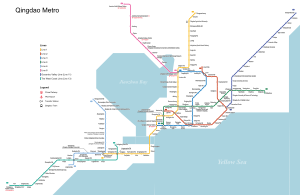
Qingdao Metro
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 15 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 15 min
| Qingdao Metro | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
 | |||
| Overview | |||
| Owner | Qingdao Metro Corporation | ||
| Locale | Qingdao, Shandong, China | ||
| Transit type | Rapid transit | ||
| Number of lines | 8 (operating) | ||
| Number of stations | 189 (operating) | ||
| Daily ridership | 2.2443 million (highest record on 1 May 2023) | ||
| Annual ridership | 410.955 million (2023)[1] | ||
| Website | www | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | December 16, 2015 | ||
| Operator(s) | Qingdao Metro Corporation | ||
| Number of vehicles | >86 | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 342.3 km (212.7 mi) (operating) | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||
| |||
| Qingdao Metro | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 青岛地铁 | ||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 青島地鐵 | ||||||
| |||||||
Qingdao Metro (Chinese: 青岛地铁; pinyin: Qīngdǎo dìtiě) is a rapid transit system in Qingdao, Shandong province, China. The first line, Line 3 (north section) began operation on December 16, 2015.[2]
Visual Recognition/Logo
[edit]The text part of the logo is the company's abbreviation Chinese “ 青岛地铁 ” and English capital “QINGDAO METRO”. The graphical part is based on the English word initials “Q” (as for Qingdao) as the main element. The overall shape is round, and the interior is shown in the subway tunnel entrance. The waves below highlight the characteristics of the coastal city. The overall green application means that the metro is a green and environmentally friendly vehicle.
Lines in operation
[edit]| Line | Terminals (District) |
Commencement | Newest Extension |
Length km |
Stations | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Wangjiagang (Huangdao) |
Dongguozhuang (Chengyang) |
2020 | 2021 | 59.82 | 41 |
| 2 | Taishan Road (Shibei) |
Licun Park (Licang) |
2017 | 2024 | 28.227 | 25 |
| 3 | Qingdao Railway Station (Shinan) |
Qingdao North Railway Station (Licang) |
2015 | 2016 | 24.472 | 22 |
| 4 | Hall of the People (Shinan) |
Dahedong (Laoshan) |
2022 | — | 30.71 | 25 |
| 6 | Hengyunshan Road (Huangdao) |
Lingshan Bay (Huangdao) |
2024 | — | 30.76 | 21 |
| 8 | Qingdao North Railway Station (Licang) |
Jiaozhou North Railway Station (Jiaozhou) |
2020 | — | 48.3 | 11 |
| Oceantec Valley | Miaoling Road (Laoshan) |
Qiangu Mountain (Jimo) |
2018 | — | 54.371 | 21 |
| West Coast | Jialingjiang West Road (Huangdao) |
Dongjiakou Railway Station (Huangdao) |
2018 | 2023 | 69.6 | 23 |
| Total | 346.3 | 189 | ||||
Line 1
[edit]
The northern section between Qingdao North Railway Station and Dongguozhuang Station was opened on 24 December 2020. The southern section between Qingdao North Railway Station and Wangjiagang Station was opened on 30 December 2021.[3] The north section is 22 km (13.7 mi) and the south section is 38 km (23.6 mi), the entire of Line 1 is 60 km (37.3 mi) in length. Line 1's color is yellow.[4]
Line 2
[edit]
Construction on Line 2 began in 2012, and the completed line will comprise 22 stations, with a total length of 24.4 km (15.2 mi). Line 2 began passenger service on December 10, 2017, between Zhiquan Road station and Licun Park station.[5][6][7] The western section from Zhiquan Road station to Taishan Road station opened on December 16, 2019. Line 2's color is red.[8]
Line 3
[edit]
The construction of the first line, Line 3, began on November 30, 2009. With 13 billion yuan ($1.9 billion) of funding, the line comprises 22 stations, with a total length of 24.5 km (15.2 mi). The northern half of Line 3 began trial passenger operation on December 16, 2015, and the southern half opened a year later, on December 18, 2016. Line 3's color is blue.[6][9]
Line 4
[edit]
Line 4 between Hall of the People station and Dahedong station operation on December 26, 2022, with 25 stations and 30.7 km (19.1 mi) of track. Line 4's color is green.
