- Pontius Proculus Pontianus c. 219-222[9]
- Flavius Aelianus c. 228
- Iasdius Domitianus between 222 and 235[10]
- Flavius Marcianus between 230 and 235
- Lucius Ulpius Marcellus c.262-c.264[11]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ The Routledge Handbook of Archaeological Human Remains and Legislation, Taylor & Francis, page 381.
- ^ Unless otherwise noted, governors from 106 to 137 are taken from Werner Eck, "Jahres- und Provinzialfasten der senatorischen Statthalter von 69/70 bis 138/139", Chiron, 12 (1982), pp. 281-362; 13 (1983), pp. 147-237
- ^ Ronald Syme's dates ("Governors of Pannonia Inferior", Historia: Zeitschrift für Alte Geschichte, 14 (1965), p. 344); Eck less precisely states he was governor during the reign of Hadrian.
- ^ Margaret Roxan, "Two Complete Diplomas of Pannonia Inferior: 19 May 135 and 7 August 143", Zeitschrift für Papyrologie und Epigraphik, 127 (1999), pp. 249-273
- ^ Unless otherwise noted, governors from 149 to 182 are taken from Géza Alföldy, Konsulat und Senatorenstand unter der Antoninen (Bonn: Rudolf Habelt Verlag, 1977), pp. 250-252
- ^ Unless otherwise noted, governors from 183 to 212 are taken from Paul M. M. Leunissen, Konsuln und Konsulare in der Zeit von Commodus bis Severus Alexander (Amsterdam: J.C. Gieben, 1989), pp. 277-279
- ^ Attested in office 11 August 192 by RMD V.446 and V.447
- ^ Unless otherwise noted, governors from 215 to 235 are taken from Leunissen, Konsuln und Konsulare, pp. 256f
- ^ a b Davenport, Caillan (2012). "The Provincial Appointments of the Emperor Macrinus". Antichthon. 46: 184–203. doi:10.1017/S0066477400000198. ISSN 0066-4774. S2CID 145052620.
- ^ CIL VI, 41225
- ^ CIL III, 10285
Sources
[edit]- Mirković, Miroslava B. (2017). Sirmium: Its History from the First Century AD to 582 AD. Novi Sad: Center for Historical Research.
- Mócsy, András (2014) [1974]. Pannonia and Upper Moesia: A History of the Middle Danube Provinces of the Roman Empire. New York: Routledge. ISBN 9781317754251.
- Syme, Ronald (1965). "Governors of Pannonia Inferior". Historia: Zeitschrift für Alte Geschichte. 14 (3): 342–361. ISSN 0018-2311. JSTOR 4434890.
 KSF
KSF