Phloroglucinol carboxylic acid
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 5 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 5 min
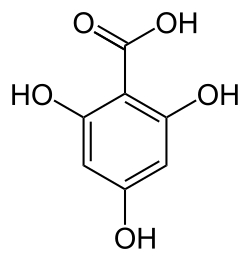 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,4,6-Trihydroxybenzoic acid | |
| Other names
PGCA
Phloroglucinic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.334 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H6O5 | |
| Molar mass | 170.11954 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Phloroglucinol carboxylic acid, also called ‘Phloroglucinic acid’ or simply ‘PGCA’, is a trihydroxybenzoic acid, a type of phenolic acid. It can be encountered in nature were it is produced by plants or microorganisms. Structurally, the molecule can be perceived as Gallic acid in which the 2 hydroxy groups at positions 3 and 5 respectively on the benzene ring backbone have been moved “up” to positions 2 and 6, closely neighboring the carboxylic acid functional group. Salts and esters of PGCA (e.g. potassium salt or methyl ester) are known as Phloroglucinates.
It is produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens.[1] It is a catechin degradation product excreted by the bacterium Acinetobacter calcoaceticus, a species of bacteria part of the human body normal flora, grown on catechin as sole source of carbon.[2] It is also found in wine.[3]
References
[edit]- ^ Biosynthesis of Phloroglucinol. Jihane Achkar, Mo Xian, Huimin Zhao and J. W. Frost, J. AM. CHEM. SOC., 2005, volume 127, pages 5332-5333, doi:10.1021/ja042340g
- ^ M. Arunachalam, N. Mohan, R. Sugadev, P. Chellappan and A. Mahadevan: Degradation of (+)-catechin by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus MTC 127, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA), Volume 1621, Issue 3, 11 June 2003, pages 261–265, doi:10.1016/S0304-4165(03)00077-1.
- ^ C. García Barroso, R. Cela Torrijos and J. A. Pérez-Bustamante: HPLC separation of benzoic and hydroxycinnamic acids in wines, Chromatographia, Volume 17, Number 5, pages 249–252, doi:10.1007/BF02263033.
 KSF
KSF