Line 6
[edit]Construction for Line 6 Phase I started on December 16, 2019. Line 6 (Phase 1, Lingshan Bay station to Hengyunshan Rd station) is a 30.762 km (19.115 mi) line with 21 underground stations.[10][11] Phase 1 of Line 6 opened on April 26, 2024.[12] Line 6's color is light blue, and is currently the only line with driverless capacity.
Line 8
[edit]
The northern section opened in December 2020, and the southern section and the branch is currently under construction. Line 8's color is pink.
Oceantec Valley Line (Line 11)
[edit]
Phase I of Line 11 between Miaoling Road station and Qiangu Mountain station, which extends from Laoshan District to Jimo District, with 21 stations and 54.4 km (33.8 mi) of track, began operation on April 23, 2018. Line 11's (renamed the Oceantec Valley Line in 2024) color is dark blue.
West Coast Line (Line 13)
[edit]
Phase I and Phase II of Line 13 between Jinggangshan Road and Dongjiakou Railway Station started operation on December 26, 2018, with 21 stations and 66.813 km (41.516 mi) of track. Line 13's (renamed the West Coast Line in 2024) color is teal. A 2.8 km (1.7 mi) extension to the north opened in 2023.
History
[edit]Project Proposal (1935)

In 1935, Qingdao proposed an urban development plan that included the construction of "inner city high-speed transportation" systems, specifically rail transit express lines. This made Qingdao the first city in China to propose building a metro. The planners emphasized the importance of early preparation, cautioning against neglecting the project simply because the need for high-speed transportation seemed distant. The plan outlined a total of 42 kilometers of track, with underground lines in the city center and elevated lines out in the suburbs. All vehicles were to be powered by electricity to maintain a clean and hygienic city environment. However, due to the social unrest of the time, these plans remained on paper and were never realized.
First Construction Attempt (1987-2000)
In April 1987, Qingdao officially began planning and conducting feasibility studies for a rail transit network. By 1989, an initial plan for a "two lines and one loop" network, covering about 48 km, was developed. In 1990, the Qingdao Municipal Planning Commission submitted a proposal for the first phase of the Qingdao metro project to the National Planning Commission. By June 1991, the project had gained approval from the State Council, with the official project document numbered (1991).
In 1993, the Qingdao Metro Engineering Construction Office was set up, followed by the formation of the Qingdao Metro Company to oversee the metro planning and construction. In 1994, the "Qingdao Urban Comprehensive Transportation Plan" expanded the network plan to a "four lines and one loop" structure, totaling approximately 96 km. That same year, the Qingdao Metro Company was officially established, and on December 24th, construction began on a test section of the Line 1 Phase 1 project, which included "two stations and one section of track."
However, on December 28, 1995, the State Council issued a notice to halt the approval of urban metro projects, requiring that several approved projects stop signing external contracts. The National Planning Commission suspended the approval of feasibility study reports and construction starts. By 2000, the test section of the Metro was completed and inspected, and the "Qingdao Metro Phase 1 Feasibility Study Report" was submitted to the National Planning Commission for approval, but no response was received.
Substantial Construction (2008-Present)
In September 2008, the "Qingdao Urban Rapid Transit Construction Plan"—which included Lines 1, 2, and 3—was submitted to the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) for approval. In December, the Ministry of Environmental Protection issued a document (No. 85 [2009]) approving the environmental impact report, and the NDRC's expert review approved the construction plan. This marked the official start of preliminary work on the new metro test section, with its scope initially defined.
On February 20, 2009, the construction of a new metro test section, which included one station, Hexi Station (now called Metro Building) and one section of track from Hexi Station to Bao'er Station (now called Changsha Road), was confirmed. In April, a review meeting was held for the "Qingdao Urban Rapid Transit Construction Plan (2009-2016)," which resulted in the adjustment of the plan to focus only on Lines 2 and 3. The first phase of Line 2 and Line 3 were scheduled for construction in two phases from 2010 to 2016, with a total length of 54.7 km and 46 stations.
