Raspberry Pi
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 70 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 70 min
 | |
 Various Raspberry Pi computers | |
| Also known as | RPi, Raspi |
|---|---|
| Type | Single-board computer |
| Release date | 29 February 2012 |
| Operating system |
|
| Storage | MicroSDXC slot, USB mass storage device for booting[2] |
| Website | www |
Raspberry Pi (/paɪ/) is a series of small single-board computers (SBCs) developed in the United Kingdom. The original Raspberry Pi computer was developed by the Raspberry Pi Foundation in association with Broadcom. Since 2012, all Raspberry Pi products have been developed by Raspberry Pi Ltd, which began as a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Foundation and began trading as a public company on the London Stock Exchange in June 2024.[3]
The Raspberry Pi device attracted attention because they were fully fledged computers, but were small — some as small as a credit card — and inexpensive — with some of them costing as little as $35 as of 2024. As a result Raspberry Pis were used in a variety of ways, ranging from components used to power machines such as smart speakers and robots, to being connected to bigger devices, such as desktop screens.[3] The first model sold well beyond its original target market of education,[4] ending up in robotics, home automation, industrial automation and used by hobbyists. The devices crop up in uses from high-tech farming systems to self-pouring beer taps.[3] At the time of the public listing in 2024, the company said more than 60 million Raspberry Pi devices had been sold.[3]
Originally, the Raspberry Pi project was created with the promotion of teaching basic computer science in schools in mind,[5][6][7] leading to low cost, modularity, open design, and its adoption of the HDMI and USB standards.
Later models have much more memory (RAM), up to 16 GB while the original was much more limited in memory (512 MB or 256 MB, with the former capacity still sold), and also more limited in other areas such as having no wireless networking.
The Raspberry Pi became the best-selling British computer in 2015, when it surpassed the ZX Spectrum in unit sales.[8]
Origins and company history
[edit]The Raspberry Pi Foundation was created as a private company limited by guarantee in 2008,[9] and was registered as a charity in 2009[10] by people at the University of Cambridge Computer Laboratory who had noticed a decline in the number and skills of young people applying for computer science courses.[11]
In 2012, after the release of the second board type, the Raspberry Pi Foundation set up a new entity responsible for developing their computers, named Raspberry Pi (Trading) Ltd,[12] and installed Eben Upton (one of the 2008 group) as CEO.[13] The Foundation was rededicated as an educational charity for promoting the teaching of basic computer science in schools and developing countries.[14]
In 2021, Raspberry Pi (Trading) Ltd changed its name to Raspberry Pi Ltd.[12][15] Its newly-formed parent company, Raspberry Pi Holdings Ltd, became a public company in June 2024, launching on the London Stock Exchange where it trades with the stock symbol RPI.[16][17][18][19]
Most Raspberry Pis are made in a Sony factory in Pencoed, Wales,[20] while others are made in China and Japan.[21][22]
Series and generations
[edit]There are three series of Raspberry Pi, and several generations of each have been released. Raspberry Pi SBCs feature a Broadcom system on a chip (SoC) with an integrated ARM-compatible central processing unit (CPU) and on-chip graphics processing unit (GPU), while Raspberry Pi Pico has a RP2040 system on chip with an integrated ARM-compatible central processing unit (CPU).
Raspberry Pi
[edit]- The first-generation Raspberry Pi Model B was released in February 2012, followed by the simpler and cheaper Model A.
- Raspberry Pi Model B+, an improved design, was released in 2014. These first-generation boards feature ARM11 processors, are approximately credit-card sized, and represent the standard mainline form factor. The A+ and an improved B model were released within a year. A "Compute Module" was released in April 2014 for embedded applications.
- The Raspberry Pi 2 B was released in February 2015 and initially featured a 900 MHz 32-bit quad-core ARM Cortex-A7 processor with 1 GB RAM. Revision 1.2 features a 900 MHz 64-bit quad-core ARM Cortex-A53 processor (the same as that in the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B, but underclocked to 900 MHz).[23]
- The Raspberry Pi 3 Model B was released in February 2016 with a 1.2 GHz 64-bit quad core ARM Cortex-A53 processor, on-board 802.11n Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and USB boot capabilities.[24]
- The Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ was launched on Pi Day 2018 with a faster 1.4 GHz processor, a three-times faster Gigabit Ethernet (throughput limited to ca. 300 Mbit/s by the internal USB 2.0 connection), and 2.4 / 5 GHz dual-band 802.11ac Wi-Fi (100 Mbit/s).[25] Other features are Power over Ethernet (PoE) (with the add-on PoE HAT), USB boot and network boot (an SD card is no longer required).
- The Raspberry Pi 3 Model A+ was launched in November 2018 as a similar board to the first Model A. It has a 1.4 GHz 64-bit quad-core processor, with 2.4 GHz dual-band and 5 GHz wireless LAN & Bluetooth 4.2. It also has a 40-pin GPIO header, 512 MB of DDR2 RAM, is powered by 5V of DC power via microUSB. A full-size HDMI port is used for connectivity, and one USB 2.0 port is on the board.[26]
- The Raspberry Pi 4 Model B was released in June 2019[27] with a 1.5 GHz 64-bit quad core ARM Cortex-A72 processor, on-board 802.11ac Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 5, full gigabit Ethernet (throughput not limited), two USB 2.0 ports, two USB 3.0 ports, 1, 2, 4, or 8 GB of RAM, and dual-monitor support via a pair of micro HDMI (HDMI Type D) ports for up to 4K resolution. The version with 1 GB RAM has been abandoned and the prices of the 2 GB version have been reduced. The 8 GB version has a revised circuit board. The Raspberry Pi 4 is also powered via a USB-C port, enabling additional power to be provided to downstream peripherals, when used with an appropriate PSU. But the Pi can only be operated with 5 volts and not 9 or 12 volts like other mini computers of this class. The initial Raspberry Pi 4 board had a design flaw where third-party e-marked USB cables, such as those used on MacBooks, incorrectly identify it and refuse to provide power.[28][29] Tom's Hardware tested 14 different cables and found that 11 of them turned on and powered the Pi without issue.[30] The design flaw was fixed in revision 1.2 of the board, released in late 2019.[31] In mid-2021, Pi 4 B models appeared with the improved Broadcom BCM2711C0. The manufacturer is now using this chip for the Pi 4 B and Pi 400. However, the clock frequency of the Pi 4 B was not increased in the factory.
- The Raspberry Pi 400 was released in November 2020. A modern example of a keyboard computer, it features 4 GB of LPDDR4 RAM on a custom board derived from the existing Raspberry Pi 4 combined with a keyboard in a single case. The case was derived from that of the Raspberry Pi Keyboard.[32] A robust cooling solution (i.e. a broad metal plate) and an upgraded switched-mode power supply[33] allow the Raspberry Pi 400's Broadcom BCM2711C0 processor to be clocked at 1.8 GHz, which is 20% faster than the Raspberry Pi 4 upon which it is based.[34]
- The Raspberry Pi 5 was announced in September 2023.[35] It uses a 2.4 GHz quad-core 64-bit ARM Cortex-A76 CPU and a VideoCore VII GPU, with the improvements in hardware and software reportedly making the Pi 5 more than twice as powerful as the Pi 4.[36] It has an I/O controller designed in-house, a power button, and an RTC chip (which requires an external battery). At launch, the Pi 5 was available with either 4 or 8 GB of RAM, at US$60 and US$80;[37] a 2 GB variant was released in August 2024 at US$50.[38] The Pi 5 lacks a 3.5 millimeter audio jack, so Bluetooth, HDMI, USB audio or an Audio HAT are the options for audio output.
- In December 2024, Raspberry Pi introduced the keyboard-based Raspberry Pi 500, successor to the Pi 400.[39][40]
- In January 2025, the 16GB Raspberry Pi 5 was released, sold for $120.
Raspberry Pi Zero
[edit]- The Raspberry Pi Zero with smaller size and reduced input/output (I/O) and general-purpose input/output (GPIO) capabilities was released in November 2015 for US$5.
- The Raspberry Pi Zero v1.3 was released in May 2016, which added a camera connector.[41]
- The Raspberry Pi Zero W was launched in February 2017, a version of the Zero with Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, for US$10.[42][43]
- The Raspberry Pi Zero WH was launched in January 2018, a version of the Zero W with pre-soldered GPIO headers.[44]
- The Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W was launched in October 2021, a version of the Zero W with a system in a package (SiP) designed by Raspberry Pi and based on the Raspberry Pi 3.[45] In contrast to the older Zero models, the Pi Zero 2 W is 64-bit capable. The price is around US$15.
Raspberry Pi Pico
[edit]- Raspberry Pi Pico was released in January 2021 with a retail price of $4.[46] It was Raspberry Pi's first board based upon a single microcontroller chip; the RP2040, which was designed by Raspberry Pi in the UK.[47] The Pico has 264 KB of RAM and 2 MB of flash memory. It is programmable in C, C++, Assembly, MicroPython, CircuitPython and Rust. Raspberry Pi has partnered with Adafruit, Pimoroni, Arduino and SparkFun to build accessories for Raspberry Pi Pico and variety of other boards using RP2040 Silicon Platform.[48] Rather than perform the role of general purpose computer (like the others in the range) it is designed for physical computing, similar in concept to an Arduino.[49]
- The Raspberry Pi Pico W was launched in June 2022, a version of the Pico with 802.11n Wi-Fi capability, for US$6. The CYW43439 wireless chip in the Pico W also supports Bluetooth, but the capability was not enabled at launch.[50]
- The Raspberry Pi Pico 2 was launched in August 2024 with a retail price of US$5, based on a new RP2350 ARM/RISC-V microcontroller. The Pico 2 has 520 KB of RAM and 4 MB of flash memory and is hardware and software compatible with the original Pico.[51]
- The Raspberry Pi Pico 2 W was released in November 2024, with a retail price of US$7, and includes Wi-Fi (2.4 GHz 802.11n) and Bluetooth 5.2 capabilities.[52]
Model comparison
[edit]This section needs expansion with: information on compute modules. You can help by adding to it. (August 2024) |
| Family | Model | SoC | Memory | Form factor | Ethernet | Wireless | GPIO | Released | Discontinued |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raspberry Pi | B | BCM2835 | 256 MB | Standard[a] | Yes | No | 26-pin | 2012 | Yes |
| 512 MB | 2012[53] | ||||||||
| A | 256 MB | No | 2013 | ||||||
| B+ | 512 MB | Yes | 40-pin | 2014 | No | ||||
| A+ | 256 MB | Compact[b] | No | Yes | |||||
| 512 MB | No | ||||||||
| Raspberry Pi 2 | B | BCM2836 / 7 | 1 GB | Standard[a] | Yes | No | 40-pin | 2015 | No |
| Raspberry Pi Zero | Zero | BCM2835 | 512 MB | Ultra-compact[c] | No | No | 40-pin | 2015 | No |
| W / WH | Yes | 2017 | |||||||
| 2 W | BCM2710A1[d][54] | 2021 | |||||||
| Raspberry Pi 3 | B | BCM2837A0 / B0 | 1 GB | Standard[a] | Yes | Yes | 40-pin | 2016 | No |
| A+ | BCM2837B0 | 512 MB | Compact[b] | No | Yes[e] | 2018 | |||
| B+ | 1 GB | Standard[a] | Yes[f] | 2018 | |||||
| Raspberry Pi 4 | B[55] | BCM2711B0 / C0[56] | 1 GB | Standard[a] | Yes[g] | Yes[e] | 40-pin | 2019[57] | Temporarily (2020–2021)[58][59] |
| 2 GB | No | ||||||||
| 4 GB | |||||||||
| 8 GB | 2020 | ||||||||
| 400 | 4 GB | Keyboard | |||||||
| Raspberry Pi Pico | Pico | RP2040 | 264 KB | Pico[h] | No | No | 40-pin | 2021 | No |
| W | Yes[i] | 2022 | |||||||
| 2 | RP2350A | 520 KB | No | 2024 | |||||
| 2 W | Yes[i] | ||||||||
| Raspberry Pi 5[60] | B | BCM2712 | 2 GB | Standard[a] | Yes[g] | Yes[e] | 40-pin | 2024 | No |
| 4 GB | 2023 | ||||||||
| 8 GB | |||||||||
| 16 GB | 2025[61] | ||||||||
| 500 | 8 GB | Keyboard | 2024[62] |
- ^ a b c d e f 85.6 mm × 56.5 mm (3.37 in × 2.22 in)
- ^ a b 65 mm × 56.5 mm (2.56 in × 2.22 in)
- ^ 65 mm × 30 mm (2.6 in × 1.2 in)
- ^ Custom Raspberry Pi SiP RP3A0
- ^ a b c Dual band
- ^ Gigabit Ethernet; Throughput limited to ca. 300 Mbit/s by the internal USB 2.0 connection
- ^ a b Gigabit Ethernet
- ^ 21 mm × 51 mm (0.83 in × 2.01 in)
- ^ a b 2.4 GHz band
Hardware
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (November 2020) |
The Raspberry Pi hardware has evolved through several versions that feature variations in the type of the central processing unit, amount of memory capacity, networking support, and peripheral-device support.[63]

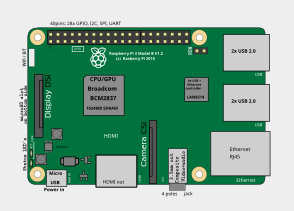
This block diagram describes models B, B+, A and A+. The Pi Zero models are similar, but lack the Ethernet and USB hub components. The Ethernet adapter is internally connected to an additional USB port. The boards have one to five USB ports. In Model A, A+, and the Pi Zero, the USB port is connected directly to the system on a chip (SoC). On the Pi 1 Model B+ and later models the USB/Ethernet chip contains a five-port USB hub, of which four ports are available, while the Pi 1 Model B only provides two. On the Pi Zero, the USB port is also connected directly to the SoC, but it uses a micro USB (OTG) port. Unlike all other Pi models, the 40 pin GPIO connector is omitted on the Pi Zero, with solderable through-holes only in the pin locations. The Pi Zero WH remedies this.
Processor speed ranges from 700 MHz to 2.4 GHz for the Pi 5; on-board memory ranges from 256 MB to 16 GB random-access memory (RAM), with only the Raspberry Pi 4 and the Raspberry Pi 5 having more than 1 GB.
Secure Digital (SD) cards in MicroSDHC form factor (SDHC on early models) are used to store the operating system and program memory, however some models also come with onboard eMMC storage[64] and the Raspberry Pi 4 and newer can also make use of USB-attached SSD storage for its operating system.[65] Raspberry Pi 5 supports booting from NVMe SSDs attached directly to the PCIe bus with an appropriate adapter or HAT.
For video output, HDMI is supported on all versions, and composite video is supported on Raspberry Pi 4 and earlier, with a standard 3.5 mm tip-ring-sleeve jack carrying mono audio together with composite video.
Lower-level output is provided by a number of GPIO pins, which support common protocols like I²C.
The B-models have an 8P8C Ethernet port and the Pi 3 and newer, and Pi Zero W series have on-board Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.[66]
Processor
[edit]
The Broadcom BCM2835 SoC used in the first generation Raspberry Pi[67] includes a RISC-based 700 MHz 32-bit ARM1176JZF-S processor, VideoCore IV graphics processing unit (GPU),[68] and RAM. It has a level 1 (L1) cache of 16 KB and a level 2 (L2) cache of 128 KB. The level 2 cache is used primarily by the GPU. The SoC is stacked underneath the RAM chip, so only its edge is visible. The ARM1176JZ(F)-S is the same CPU used in the original iPhone,[69] although at a higher clock rate, and mated with a much faster GPU.
The earlier V1.1 model of the Raspberry Pi 2 used a Broadcom BCM2836 SoC with a 900 MHz 32-bit, quad-core ARM Cortex-A7 processor, with 256 KB shared L2 cache.[70] The Raspberry Pi 2 V1.2 was upgraded to a Broadcom BCM2837 SoC with a 1.2 GHz 64-bit quad-core ARM Cortex-A53 processor,[23] the same one which is used on the Raspberry Pi 3, but underclocked (by default) to the same 900 MHz CPU clock speed as the V1.1. The BCM2836 SoC is no longer in production as of late 2016.
The Raspberry Pi 3 Model B uses a Broadcom BCM2837 SoC with a 1.2 GHz 64-bit quad-core ARM Cortex-A53 processor, with 512 KB shared L2 cache. The Model A+ and B+ are 1.4 GHz[71][72][73]
The Raspberry Pi 4 uses a Broadcom BCM2711 SoC with a 1.5 GHz (later models: 1.8 GHz) 64-bit quad-core ARM Cortex-A72 processor, with 1 MB shared L2 cache.[74][75] Unlike previous models, which all used a custom interrupt controller poorly suited for virtualisation, the interrupt controller on this SoC is compatible with the ARM Generic Interrupt Controller (GIC) architecture 2.0, providing hardware support for interrupt distribution when using ARM virtualisation capabilities.[76][77] The VideoCore IV of the previous models has also been replaced with a VideoCore VI running at 500 MHz.
The Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W use the same Broadcom BCM2835 SoC as the first generation Raspberry Pi, although now running at 1 GHz CPU clock speed.[78]
The Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W uses the RP3A0-AU, which is a System-in-Package (SiP) design. The package contains a Broadcom BCM2710A1 processor, which is a 64-bit quad-core ARM Cortex-A53 clocked at 1 GHz, along with 512 MB of LPDDR2 SDRAM layered above.[79][80] The Raspberry Pi 3 also uses the BCM2710A1 in its Broadcom BCM2837 SoC, but clocked at a higher 1.2 GHz.
The Raspberry Pi Pico uses the RP2040,[81] a microcontroller containing dual ARM Cortex-M0+ cores running at 133 MHz, 6 banks of SRAM totalling 264 KB, and programmable IO for peripherals.[82]

The Raspberry Pi 5 uses the Broadcom BCM2712 SoC, which is a chip designed in collaboration with Raspberry Pi. The SoC features a quad-core ARM Cortex-A76 processor clocked at 2.4 GHz, alongside a VideoCore VII GPU clocked at 800 MHz. The BCM2712 SoC also features support for cryptographic extensions for the first time on a Raspberry Pi model. Alongside the new processor and graphics unit, the monolithic design of the earlier BCM2711 has been replaced with a CPU and chipset (southbridge) architecture, as the IO functionality has been moved to the Raspberry Pi 5's custom RP1 chip.[83]
Performance
[edit]While operating at 700 MHz by default, the first generation Raspberry Pi provided a real-world performance roughly equivalent to 0.041 GFLOPS.[84][85] On the CPU level the performance is similar to a 300 MHz Pentium II of 1997–99. The GPU provides 1 Gpixel/s or 1.5 Gtexel/s of graphics processing or 24 GFLOPS of general purpose computing performance. The graphical capabilities of the Raspberry Pi are roughly equivalent to the performance of the Xbox of 2001.
Raspberry Pi 2 V1.1 included a quad-core Cortex-A7 CPU running at 900 MHz and 1 GB RAM. It was described as 4–6 times more powerful than its predecessor. The GPU was identical to the original.[70] In parallelised benchmarks, the Raspberry Pi 2 V1.1 could be up to 14 times faster than a Raspberry Pi 1 Model B+.[86]
The Raspberry Pi 3, with a quad-core Cortex-A53 processor, is described as having ten times the performance of a Raspberry Pi 1.[87] Benchmarks showed the Raspberry Pi 3 to be approximately 80% faster than the Raspberry Pi 2 in parallelised tasks.[88]
The Raspberry Pi 4, with a quad-core Cortex-A72 processor, is described as having three times the performance of a Raspberry Pi 3.[27]
Overclocking
[edit]This section needs expansion with: information on later models such as Pi4 and Pi5. You can help by adding to it. (February 2025) |
Most Raspberry Pi systems-on-chip can be overclocked to various degrees utilising the built in config.txt file in the boot sector of the Raspberry Pi OS. Overclocking is generally safe and does not automatically void the warranty of the Raspberry Pi; however, setting the "force_turbo" option to 1 bypasses voltage and temperature limits and voids the users warranty.[89] In Raspberry Pi OS the overclocking options on boot can also be made by a software command running "sudo raspi-config" on Raspberry Pi 1, 2, and original 3B without voiding the warranty.[90] In those cases the Pi automatically shuts the overclocking down if the chip temperature reaches 85 °C (185 °F); an appropriately sized heat sink is needed to protect the chip from thermal throttling.
Newer versions of the firmware contain the option to choose between five overclock ("turbo") presets that, when used, attempt to maximise the performance of the SoC without impairing the lifetime of the board. This is done by monitoring the core temperature of the chip and the CPU load, and dynamically adjusting clock speeds and the core voltage. When the demand is low on the CPU or it is running too hot, the performance is throttled, but if the CPU has much to do and the chip's temperature is acceptable, performance is temporarily increased with CPU clock speeds of up to 1.1 GHz, depending on the board version and on which of the turbo settings is used.
The overclocking modes are:
| none | 700 MHz ARM | 250 MHz core | 400 MHz SDRAM | 0 overvolting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| modest | 800 MHz ARM | 250 MHz core | 400 MHz SDRAM | 0 overvolting |
| medium | 900 MHz ARM | 250 MHz core | 450 MHz SDRAM | 2 overvolting |
| high | 950 MHz ARM | 250 MHz core | 450 MHz SDRAM | 6 overvolting |
| turbo | 1000 MHz ARM | 500 MHz core | 600 MHz SDRAM | 6 overvolting |
| Pi 2 | 1000 MHz ARM | 500 MHz core | 500 MHz SDRAM | 2 overvolting |
| Pi 3 | 1100 MHz ARM | 550 MHz core | 500 MHz SDRAM | 6 overvolting. In system information, the CPU speed is indicated as 1200 MHz. When idling, speed lowers to 600 MHz.[90][91] |
In the highest (turbo) mode the SDRAM clock speed was originally 500 MHz, but this was later changed to 600 MHz because of occasional SD card corruption. Simultaneously, in high mode the core clock speed was lowered from 450 to 250 MHz, and in medium mode from 333 to 250 MHz.
The CPU of the first and second generation Raspberry Pi board did not require cooling with a heat sink or fan, even when overclocked, but the Raspberry Pi 3 may generate more heat when overclocked.[92]
RAM
[edit]The early designs of the Raspberry Pi Model A and B boards included 256 MB of random-access memory (RAM). Of this, the early beta Model B boards allocated 128 MB to the GPU by default, leaving only 128 MB for the CPU.[93] On the early 256 MB releases of models A and B, three different splits were possible. The default split was 192 MB for the CPU, which should be sufficient for standalone 1080p video decoding, or for simple 3D processing. 224 MB was for Linux processing only, with only a 1080p framebuffer, and was likely to fail for any video or 3D. 128 MB was for heavy 3D processing, possibly also with video decoding.[94] In comparison, the Nokia 701 uses 128 MB for the Broadcom VideoCore IV.[95]
The later Model B with 512 MB RAM, was released on 15 October 2012 and was initially released with new standard memory split files (arm256_start.elf, arm384_start.elf, arm496_start.elf) with 256 MB, 384 MB, and 496 MB CPU RAM, and with 256 MB, 128 MB, and 16 MB video RAM, respectively. But about one week later, the foundation released a new version of start.elf that could read a new entry in config.txt (gpu_mem=xx) and could dynamically assign an amount of RAM (from 16 to 256 MB in 8 MB steps) to the GPU, obsoleting the older method of splitting memory, and a single start.elf worked the same for 256 MB and 512 MB Raspberry Pis.[96]
The Raspberry Pi 2 has 1 GB of RAM.
The Raspberry Pi 3 has 1 GB of RAM in the B and B+ models, and 512 MB of RAM in the A+ model.[97][98][99] The Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W have 512 MB of RAM.
The Raspberry Pi 4 is available with 1, 2, 4 or 8 GB of RAM.[100] A 1 GB model was originally available at launch in June 2019 but was discontinued in March 2020,[58] and the 8 GB model was introduced in May 2020.[101] The 1 GB model returned in October 2021.[59]
The Raspberry Pi 5 is available with 2, 4, 8 or 16 GB of RAM.[102]
Networking
[edit]The Model A, A+ and Pi Zero have no Ethernet circuitry and are commonly connected to a network using an external user-supplied USB Ethernet or Wi-Fi adapter. On the Model B and B+ the Ethernet port is provided by a built-in USB Ethernet adapter using the SMSC LAN9514 chip.[103] The Raspberry Pi 3 and Pi Zero W (wireless) are equipped with 2.4 GHz WiFi 802.11n (150 Mbit/s) and Bluetooth 4.1 (24 Mbit/s) based on the Broadcom BCM43438 FullMAC chip with no official support for monitor mode (though it was implemented through unofficial firmware patching[104]) and the Pi 3 also has a 10/100 Mbit/s Ethernet port. The Raspberry Pi 3B+ features dual-band IEEE 802.11b/g/n/ac WiFi, Bluetooth 4.2, and Gigabit Ethernet (limited to approximately 300 Mbit/s by the USB 2.0 bus between it and the SoC). The Raspberry Pi 4 has full gigabit Ethernet (throughput is not limited as it is not funnelled via the USB chip.)
Special-purpose features
[edit]The RPi Zero, RPi1A, RPi3A+[105] and RPi4 can be used as a USB device or "USB gadget", plugged into another computer via a USB port on another machine. It can be configured in multiple ways, such as functioning as a serial or Ethernet device.[106] Although originally requiring software patches, this was added into the mainline Raspbian distribution in May 2016.[106]
Raspberry Pi models with a newer chipset can boot from USB mass storage, such as from a flash drive. Booting from USB mass storage is not available in the original Raspberry Pi models, the Raspberry Pi Zero, the Raspberry Pi Pico, the Raspberry Pi 2 A models, and the Raspberry Pi 2 B models with versions lower than 1.2.[107]
Peripherals
[edit]
Although often pre-configured to operate as a headless computer, the Raspberry Pi may also optionally be operated with any generic USB computer keyboard and mouse.[108] It may also be used with USB storage, USB to MIDI converters, and virtually any other device/component with USB capabilities, depending on the installed device drivers in the underlying operating system (many of which are included by default).
Other peripherals can be attached through the various pins and connectors on the surface of the Raspberry Pi.[109]
Video
[edit]
The video controller can generate standard modern TV resolutions, such as HD and Full HD, and higher or lower monitor resolutions as well as older NTSC or PAL standard CRT TV resolutions. As shipped (i.e., without custom overclocking) it can support the following resolutions: 640×350 EGA; 640×480 VGA; 800×600 SVGA; 1024×768 XGA; 1280×720 720p HDTV; 1280×768 WXGA variant; 1280×800 WXGA variant; 1280×1024 SXGA; 1366×768 WXGA variant; 1400×1050 SXGA+; 1600×1200 UXGA; 1680×1050 WXGA+; 1920×1080 1080p HDTV; 1920×1200 WUXGA.[110]
Higher resolutions, up to 2048×1152, may work[111][112] or even 3840×2160 at 15 Hz (too low a frame rate for convincing video).[113] Allowing the highest resolutions does not imply that the GPU can decode video formats at these resolutions; in fact, the Raspberry Pis are known to not work reliably for H.265 (at those high resolutions),[114] commonly used for very high resolutions (however, most common formats up to Full HD do work).
Although the Raspberry Pi 3 does not have H.265 decoding hardware, the CPU is more powerful than its predecessors, potentially fast enough to allow the decoding of H.265-encoded videos in software.[115] The GPU in the Raspberry Pi 3 runs at higher clock frequencies of 300 MHz or 400 MHz, compared to previous versions which ran at 250 MHz.[116]
The Raspberry Pis can also generate 576i and 480i composite video signals, as used on old-style (CRT) TV screens and less-expensive monitors through standard connectors – either RCA or 3.5 mm phono connector depending on model. The television signal standards supported are PAL-B/G/H/I/D, PAL-M, PAL-N, NTSC and NTSC-J.[117]
Real-time clock
[edit]When booting, the time defaults to being set over the network using the Network Time Protocol (NTP). The source of time information can be another computer on the local network that does have a real-time clock, or to a NTP server on the internet. If no network connection is available, the time may be set manually or configured to assume that no time passed during the shutdown. In the latter case, the time is monotonic (files saved later in time always have later timestamps) but may be considerably earlier than the actual time. For systems that require a built-in real-time clock, a number of small, low-cost add-on boards with real-time clocks are available.[118][119] The Raspberry Pi 5 is the first to include a real-time clock.[102] If an external battery is not plugged in, the Pi 5 will use the Network Time Protocol, or will need to be set manually, as was the case in previous models.
The RP2040 microcontroller has a built-in real-time clock, but it can not be set without some form of user entry or network facility being added.
Connectors
[edit]
Pi Pico[edit]
Pi Compute Module[edit]
Pi Zero[edit]
Model A[edit]
|
Model B[edit]
|
J8 header and general purpose input-output (GPIO)
[edit]Raspberry Pi 1 Models A+ and B+, Pi 2 Model B, Pi 3 Models A+, B and B+, Pi 4, and Pi Zero, Zero W, Zero WH and Zero W 2 have the same 40-pin pinout (designated J8 across all models).[120] Raspberry Pi 1 Models A and B have only the first 26 pins.[121][122][123] The J8 header is commonly referred to as the GPIO connector as a whole, even though only a subset of the pins are GPIO pins. In the Pi Zero and Zero W, the 40 GPIO pins are unpopulated, having the through-holes exposed for soldering instead. The Zero WH (Wireless + Header) has the header pins preinstalled.
| GPIO# | func. | Pin# | Pin# | func. | GPIO# | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +3.3 V | 1 | 2 | +5 V | |||
| 2 | SDA1 (I2C) | 3 | 4 | +5 V | ||
| 3 | SCL1 (I2C) | 5 | 6 | GND | ||
| 4 | GCLK | 7 | 8 | TXD0 (UART) | 14 | |
| GND | 9 | 10 | RXD0 (UART) | 15 | ||
| 17 | GEN0 | 11 | 12 | GEN1 | 18 | |
| 27 | GEN2 | 13 | 14 | GND | ||
| 22 | GEN3 | 15 | 16 | GEN4 | 23 | |
| +3.3 V | 17 | 18 | GEN5 | 24 | ||
| 10 | MOSI (SPI) | 19 | 20 | GND | ||
| 9 | MISO (SPI) | 21 | 22 | GEN6 | 25 | |
| 11 | SCLK (SPI) | 23 | 24 | CE0_N (SPI) | 8 | |
| GND | 25 | 26 | CE1_N (SPI) | 7 | ||
| 0 | ID_SD (I2C) | 27 | 28 | ID_SC (I2C) | 1 | |
| 5 | N/A | 29 | 30 | GND | ||
| 6 | N/A | 31 | 32 | N/A | 12 | |
| 13 | N/A | 33 | 34 | GND | ||
| 19 | N/A | 35 | 36 | N/A | 16 | |
| 26 | N/A | 37 | 38 | Digital IN | 20 | |
| GND | 39 | 40 | Digital OUT | 21 |
Model B rev. 2 also has a pad (called P5 on the board and P6 on the schematics) of 8 pins offering access to an additional 4 GPIO connections.[124] These GPIO pins were freed when the four board version identification links present in revision 1.0 were removed.[125]
| GPIO# | func. | Pin# | Pin# | func. | GPIO# | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +5 V | 1 | 2 | +3.3 V | |||
| 28 | GPIO_GEN7 | 3 | 4 | GPIO_GEN8 | 29 | |
| 30 | GPIO_GEN9 | 5 | 6 | GPIO_GEN10 | 31 | |
| GND | 7 | 8 | GND |
Models A and B provide GPIO access to the ACT status LED using GPIO 16. Models A+ and B+ provide GPIO access to the ACT status LED using GPIO 47, and the power status LED using GPIO 35.
Specifications
[edit]This section needs expansion with: information on compute module 5 'CM5'. You can help by adding to it. (February 2025) |
| Version | Pico | Model A (no Ethernet) | Model B (with Ethernet) | Compute Module[a] | Zero | Keyboard | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raspberry Pi Pico | Raspberry Pi Pico W | Raspberry Pi Pico 2 | RPi 1 Model A | RPi 1 Model A+ | RPi 3 Model A+ | RPi 1 Model B | RPi 1 Model B+ | RPi 2 Model B | RPi 2 Model B v1.2 | RPi 3 Model B | RPi 3 Model B+ | RPi 4 Model B | RPi 5 | Compute Module 1 | Compute Module 3 | Compute Module 3 Lite | Compute Module 3+ | Compute Module 3+ Lite | Compute Module 4 | Compute Module 4 Lite | RPi Zero PCB v1.2 | RPi Zero PCB v1.3 | RPi Zero W | RPi Zero 2 W | RPi 400 | |
| Release date | Jan 2021[citation needed] | Jun 2022[citation needed] | Late 2024[citation needed] | Feb 2013 |
Nov 2014 |
Nov 2018 | Apr–Jun 2012 | Jul 2014 |
Feb 2015 |
Oct 2016 |
Feb 2016 |
Mar 2018 |
Jun 2019 May 2020 (8 GB)[101] |
Oct 2023 (4GB & 8GB) Aug 2024 (2GB)[131] |
Apr 2014 |
Jan 2017 |
Jan 2019 |
Oct 2020 | Nov 2015 |
May 2016 | Feb 2017 | Oct 2021 |
Nov 2020 | |||
| Target price (USD) | $4[citation needed] | $6[citation needed] | $5[citation needed] | $25[126] | $20[127] | $25[citation needed] | $35[137] | $25[138] | $35 | $35/55/75 |
$50 (2 GB)[131] $60 (4 GB) $80 (8 GB)[139][102] |
$30 (in batches of 100)[140] | $30[citation needed] | $25[citation needed] | $30/35/40[citation needed] | $25[citation needed] | $30–$90 (in $5 increments)[citation needed] | $25–$75 (in $5 increments)[citation needed] | $5[136] | $10[citation needed] | $15[citation needed] | $70[citation needed] | ||||
| Instruction set | 32-bit Armv6-M (32-bit)[citation needed] | ARMv8-M (64/32-bit) and/or 32-bit RV32IMAC[citation needed] | ARMv6Z (32-bit)[citation needed] | ARMv8-A (64/32-bit)[citation needed] | ARMv6Z (32-bit)[citation needed] | ARMv7-A (32-bit)[citation needed] | ARMv8-A (64/32-bit)[citation needed] | ARMv8.2-A (64/32-bit)[citation needed] | ARMv6Z (32-bit)[citation needed] | ARMv8-A (64/32-bit)[141] | ARMv8-A (64/32-bit)[citation needed] | ARMv6Z (32-bit)[citation needed] | ARMv8-A (64/32-bit)[citation needed] | ARMv8-A (64/32-bit)[citation needed] | ||||||||||||
| Fabrication node | 40 nm[142] | 40 nm[citation needed] | 40 nm[143] | 40 nm[144] | 40 nm[143] | 40 nm[145] | 40 nm[144] | 28 nm[35] | 16 nm[35] | 40 nm[143] | 40 nm[144] | 28 nm[35] | 40 nm[143] | 28 nm[35] | ||||||||||||
| SoC | RP2040 | RP2350A | Broadcom BCM2835[67] | Broadcom BCM2837B0 |
Broadcom BCM2835[67] | Broadcom BCM2836 | Broadcom BCM2837 | Broadcom BCM2837B0 |
Broadcom BCM2711 |
Broadcom BCM2712 |
Broadcom BCM2835 | Broadcom BCM2837 | Broadcom BCM2837B0 | Broadcom BCM2711 | Broadcom BCM2835 | Broadcom BCM2710A1 | Broadcom BCM2711C0 | |||||||||
| FPU | Software emulation | FPv5 (for ARM, none for RISC-V) | VFPv2 | VFPv4 + NEON | VFPv2 | VFPv4 + NEON | VFPv2 | VFPv4 + NEON | VFPv2 | VFPv4 + NEON | VFPv4 + NEON | |||||||||||||||
| CPU | 2× Arm Cortex-M0+ | 2× of either Cortex-M33 or Hazard3 (selectable at boot) | 1× ARM1176JZF-S 700 MHz | 4× Cortex-A53 1.4 GHz | 1× ARM1176JZF-S 700 MHz | 4× Cortex-A7 900 MHz | 4× Cortex-A53 900 MHz | 4× Cortex-A53 1.2 GHz | 4× Cortex-A53 1.4 GHz | 4× Cortex-A72 1.5 GHz or 1.8 GHz[33] | 4× Cortex-A76 2.4 GHz[146] | 1× ARM1176JZF-S 700 MHz | 4× Cortex-A53 1.2 GHz | 4× Cortex-A72 1.5 GHz | 1× ARM1176JZF-S 1 GHz | 4× Cortex-A53 1 GHz | 4× Cortex-A72 1.8 GHz | |||||||||
| GPU | None | Broadcom VideoCore IV @ 250 MHz[b] | Broadcom VideoCore IV @ 400 MHz (Core) / 300 MHz (V3D) | Broadcom VideoCore VI @ 500 MHz[147] | Broadcom VideoCore VII @ 800 MHz[146] | Broadcom VideoCore IV @ 250 MHz[b] | Broadcom VideoCore VI @ 500 MHz[147] | Broadcom VideoCore IV @ 400 MHz (Core) / 300 MHz (V3D) | Broadcom VideoCore VI @ 500 MHz | |||||||||||||||||
| Memory (SDRAM)[148] | 264 KiB | 520 KiB | 256 MiB[c] | 256 or 512 MiB[c] Changed to 512 MB on 10 August 2016[149] |
512 MiB[c] | 256 or 512 MiB[c] Changed to 512 MB on 15 October 2012[53] |
512 MiB[c] | 1 GiB[c] | 1, 2, 4 or 8 GiB[c] | 2, 4, 8 or 16 GiB | 512 MB[c] | 1 GiB[c] | 1, 2, 4 or 8 GiB[c] | 512 MiB[c] | 4 GiB | |||||||||||
| USB 2.0 ports[108] | None | 1[d] | 1[e] | 2[f][150] | 4[g][103][128] | 2[130][35] | 1[d][a] | 1[d][a] | 1[e][a] | 1 | 1 Micro-USB[d] | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| USB 3.0 ports | 0 | 2[130][35] | 0 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| USB OTG ports | 0 | 1 (Power USB-C) |
0 | ? | 1 Micro-USB[d] | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| PCIe interface | 0 | PCIe Gen 2 x1 | 0 | PCIe Gen 2 x1 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Video input | 15-pin MIPI camera interface (CSI) connector, used with the Raspberry Pi camera or Raspberry Pi NoIR camera[152] | 2× 22-pin mini-MIPI display/camera interface (DSI/CSI)[153] | 2× MIPI camera interface (CSI)[a][140][154][155] | 2-lane MIPI CSI camera interface, 4-lane MIPI CSI camera interface | None | MIPI camera interface (CSI)[156] | None | |||||||||||||||||||
| HDMI | 1× HDMI (rev 1.3) | 2× HDMI (rev 2.0) via Micro-HDMI[57] | 2x HDMI (rev?) | 1 × HDMI[a] | 2 × HDMI | 1 × Mini-HDMI | 2× HDMI (rev 2.0) via Micro-HDMI | |||||||||||||||||||
| Composite video | via RCA jack | via 3.5 mm CTIA style TRRS jack | via RCA jack | via 3.5 mm CTIA style TRRS jack | pair of 0.1"-spaced pads | Yes[a][154][157] | ? | via marked points on PCB for optional header pins[158] | ? | |||||||||||||||||
| MIPI display interface (DSI)[h] | 1× standard size (15-pin, 1 mm pitch), for a display only | 2× mini[159] (22-pin, 0.5 mm pitch), each for a display or camera | Yes[a][140][155][160][161] | Yes | No | ? | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Audio inputs | As of revision 2 boards via I²S[162] | ? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Audio outputs | Analog via 3.5 mm phone jack; digital via HDMI and, as of revision 2 boards, I²S | HDMI | Analog, HDMI, I²S[a] | Mini-HDMI, stereo audio through PWM on GPIO | Micro-HDMI | |||||||||||||||||||||
| On-board storage[108] | None | 0 or 2 MB internal flash | SD, MMC, SDIO card slot (3.3 V with card power only) | MicroSDHC slot[128] | SD, MMC, SDIO card slot | MicroSDHC slot | MicroSDHC slot, USB Boot Mode[163] | MicroSDHC UHS-1 Slot | 4 GB eMMC flash memory chip[140] | MicroSDHC slot | 8/16/32 GB eMMC flash memory chip[140] | MicroSDHC slot | 8/16/32 GB eMMC flash memory chip[140] | MicroSDHC slot | MicroSDHC slot | MicroSDHC slot | ||||||||||
| Ethernet (8P8C)[108] | None | None[164] | None | 10/100 Mbit/s USB adapter on the USB hub[150] |
10/100 Mbit/s | 10/100/1000 Mbit/s (real max speed 300 Mbit/s)[165] | 10/100/1000 Mbit/s[130](Broadcom BCM54213 PHY)[35] | None | 10/100/1000 Mbit/s | None | None | 10/100/1000 Mbit/s | ||||||||||||||
| WiFi IEEE 802.11 wireless | None | b/g/n single band 2.4 GHz | None | b/g/n/ac dual band 2.4/5 GHz | None | b/g/n single band 2.4 GHz | b/g/n/ac dual band 2.4/5 GHz | b/g/n/ac dual band 2.4/5 GHz (Infineon CYW43455)[35] | b/g/n/ac dual band 2.4/5 GHz (optional) | b/g/n single band 2.4 GHz | b/g/n/ac dual band 2.4/5 GHz | |||||||||||||||
| Bluetooth | None | 5.2 BLE | None | 4.2 BLE | 4.1 BLE | 4.2 LS BLE | 5.0[130] | 5.0, BLE (optional) | 4.1 BLE | 4.2 BLE | 5.0 | |||||||||||||||
| Low-level peripherals | UART | 8× GPIO[166] plus the following, which can also be used as GPIO: UART, I²C bus, SPI bus with two chip selects, I²S audio[167] +3.3 V, +5 V, ground[168][169] | 17× GPIO plus the same specific functions, and HAT ID bus | 8× GPIO plus the following, which can also be used as GPIO: UART, I²C bus, SPI bus with two chip selects, I²S audio +3.3 V, +5 V, ground. | 17× GPIO plus the same specific functions, and HAT ID bus | 17× GPIO plus the same specific functions, HAT, and an additional 4× UART, 4× SPI, and 4× I2C connectors. |
46× GPIO, some of which can be used for specific functions including I²C, SPI, UART, PCM, PWM[a][171] | 28 × GPIO supporting either 1.8v or 3.3v signalling and peripheral options | 17× GPIO plus the same specific functions, and HAT ID bus[136] | ? | ||||||||||||||||
| Power ratings | ? | ? | ? | 300 mA (1.5 W)[172] | 200 mA (1 W)[173] | ? | 700 mA (3.5 W) | 200 mA (1 W) average when idle, 350 mA (1.75 W) maximum under stress (monitor, keyboard and mouse connected) |
220 mA (1.1 W) average when idle, 820 mA (4.1 W) maximum under stress (monitor, keyboard and mouse connected) |
300 mA (1.5 W) average when idle, 1.34 A (6.7 W) maximum under stress (monitor, keyboard, mouse and WiFi connected) |
459 mA (2.295 W) average when idle, 1.13 A (5.661 W) maximum under stress (monitor, keyboard, mouse and WiFi connected) |
600 mA (3 W) average when idle, 1.25 A (6.25 W) maximum under stress (monitor, keyboard, mouse and Ethernet connected),
1.6 A (8 W) for "power virus" workloads[35] |
12 W for "power virus" workloads[35] | 200 mA (1 W) | 700 mA (3.5 W) | ? | ? | ? | 100 mA (0.5 W) average when idle, 350 mA (1.75 W) maximum under stress (monitor, keyboard and mouse connected) |
120 mA (0.6 W) average when idle[176] | ? | |||||
| Power source | MicroUSB or GPIO Header 1.8 V to 5 V | 5 V via MicroUSB or GPIO header | 5 V via MicroUSB, GPIO header, or PoE (with the PoE HAT) | 5 V via USB-C, GPIO header, or PoE (with the PoE HAT) | 2.5–5 V, 3.3 V, 2.5–3.3 V, and 1.8 V[a] | 5 V | 5 V via MicroUSB or GPIO header | 5 V via USB-C | ||||||||||||||||||
| Size | 51 mm × 21 mm | 85.6 mm × 56.5 mm (3.37 in × 2.22 in)[i] |
65 mm × 56.5 mm × 10 mm (2.56 in × 2.22 in × 0.39 in)[j] |
65 mm × 56.5 mm (2.56 in × 2.22 in) |
85.60 mm × 56.5 mm (3.370 in × 2.224 in)[i] |
85.60 mm × 56.5 mm × 17 mm (3.370 in × 2.224 in × 0.669 in)[177] |
85 mm x 56 mm | 67.6 mm × 30 mm (2.66 in × 1.18 in) |
67.6 mm × 31 mm (2.66 in × 1.22 in) |
55 mm × 40 mm | 65 mm × 30 mm × 5 mm (2.56 in × 1.18 in × 0.20 in) |
286 mm × 113 mm × 23 mm | ||||||||||||||
| Weight | ? | ? | ? | 31 g (1.1 oz) |
23 g (0.81 oz) |
45 g (1.6 oz) |
46 g (1.6 oz)[178] |
7 g (0.25 oz)[179] |
9 g (0.32 oz)[180] |
10.8 g (0.38 oz) |
||||||||||||||||
| Console[clarification needed] | ? | ? | ? | Adding a USB network interface via tethering[164] or a serial cable with optional GPIO power connector[181] | ? | ? | ? | |||||||||||||||||||
| Generation | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1+ | 3+ | 1 | 1+ | 2 | 2 ver 1.2 | 3 | 3+ | 4 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 3 Lite | 3+ | 3+ Lite | 4 | 4 Lite | PCB ver 1.2 | PCB ver 1.3 | W (wireless) | 2 W (wireless) | 4 | |
| Obsolescence Statement |
in production until at least January 2028[citation needed] | in production until at least January 2040[citation needed] | in production until at least January 2026[citation needed] | in production until at least January 2026[citation needed] | —[clarification needed] | in production until at least January 2026[citation needed] | — see PCB ver 1.2[clarification needed] | — see ver 1.2[clarification needed] | in production until at least January 2026 |
in production until at least January 2026[citation needed] | in production until at least January 2028[183] | in production until at least January 2026[citation needed] | in production until at least January 2035[citation needed] | in production until at least January 2026[citation needed] | in production until at least January 2028[citation needed] | — or see PCB ver 1.3[clarification needed] | in production until at least January 2026 |
in production until at least January 2026[citation needed] | in production until at least January 2028[citation needed] | ? | ||||||
| Type | Pico | Model A (no Ethernet) | Model B (with Ethernet) | Compute Module[a] | Zero | Keyboard | ||||||||||||||||||||
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l 200-pin DDR2 SO-DIMM interface till CM3+,
- ^ a b BCM2837: 3D part of GPU at 300 MHz, video part of GPU at 400 MHz,[168][184] OpenGL ES 2.0 (BCM2835, BCM2836: 24 GFLOPS / BCM2837: 28.8 GFLOPS). MPEG-2 and VC-1 (with licence),[185] 1080p30 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC high-profile decoder and encoder[67] (BCM2837: 1080p60)
- ^ a b c d e Direct from the BCM2835 chip
- ^ a b Direct from the BCM2837B0 chip
- ^ via on-board 3-port USB hub; one USB port internally connected to the Ethernet port.
- ^ via on-board 5-port USB hub; one USB port internally connected to the Ethernet port.
- ^ for raw LCD panels
- ^ a b Excluding protruding connectors
- ^ Same as HAT board.
Simplified Model B changelog
[edit]| Model | Gen | Variant | Year | SoC | Clockspeed | Cores / Threads |
64-bit | GFLOPS | RAM (GB) |
Video Output |
4K Ready |
USB | Alt Boot |
Ethernet (Max. Gbit/s) |
Wi-Fi | BT | Power Source | MSRP (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPi 1 Model B | 1B | (256 MB) | 2012 | BCM2835 | 0.7 GHz | 1/1 | 0.213 | 0.25 | HDMI1.3 Composite |
2 × USB2.0 | 0.1 | Micro-USB | $35 | |||||
| RPi 1 Model B | (512 MB) | 0.5 | ||||||||||||||||
| RPi 1 Model B+ | 1B+ | 2014 | 4 × USB2.0 | $25 | ||||||||||||||
| RPi 2 Model B | 2B | 2015 | BCM2836 | 0.9 GHz | 4/4 | 1.47 | 1 | HDMI1.3 | $35 | |||||||||
| RPi 2 Model B v1.2 | v1.2 | 2016 | BCM2837 | ✔ | 4.43 | |||||||||||||
| RPi 3 Model B | 3B | 1.2 GHz | ✔ | 3.62 | USB Network (through OTP bit setting) |
b/g/n single-band
(2.4 GHz only) |
4.1 BLE | |||||||||||
| RPi 3 Model B+ | 3B+ | 2018 | BCM2837B0 | 1.4 GHz | ✔ | 5.3 | USB Network |
0.35 | b/g/n/ac dual-band
|
4.2 LS BLE | ||||||||
| RPi 4 Model B | 4B | (1 GB) | 2019 | BCM2711 | 1.5 GHz/1.8 GHz | ✔ | 9.92 | 2 × Micro-HDMI2.0 | ✔ | 2 × USB2.0 2 × USB3.0 |
1.0 | 5.0 | USB-C | |||||
| RPi 4 Model B | (2 GB) | ✔ | 2 | ✔ | $35 from $45
| |||||||||||||
| RPi 4 Model B | (4 GB) | ✔ | 13.5 | 4 | ✔ | $55 | ||||||||||||
| RPi 4 Model B | (8 GB) | 2020 | ✔ | 8 | ✔ | $75 | ||||||||||||
| RPi 5 | 5B | (2 GB) | 2024 | BCM2712D0 | 2.4 GHz | ✔ | 2 | ✔ | $50 | |||||||||
| RPi 5 | (4 GB) | 2023 | BCM2712 | ✔ | 4 | ✔ | $60 | |||||||||||
| RPi 5 | (8 GB) | ✔ | 8 | ✔ | $80 | |||||||||||||
| RPi 5 | (16 GB) | 2025 | BCM2712D0 | ✔ | 16 | ✔ | $120 |
Software
[edit]Operating systems
[edit]
Raspberry Pi provides Raspberry Pi OS (formerly called Raspbian), a Debian-based Linux distribution for download, as well as third-party Ubuntu, Windows 10 IoT Core, RISC OS, LibreELEC (specialised media centre distribution) and specialised distributions for the Kodi media centre and classroom management.[186] It promotes Python and Scratch as the main programming languages, with support for many other languages.[187] The default firmware is closed source, while unofficial open source firmware is available.[188][189][190] Many other operating systems can also run on the Raspberry Pi. The formally verified microkernel seL4 is also supported.[191] There are several ways of installing multiple operating systems on one mSD card.[192]
- Other operating systems (not Linux- nor BSD-based)
- Broadcom VCOS – Proprietary operating system which includes an abstraction layer designed to integrate with existing kernels, such as ThreadX (which is used on the VideoCore4 processor), providing drivers and middleware for application development. In the case of the Raspberry Pi, this includes an application to start the ARM processor(s) and provide the publicly documented API over a mailbox interface, serving as its firmware. An incomplete source of a Linux port of VCOS is available as part of the reference graphics driver published by Broadcom.[193]
- Haiku – an open source BeOS clone that has been compiled for the Raspberry Pi and several other ARM boards.[194] Work on Pi 1 began in 2011, but only the Pi 2 will be supported.[195]
- HelenOS – a portable microkernel-based multiserver operating system; has basic Raspberry Pi support since version 0.6.0[196]
- Plan 9 from Bell Labs[197][198] and Inferno[199] (in beta)
- QNX
- RISC OS Pi (a cut-down version of RISC OS Pico, for 16 MB cards and larger for all models of Pi 1 & 2, has also been made available)
- Ultibo Core – OS-less unikernel Run Time Library based on Free Pascal. Lazarus IDE (Windows with 3rd party ports to Linux and MacOS). Most Pi models supported.[200]
- Windows 10 IoT Core – a zero-price edition of Windows 10 offered by Microsoft that runs natively on the Raspberry Pi 2.[201]
- Other operating systems (Linux-based)
- Alpine Linux – a Linux distribution based on musl and BusyBox, "designed for power users who appreciate security, simplicity and resource efficiency".[202]
- Android is available for non-commercial use from KonstaKANG[203]
- Arch Linux ARM – a port of Arch Linux for ARM processors; the Arch-based Manjaro is also available for ARM
- arkOS – designed for website and email self-hosting
- CentOS for Raspberry Pi 2 and later
- Devuan
- emteria.OS – an embedded, managed version of the Android operating system for professional fleet management
- Fedora (supports Pi 2 and later since Fedora 25, Pi 1 is supported by some unofficial derivatives) and RedSleeve (a RHEL port) for Raspberry Pi 1
- Gentoo Linux[204]
- Kali Linux – a Debian-derived distribution designed for digital forensics and penetration testing
- MX Linux – based on Debian Stable and including antiX components, this OS is available in Xfce, from which KDE and Fluxbox versions can be produced
- openSUSE,[205] SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP2[206] and Server 12 SP3 (commercial support)[206]
- OpenWrt – a highly extensible Linux distribution for embedded devices (typically wireless routers). It supports Pi 1, 2, 3, 4 and Zero W.[207]
- Pop!_PI for Raspberry Pi 4 is a distribution of Pop!_OS 22.04[208]
- postmarketOS – distribution based on Alpine Linux, primarily developed for smartphones
- RetroPie – an offshoot of Raspbian OS that uses Emulation Station as its frontend for RetroArch and other emulators like Mupen64 for retro gaming.[209] Hardware like Freeplay tech can help replace Game boy internals with RetroPie emulation.[210]
- NixOS – a Linux distribution based on the purely functional package management system Nix. NixOS is composed using modules and packages defined in the Nixpkgs project.[211]
- Rocky Linux[212]
- Sailfish OS with Raspberry Pi 2 (due to use ARM Cortex-A7 CPU; Raspberry Pi 1 uses different ARMv6 architecture and Sailfish requires ARMv7.)[213]
- Slackware ARM – version 13.37 and later runs on the Raspberry Pi without modification.[214][215][216][217] The 128–496 MB of available memory on the Raspberry Pi is at least twice the minimum requirement of 64 MB needed to run Slackware Linux on an ARM or i386 system.[218] (Whereas the majority of Linux systems boot into a graphical user interface, Slackware's default user environment is the textual shell / command line interface.[219]) The Fluxbox window manager running under the X Window System requires an additional 48 MB of RAM.[220]
- SolydXK – a light Debian-derived distro with Xfce
- Tiny Core Linux – a minimal Linux operating system focused on providing a base system using BusyBox and FLTK. Designed to run primarily in RAM.
- Tizen – a Linux-based mobile operating system that was backed by the Linux Foundation and was mainly developed and primarily used by Samsung
- Trisquel, a fully free GNU/Linux distribution[221]
- Linux Q83 is a fast, secure, and innovative Linux distribution
- Ubuntu-based: Lubuntu[222] and Xubuntu[222]
- Void Linux – a rolling release Linux distribution which was designed and implemented from scratch, provides images based on musl or glibc
- webOS Open Source Edition – an open source version of webOS
- Other operating systems (BSD-based)
Driver APIs
[edit]
Raspberry Pi can use a VideoCore IV GPU via a binary blob, which is loaded into the GPU at boot time from the SD-card, and additional software, that initially was closed source.[226] This part of the driver code was later released.[227] However, much of the actual driver work is done using the closed source GPU code. Application software makes calls to closed source run-time libraries (OpenMAX IL, OpenGL ES or OpenVG), which in turn call an open source driver inside the Linux kernel, which then calls the closed source VideoCore IV GPU driver code. The API of the kernel driver is specific for these closed libraries. Video applications use OpenMAX IL, 3D applications use OpenGL ES and 2D applications use OpenVG, which both in turn use EGL. OpenMAX IL and EGL use the open source kernel driver in turn.[228]
Vulkan driver
[edit]Raspberry Pi first announced it was working on a Vulkan driver in February 2020.[229] A working Vulkan driver running Quake 3 at 100 frames per second on a 3B+ was revealed by a graphics engineer who had been working on it as a hobby project on 20 June.[230] On 24 November 2020 Raspberry Pi announced that their driver for the Raspberry Pi 4 is Vulkan 1.0 conformant.[231] Raspberry Pi Trading announced further driver conformance for Vulkan 1.1 and 1.2 on 26 October 2021[232] and 1 August 2022.[233]
Firmware
[edit]The official firmware is a freely redistributable[234] binary blob, that is proprietary software.[194] A minimal proof-of-concept open source firmware is also available, mainly aimed at initialising and starting the ARM cores as well as performing minimal startup that is required on the ARM side. It is also capable of booting a very minimal Linux kernel, with patches to remove the dependency on the mailbox interface being responsive. It is known to work on Raspberry Pi 1, 2 and 3, as well as some variants of Raspberry Pi Zero.[235]
Third-party application software
[edit]- AstroPrint – AstroPrint's wireless 3D printing software can be run on the Pi 2.[236]
- C/C++ Interpreter Ch – Released 3 January 2017, C/C++ interpreter Ch and Embedded Ch are released free for non-commercial use for Raspberry Pi, ChIDE is also included for the beginners to learn C/C++.[237]
- Minecraft (Pi edition) – Released 11 February 2013 and support ended on 24 January 2016, a modified version that allows players to directly alter the world with computer code.[238]
- RealVNC – Since 28 September 2016, Raspbian includes RealVNC's remote access server and viewer software.[239][240][241] This includes a new capture technology which allows directly rendered content (e.g. Minecraft, camera preview and omxplayer) as well as non-X11 applications to be viewed and controlled remotely.[242][243]
- Steam Link – On 13 December 2018, Valve released official Steam Link game streaming client for the Raspberry Pi 3 and 3 B+.[244][245]
- UserGate Web Filter – On 20 September 2013, Florida-based security vendor Entensys announced porting UserGate Web Filter to Raspberry Pi platform.[246]
Software development tools
[edit]- Algoid – for teaching programming to children and beginners.
- Arduino IDE – for programming an Arduino.
- BlueJ – for teaching Java to beginners.
- C-STEM Studio – a platform for hands-on integrated learning of computing, science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (C-STEM) with robotics.
- CircuitPython - an educational fork of MicroPython for microcontrollers and single-board computers
- Erlang – a functional language for building concurrent systems with light-weight processes and message passing.
- Greenfoot – Greenfoot teaches object orientation with Java. Create 'actors' which live in 'worlds' to build games, simulations, and other graphical programs.
- Julia – an interactive and cross-platform programming language/environment, that runs on the Pi 1 and later.[247] IDEs for Julia, such as Visual Studio Code, are available. See also Pi-specific GitHub repository JuliaBerry.
- LabVIEW Community Edition – a system-design platform and development environment for a visual programming language from National Instruments.
- Mathematica – a powerful multi-paradigm mathematical programming environment and kernel.[248]
- Lazarus[249] – a Free Pascal RAD IDE
- LiveCode – an educational RAD IDE descended from HyperCard using English-like language to write event-handlers for WYSIWYG widgets runnable on desktop, mobile and Raspberry Pi platforms.
- Ninja-IDE – a cross-platform integrated development environment (IDE) for Python.
- Processing – an IDE built for the electronic arts, new media art, and visual design communities with the purpose of teaching the fundamentals of computer programming in a visual context.
- Scratch – a cross-platform teaching IDE using visual blocks that stack like Lego blocks, originally developed by MIT's Life Long Kindergarten group. The Pi version is heavily optimized[250] for the limited computer resources available and is implemented in the Squeak Smalltalk system.
- Squeak Smalltalk – a full-scale open Smalltalk.
- TensorFlow – an artificial intelligence framework developed by Google. Raspberry Pi worked with Google to simplify the installation process through pre-built binaries.[251]
- Thonny – a Python IDE for beginners.
- V-Play Game Engine – a cross-platform development framework that supports mobile game and app development with the V-Play Game Engine, V-Play apps, and V-Play plugins.
- Xojo – a cross-platform RAD tool that can create desktop, web and console apps for Pi 2 and Pi 3.
Accessories
[edit]



- Gertboard – A Raspberry Pi-sanctioned device, designed for educational purposes, that expands the Raspberry Pi's GPIO pins to allow interface with and control of LEDs, switches, analogue signals, sensors and other devices. It may include an optional Arduino-compatible controller to interface with the Pi.[252]
- Camera – In May 2013, Raspberry Pi and their distributors RS Components and Premier Farnell/Element 14 launched the Raspberry Pi Camera alongside a firmware update to accommodate it.[253] The camera has a flexible flat cable that plugs into the CSI connector, between the Ethernet and HDMI ports. In Raspbian, the user must enable the use of the camera board by running Raspi-config and selecting the camera option. The camera module costs €20 in Europe (9 September 2013).[254] It uses the OmniVision OV5647 image sensor and can produce 1080p, 720p and 640x480p video. The dimensions are 25 mm × 20 mm × 9 mm.[254] In May 2016, v2 of the camera was launched: it is an 8-megapixel camera using a Sony IMX219.[255] In January 2023, v3 of the camera was launched: it is a 12-megapixel camera using a Sony IMX708.[256]
- Infrared camera – In October 2013, Raspberry Pi announced that they would begin producing a camera module without an infrared filter, called the Pi NoIR.[257]
- Official display – In September 2015, Raspberry Pi and their distributors RS Components and Premier Farnell/Element 14 launched the Raspberry Pi Touch Display[258]
- HAT (Hardware Attached on Top) expansion boards – Together with the Model B+, inspired by Arduino shield boards, the interface for HAT boards was devised by Raspberry Pi. Each HAT board carries a small EEPROM (typically a CAT24C32WI-GT3)[259] containing the relevant details of the board,[260] so that the Raspberry Pi's OS is informed of the HAT, and the technical details of it.[261] Mechanical details of a HAT board, which uses the four mounting holes in their rectangular formation, are available online.[262]
- High quality camera – In May 2020, the 12.3-megapixel Sony IMX477 Exmor sensor camera module was released with support for C- and CS-mount lenses.[263] The unit initially retailed for US$50, with interchangeable lenses starting at US$25.
Vulnerability to flashes of light
[edit]In February 2015, a switched-mode power supply chip, designated U16, of the Raspberry Pi 2 Model B version 1.1 (the initially released version) was found to be vulnerable to flashes of light,[264] particularly the light from xenon camera flashes and green[265] and red laser pointers. The U16 chip has WL-CSP packaging, which exposes the bare silicon die. The Raspberry Pi Foundation blog recommended covering U16 with opaque material (such as Sugru or Blu-Tak) or putting the Raspberry Pi 2 in a case.[266][265] This issue was not discovered before the release of the Raspberry Pi 2 because it is not standard or common practice to test susceptibility to optical interference,[264] while commercial electronic devices are routinely subjected to tests of susceptibility to radio interference.
Reception and use
[edit]
Technology writer Glyn Moody described the project in May 2011 as a "potential BBC Micro 2.0", not by replacing PC compatible machines but by supplementing them.[267] In March 2012 Stephen Pritchard echoed the BBC Micro successor sentiment in ITPRO.[268] Alex Hope, co-author of the Next Gen report, is hopeful that the computer will engage children with the excitement of programming.[269] Co-author Ian Livingstone suggested that the BBC could be involved in building support for the device, possibly branding it as the BBC Nano.[270] The Centre for Computing History strongly supports the Raspberry Pi project, feeling that it could "usher in a new era".[271] Before release, the board was showcased by ARM's CEO Warren East at an event in Cambridge outlining Google's ideas to improve UK science and technology education.[272]
Harry Fairhead, however, suggests that more emphasis should be put on improving the educational software available on existing hardware, using tools such as Google App Inventor to return programming to schools, rather than adding new hardware choices.[273] Simon Rockman, writing in a ZDNet blog, was of the opinion that teens will have "better things to do", despite what happened in the 1980s.[274]
In October 2012, the Raspberry Pi won T3's Innovation of the Year award,[275] and futurist Mark Pesce cited a (borrowed) Raspberry Pi as the inspiration for his ambient device project MooresCloud.[276] In October 2012, the British Computer Society responded to the announcement of enhanced specifications by stating, "it's definitely something we'll want to sink our teeth into."[277]
In June 2017, Raspberry Pi won the Royal Academy of Engineering MacRobert Award.[278] The citation for the award to the Raspberry Pi said it was "for its inexpensive credit card-sized microcomputers, which are redefining how people engage with computing, inspiring students to learn coding and computer science and providing innovative control solutions for industry."[279]
Clusters of hundreds of Raspberry Pis have been used for testing programs destined for supercomputers.[280]
Community
[edit]The Raspberry Pi community was described by Jamie Ayre of FOSS software company AdaCore as one of the most exciting parts of the project.[281] Community blogger Russell Davis said that the community strength allows the Foundation to concentrate on documentation and teaching.[281] The community developed a fanzine around the platform called The MagPi[282] which in 2015, was handed over to Raspberry Pi (Trading) Ltd by its volunteers to be continued in-house.[283] A series of community Raspberry Jam events have been held across the UK and around the world.[284]
Education
[edit]As of January 2012[update], enquiries about the board in the United Kingdom have been received from schools in both the state and private sectors, with around five times as much interest from the latter. It is hoped that businesses will sponsor purchases for less advantaged schools.[285] The CEO of Premier Farnell said that the government of a country in the Middle East has expressed interest in providing a board to every schoolgirl, to enhance her employment prospects.[286][287]
In 2014, the Raspberry Pi Foundation hired a number of its community members including ex-teachers and software developers to launch a set of free learning resources for its website.[288] The Foundation also started a teacher training course called Picademy with the aim of helping teachers prepare for teaching the new computing curriculum using the Raspberry Pi in the classroom.[289]
In 2018, NASA launched the JPL Open Source Rover Project, which is a scaled down version of Curiosity rover and uses a Raspberry Pi as the control module, to encourage students and hobbyists to get involved in mechanical, software, electronics, and robotics engineering.[290]
Home automation
[edit]There are a number of developers and applications that are using the Raspberry Pi for home automation. These programmers are making an effort to modify the Raspberry Pi into a cost-affordable solution in energy monitoring and power consumption. Because of the relatively low cost of the Raspberry Pi, this has become a popular and economical alternative to the more expensive commercial solutions.[citation needed]
Industrial automation
[edit]

In June 2014, Polish industrial automation manufacturer TECHBASE released ModBerry, an industrial computer based on the Raspberry Pi Compute Module. The device has a number of interfaces, most notably RS-485/232 serial ports, digital and analogue inputs/outputs, CAN and economical 1-Wire buses, all of which are widely used in the automation industry. The design allows the use of the Compute Module in harsh industrial environments, leading to the conclusion that the Raspberry Pi is no longer limited to home and science projects, but can be widely used as an Industrial IoT solution and achieve goals of Industry 4.0.[291]
In March 2018, SUSE announced commercial support for SUSE Linux Enterprise on the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B to support a number of undisclosed customers implementing industrial monitoring with the Raspberry Pi.[292]
In January 2021, TECHBASE announced a Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4 cluster for AI accelerator, routing and file server use. The device contains one or more standard Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4s in an industrial DIN rail housing, with some versions containing one or more Coral Edge tensor processing units.[293]
Commercial products
[edit]The Organelle is a portable synthesiser, a sampler, a sequencer, and an effects processor designed and assembled by Critter & Guitari. It incorporates a Raspberry Pi computer module running Linux.[294]
OTTO is a digital camera created by Next Thing Co. It incorporates a Raspberry Pi Compute Module. It was successfully crowd-funded in a May 2014 Kickstarter campaign.[295]
Slice is a digital media player which also uses a Compute Module as its heart. It was crowd-funded in an August 2014 Kickstarter campaign. The software running on Slice is based on Kodi.[296]
Numerous commercial thin client computer terminals use the Raspberry Pi.[297]
COVID-19 pandemic
[edit]During the COVID-19 pandemic, demand increased primarily due to the increase in remote work, but also because of the use of many Raspberry Pi Zeros in ventilators for COVID-19 patients in countries such as Colombia,[298] which were used to combat strain on the healthcare system. In March 2020, Raspberry Pi sales reached 640,000 units, the second largest month of sales in the company's history.[299]
Astro Pi and Proxima
[edit]A project was launched in December 2014 at an event held by the UK Space Agency. The Astro Pi was an augmented Raspberry Pi that included a sensor hat with a visible light or infrared camera. The Astro Pi competition, called Principia, was officially opened in January and was opened to all primary and secondary school aged children who were residents of the United Kingdom. During his mission, British ESA astronaut Tim Peake deployed the computers on board the International Space Station.[300] He loaded the winning code while in orbit, collected the data generated and then sent this to Earth where it was distributed to the winning teams. Covered themes during the competition included spacecraft sensors, satellite imaging, space measurements, data fusion and space radiation.
The organisations involved in the Astro Pi competition include the UK Space Agency, UKspace, Raspberry Pi, ESERO-UK and ESA.
In 2017, the European Space Agency ran another competition open to all students in the European Union called Proxima. The winning programs were run on the ISS by Thomas Pesquet, a French astronaut.[301] In December 2021, the Dragon 2 spacecraft launched by NASA had a pair of Astro Pi in it.[302]
History
[edit]
The computer is inspired by Acorn's BBC Micro of 1981.[303][304] The Model A, Model B and Model B+ names are references to the original models of the British educational BBC Micro computer, developed by Acorn Computers.[305]
According to Upton, the name "Raspberry Pi" was chosen with "Raspberry" as an ode to a tradition of naming early computer companies after fruit, and "Pi" as a reference to the Python programming language.[306]
In 2006, early concepts of the Raspberry Pi were based on the Atmel ATmega644 microcontroller. Its schematics and PCB layout are publicly available.[307] Foundation trustee Eben Upton assembled a group of teachers, academics and computer enthusiasts to devise a computer to inspire children.[285]
The first ARM prototype version of the computer was mounted in a package the same size as a USB memory stick.[308] It had a USB port on one end and an HDMI port on the other.
The Foundation's goal was to offer two versions, priced at US$25 and $35. They started accepting orders for the higher priced Model B on 29 February 2012,[309] the lower cost Model A on 4 February 2013.[310] and the even lower cost (US$20) A+ on 10 November 2014.[127] On 26 November 2015, the cheapest Raspberry Pi yet, the Raspberry Pi Zero, was launched at US$5 or £4.[311]
Pre-launch
[edit]- July 2011 – Trustee Eben Upton publicly approached the RISC OS Open community in July 2011 to inquire about assistance with a port.[312] Adrian Lees at Broadcom has since worked on the port,[313][314] with his work being cited in a discussion regarding the graphics drivers.[315] This port is now included in NOOBS.
- August 2011 – 50 alpha boards are manufactured. These boards were functionally identical to the planned Model B,[316] but they were physically larger to accommodate debug headers. Demonstrations of the board showed it running the LXDE desktop on Debian, Quake 3 at 1080p,[317] and Full HD MPEG-4 video over HDMI.[318]
- October 2011 – A version of RISC OS 5 was demonstrated in public, and following a year of development the port was released for general consumption in November 2012.[319][320][321][322]
- December 2011 – Twenty-five Model B Beta boards were assembled and tested[323] from one hundred unpopulated PCBs.[324] The component layout of the Beta boards was the same as on production boards. A single error was discovered in the board design where some pins on the CPU were not held high; it was fixed for the first production run.[325] The Beta boards were demonstrated booting Linux, playing a 1080p movie trailer and the Rightware Samurai OpenGL ES benchmark.[326]
- Early 2012 – During the first week of the year, the first 10 boards were put up for auction on eBay.[327][328] One was bought anonymously and donated to the museum at The Centre for Computing History in Cambridge, England.[271][329] The ten boards (with a total retail price of £220) together raised over £16,000,[330] with the last to be auctioned, serial number No. 01, raising £3,500.[331] In advance of the anticipated launch at the end of February 2012, the Foundation's servers struggled to cope with the load placed by watchers repeatedly refreshing their browsers.[332]
Launch
[edit]- 19 February 2012 – The first proof of concept SD card image that could be loaded onto an SD card to produce a preliminary operating system is released. The image was based on Debian 6.0 (Squeeze), with the LXDE desktop and the Midori browser, plus various programming tools. The image also runs on QEMU allowing the Raspberry Pi to be emulated on various other platforms.[333][334]
- 29 February 2012 – Initial sales commence 29 February 2012[335] at 06:00 UTC;. At the same time, it was announced that the model A, originally to have had 128 MB of RAM, was to be upgraded to 256 MB before release.[309] The Foundation's website also announced: "Six years after the project's inception, we're nearly at the end of our first run of development – although it's just the beginning of the Raspberry Pi story."[336] The web-shops of the two licensed manufacturers selling Raspberry Pi's within the United Kingdom, Premier Farnell and RS Components, had their websites stalled by heavy web traffic immediately after the launch (RS Components briefly going down completely).[337][338] Unconfirmed reports suggested that there were over two million expressions of interest or pre-orders.[339] The official Raspberry Pi Twitter account reported that Premier Farnell sold out within a few minutes of the initial launch, while RS Components took over 100,000 pre orders on day one.[309] Manufacturers were reported in March 2012 to be taking a "healthy number" of pre-orders.[281]
- March 2012 – Shipping delays for the first batch were announced in March 2012, as the result of installation of an incorrect Ethernet port,[340][341] but the Foundation expected that manufacturing quantities of future batches could be increased with little difficulty if required.[342] "We have ensured we can get them [the Ethernet connectors with magnetics] in large numbers and Premier Farnell and RS Components [the two distributors] have been fantastic at helping to source components," Upton said. The first batch of 10,000 boards was manufactured in Taiwan and China.[343][344]
- 8 March 2012 – Release Raspberry Pi Fedora Remix, the recommended Linux distribution,[345] developed at Seneca College in Canada.[346]
- March 2012 – The Debian port is initiated by Mike Thompson, former CTO of Atomz. The effort was largely carried out by Thompson and Peter Green, a volunteer Debian developer, with some support from the Foundation, who tested the resulting binaries that the two produced during the early stages (neither Thompson nor Green had physical access to the hardware, as boards were not widely accessible at the time due to demand).[347] While the preliminary proof of concept image distributed by the Foundation before launch was also Debian-based, it differed from Thompson and Green's Raspbian effort in a couple of ways. The POC image was based on then-stable Debian Squeeze, while Raspbian aimed to track then-upcoming Debian Wheezy packages.[334] Aside from the updated packages that would come with the new release, Wheezy was also set to introduce the armhf architecture,[348] which became the raison d'être for the Raspbian effort. The Squeeze-based POC image was limited to the armel architecture, which was, at the time of Squeeze's release, the latest attempt by the Debian project to have Debian run on the newest ARM embedded-application binary interface (EABI).[349] The armhf architecture in Wheezy intended to make Debian run on the ARM VFP hardware floating-point unit, while armel was limited to emulating floating point operations in software.[350][351] Since the Raspberry Pi included a VFP, being able to make use of the hardware unit would result in performance gains and reduced power use for floating point operations.[347] The armhf effort in mainline Debian, however, was orthogonal to the work surrounding the Pi and only intended to allow Debian to run on ARMv7 at a minimum, which would mean the Pi, an ARMv6 device, would not benefit.[348] As a result, Thompson and Green set out to build the 19,000 Debian packages for the device using a custom build cluster.[347]
Post-launch
[edit]- 16 April 2012 – Reports emerge from the first buyers who had received their Raspberry Pi.[352][353]
- 20 April 2012 – The schematics for the Model A and Model B are released.[354]
- 18 May 2012 – The Foundation reported on its blog about a prototype camera module they had tested.[355] The prototype used a 14-megapixel module.
- 22 May 2012 – Over 20,000 units had been shipped.[356]
- July 2012 – Release of Raspbian.[357]
- 16 July 2012 – It was announced that 4,000 units were being manufactured per day, allowing Raspberry Pis to be purchased in bulk.[358][359]
- 24 August 2012 – Hardware accelerated video (H.264) encoding becomes available after it became known that the existing licence also covered encoding. Formerly it was thought that encoding would be added with the release of the announced camera module.[360][361] However, no stable software exists for hardware H.264 encoding.[362] At the same time the Foundation released two additional codecs that can be bought separately, MPEG-2 and Microsoft's VC-1. Also it was announced that the Pi will implement CEC, enabling it to be controlled with the television's remote control.[185]
- 5 September 2012 – The Foundation announced a second revision of the Raspberry Pi Model B.[363] A revision 2.0 board is announced, with a number of minor corrections and improvements.[364]
- 6 September 2012 – Announcement that in future the bulk of Raspberry Pi units would be manufactured in the UK, at Sony's manufacturing facility in Pencoed, Wales. The Foundation estimated that the plant would produce 30,000 units per month, and would create about 30 new jobs.[365][366]
- 15 October 2012 – It is announced that new Raspberry Pi Model Bs are to be fitted with 512 MB instead of 256 MB RAM.[367]
- 24 October 2012 – The Foundation announces that "all of the VideoCore driver code which runs on the ARM" had been released as free software under a BSD-style licence, making it "the first ARM-based multimedia SoC with fully-functional, vendor-provided (as opposed to partial, reverse engineered) fully open-source drivers", although this claim has not been universally accepted.[227] On 28 February 2014, they also announced the release of full documentation for the VideoCore IV graphics core, and a complete source release of the graphics stack under a 3-clause BSD licence[368][369]
- October 2012 – It was reported that some customers of one of the two main distributors had been waiting more than six months for their orders. This was reported to be due to difficulties in sourcing the CPU and conservative sales forecasting by this distributor.[370]
- 17 December 2012 – The Foundation, in collaboration with IndieCity and Velocix, opens the Pi Store, as a "one-stop shop for all your Raspberry Pi (software) needs". Using an application included in Raspbian, users can browse through several categories and download what they want. Software can also be uploaded for moderation and release.[371]
- 3 June 2013 – "New Out of Box Software" or NOOBS is introduced. This makes the Raspberry Pi easier to use by simplifying the installation of an operating system. Instead of using specific software to prepare an SD card, a file is unzipped and the contents copied over to a FAT formatted (4 GB or bigger) SD card. That card can then be booted on the Raspberry Pi and a choice of six operating systems is presented for installation on the card. The system also contains a recovery partition that allows for the quick restoration of the installed OS, tools to modify the config.txt and an online help button and web browser which directs to the Raspberry Pi Forums.[372]
- October 2013 – Raspberry Pi announces that the one millionth Pi had been manufactured in the United Kingdom.[373]
- November 2013: they announce that the two millionth Pi shipped between 24 and 31 October.[374]
- 28 February 2014 – On the day of the second anniversary of the Raspberry Pi, Broadcom, together with Raspberry Pi, announced the release of full documentation for the VideoCore IV graphics core,[clarification needed] and a complete source release of the graphics stack under a 3-clause BSD licence.[368][369]



- 7 April 2014 – The official Raspberry Pi blog announced the Raspberry Pi Compute Module, a device in a 200-pin DDR2 SO-DIMM-configured memory module (though not in any way compatible with such RAM), intended for consumer electronics designers to use as the core of their own products.[140]
- June 2014 – The official Raspberry Pi blog mentioned that the three millionth Pi shipped in early May 2014.[375]
- 14 July 2014 – The official Raspberry Pi blog announced the Raspberry Pi Model B+, "the final evolution of the original Raspberry Pi. For the same price as the original Raspberry Pi model B, but incorporating numerous small improvements people have been asking for".[128]
- 10 November 2014 – The official Raspberry Pi blog announced the Raspberry Pi Model A+.[127] It is the smallest and cheapest (US$20) Raspberry Pi so far and has the same processor and RAM as the Model A. Like the A, it has no Ethernet port, and only one USB port, but does have the other innovations of the B+, like lower power, micro-SD-card slot, and 40-pin HAT compatible GPIO.
- 2 February 2015 – The official Raspberry Pi blog announced the Raspberry Pi 2. Looking like a Model B+, it has a 900 MHz quad-core ARMv7 Cortex-A7 CPU, twice the memory (for a total of 1 GB) and complete compatibility with the original generation of Raspberry Pis.[376]
- 14 May 2015 – The price of Model B+ was decreased from US$35 to $25, purportedly as a "side effect of the production optimizations" from the Pi 2 development.[377] Industry observers have sceptically noted, however, that the price drop appeared to be a direct response to the CHIP, a lower-priced competitor discontinued in April 2017.[378]
- 29 September 2015 – A new version of the Raspbian operating system, based on Debian Jessie, is released.[379]
- 26 November 2015 – Raspberry Pi launched the Raspberry Pi Zero, the smallest and cheapest member of the Raspberry Pi family yet, at 65 mm × 30 mm, and US$5. The Zero is similar to the Model A+ without camera and LCD connectors, while smaller and uses less power. It was given away with the Raspberry Pi magazine Magpi No. 40 that was distributed in the UK and US that day – the MagPi was sold out at almost every retailer internationally due to the freebie.[136]
- 29 February 2016 – Raspberry Pi 3 with a BCM2837 1.2 GHz 64-bit quad processor based on the ARMv8 Cortex-A53, with built-in Wi-Fi BCM43438 802.11n 2.4 GHz and Bluetooth 4.1 Low Energy (BLE). Starting with a 32-bit Raspbian version, with a 64-bit version later to come if "there is value in moving to 64-bit mode". In the same announcement it was said that a new BCM2837 based Compute Module was expected to be introduced a few months later.[87]
- February 2016 – Raspberry Pi announces that they had sold eight million devices (for all models combined), making it the best-selling UK personal computer, ahead of the Amstrad PCW.[380][87] Sales reached ten million in September 2016.[4]
- 25 April 2016 – Raspberry Pi Camera v2.1 announced with 8 Mpixels, in normal and NoIR (can receive IR) versions. The camera uses the Sony IMX219 chip with a resolution of 3280 × 2464. To make use of the new resolution the software has to be updated.[381]
- 10 October 2016 – NEC Display Solutions announces that select models of commercial displays to be released in early 2017 will incorporate a Raspberry Pi 3 Compute Module.[382]
- 14 October 2016 – Raspberry Pi announces their co-operation with NEC Display Solutions. They expect that the Raspberry Pi 3 Compute Module will be available to the general public by the end of 2016.[383]
- 25 November 2016 – 11 million units sold.[384]
- 16 January 2017 – Compute Module 3 and Compute Module 3 Lite are launched.[134]
- 28 February 2017 – Raspberry Pi Zero W with WiFi and Bluetooth via chip scale antennas launched.[42][385]
- 17 August 2017 – The Raspbian operating system is upgraded to a new version, based on Debian Stretch.[386]
- 14 March 2018 – On Pi Day, Raspberry Pi introduced Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ with improvements in the Raspberry PI 3B computers performance, updated version of the Broadcom application processor, better wireless Wi-Fi and Bluetooth performance and addition of the 5 GHz band.[387]
- 15 November 2018 – Raspberry Pi 3 Model A+ launched.[388]
- 28 January 2019 – Compute Module 3+ (CM3+/Lite, CM3+/8 GB, CM3+/16 GB and CM3+/32 GB) launched.[135]
- 24 June 2019 – Raspberry Pi 4 Model B launched,[27] along with a new version of the Raspbian operating system based on Debian Buster.[389]
- 10 December 2019 – 30 million units sold;[390] sales are about 6 million per year.[391][392]
- 28 May 2020 – An 8 GB version of the Raspberry Pi 4 is announced for $75.[101] Raspberry Pi OS is split off from Raspbian, and now includes a beta of a 64-bit version that allows programs to use more than 4 GB of RAM.[393]
- 19 October 2020 – Compute Module 4 launched.[394]
- 2 November 2020 – Raspberry Pi 400 launched. It is a keyboard which incorporates Raspberry Pi 4 into it. GPIO pins of the Raspberry Pi 4 are accessible.[395]
- 21 January 2021 – Raspberry Pi Pico launched. It is the first microcontroller-class product from Raspberry Pi. It is based on RP2040 Microcontroller developed by Raspberry Pi.[48]
- 11 May 2021 – 40 million units sold.[396]
- 21 September 2021 – 42 million units sold.[397]
- 30 October 2021 – Raspberry Pi OS (formerly Raspbian) is updated version 11, based on Debian Bullseye.[398] With this release, the default clock speed for revision 1.4 of the Raspberry Pi 4 is increased to 1.8 GHz.[33]
- 16 November 2021 – 43 million units sold.[399]
- 28 February 2022, exactly 10 years after the first shipment, 46 million units sold.[400]

Sales
[edit]According to Raspberry Pi, more than 5 million Raspberry Pis were sold by February 2015, making it the best-selling British computer.[8] By November 2016 they had sold 11 million units,[384][401] and 12.5 million by March 2017, making it the third best-selling "general purpose computer".[402] In July 2017, sales reached nearly 15 million,[403] climbing to 19 million in March 2018.[25] By December 2019, a total of 30 million devices had been sold.[404][405]
Supply and demand difficulties
[edit]The global chip shortage starting in 2020, as well as an uptake in demand starting in early 2021, notably affected the Raspberry Pi, causing significant availability issues from that time onward.[406] The company explained its approach to the shortages in 2021,[59] and April 2022,[407] explaining that it was prioritising business and industrial customers.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Upton, Liz (30 April 2015). "Windows 10 for IoT". Raspberry Pi.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi hardware". Raspberry Pi.
- ^ a b c d Cooban, Anna (11 June 2024). "Why investors are going gaga over a tiny, $35 computer | CNN Business". CNN. Retrieved 9 March 2025.
- ^ a b "Ten millionth Raspberry Pi, and a new kit – Raspberry Pi". 8 September 2016. Retrieved 9 September 2016.
we've beaten our wildest dreams by three orders of magnitude
- ^ Cellan-Jones, Rory (5 May 2011). "A£15 computer to inspire young programmers". BBC News.
- ^ Price, Peter (3 June 2011). "Can a £15 computer solve the programming gap?". BBC Click. Retrieved 2 July 2011.
- ^ Bush, Steve (25 May 2011). "Dongle computer lets kids discover programming on a TV". Electronics Weekly. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ a b Gibbs, Samuel (18 February 2015). "Raspberry Pi becomes best selling British computer". The Guardian. Retrieved 28 December 2016.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Foundation". Companies House. Retrieved 18 June 2024.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Foundation, registered charity no. 1129409". Charity Commission for England and Wales.
- ^ "About Us". RaspberryPi.org. Archived from the original on 25 April 2014 – via Internet Archive.
- ^ a b "Raspberry Pi Ltd". Companies House. Retrieved 18 June 2024.
- ^ "Eben Upton CBE". Archives of IT. Retrieved 17 November 2020.
- ^ "Register of Charities - The Charity Commission - Raspberry Pi Foundation Charity number: 1129409". Charity Commission for England and Wales. 6 June 2011.
The object of the charity is to further the advancement of education of adults and children, particularly in the field of Computers, Computer Science and related subjects
- ^ Upton, Liz (6 October 2021). "Welcome to our new website!". raspberrypi.com. Retrieved 24 October 2023.
- ^ "London Stock Exchange | London Stock Exchange". www.londonstockexchange.com. Retrieved 11 June 2024.
- ^ Weatherbed, Jess (15 May 2024). "Raspberry Pi prepares to go public and expand its lineup of supercheap computers". The Verge. Retrieved 8 June 2024.
- ^ Pounder, Les (22 May 2024). "$40 million Raspberry Pi IPO is set for June". Tom's Hardware. Retrieved 8 June 2024.
- ^ Kharpal, Arjun (11 June 2024). "Computing firm Raspberry Pi pops 31% in rare London market debut". CNBC. Retrieved 11 June 2024.
- ^ "About Us". sonypencoed.co.uk. Retrieved 27 September 2017.
- ^ Tung, Liam (27 July 2017). "Raspberry Pi: 14 million sold, 10 million made in the UK". ZDNet.
- ^ @chrisfleck (11 May 2021). "Great call with @EbenUpton today. Congrats on 40 Million #RaspberryPi sold! A lot more headed to The enterprise wit…" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ a b "Raspberry Pi 2, Model B V1.2 Technical Specifications" (PDF). RS Components. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 September 2017. Retrieved 20 September 2017.
- ^ "Eben Upton talks Raspberry Pi 3". The MagPi Magazine. 29 February 2016.
- ^ a b c d e Upton, Eben (14 March 2018). "Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ on Sale at $35". Raspberry Pi Blog. Raspberry Pi Foundation. Retrieved 4 May 2018.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi 3 Model A+" (PDF). Raspberry Pi. Retrieved 24 August 2024.
- ^ a b c d Upton, Eben (24 June 2019). "Raspberry Pi 4 on sale now from $35". Raspberry Pi Foundation.
- ^ "Confirmed: Raspberry Pi 4 suffers from significant USB-C design flaw". Android Authority. 10 July 2019.
- ^ "The Raspberry Pi 4 doesn't work with all USB-C cables". TechCrunch. 9 July 2019. Retrieved 2 March 2022.
- ^ "Tested: 10+ Raspberry Pi 4 USB-C Cables That Work". Tom's Hardware. 13 July 2019. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
you'll still need an AC adapter that delivers 5 volts and at least 3 amps of power so, unless you already have one, your best bet might be to buy the official Raspberry Pi 4 power supply, which comes with a built-in cable and goes for $8 to $10.
- ^ Speed, Richard (21 February 2020). "Get in the C: Raspberry Pi 4 can handle a wider range of USB adapters thanks to revised design's silent arrival". The Register.
- ^ "Designing Raspberry Pi 400". Raspberry Pi. 3 November 2020. Retrieved 7 July 2021.
- ^ a b c Upton, Eben (9 November 2021). "Bullseye bonus: 1.8GHz Raspberry Pi 4". Raspberry Pi. Retrieved 14 November 2021.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi 400 Review". TechReportArticles. 4 January 2021. Archived from the original on 5 January 2021. Retrieved 5 January 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Upton, Eben (28 September 2023). "Introducing: Raspberry Pi 5!". Raspberry Pi. Retrieved 28 September 2023.
- ^ Rudra, Sourav (29 September 2023). "Wow! Raspberry Pi 5 Already Sounds Like a Tinkerer's Favorite!". itsfoss.com. Retrieved 29 September 2023.
- ^ Humphries, Matthew (28 September 2023). "Raspberry Pi 5 Arrives in October With a Huge Performance Boost". PC Mag. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Roth, Emma (19 August 2024). "Raspberry Pi 5 gets a cheaper 2GB option". The Verge. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Dillet, Romain (9 December 2024). "It's a Raspberry Pi 5 in a keyboard, and it's called the Raspberry Pi 500". TechCrunch. Retrieved 9 December 2024.
- ^ Pounder, Les (9 December 2024). "Raspberry Pi 500 Review: The keyboard is the computer, again". Tom's Hardware. Retrieved 9 December 2024.
- ^ Upton, Eben (16 May 2016). "Zero grows a camera connector". Raspberry Pi. Retrieved 31 July 2022.
- ^ a b "New $10 Raspberry Pi Zero comes with Wi-Fi and Bluetooth". arstechnica.com. 28 February 2017.
- ^ "The $10 Raspberry Pi Zero W brings Wi-Fi and Bluetooth to the minuscule micro". PC World. Retrieved 28 February 2017.
- ^ Bate, Alex (12 January 2018). "Zero WH: Pre-soldered headers and what to do with them". Raspberry Pi Foundation.
- ^ a b Upton, Eben (28 October 2021). "New product: Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W on sale now at $15". Raspberry Pi Foundation.
- ^ Campbell, Ian (21 January 2021). "The Raspberry Pi Pico is a tiny $4 microcontroller running off the company's very own chip". the verge. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ^ Foundation, The Raspberry Pi. "Raspberry Pi Pico specifications". Raspberry Pi. Retrieved 21 January 2021.
- ^ a b "Meet Raspberry Silicon: Raspberry Pi Pico now on sale at $4". 21 January 2021.
- ^ January 2021, Les Pounder 28 (28 January 2021). "Raspberry Pi Pico vs Arduino: Which Board Is Better?". Tom's Hardware. Retrieved 11 March 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Raspberry Pi Pico W: your $6 IoT platform". Raspberry Pi. Retrieved 30 June 2022.
- ^ Upton, Eben. "Raspberry Pi Pico 2, our new $5 microcontroller board, on sale now". Raspberry Pi (Press release). Retrieved 8 August 2024.
- ^ Dillet, Romain (25 November 2024). "Raspberry Pi releases the Pico 2 W, a $7 wireless-enabled microcontroller board". TechCrunch. Retrieved 25 November 2024.
- ^ a b "Model B Now Ships with 512MB of RAM". Raspberry Pi Blog. 15 October 2012. Retrieved 31 May 2020.
- ^ Upton, Eben (28 October 2021). "New product: Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W on sale now at $15". Raspberry Pi Trading. Retrieved 2 December 2021.
Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W uses the same Broadcom BCM2710A1 SoC die as the launch version of Raspberry Pi 3
- ^ Les Pounder (14 July 2021). "Raspberry Pi 4A Could Skip USB 3, Have PCIe Port". Tom's Hardware. Retrieved 20 August 2024.
- ^ Aufranc (CNXSoft), Jean-Luc (2 November 2020). "Raspberry Pi 400 Keyboard Computer Features 1.8 GHz BCM2711C0 Processor - CNX Software". CNX Software - Embedded Systems News. Retrieved 14 October 2023.
- ^ a b Nick Heath (23 June 2019). "Raspberry Pi 4 Model B review: This board really can replace your PC". TechRepublic. Retrieved 24 June 2019.
- ^ a b c Halfacree, Gareth (March 2020). "Raspberry Pi 4 now comes with 2GB RAM Minimum". The MagPi. No. 91. Raspberry Pi Press. p. 6. Retrieved 28 May 2020.
we say farewell to the 1GB model
- ^ a b c "Supply chain, shortages, and our first-ever price increase". Rapsberry Pi. 20 October 2021.
- ^ Upton, Liz (1 October 2023), Re: What is the full name of the new Raspberry Pi 5 model?, Raspberry Pi Ltd, retrieved 3 October 2023
- ^ "Raspberry Pi 5 16GB Model Launches For $120 USD". www.phoronix.com. Retrieved 11 February 2025.
- ^ Cunningham, Andrew (9 December 2024). "Raspberry Pi 500 makes an 8GB Pi 5 into a compact, inexpensive desktop PC". Ars Technica. Retrieved 11 February 2025.
- ^ Khaliq, Azzief (27 April 2024). "The Evolution Of Raspberry Pi: From Prototype To Single-Board Computing Workhorse". SlashGear. Retrieved 26 November 2024.
- ^ "Flashing the Compute Module eMMC – Raspberry Pi Documentation". www.raspberrypi.org. Retrieved 14 July 2021.
- ^ "I'm booting my Raspberry Pi 4 from a USB SSD | Jeff Geerling". www.jeffgeerling.com. Retrieved 14 July 2021.
- ^ Team, Device Plus Editorial (15 September 2016). "Raspberry Pi 3 Model B WiFi & Bluetooth Setup". Device Plus. Retrieved 17 November 2020.
- ^ a b c d "BCM2835 Media Processor; Broadcom". Broadcom.com. 1 September 2011. Archived from the original on 13 May 2012. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ Brose, Moses (30 January 2012). "Broadcom BCM2835 SoC has the most powerful mobile GPU in the world?". Grand MAX. Archived from the original on 18 February 2012. Retrieved 13 April 2012.
- ^ Shimpi, Anand Lal. "The iPhone 3GS Hardware Exposed & Analyzed". Retrieved 11 October 2018.
- ^ a b c Upton, Eben (2 February 2015). "Raspberry Pi 2 on sale now at $35". Raspberry Pi Foundation. Retrieved 5 August 2015.
- ^ "Buy a Raspberry Pi 3 Model B – Raspberry Pi". raspberrypi.org.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi 3 Model A+"./
- ^ "Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+"./
- ^ "Raspberry Pi 4 Model B specifications". Retrieved 28 June 2019.
- ^ Merten, Dr. Maik (14 September 2019). "Raspi-Kernschau – Das Prozessor-Innenleben des Raspberry Pi 4 im Detail" [Raspi-kernel-show – The inner life of the Raspberry Pi 4 processor in detail]. C't (in German). 2019 (20): 164–169.
- ^ "22. Raspberry Pi 4 — Trusted Firmware-A documentation". trustedfirmware-a.readthedocs.io. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ "Playing with a Raspberry Pi 4 64-bit | CloudKernels". blog.cloudkernels.net. 10 July 2019. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ a b "Raspberry Pi Zero". Retrieved 16 April 2019.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Documentation - Processors". www.raspberrypi.com. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W Product Brief" (PDF). Raspberry Pi Datasheets. October 2021. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "Pico Product Brief" (PDF). Raspberry Pi Datasheets. July 2022. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "RP2040 Datasheet" (PDF). Raspberry Pi Datasheets. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi 5 Product Brief" (PDF). Raspberry Pi. September 2023. Retrieved 2 October 2023.
- ^ "Performance – measures of the Raspberry Pi's performance". RPi Performance. eLinux.org. Retrieved 30 March 2014.
- ^ Benchoff, Brian (12 September 2012). "64 Rasberry Pis turned into a supercomputer". Hackaday. Retrieved 30 March 2014.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi2 – Power and Performance Measurement". RasPi.TV. 3 February 2015. Retrieved 6 July 2016.
- ^ a b c d Upton, Eben (29 February 2016). "Raspberry Pi 3 on sale now at $35". Raspberry Pi. Retrieved 29 February 2016.
- ^ "How Much Power Does Raspberry Pi3B Use? How Fast Is It Compared To Pi2B?". RasPi.TV. RasPi.TV. 3 March 2016. Retrieved 6 July 2016.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Documentation - The config.txt file". www.raspberrypi.com. Retrieved 24 July 2023.
- ^ a b "Introducing turbo mode: up to 50% more performance for free". Raspberrypi.org. 19 September 2012. Archived from the original on 12 April 2015. Retrieved 20 September 2012.
- ^ "asb/raspi-config on Github". asb. Retrieved 11 May 2017.
- ^ "Configuration: Overclocking options". raspberrypi.org. Retrieved 20 July 2022.
- ^ "I have a Raspberry Pi Beta Board AMA". reddit.com. 15 January 2012. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi boot configuration text file". raspberrypi.org. Archived from the original on 16 March 2012.
- ^ "Nokia 701 has a similar Broadcom GPU". raspberrypi.org. 2 February 2012. Archived from the original on 5 February 2012. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- ^ "introducing new firmware for the 512 MB Pi". 30 October 2012. Archived from the original on 25 March 2014. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi 3 A+ specs". raspberrypi.org. Retrieved 15 October 2019.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi 3 specs". raspberrypi.org. 29 February 2016. Retrieved 1 October 2016.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi 2 specs". raspberrypi.org. Retrieved 1 October 2016.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi 4 specs". raspberrypi.org. Retrieved 25 June 2019.
- ^ a b c d Upton, Eben (28 May 2020). "8GB Raspberry Pi 4 on sale now at $75". Raspberry Pi Blog. Retrieved 28 May 2020.
- ^ a b c "Buy a Raspberry Pi 5". Raspberrypi.com. Retrieved 9 January 2025.
- ^ a b "Microchip/SMSC LAN9514 data sheet;" (PDF). Microchip. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 October 2014. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- ^ "seemoo-lab/nexmon". GitHub. 2 November 2021.
- ^ "USB Gadget mode on new 3 A+? – Raspberry Pi Forums". www.raspberrypi.org.
- ^ a b "Turning your Raspberry PI Zero into a USB Gadget". Adafruit Learning System.
- ^ "USB mass storage device boot – Raspberry Pi Documentation". raspberrypi.org.
- ^ a b c d "Verified USB Peripherals and SDHC Cards;". Elinux.org. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ "GPIO – Raspberry Pi Documentation". raspberrypi.org. Retrieved 2 June 2019.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi, supported video resolutions". eLinux.org. 30 November 2012. Retrieved 11 December 2012.
- ^ "Pi Screen limited to 1920 by RISC OS:-". RISC OS Open. Retrieved 6 January 2016.
2048 × 1152 monitor is the highest resolution the Pi's GPU can handle [presumably with non-low frame-rate ..] The monitors screen info confirms the GPU is outputting 2048×1152
- ^ "RISC OS Open: Forum: Latest Pi firmware?". riscosopen.org.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi and 4k @ 15Hz". Retrieved 6 January 2016.
I have managed to get 3840 x 2160 (4k x 2k) at 15Hz on a Seiki E50UY04 working
- ^ Aufranc, Jean-Luc (24 June 2019). "Raspberry Pi 4 Benchmarks & Mini Review". www.cnx-software.com. Retrieved 2 January 2021.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi 3 announced with OSMC support". 28 February 2016.
- ^ articles with bare URLs for citations[permanent dead link]
- ^ Ozolins, Jason. "examples of Raspberry Pi composite output". Raspberrypi.org. Archived from the original on 13 January 2013. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- ^ Shovic, John (July 2014). "Keeping Time". Raspberry Pi Geek Magazine. Retrieved 30 July 2020.
- ^ Shovic, John (August 2014). "In Time". Raspberry Pi Geek Magazine. Retrieved 30 July 2020.
- ^ Adams, James (28 July 2014). "Raspberry Pi B+ (Reduced Schematics) 1.2" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 July 2014.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Rev 1.0 Model AB schematics" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 August 2014.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Rev 2.0 Model AB schematics" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 August 2014.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Rev 2.1 Model AB schematics" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 August 2014.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Rev 1.0 Model AB schematics" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 August 2014.
- ^ Upton, Eben (5 September 2012). "Upcoming board revision". Retrieved 2 June 2019.
- ^ a b "Model A now for sale in Europe – buy one today!". Raspberry Pi Foundation. 4 February 2013. Retrieved 25 February 2017.
- ^ a b c d "RASPBERRY PI MODEL A+ ON SALE NOW AT $20". Raspberry Pi Foundation. 10 November 2014. Archived from the original on 10 November 2014. Retrieved 10 November 2014.
- ^ a b c d "Introducing Raspberry Pi Model B+". Raspberry Pi Foundation. 14 July 2014. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 14 July 2014.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi2 Model B v1.2" (PDF). Farnell.com. Retrieved 2 March 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g Amadeo, Ron (24 June 2019). "The Raspberry Pi 4 brings faster CPU, up to 4 GB of RAM". Ars Technica. Retrieved 24 June 2019.
- ^ a b Upton, Eben (19 August 2024). "2GB Raspberry Pi 5 on sale now at $50". Raspberry Pi. Retrieved 11 February 2025.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi gets more Arduino-y with new open source modular hardware". Ars Technica. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
- ^ Brodkin, Jon (16 January 2017). "Raspberry Pi upgrades Compute Module with 10 times the CPU performance". Ars Technica. Retrieved 16 January 2017.
- ^ a b Compute Module 3 Launch, Raspberry Pi Foundation, 16 January 2017
- ^ a b Adams, James (28 January 2019). "Compute Module 3+ on sale now from $25". raspberrypi.org. Retrieved 29 January 2019.
- ^ a b c d "Raspberry Pi Zero: the $5 Computer". Raspberry Pi Foundation. 26 November 2015. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- ^ Bowater, Donna (29 February 2012). "Mini Raspberry Pi computer goes on sale for £22". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 11 January 2022.
- ^ Upton, Eben (14 May 2015). "Price Cut! Raspberry Pi Model B+ Now Only $25".
- ^ Avram Piltch (23 October 2023). "Where to Buy a Raspberry Pi 5 in the U.S or UK". Tom's Hardware. Retrieved 15 December 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Raspberry Pi Compute Module: New Product!". Raspberry Pi Foundation. Archived from the original on 21 September 2014. Retrieved 22 September 2014.
- ^ "Cortex-A53". developer.arm.com. Retrieved 18 December 2024.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Documentation - RP2040". www.raspberrypi.com. Retrieved 28 September 2023.
- ^ a b c d "Broadcom 2835 SoC - Raspberry Pi Forums". forums.raspberrypi.com. Retrieved 28 September 2023.
- ^ a b c "BCM2837 datasheet? - Raspberry Pi Forums". forums.raspberrypi.com. Retrieved 28 September 2023.
- ^ "Are the 2836 and the 2837 made in different nm? - Raspberry Pi Forums". forums.raspberrypi.com. Retrieved 28 September 2023.
- ^ a b c ""Buy a Raspberry 5 - Specifications"". raspberrypi.com. Archived from the original on 4 September 2024.
- ^ a b "Raspberry Pi 4 specs and benchmarks". The MagPi Magazine. 24 June 2019. Retrieved 24 June 2019.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi revision codes". Raspberry Pi Documentation. 28 May 2020. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Modal A+ 512MB RAM". Adafruit. 10 August 2016. Retrieved 31 May 2020.
- ^ a b "SMSC LAN9512 Website;". Smsc.com. Archived from the original on 10 May 2013. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ "Very simple OTG on pi4 – Raspberry Pi Forums". www.raspberrypi.org.
- ^ "diagram of Raspberry Pi with CSI camera connector". Elinux.org. 2 March 2012. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Documentation - Raspberry Pi 5". Raspberry Pi Foundation. Retrieved 3 February 2024.
- ^ a b Adams, James (3 April 2014). "Raspberry Pi Compute Module electrical schematic diagram" (PDF). Raspberry Pi Foundation. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 May 2014. Retrieved 22 September 2014.
- ^ a b Adams, James (3 April 2014). "Raspberry Pi Compute Module IO Board electrical schematic diagram" (PDF). Raspberry Pi Foundation. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 May 2014. Retrieved 22 September 2014.
- ^ Upton, Eben (16 May 2016). "zero grows camera connector". Raspberry Pi Foundation. Retrieved 17 May 2016.
- ^ Adams, James (7 April 2014). "Comment by James Adams on Compute Module announcement". Raspberry Pi Foundation. Archived from the original on 21 September 2014. Retrieved 22 September 2014.
- ^ "Pi Zero – The New Raspberry Pi Board • Pi Supply". Pi Supply. 26 November 2015.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Documentation - Raspberry Pi 5 - Attaching cameras". Raspberry Pi Foundation. Retrieved 3 February 2024.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Wiki, section screens". Elinux.org. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ "diagram of Raspberry Pi with DSI LCD connector". Elinux.org. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ "I2S driver development thread". Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ^ "How to boot from a USB Mass Storage Device on a Raspberry Pi 3". Raspberry Pi Documentation.
- ^ a b "Use an Android tablet as a Raspberry Pi Console terminal and Internet router". Elinux.org. Retrieved 2 October 2015.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi 3B+ Specs and Benchmarks – The MagPi Magazine". The MagPi Magazine. 14 March 2018. Retrieved 17 August 2018.
- ^ More GPIOs can be used if the low-level peripherals are unused
- ^ Since the release of the revision 2 model
- ^ a b "Q&A with our hardware team". Raspberry Pi Foundation. Archived from the original on 24 September 2011. Retrieved 20 September 2011.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi GPIO Connector;". Elinux.org. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ Allan, Alasdair (24 June 2019). "Meet the New Raspberry Pi 4, Model B". Hackster Blog. Retrieved 30 June 2019.
- ^ Adams, James (7 April 2014). "Comment by James Adams on Compute Module announcement". Raspberry Pi Foundation. Archived from the original on 21 September 2014. Retrieved 22 September 2014.
- ^ "Power supply confirmed as 5V micro USB". Raspberrypi.org. 20 October 2011. Archived from the original on 1 April 2014. Retrieved 25 July 2012.
- ^ raspi.today. "Features". Raspberry Pi Today. Archived from the original on 27 July 2015.
- ^ a b c d e "Raspberry Pi FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions". Raspberry Pi. Retrieved 30 June 2019.
- ^ "Power Draw". Archived from the original on 15 March 2018. Retrieved 14 March 2018.
- ^ Aufranc, Jean-Luc (9 December 2021). "A deep dive into Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W's power consumption". CNX Software. Retrieved 22 December 2022.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi 3". SocialCompare.
- ^ Piltch, Avram; Halfacree 2019-11-14T19:43:44Z, Gareth. "Raspberry Pi 4 Review: The New Gold Standard for Single-Board Computing". Tom's Hardware. Retrieved 23 December 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Adams, James (7 April 2014). "Comment by James Adams on Compute Module announcement". Raspberry Pi Foundation. Archived from the original on 21 September 2014. Retrieved 22 September 2014.
- ^ "MagPi, issue 40, Raspberry Pi Zero release article" (PDF). Raspberry Pi Foundation. 26 November 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 January 2017. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi USB Serial Connection and power supply". Elinux.org. Retrieved 2 October 2015.
- ^ "Buy a Raspberry Pi 3 Model B". Raspberry Pi Foundation. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- ^ Ltd, Raspberry Pi. "Buy a Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+". Raspberry Pi. Retrieved 1 January 2024.
- ^ Halfacree, Gareth. "Raspberry Pi review". bit-tech.net. Dennis Publishing Limited. Retrieved 10 June 2013.
The Model B
- ^ a b "New video features! MPEG-2 and VC-1 decode, H.264 encode, CEC". Raspberry Pi Foundation. Archived from the original on 25 August 2012. Retrieved 26 August 2012.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Downloads – Software for the Raspberry Pi". Retrieved 12 August 2016.
- ^ "Usage – Raspberry Pi Documentation". raspberrypi.org. Retrieved 12 August 2016.
- ^ "Blobless Linux on Raspberry Pi (rpi-open-firmware)". Archived from the original on 16 January 2017. Retrieved 20 July 2017.
- ^ "christinaa/rpi-open-firmware: Open source VPU side bootloader for Raspberry Pi". GitHub. Retrieved 20 July 2017.
- ^ "Preliminary Open Source Bootloader for Raspberry Pi Boards Released". 16 May 2016. Retrieved 20 July 2017.
- ^ "Supported Platforms". docs.sel4.systems. Retrieved 23 November 2018.
- ^ Cawley, Christian (17 February 2013). "3 Ways to Boot Multiple OSes on a Raspberry Pi". makeuseof.com. Retrieved 2 October 2021.
- ^ "Broadcom releases SoC graphics driver source [LWN.net]". lwn.net.
- ^ a b "Compiling Haiku for Arm". haiku-os.org. Retrieved 30 April 2015.
- ^ "Haiku port status". Haiku Project. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ^ "ReleaseNotes/0.6.0 – HelenOS". helenos.org. Archived from the original on 27 January 2022. Retrieved 12 February 2022.
- ^ Miller, Richard (18 August 2012). "9pi". 9fans.net mail archive. Archived from the original on 12 October 2014.
- ^ Liz (5 December 2012). "Wednesday grab bag". Raspberry Pi. Raspberry Pi Foundation. See the "Plan 9" section.
- ^ "Inferno Raspberry Pi image – beta release (beta1)". lynxline.com. Archived from the original on 24 February 2022. Retrieved 12 February 2022.
- ^ "Ultibo Core". Ultibo.org.
- ^ Sauter, Marc (2 February 2015). "Internet der Dinger: Windows 10 läuft kostenlos auf dem Raspberry Pi 2" [Internet of Things: Windows 10 runs free on the Raspberry Pi 2] (in German). Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "Alpine Linux about". Alpinelinux.org. Retrieved 21 July 2021.
- ^ "Raspberry". konstakang.com. Retrieved 6 May 2024.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi – Gentoo Wiki". Retrieved 20 March 2016.
- ^ "HCL:Raspberry Pi – openSUSE Wiki". en.opensuse.org.
- ^ a b "Linux Enterprise Server on Arm Systems & Raspberry Pi | SUSE". suse.com.[verification needed]
- ^ "OpenWrt Project: Raspberry Pi Foundation". openwrt.org. 16 December 2016. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ "Pop!_OS by System76". Retrieved 15 April 2024.
- ^ "RetroPie". RetroPie. Retrieved 25 August 2020.
- ^ Maker Retro (5 October 2021). "Freeplay GBA retropi, is it worth?". Platformer. Archived from the original on 5 October 2021. Retrieved 5 October 2021.
- ^ "Installing NixOS on a Raspberry Pi". Retrieved 7 December 2023.
- ^ "Alternative Images - Rocky Linux". Retrieved 1 October 2023.
- ^ "Sailfish on a Raspberry Pi". together.jolla.com. Jolla. Retrieved 26 February 2015.
- ^ "SlackwareARM for the Raspberry Pi". Archived from the original on 10 February 2013.
- ^ "ArmedSlack working :)". raspberrypi.org. 18 May 2012.
- ^ "ARMed Slack running on Raspberry Pi". alt.os.linux.slackware. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ^ "raspberrypi.org – ArmedSlack 13.37". Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ^ "The Slackware Linux Project: Installation Help". Slackware.com. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- ^ "Slackware Linux Essentials: The Shell". Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ^ v1.0.2 (en), xiando. "Desktops: KDE vs Gnome". Linux Reviews. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Trisquel GNU/Linux - Run free!". trisquel.info.
- ^ a b Martin Wimpress (29 February 2016). "Ubuntu Pi Flavours for Raspberry Pi 3 are released". Ubuntu Pi Flavour Maker. Archived from the original on 11 November 2017. Retrieved 30 July 2018.
- ^ "arm/Raspberry Pi - FreeBSD Wiki". Wiki.freebsd.org. Archived from the original on 4 July 2024. Retrieved 16 July 2024.
- ^ "NetBSD/evbarm on Raspberry Pi". wiki.netbsd.org.
- ^ "OpenBSD/arm64". openbsd.org.
- ^ djwm (13 September 2011). "Raspberry Pi warms up". The H. Archived from the original on 25 January 2012. Retrieved 12 March 2012.
- ^ a b "Raspberry Pi maker says code for ARM chip is now open source". Ars Technica. 24 October 2012. Retrieved 3 November 2012.
- ^ "Libraries, codecs, OSS". raspberrypi.org. 31 January 2012. Archived from the original on 30 October 2013. Retrieved 12 February 2022.
- ^ February 2020, Nathaniel Mott 03 (3 February 2020). "Raspberry Pi to Get Vulkan Graphics Driver (Eventually)". Tom's Hardware.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ June 2020, Zhiye Liu 20 (20 June 2020). "Nvidia Engineer's Vulkan Driver For Raspberry Pi Runs Quake III Over 100 FPS at 720p". Tom's Hardware.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Vulkan update: we're conformant!". Raspberry Pi Foundation. 24 November 2020.
- ^ "Vulkan update: version 1.1 conformance for Raspberry Pi 4". Raspberry Pi. 26 October 2021. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ^ Upton, Eben (1 August 2022). "Vulkan update: version 1.2 conformance for Raspberry Pi 4". Raspberry Pi. Retrieved 4 August 2022.
- ^ "Hexxeh/rpi-firmware". Github.com. 28 October 2021.
- ^ "christinaa/rpi-open-firmware". Github.com. 3 November 2021.
- ^ Brothers, Ruiz. "WiFi 3D Printing". Learn.adafruit.com. Retrieved 22 September 2015.
- ^ "C/C++ Interpreter Ch 7.5 released for Raspberry Pi, and Pi Zero". Softintegration.com. Archived from the original on 21 April 2022. Retrieved 2 March 2022.
- ^ "Minecraft: Pi Edition – Minecraft: Pi Edition updates and downloads". Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ^ "Introducing PIXEL – Raspberry Pi". Raspberry Pi. 28 September 2016. Retrieved 2 February 2017.
- ^ "RealVNC and Raspberry Pi announce new partnership". Retrieved 2 February 2017.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi | RealVNC". www.realvnc.com. Retrieved 2 February 2017.
- ^ "Minecraft Pi (and more) over VNC – Raspberry Pi". Raspberry Pi. 9 May 2016. Retrieved 2 February 2017.
- ^ "Docs | Using VNC 5.x on the Raspberry Pi | RealVNC". www.realvnc.com. Archived from the original on 3 February 2017. Retrieved 2 February 2017.
- ^ "Steam Link now available on Raspberry Pi :: Steam Link Raspberry Pi". steamcommunity.com. Retrieved 15 December 2018.
- ^ "Valve's Steam Link For Raspberry Pi Now Available – Phoronix". phoronix.com. Retrieved 15 December 2018.
- ^ Pearce, Rohan (20 September 2013). "Entensys builds mini Web filtering appliance with Raspberry Pi". Techworld Australia.
- ^ "Julia Downloads". Retrieved 21 January 2016.
- ^ "Wolfram + Raspberry Pi Project: A Wolfram Engine on Every Raspberry Pi". Retrieved 31 July 2024.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi". 21 January 2016.
- ^ "A NEW VERSION OF SCRATCH FOR RASPBERRY PI: NOW WITH ADDED GPIO". 7 October 2015. Retrieved 5 August 2016.
- ^ Tung, Liam. "Google AI on Raspberry Pi: Now you get official TensorFlow support". ZDNet. Retrieved 6 August 2018.
- ^ "Gertboard is here!". Raspberry Pi Foundation. 8 August 2012. Archived from the original on 10 August 2012. Retrieved 9 August 2012.
- ^ "Elinux Wiki: Description of Raspberry Pi Camera Board". Retrieved 3 September 2013.
- ^ a b "RPI Camera board – Raspberry-Pi – Raspberry Pi Kamera-Board, 5MP" (in German). Farnell. Archived from the original on 9 May 2014. Retrieved 9 June 2013.
- ^ "Camera Documenation". raspberrypi.org. Retrieved 7 December 2020.
- ^ Upton, Eben (9 January 2023). "New autofocus camera modules!". Raspberry Pi. Retrieved 14 January 2023.
- ^ "Pi NoIR". Raspberry Pi Foundation. Retrieved 16 August 2014.
- ^ "The Eagarly awaited Raspberry Pi Display". Raspberry Pi Foundation. 8 September 2015. Retrieved 18 November 2017.
- ^ "hats/eeprom-circuit.png at master · raspberrypi/hats". GitHub. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ^ "hats/eeprom-format.md at master · raspberrypi/hats". GitHub. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ^ "raspberrypi/hats". GitHub. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ^ raspberrypi (November 2021). "hats/hat-board-mechanical.pdf at master · raspberrypi/hats" (PDF). GitHub.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera". Raspberrypi.org. 30 April 2020. Retrieved 1 May 2020.
- ^ a b several authors (7–9 February 2015). "Raspberry Pi Forums: Why is the PI2 camera-shy?". Raspberry Pi Forums. Raspberry Pi Foundation. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ^ a b Benchoff, Brian (8 February 2015). "Photonic Reset of the Raspberry Pi 2". Hackaday. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ Upton, Liz (9 February 2015). "Xenon Death Flash: a free physics lesson". Raspberry Pi. Retrieved 18 January 2022.
- ^ Glyn, Moody (9 May 2011). "As British as Raspberry Pi?". Computerworld UK Open Enterprise blog. Archived from the original on 2 January 2013. Retrieved 2 February 2012.
- ^ Pritchard, Stephen (1 March 2012). "Raspberry Pi: A BBC Micro for today's generation". ITPRO. Retrieved 15 March 2012.
- ^ Stanford, Peter (3 December 2011). "Computing classes don't teach programming skills". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 11 January 2022. Retrieved 27 February 2012.
- ^ Vallance, Chris (10 January 2012). "Raspberry Pi bids for success with classroom coders". BBC News. Retrieved 29 February 2012.
- ^ a b "One of the First Raspberry Pi Computers Donated to Museum". The Centre for Computing History. 9 January 2012. Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ^ Osborn, George (23 February 2012). "How Google can really help improve STEM teaching in the UK". Cabume. Archived from the original on 2 March 2012. Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ^ Fairhead, Harry (2 December 2011). "Raspberry Pi or Programming – What shall we teach the children?". I Programmer. Retrieved 7 February 2012.
- ^ Rockman, Simon (21 February 2012). "Is Raspberry Pi a mid-life crisis?". ZDNet. Retrieved 24 February 2012.
Just because young teens led the way in computing in the 1980s doesn't mean it should, will or can happen again. Those outside the tech age bubble have better things to do.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi – Innovation of the Year". T3 Gadget Awards. Retrieved 9 October 2012.
- ^ "Showtime". Crowdfunding the Light. 5 October 2012. Archived from the original on 9 May 2013. Retrieved 17 April 2013.
- ^ "Latest Raspberry Pi has double the RAM". BCS website. BCS. 16 October 2012. Archived from the original on 14 April 2013. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- ^ "Chips that changed the classroom" Archived 13 August 2018 at the Wayback Machine Ingenia, September 2017
- ^ "The coding revolution marches on: Raspberry Pi wins UK's top engineering innovation prize". Royal Academy of Engineering. Archived from the original on 10 March 2022. Retrieved 2 March 2022.
- ^ "750 Raspberry Pi Boards Used To Create Supercomputer Testbed". Digital Trends. 28 November 2017.
- ^ a b c Bridgwater, Adrian (15 March 2012). "Community strength blossoms for Raspberry Pi". Computer Weekly. Retrieved 15 March 2012.
- ^ "The MagPi – Raspberry Pi online magazine launched". The Digital Lifestyle.com. 6 May 2012. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ^ "All change – meet the new MagPi". Raspberry Pi. 27 February 2015. Archived from the original on 12 March 2015. Retrieved 15 March 2015.
- ^ "Raspberry Jam". Raspberry Pi web. Retrieved 15 March 2015.[permanent dead link]
- ^ a b Moorhead, Joanna (9 January 2012). "Raspberry Pi device will 'reboot computing in schools'". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 20 January 2012.
- ^ Arthur, Charles (5 March 2012). "Raspberry Pi demand running at '700 per second'". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 12 March 2012.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi mini computer sells out after taking 700 orders per second". Digital Trends. Retrieved 9 June 2012.
- ^ Upton, Liz (2 April 2014). "Welcome to our new website". Cambridge: Raspberry Pi Foundation. Archived from the original on 7 April 2015. Retrieved 15 March 2015.
- ^ Philbin, Carrie Anne (17 March 2014). "Picademy – free CPD for teachers". Cambridge: Raspberry Pi Foundation. Retrieved 15 March 2015.
- ^ "nasa-jpl/open-source-rover". GitHub. 3 November 2021.
- ^ "Automation controller taps Raspberry Pi Compute Module". LinuxGizmos.com. 25 June 2014. Retrieved 10 March 2017.
- ^ Kruemcke, Jay (26 March 2018). "A small server for big companies – New Raspberry Pi support in SLES for ARM". SUSE Communities. Retrieved 2 March 2022.
