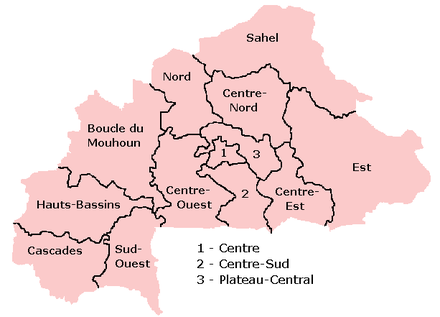
Regions of Burkina Faso
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 6 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 6 min
 |
|---|
Per Law No.40/98/AN in 1998, Burkina Faso adhered to decentralization to provide administrative and financial autonomy to local communities. Most of these, according to their individual articles, were implemented on 2 July 2001.
Burkina Faso is divided into 13 administrative regions. Each region is administered by a governor.
 |
| Region | Area (km2) [1] |
Population (2024)[2] |
Density
(per km2 in 2024) |
Administrative capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boucle du Mouhoun | 34,333 | 2,120,626 | 62.1 | Dédougou |
| Cascades | 18,424 | 944,950 | 51.3 | Banfora |
| Centre | 2,869 | 3,623,784 | 1,292 | Ouagadougou |
| Centre-Est | 14,710 | 1,787,201 | 121.9 | Tenkodogo |
| Centre-Nord | 19,677 | 2,134,352 | 107.6 | Kaya |
| Centre-Ouest | 21,752 | 1,866,251 | 85.9 | Koudougou |
| Centre-Sud | 11,457 | 872,845 | 77.2 | Manga |
| Est | 46,694 | 2,240,243 | 48.5 | Fada N'gourma |
| Hauts-Bassins | 25,343 | 2,572,566 | 101.5 | Bobo Dioulasso |
| Nord | 16,414 | 1,939,319 | 119.7 | Ouahigouya |
| Plateau-Central | 8,545 | 1,096,483 | 128.3 | Ziniaré |
| Sahel | 35,360 | 1,223,695 | 34.6 | Dori |
| Sud-Ouest | 16,153 | 986,700 | 61.1 | Gaoua |
These regions are divided into 45 provinces and subdivided into 351 communes.
See also
[edit]- List of regions of Burkina Faso by Human Development Index
- Provinces of Burkina Faso
- Departments/Communes of Burkina Faso
- Geography of Burkina Faso
- ISO 3166-2:BF
References
[edit]- ^ Burkina Faso at Geohive
- ^ "Burkina Faso: Administrative Division (Regions and Provinces) - Population Statistics, Charts and Map". www.citypopulation.de. Retrieved 2024-01-17.
See also
[edit]Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Regions_of_Burkina_Faso1 views | ↧ Download as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF