Provincial Assembly of Sindh
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 19 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 19 min
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2023) |
Provincial Assembly of Sindh | |
|---|---|
| 16th Provincial Assembly of Sindh | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Leadership | |
Speaker | |
Deputy Speaker | |
Leader of Opposition | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 168 |
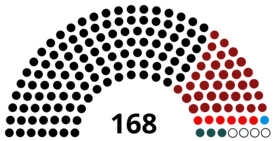 | |
Political groups | Government (118)
Opposition (46) |
| Elections | |
| Mixed member majoritarian: | |
Last election | 8 February 2024 |
Next election | 2029 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Provincial Assembly House of Sindh, Karachi | |
| Website | |
| Official website | |
| Constitution | |
| Constitution of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan | |
 |
|---|
|
|
The Provincial Assembly of Sindh[a] is a unicameral legislature of elected representatives of the Pakistani province of Sindh, and is located in Karachi, its provincial capital. It was established under Article 106 of the Constitution of Pakistan having a total of 168 seats, with 130 general seats, 29 seats reserved for women and 9 seats reserved for non-Muslims.
There was previously a Sind Legislative Assembly in the Sind Province of British India and in the early years of the state of Pakistan.
History
[edit]A large part of Sindh was captured by the British commander General Sir Charles Napier status as a State and became a Commissionerate of India's Bombay Presidency, being controlled by a Commissioner.[citation needed]
In 1890, after the Minto reforms, Sindh gained representation for the first time in the Bombay Legislative Assembly, with four members representing it. From that time, a movement to separate Sindh from the Bombay Presidency was established, and in 1935, after a long struggle, a new chapter in the history of Sindh opened. Under Section 40(3) of Government of India Act 1935, Sindh was separated from the Bombay presidency with effect from 1 April 1936. With the introduction by the same Act of Provincial Autonomy, the newly created Province of Sindh secured a Legislative Assembly of its own, consisting of sixty members, who were elected on the basis of communal representation and weight age to the minority community.
Sir Lancelot Graham was appointed as the first Governor of Sindh by the British Government on 1 April 1936. Until 1937, he was also the head of an Executive Council of 25 members, which administered the affairs of Sindh and included two advisers from the Council of Bombay.
Assembly building
[edit]The two-story building of the Sindh Assembly consists of the camp office of the Chief Minister of Sindh, offices of the Speaker, Deputy Speaker, ministers, Leader of the Opposition, Secretariat, Law Department of the Government of Sindh, and Library.
The foundation stone of the building was laid by Sir Lancelot Graham, the Governor of Sindh, on 11 March 1940. The construction of the building – declared open by Sir Hugh Dow, the Governor of Sindh, on 4 March 1942 – was completed within a span of two years.
In 1971, after a lapse of about 24 years, it was again declared as the Sindh Assembly building. Since then it has been used as such. Presently, the central portion of the building, the Assembly Hall, seats a capacity of 168 Legislators.[2]
List of Assemblies
[edit]| Order | Terms | |
|---|---|---|
| First Assembly | 27 April 1937 to 1945 | |
| Second Assembly | 12 March 1946 to 1946 | |
| Third Assembly | 17 February 1947 to 1951 | |
| Fourth Assembly | 12 September 1953 to 1955 | |
| Fifth Assembly | 1972 to 1977 | |
| Sixth Assembly | 30 March 1977 to 5 July 1977 | |
| Seventh Assembly | 28 February 1985 to 30 May 1988 | |
| Eighth Assembly | 19 November 1988 to 6 August 1990 | |
| Ninth Assembly | 27 October 1990 to 19 July 1993 | |
| Tenth Assembly | 9 October 1993 to 5 November 1996 | |
| Eleventh Assembly | 3 February 1997 to 12 October 1999 | |
| Twelfth Assembly | 10 October 2002 to 15 November 2007 | |
| Thirteenth Assembly | 18 February 2008 to 2013 | |
| Fourteenth Assembly | 2013-2018 | |
| Fifteenth Assembly | 13 August 2018 to 11 August 2023 | |
| Sixteenth Assembly | 2024–present |
Chief Ministers of Sindh
[edit]The Leader of the House for the assembly is known as the Chief Minister of Sindh, the current Chief Minister of Sindh is Murad Ali Shah of the Pakistan People’s Party.