- ^ "ClusBerry 9500-CM4 – A Raspberry Pi CM4 cluster, industrial style". www.cnx-software.com. 18 January 2021. Retrieved 27 January 2021.
- ^ O'Brien, Terrence (8 November 2019). "The Organelle is a music computer that can do almost anything". Engadget. Retrieved 12 December 2020.
- ^ "Meet OTTO – The Hackable GIF Camera". Kickstarter. 6 October 2015. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- ^ "Slice : A media player and more by Five Ninjas". Kickstarter. 4 December 2015. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- ^ "How good is the new Raspberry Pi 4 as a thin client?". Citrix Systems. 8 July 2019. Retrieved 27 March 2021.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi will power ventilators for COVID-19 patients". Engadget. 13 April 2020. Retrieved 22 April 2020.
- ^ Hughes, Owen (17 April 2020). "Raspberry Pi sales are rocketing in the middle of the coronavirus outbreak: Here's why". TechRepublic.
- ^ "Watch Tim Peake with the Astro Pi flight units in space!". Raspberry Pi Foundation. 7 March 2016.
- ^ "Proxima – AstroPi!". Raspberry Pi Foundation. Archived from the original on 1 March 2020. Retrieved 1 March 2020.
- ^ Xavier, John (3 January 2022). "Bridging the learning gap with a Pi". The Hindu. ISSN 0971-751X. Retrieved 6 January 2022.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi • View topic – Raspberry Pi as the successor of BBC Micro". raspberrypi.org. 22 April 2012. Retrieved 12 June 2013.
The Foundation trustees tried very hard to get an agreement to use the BBC Micro name, right up to May 2011. /../ Eben touched on the subject a bit during his speech at the Beeb@30 celebration at the beginning of the month
- ^ Quested, Tony (29 February 2012). "Raspberry blown at Cambridge software detractors". Business Weekly. Retrieved 13 March 2012.
- ^ Williams, Chris (28 November 2011). "Psst, kid... Wanna learn how to hack?". The Register. Retrieved 24 December 2011.
- ^ "Interview with Raspberry's Founder Eben Upton". TechSpot. 22 May 2012. Retrieved 28 February 2020.
- ^ Wong, George (24 October 2011). "Build your own prototype Raspberry Pi minicomputer". ubergizmo. Retrieved 2 November 2011.
- ^ "Tiny USB-Sized PC Offers 1080p HDMI Output". 6 May 2011. Retrieved 1 February 2012.
- ^ a b c Richard Lawler, 29 February 2012, Raspberry Pi credit-card sized Linux PCs are on sale now, $25 Model A gets a RAM bump, Engadget
- ^ "launch of the model A announced". 4 February 2013. Archived from the original on 9 February 2014. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Zero, at swag store". Archived from the original on 8 February 2016.
- ^ Upton, Eben (23 July 2011). "Yet another potential RISC OS target?". RISC OS Open. Retrieved 12 March 2012.
- ^ Hansen, Martin (31 October 2011). "Raspberry Pi To Embrace RISC OS". RISCOScode. Archived from the original on 8 March 2012. Retrieved 12 March 2012.
- ^ Lees, Adrian (8 February 2012). "RISC OS on the Raspberry Pi". RISC OS Open. Retrieved 12 March 2012.
- ^ JamesH (29 December 2011). "GPU binary blob question". Raspberry Pi. Retrieved 12 March 2012.
- ^ Humphries, Matthew (28 July 2011). "Raspberry Pi $25 PC goes into alpha production". Geek.com. Archived from the original on 2 November 2012. Retrieved 1 August 2011.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi YouTube Channel". YouTube. 27 August 2011. Retrieved 28 August 2011.
- ^ "Full HD video demo at TransferSummit Oxford". YouTube. 7 September 2011. Retrieved 12 September 2011.
- ^ Holwerda, Thom (31 October 2011). "Raspberry Pi To Embrace RISC OS". OSNews. Retrieved 1 November 2011.
- ^ Dewhurst, Christopher (December 2011). "The London show 2011". Archive. Vol. 23, no. 3. p. 3.
- ^ Lee, Jeffrey. "Newsround". The Icon Bar. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ eben (5 November 2012). "RISC OS for Raspberry Pi". Archived from the original on 9 November 2012. Retrieved 12 November 2012.
- ^ "What happened to the beta boards?". Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ^ "We have PCBs!". December 2011. Archived from the original on 19 February 2014. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ^ "More on the beta boards". Archived from the original on 1 April 2014. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ^ "Bringing up a beta board". Archived from the original on 22 January 2014. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ^ "We're auctioning ten beta Raspberry Pi's;". Raspberrypi.org. 31 December 2011. Archived from the original on 11 May 2012. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ Williams, Chris (3 January 2012). "That Brit-built £22 computer: Yours for just £1,900 or more". The Register. Retrieved 10 January 2012.
- ^ Cheerin, Iris (11 January 2012). "Raspberry Pi Goes into Production". TechWeekEurope UK. Retrieved 11 January 2012.
- ^ "eBay list of items sold by Raspberry Pi (retrieved 13 January 2012)". Ebay.co.uk. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Model B beta board – No. 01 of a limited series of 10". Ebay.co.uk. 11 January 2012. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ ""Set your alarms!" – Raspberry Pi looks ready for early Wednesday launch". Cabume. 28 February 2012. Archived from the original on 1 March 2012. Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ^ "linuxnews showing the first release of Debian Squeeze for Raspberry running on QEMU". Linuxnewshere.com. Archived from the original on 2 April 2012. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- ^ a b "Getting ready for launch: first root filesystem available for download". Raspberry Pi Foundation. 17 February 2012. Archived from the original on 20 February 2012. Retrieved 16 July 2013.
- ^ "The Raspberry Pi £22 computer goes on general sale". BBC News. 29 February 2012. Retrieved 29 February 2012.
- ^ Subramanian, Karthik (2 March 2012). "Low-cost mini-PC Raspberry Pi gets heavily booked". The Hindu. Chennai, India. Retrieved 12 March 2012.
- ^ Paul, Ryan (29 February 2012). "Raspberry Pi retailers toppled by demand as $35 Linux computer launches". Ars Technica. Retrieved 29 February 2012.
- ^ Naughton, John (4 March 2012). "The Raspberry Pi can help schools get with the programme". The Observer. London. Retrieved 12 March 2012.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Buying Guide". Elinux.org. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ Upton, Liz (8 March 2012). "Manufacturing hiccup". Raspberry Pi Foundation. Archived from the original on 23 March 2012. Retrieved 19 March 2012.
- ^ Gilbert, David (9 March 2012). "Raspberry Pi £22 Computer Delayed Due to 'Manufacturing Hiccup'". International Business Times. Retrieved 19 March 2012.
- ^ Gilbert, David (13 March 2012). "Interview with Eben Upton – Raspberry Pi Founder". International Business Times. Retrieved 19 March 2012.
- ^ Lee, Robert (17 January 2012). "Raspberry Pi Balks at UK Tax Regime". Tax-News.com. Archived from the original on 8 March 2012. Retrieved 20 January 2012.
- ^ Weakley, Kirsty. "UK computing charity opts to manufacture product abroad". Civil Society Media. Retrieved 20 January 2012.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Fedora Remix, our recommended distro, is ready for download!". Raspberrypi.org. 8 March 2012. Archived from the original on 15 June 2012. Retrieved 22 June 2012.
- ^ Chung, Emily (24 February 2012). "$35 computer 'Raspberry Pi' readies for launch". Canada: Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ^ a b c Brodkin, Jon (6 March 2013). "How two volunteers built the Raspberry Pi's operating system". Ars Technica. Technology Lab / Information Technology. Archived from the original on 26 May 2013. Retrieved 17 July 2012.
- ^ a b "ArmHardFloatPort". Debian Wiki. Debian. 20 August 2012. Archived from the original on 21 May 2013. Retrieved 17 July 2012.
- ^ "ArmEabiPort". Debian Wiki. Debian. 28 June 2013. Archived from the original on 15 May 2013. Retrieved 17 July 2012.
- ^ Connors, Jim (16 March 2013). "Is it armhf or armel?". Jim Connors' Weblog. Oracle Blogs. Archived from the original on 9 May 2013. Retrieved 17 July 2012.
- ^ "ArmHardFloatPort VfpComparison". Debian Wiki. Debian. 27 April 2011. Archived from the original on 1 February 2013. Retrieved 17 July 2012.
- ^ "the first reports of forum members reporting they received their Raspberry Pi". Raspberrypi.org. 16 April 2012. Archived from the original on 18 April 2012. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi boards begin shipping today (video)". Engadget. 16 April 2012. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ "schematic design, applicable for both version A and B of the Raspberry Pi revision 1.0". Raspberrypi.org. 19 April 2012. Archived from the original on 3 May 2012. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ "CAMERA MODULE – FIRST PICTURES!". Archived from the original on 8 August 2014. Retrieved 9 August 2014.
- ^ "Add your Raspberry Pi to the Rastrack map". Raspberrypi.org. 22 May 2012. Archived from the original on 14 June 2012. Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- ^ Owano, Nancy (18 July 2012). "Raspberry Pi gets customized OS called Raspbian". PhysOrg. Retrieved 5 September 2012.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi lifts sale restrictions, open to bulk buyers". Electronista. Macintosh News Network. 16 July 2012. Archived from the original on 17 August 2012. Retrieved 29 August 2012.
- ^ "Want to buy more than one Raspberry Pi? Now you can!". Raspberrypi.org. 16 July 2012. Archived from the original on 19 July 2012. Retrieved 16 July 2012.
- ^ "Hardware-assisted H.264 video encoding". raspberrypi.org. 7 February 2012.
- ^ Jurczak, Paul. "Raspberry Pi camera module". Raspberrypi.org. Retrieved 15 October 2012.
- ^ "performance – What speed can I expect from the hardware-H264-encoding?". Raspberry Pi Stack Exchange.
- ^ "Upcoming board revision". Raspberrypi.org. 6 September 2012. Archived from the original on 7 September 2012. Retrieved 5 September 2012.
- ^ "board revision for rev 2.0". Raspberrypi.org. 5 September 2012. Archived from the original on 14 October 2012. Retrieved 15 October 2012.
- ^ Dunn, John E (7 September 2012). "Raspberry Pi resurrects UK computer industry with new jobs". Computerworld UK. Retrieved 13 September 2012.
- ^ "Made in the UK!". Raspberrypi.org. 6 September 2012. Archived from the original on 7 September 2012. Retrieved 6 September 2012.
- ^ "Model B now ships with 512 MB of RAM". Raspberrypi.org. Archived from the original on 16 October 2012. Retrieved 15 October 2012.
- ^ a b Brodkin, Jon (28 February 2014). "Raspberry Pi marks 2nd birthday with plan for open source graphics driver". Ars Technica. Retrieved 27 July 2014.
- ^ a b Upton, Eben (28 February 2014). "A birthday present from Broadcom". Raspberry Pi Foundation. Archived from the original on 27 July 2014. Retrieved 27 July 2014.
- ^ Shead, Sam (18 October 2012). "Raspberry Pi delivery delays leave buyers hungry (and angry)". ZDNet. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- ^ "Introducing the Pi Store". Raspberry Pi Foundation. 17 December 2012. Archived from the original on 14 February 2014. Retrieved 12 February 2022.
- ^ Upton, Liz (3 June 2013). "Introducing the New Out of Box Software (NOOBS)". RPF. Archived from the original on 7 June 2013. Retrieved 4 June 2013.
- ^ "Baked in Britain, the millionth Raspberry Pi". BBC News. 7 October 2013. Retrieved 8 October 2013.
- ^ "Two Million!". Archived from the original on 17 November 2013. Retrieved 18 November 2013.
- ^ "RASPBERRY PI AT BUCKINGHAM PALACE, 3 MILLION SOLD". Archived from the original on 20 June 2014. Retrieved 22 June 2014.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi 2 on sale now at $35 Raspberry Pi". Archived from the original on 2 February 2015. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ^ "Price cut! Raspberry Pi Model B+ now only $25". 14 May 2015. Archived from the original on 20 May 2015. Retrieved 19 May 2015.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi slashes price after rival launches on Kickstarter". 18 May 2015. Retrieved 19 May 2015.
- ^ Long, Simon (29 September 2015). "Raspbian Jessie is here". Raspberry Pi. Retrieved 14 November 2021.
- ^ Hern, Alex (29 February 2016). "Raspberry Pi 3: the credit card-sized 1.2 GHz PC that costs $35". The Guardian.
- ^ "New 8-megapixel camera board on sale at $25". 25 April 2016. Retrieved 6 May 2016.
both visible-light and infrared cameras based on the Sony IMX219 8-megapixel sensor, at the same low price of $25. They're available today from our partners RS Components and element14
- ^ "NEC Display Solutions announces collaboration with Raspberry Pi". NEC. 10 October 2016. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- ^ Upton, Eben (14 October 2016). "The Compute Module – now in an NEC display near you". Raspberry Pi Foundation. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- ^ a b The Mag Pi Magazine issue 53, Page 10, Raspberry Pi Foundation, January 2017,
On 25 November, it was confirmed that total sales of the Raspberry Pi have now topped 11 million.
- ^ "New product! Raspberry Pi Zero W joins the family". Raspberry Pi Foundation. 28 February 2017.
- ^ Long, Simon (17 August 2017). "Raspbian Stretch has arrived for Raspberry Pi". Raspberry Pi. Retrieved 14 November 2021.
- ^ "Raspberry PI 3B+ on sale now". 14 March 2018. Retrieved 21 March 2018.
- ^ "New product: Raspberry Pi 3 Model A+ on sale now at $25 – Raspberry Pi". Raspberry Pi. 15 November 2018. Retrieved 15 November 2018.
- ^ Long, Simon (25 June 2019). "Buster – the new version of Raspbian". Raspberry Pi.
- ^ @EbenUpton (13 December 2019). "Raspberry Pi numbers get stale fast. We sold our thirty-millionth unit some time last week (we think Tuesday)" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ @EbenUpton (13 December 2019). "Happy to make an introduction. And they do about six million @Raspberry_Pi units a year, so they definitely have scale" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ @EbenUpton (14 December 2019). "Yes. We don't get sales returns from our licensees until month end. At the end of November, we were at 29.8Mu, with a monthly run rate of 500–600ku. Thus, Tuesday" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ Piltch, Avram (30 May 2020). "Raspberry Pi OS: Why It's No Longer Called 'Raspbian'". Tom's Hardware. Retrieved 14 November 2021.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4 on sale now from $25 – Raspberry Pi". Raspberry Pi. 19 October 2020. Retrieved 16 January 2021.
- ^ Foundation, The Raspberry Pi. "Buy a Raspberry Pi 400 Personal Computer Kit". Raspberry Pi.
- ^ Chris Fleck and Eben Upton on Twitter, Chris Fleck,
Great call with @EbenUpton today. Congrats on 40 Million #RaspberryPi sold!
- ^
Raspberry Pi gets $45M to meet demand for low-cost PCs and IoT, TechCrunch / Natasha Lomas@riptari(twitter), 21 September 2021,
While, in total, the Pi Foundation also said it's shipping over 42 million (Pi-powered) PCs to more than 100 countries.
- ^ Long, Simon (8 November 2021). "Bullseye – the new version of Raspberry Pi OS". Raspberry Pi. Retrieved 14 November 2021.
- ^
Impact Stories: Raspberry Pi, The Index Projewct / Ditte Fiil Ravn,
With 43 million computers sold worldwide and 95% of its products exported outside the UK, the globe has grown fond of pocket-sized computers.
- ^
One decade, 46 million units: Happy birthday, Raspberry Pi, The Register / Richard Speed,
Upton tells us that approximately 46 million units have been manufactured to date.
- ^ "Ten millionth Raspberry Pi, and a new kit – Raspberry Pi". Raspberry Pi. 8 September 2016. Retrieved 1 February 2017.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi sold over 12.5 million boards in five years". The Verge. Retrieved 27 September 2017.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi founder Eben Upton talks sales numbers, proudest moments, community projects, and Raspberry Pi 4 [Q&A]". Betanews.com. Retrieved 9 November 2017.
- ^ @EbenUpton (14 December 2019). "@lisn92 @bateskecom @arturo182 @Raspberry_Pi Raspberry Pi numbers get stale fast. We sold our thirty-millionth unit…" (Tweet). Retrieved 26 February 2020 – via Twitter.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi has now sold 30 million tiny single-board computers". ZDNET. Retrieved 23 December 2023.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi: Why they are so hard to buy right now, and what you can do about it". ZDNet.
- ^ "Production and supply-chain update". 4 April 2022.
Further reading
[edit]- Raspberry Pi For Dummies; Sean McManus and Mike Cook; 2013; ISBN 978-1118554210.
- Getting Started with Raspberry Pi; Matt Richardson and Shawn Wallace; 2013; ISBN 978-1449344214.
- Raspberry Pi User Guide; Eben Upton and Gareth Halfacree; 2014; ISBN 978-1118921661.
- Hello Raspberry Pi!; Ryan Heitz; 2016; ISBN 978-1617292453.
- The Official Raspberry Pi Beginner’s Guide; Gareth Halfacree; 2023; ISBN 978-1912047260.
External links
[edit]- Official website

- Raspberry Pi, Department of Computer Science and Technology, University of Cambridge
- Raspberry Pi Wiki, supported by the RPF
- The MagPi Magazine
- "Raspberry Pi pinout" – board GPIO pinout
- "Raspberry Pi component map" Archived 7 June 2019 at the Wayback Machine
- "RaspberryPi Boards: Hardware versions/revisions"
- ARM1176JZF-S (ARM11 CPU Core) Technical Reference Manual Archived 19 June 2020 at the Wayback Machine, ARM Ltd.
 KSF
KSF