On June 26, 2009, construction of the test section began. On November 30, a groundbreaking ceremony for the Qingdao Metro was held at Metro Building Station. During the construction of Line 3, various challenges such as geological issues and relocation difficulties caused delays. The first section of Line 3 opened December 16, 2015.
Short-term plan
[edit]Phase 2 construction plan
[edit]The Phase 2 construction plan (2013-2021) of Qingdao Metro was approved by National Development and Reform Commission in April 2016.[13]
More transfer stations such as Taidong station and Liaoyang East Road station will be built, providing the citizens with more choices in transportation.
| Line | Terminals | Construction started |
Opening date |
Length in km |
New stations |
Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 (Phase 1 Adjustment) |
Sichuan Road (Qingdao Ferry Terminal) | Taishan Road | 2019 | 2024 | 3.84 | 3 | [13] |
| 8 (South section) |
May 4th Square | Qingdao North Railway Station | 2016 | 2025 | 13.1 | 7 | [13] |
Line 2 (Western Extension)
[edit]A 3.84 km (2.39 mi) extension from Taishan Road station to Sichuan Road (Qingdao Ferry Terminal) station started construction on October 26, 2019.[14]
Line 6 (Phase 2)
[edit]Line 6 Phase 2 is also under construction. The extension is fully underground, and will end at Qingdao West railway station.
Line 8 (South Section)
[edit]The remaining Line 8 southern section brings Line 8 deeper into the urban districts of Qingdao and is planned to open by the end of 2025.[15] The extension is 13.1 km (8.1 mi) long with seven stations.[16]
Phase 3 construction plan
[edit]The Phase 3 construction plan (2021-2026) of Qingdao Metro was approved by National Development and Reform Commission on August 19, 2021.[17][18]
| Line | Terminals | Construction started |
Opening date |
Length in km |
New stations |
Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 Phase 2 |
Licun Park | International Horticultural Expo Garden | 2021 | 2026 | 8.9 | 8 | [18] |
| 5 | Maidao | Yunling Road | 2021 | 2028 | 32.7 | 29 | [18] |
| 6 (Phase 2) |
Xintun Road | Qingdao West railway station | 2022[19] | 2027 | 14.7 | 10 | [18] |
| 7 (Phase 2 North) |
Dongguozhuang | Yingpu Road | 2021 | 2025 | 12.8 | 11 | [18] |
| 7 (Phase 2 South) |
Xingguo Road | Cangkou | 2021 | 2026 | 3.7 | 3 | [18] |
| 8 (Branch) |
Dajian | Jiaozhou Railway Station[20] | 2022 | 2027 | 20.4[20] | 11 | [20] |
| 9 | Haixicun | Gongdiansuo | 2022[19] | 2027 | 16.6 | 13 | [18] |
| 15 | Xiawangbu | Sifangchang | 2022 | 2028 | 30.8 | 15 | [18] |
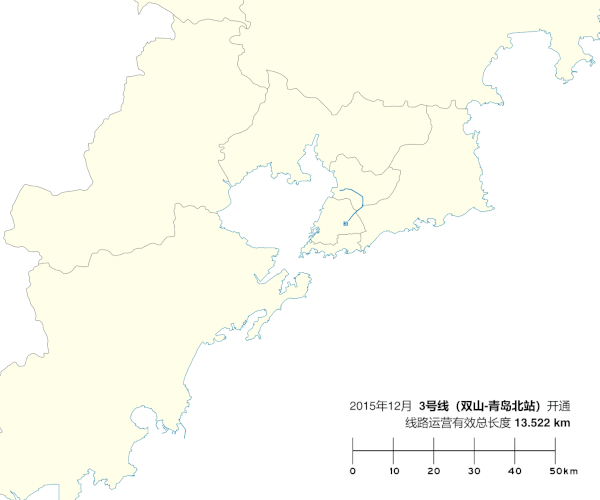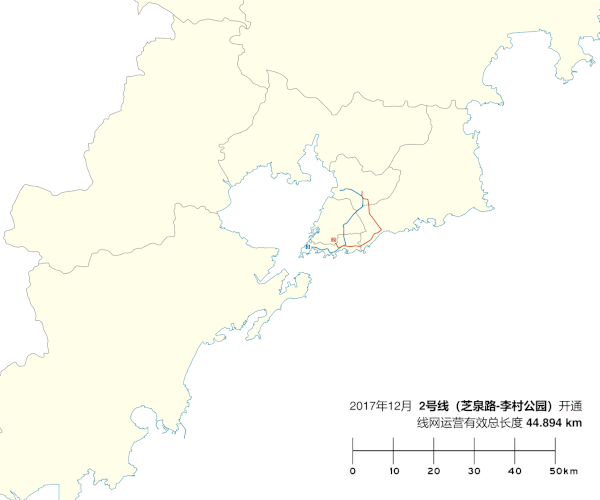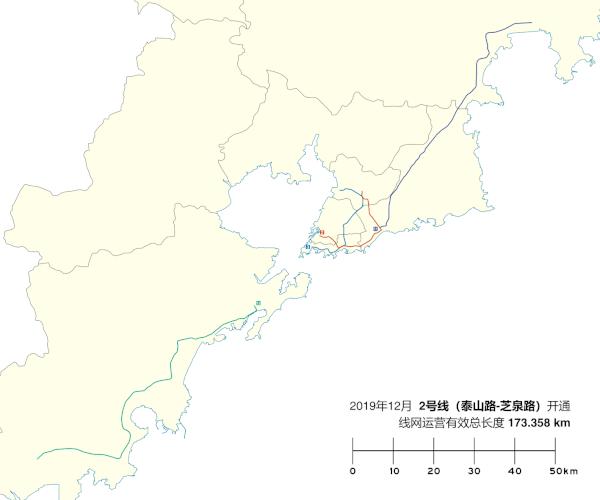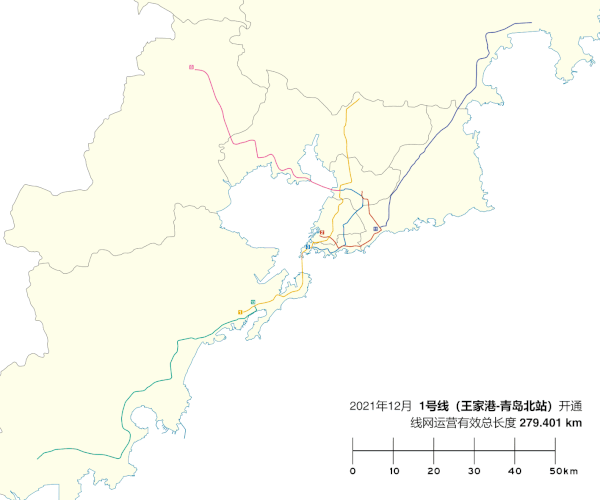
Network map
[edit]Rolling stock
[edit]All lines use standard B1 type rolling stock. Typically they operate as six-car-trains, whereas Oceantec Valley Line and West Coast Line use four-car-trains. Power is supplied via a third rail with 1500 V DC. On each line run trains with different appearance and livery.
-
Line 1
-
Line 2
-
Line 3
-
Line 8
-
Oceantec Valley Line
-
West Coast Line
-
typical interior
Ticketing
[edit]
The Automated Fare Collection (AFC) system at Qingdao Metro stations includes several key machines:
Ticket Vending Machines (TVM): Located in the non-paid area of the station, these machines allow you to buy single-ride tickets, top-up stored-value cards, or collect pre-purchased tickets. You can pay with cash, mobile payment apps like Alipay or WeChat, or scan a QR code from the Qingdao Metro app.
Ticket Checking Machines (TCM): Also in the non-paid area, these machines let you check the type, validity, balance, and recent transactions of your ticket or card.
Automatic Gates (AGM): Positioned between the non-paid and paid areas, these gates require you to swipe your card or scan a code to enter or exit. At the exit, one-way tickets are collected, and fares are deducted for stored-value card users.
Staffed Service Machines (BOM): Located at the station service center, these machines allow staff to help with issues like ticket refunds, lost or invalid cards, overcharges, and other problems that can’t be resolved by the TVMs.
Self-Service Terminals (STT): Also at the station service center, these terminals are for passengers inside the paid area to handle their own ticket-related tasks, such as card updates, balance inquiries, and resolving ticket issues.
Ticket Fares
[edit]Qingdao Metro adopts mileage-based pricing. The starting fare is RMB 2 (excluding discounts). The starting mileage is 5 km; the fare is 3 yuan for 5~10 km; the fare is 4 yuan for 10~17 km; 17 ~27 km, the fare is 5 yuan; 27~38 km, the fare is 6 yuan; for every 1 yuan increase in fare above 38 km.
Accidents and incidents
[edit]On April 13, 2018, the ground collapsed near the Haixin Bridge Station in the western section of Line 2 and there were no casualties.
On November 26, 2018, a partial detachment occurred during the 01-2 workspace jet operation of Line 8 B2, causing a worker to fall from the work platform and die after being sent to the hospital for rescue.
On December 20, 2018, a production accident occurred at a construction site on Line 4, killing one person.
On May 27, 2019, the construction section of the quicksand area of Line 4 collapsed, killing 5 people.
On February 20, 2023, At the Shilaoren Beach Station project site of Line 5, an accident occurred while repairing a rotary drilling rig, resulting in the death of a maintenance worker.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Sina Visitor System".
- ^ "Qingdao subway system to launch in December". December 14, 2015. Retrieved December 16, 2015.
- ^ "年底通车倒计时!青岛地铁1号线南段试运行进入最后阶段重点".
- ^ 视频:地铁1号线全线开通进入“倒计时” 车站内景抢先看
- ^ "地铁2号线(东段)12月10日开通试运营-地铁资讯-青岛地铁". www.qd-metro.com. Retrieved 2017-12-10.
- ^ a b "Qingdao metro Line 3 Phase 2 opens". International Rail Journal. December 19, 2016. Retrieved 2017-04-30.
- ^ chinanews. "山东省第二条地铁开通试运营 被誉为"最美海岸线地铁"-中新网". www.chinanews.com. Retrieved 2017-12-10.
- ^ "定了!地铁2号线西段将于12月16日通车". 2019-12-13.
- ^ "Qingdao metro opens". Railway Gazette. December 17, 2015. Retrieved 2017-04-30.
- ^ "青岛地铁6号线一期工程弱电安装项目站台绝缘层材料采购(第二次)招标公告". Archived from the original on 2024-04-26. Retrieved 2024-04-24.
- ^ 青岛地铁. "6号线周边信息,请您提建议!". Archived from the original on 2024-04-26. Retrieved 2024-04-24.
- ^ "青岛地铁6号线一期将于4月26日上午10:16开通!". Archived from the original on 2024-04-26. Retrieved 2024-04-24.
- ^ a b c "国家发展改革委关于青岛市城市轨道交通第二期建设规划调整方案(2013~2021年)的批复". 2016-04-26.
- ^ "青岛地铁2号线延长段开工 长3.84千米设3个站点". 2019-10-26.
- ^ "民生在线:地铁8号线南段2025年完工!还有10号线、12号线、15号线、16号线……". 2022-05-13.
- ^ "历时5年!青岛地铁8号线南段终于取得这项重大进展_腾讯新闻". new.qq.com. Retrieved 2022-07-05.
- ^ "国家发展改革委关于青岛市城市轨道交通第三期建设规划(2021-2026年)的批复". 2021-08-19. Retrieved 2021-09-06.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "青岛市城市轨道交通第三期建设规划(2021~2026年)" (PDF). Retrieved 2021-09-06.
- ^ a b "All the planned lines of the third phase of Qingdao Metro started". 2022-07-04. Archived from the original on 2022-07-08.
- ^ a b c "胶州地铁建设指挥部正式挂牌!地铁8号线支线部分站点启动基础施工".
External links
[edit]- Qingdao Metro construction (in Chinese)
- Qingdao Metro construction presentation (in Chinese)
- Qingdao at UrbanRail.net
 KSF
KSF