Speakers of the Sindh Assembly
[edit]| Names | Successive term of each |
|---|---|
| Diwan Bhoj Singh (Sukkur) | 28 April 1937 to 15 February 1938 |
| Syed Miran Muhammed Shah (Hyderabad) | 26 February 1938 to 3 May 1948 |
| Agha Badruddin Durrani (Sukkur) | 8 March 1949 to 29 December 1951 |
| Mir Ghulam Ali Talpur (senior) (Hyderabad) | 14 September 1953 to 21 March 1955 |
| Ghulam Rasool Keehar (Larkana) | 2 May 1972 to 3 March 1977 |
| Agha Sadruddin Durrani (Sukkur) | 13 March 1977 to 4 July 1977 |
| Abdullah Hussain Haroon (Karachi) | 6 April 1985 to 13 March 1986 |
| Syed Muzaffar Hussain Shah (Tharparkar) | 6 April 1986 to 1 December 1988 |
| Syed Abdullah Shah (Dadu) | 1 December 1988 to 5 November 1990 |
| Abdul Razique Khan (Karachi) | 5 November 1990 to 19 October 1993 |
| Ghous Bux Maher (Shikarpur) | 19 October 1993 to 22 February 1997 |
| Nawaz Mirza Advocate (Hyderabad) | 22 February 1997 to 26 October 1998 |
| Syed Muzaffar Hussain Shah (Mirpurkhas) | 14 December 2002 to January 2008 |
| Nisar Ahmed Khuro (Larkana) | 18 February 2008 to 30 May 2013 |
| Agha Siraj Durrani (Karachi) | 30 May 2013 to 25 Feb 2024 |
| Awais Qadir Shah (Sukkur)[3] | 25 Feb 2024 to current |
Qualification of members
[edit]According to Article 113 of the Constitution, the qualifications for membership in the National Assembly set forth in Article 62 of the Constitution also apply for membership to the Provincial Assembly. Thus, a member of the Provincial Assembly:
- must be a citizen of Sindh;
- must be at least twenty-five years of age and must be enrolled as a voter in any electoral roll in–
- any part of Sindh, for election to a general seat or a seat reserved for non-Muslims; and
- any area in Sindh from which the member seeks membership for election to a seat reserved for women.
- must be of good character and not commonly known as one who violates Islamic injunctions;
- must have adequate knowledge of Islamic teachings and practices obligatory duties prescribed by Islam as well as abstains from major sins;
- must be sagacious, righteous, non-profligate, and honest;
- must have never been convicted for a crime involving moral turpitude or for giving false evidence;
- must have never, after the establishment of Pakistan, worked against the integrity of the country or opposed the ideology of Pakistan.
The disqualifications specified in paragraphs 3 and 4 do not apply to a person who is a non-Muslim, but such a person must have a good moral reputation and possess other qualifications prescribed by an act of Parliament.
Main article: Constitution of Pakistan
[edit]Article 106 of the Constitution provides that each Provincial Assembly shall consist of general seats and seats reserved only for women and non-Muslims. The same article specifies that the Provincial Assembly of Sindh will have a total of 168 seats: 130 general seats, 29 reserved for women, and nine reserved for non-Muslims.
Disqualification of members
[edit]The criteria for disqualification of members of a Provincial Assembly is established by Articles 63, 63A, 113 and 127. A person shall be disqualified from being elected or chosen as, and from being, a member of the Provincial Assembly if the member:
- is of unsound mind and has been so declared by a competent court; or
- is an undischarged insolvent; or
- ceases to be a citizen of Sindh, Pakistan or acquires the citizenship of a foreign State; or
- holds an office of profit in the service of Pakistan other than an office declared by law not to disqualify its holder; or
- is in the service of any statutory body of any body which is owned or controlled by the Government or in which the Government has a controlling share or interest; or
- is propagating any opinion, or acting in any manner, prejudicial to the Ideology of Pakistan, or the sovereignty, integrity or security of Pakistan, or morality, or the maintenance of public order, or the integrity or independence of the judiciary of Pakistan, or which defames or brings into ridicule the judiciary or the Armed Forces of Pakistan; or
- has been convicted by a court of competent jurisdiction on a charge of corrupt practice, moral turpitude or misuse of power or authority under any law for the time being in force; or
- he has been dismissed from the service of Pakistan or service of a corporation or office set up or controlled by the Provincial Government or a Local Government on the grounds of misconduct or moral turpitude; or
- has been removed or compulsorily retired from the service of Pakistan or service of a corporation or office set up or controlled by the Provincial Government or a Local Government on the grounds of misconduct or moral turpitude; or
- has been in the service of Pakistan or of any statutory body or any body which is owned or controlled by the Government or in which the Government has a controlling share or interest, unless a period of two years has elapsed since he ceased to be in such service; or
- is found guilty of a corrupt or illegal practice under any law for the time being in force, unless a period of five years has elapsed from the date on which that order takes effect; or
- has been convicted under section 7 of the Political Parties Act, 1962 (III of 1962), unless a period of five years has elapsed from the date of such conviction; or
- whether by himself or by any person or body of persons in trust for him or for his benefit or on his account or as a member of a Hindu undivided family, has any share or interest in a contract, not being a contract between a cooperative society and Government, for the supply of goods to, or for the execution of any contract or for the performance of any service undertaken by, Government.
Article 63A, which deals with disqualification on grounds of defection, was added to the Constitution in 1997. A member of a Parliamentary Party composed of a single political party defects if the member:
- resigns from membership of the political party or joins another Parliamentary Party; or
- votes or abstains from voting in the Provincial Assembly contrary to any direction issued by the Parliamentary Party to which the member belongs, in relations to
- election of the Chief Minister; or
- a vote of confidence or a vote of no-confidence; or
- a Money Bill.
Privileges of members
[edit]Article 66 read with Article 127 confers freedom of speech on the members of the Provincial Assembly. No member is liable to any proceedings in any court of law in respect of anything said or any vote given by him in Assembly. Similarly, no member is liable in respect of any publication which is published under the authority of Provincial Assembly.
However, Article 114 of the Constitution curtails this privilege and prohibits members from discussing the conduct of judges of High Court and Supreme Court in the discharge of their duties.
First day proceedings in the Provincial Assembly
[edit](a) Oath of Members. – After general elections, elected members in the first meeting take oath in the form set out in Third Schedule of the Constitution. Article 65 read with Article 127 states "A person elected to a House shall not sit or vote until he has made before the House oath in the form set out in the Third Schedule". Those members who have not taken oath in the first meeting take oath when they attend a meeting for the first time. The first meeting is presided by the outgoing Speaker. Article 53 (8) read with Article 127 says "the Speaker shall continue in his office till the person elected to fill the office by next Assembly enters upon his office." (b) Election and oath of Speaker and Deputy Speaker. – In addition to oath taking by the members, Provincial Assembly according to Article 108 to the exclusion of any other business, elect from amongst its members a Speaker and a Deputy Speaker. When office of Speaker or Deputy Speaker becomes vacant, in any way, the Assembly elects another member as Speaker or Deputy Speaker.
The elected Speaker and Deputy Speaker according to clause 2 of Article 53 read with Article 127 take oath before the House in the form set out in the Third Schedule.
Summoning and prorogation of Provincial Assemblies
[edit]Article 109 authorizes the Governor of the Province to summon Provincial Assembly to meet at such time and place as he thinks fit. Where the Governor summons Assembly he is authorized to prorogue it too. In addition, the Speaker, on a requisition signed by not less than one-fourth of the total membership of the Provincial Assembly, can summon it, at such time and place as he thinks fit, within fourteen days of the receipt of the requisition. Article 54(3) read with Article 127 also empowers the Speaker to prorogue the session where he summons it.
Number of sessions and days during a year
[edit]Article 54 (2) and (3) read with article 127 say there are at least three sessions of Provincial Assembly every year, with not more than 120 days intervening between the last sitting of the Assembly in one session and the date appointed for its first sitting in the next session. While clause 'g' of Article 127 read with Proviso to Article 54 provides that Provincial Assembly shall meet for not less than 70 working days in each year.
Duration of Provincial Assembly
[edit]The term of Provincial Assembly in Pakistan according to Article 107 is five years unless it is sooner dissolved, from the day of its first meeting and stands dissolved at the expiration of its terms.
Other methods of dissolution of Provincial Assembly
[edit](a) Dissolution of Provincial Assembly on the advice by the Chief Minister. – Under Article 112, clause 1, the Governor of a Province is empowered to dissolve Provincial Assembly if so advised by the Chief Minister. Where the Chief Minister so advises, the Provincial Assembly stands dissolved at the expiration of 48 hours. (b) Dissolution of Provincial Assembly by the Governor on the approval by the President. – Clause 2 of the same Article again empowers the Governor to dissolve Provincial Assembly subject to the approval of the President, where he is of the opinion, that after having been passed a vote of no confidence against the Chief Minister, there is no other member of the Provincial Assembly to command the confidence of the majority of the members of the Provincial Assembly, in a session of the Provincial Assembly summoned for the purpose.
Executive Authority of a province
[edit]Executive Authority is exercised by the Governor and under Article 105, he shall act in accordance with advice of the cabinet or the Chief Minister.
Appointment and ascertainment of Chief Minister
[edit]According to clause 2-A of Article 130, the Governor of a Province invites the member of the Provincial Assembly to be the Chief Minister who commands the confidence of the majority of the members of the Provincial Assembly as ascertained in the session of the Assembly summoned for the purpose in accordance with the provisions of the constitution.
Powers and functions of Provincial Assembly
[edit]There are three major functions or powers of a Provincial Assembly:
- To make laws (Article 141 and 142 of the Constitution of Pakistan)
- To manage the purse of the province (Article 123 (3))
- To keep checks on the policies and practices of the Government (Article 130)
Limitations
[edit]One of the major functions of the Provincial Assembly is to make laws as provided in Article 141 and 142 of the Constitution for conferring of functions upon officers or authorities subordinate to the Provincial Governments, Constitutionally. This function is subject to some limitations.
- Under Article 142, a Provincial Assembly cannot legislate when an emergency is declared in the country.
- A Provincial Assembly cannot make law which is against fundamental rights.
- Principles of policy or rule of law should be the base of each law.
- A law cannot be enacted if it is not in conformity with the injunctions of Islam.
- Under Article 142, the Provincial Assembly cannot legislate on matters which fall in the Federal Legislative List.
Residuary List
[edit]The Provincial Assembly has exclusive powers to make law with respect to any matter not enumerated in the Federal Legislative List. Residuary matters are exclusively within Provincial autonomy. From the above, it cannot be extracted that the Province is subordinate to the Federation or Federation is subordinate to Province. In fact, legislative powers are distributed between Federation and Provinces via Article 142. And one institution cannot take over powers of other institution. However, this provincial law making power comes to an end and shifts to the Federation during emergency when declared vide Articles 232, 233 or 234.
Manager of purse of Sindh
[edit]The second important function of the Provincial Assembly of Sindh under Article 123 (3) is that it acts as a manager or custodian of the purse of Sindh.
Provincial Consolidated Fund
[edit]No expenditure from the Provincial Consolidated Fund is deemed to be duly authorised unless it is specified in the schedule so authenticated and is laid before the Provincial Assembly. Provincial Assembly exercises checks over executive through control over the Finance. Article 119 provides custody and withdrawal of money from Provincial Consolidated Fund, (defined in Article 118) and public accounts of a Province, unless it is regulated by the Act of the Provincial Assembly.
Annual and supplementary Budget statement
[edit]Provisions given under Article 120 dealing with annual budget statement and Article 124 dealing with supplementary budget or excess grant become effective, when it is approved by the Provincial Assembly.
Approval of budgets
[edit]Article 122(2) and Article 124 authorise Provincial Assembly to approve or refuse any demand and reduce the amount specified in the demand. Once budget is approved, the Government has no right to deviate from these sanctions. For excess expenditure, Government has to seek regularization from the Assembly. Similarly under Article 88 read with Article 127, accounts and audit reports of the Government are further scrutinized by the public accounts Committee of the Assembly.
To keep checks on the policies and practices of the Government
[edit]The significance of Provincial Assembly is that it is a representative institution and keeps checks upon policies, practices and performance of the Government. Article 130 (4) says that the Cabinet shall be collectively responsible to the Provincial Assembly.
Devices of accountability
[edit]Issues relating to Public interest are raised by the Members for discussion in the House in the form of questions, adjournment motions, call attention notices, general discussion, resolutions and various Reports.
The Members make the Executive accountable to the legislature through these devices according to the Rules of Procedure of the Provincial Assembly of Sindh, 1997.
Members Support Programme
[edit]This programme is meant to serve Members of the Provincial Assembly in different areas. They are provided legislative help in drafting private members bills. They are provided useful and informative books. An Internet facility is also available to them, and through Internet research they can polish their ideas.
To provide these facilities to the Members, in 1997 the Research and Reference Division was formed. It was established to provide information to the Members when needed, and to collect up-to-date information from the resources available. The Library and Computer Sections were included in this division. It was also meant to provide help to the representatives in legislative procedures, such as the drafting of a bill. Prior to the establishment of the Research and Reference Wing, this service was performed by the Legislation Branch. Salman
Information Technology and Legislative Section
[edit]The primary function of Library Section is to provide data to the Members and to the Research Section. Information such as the Assembly's agenda, date of next sitting, schedule of committee meetings and information about Members is available due to installation of the latest PBX. The Assembly Secretariat has stored vital information in the computer and it is accessible from anywhere around the clock.
Moreover, Research and Reference Division has designed a web page to provide information to the Members about the Assembly Secretariat and proceedings of the Assembly including its schedule and agenda, and a summary of its proceedings. This web page also includes the procedural rules for the Provincial Assembly of Sindh and some other important laws of the country.
Explanatory notes
[edit]See also
[edit]Explanatory notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Welcome to the Website of Provincial Assembly of Sindh". Provincial Assembly of Sindh.
- ^ "Provincial Assembly of Sindh - History".
- ^ "PPP's Owais Qadir Shah Elected Sindh Assembly Speaker | Dawn News English". DAWN.COM. 25 February 2024. Retrieved 26 February 2024.
External links
[edit]- Provincial Assembly of Sindh official website of Sind Assembly
- Sindh Assembly restores Local Government Act of 1979
 KSF
KSF

