Road signs in India
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 11 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 11 min
This article may need to be rewritten to comply with Wikipedia's quality standards. (April 2022) |







Road signs in India are governed by the Indian Roads Congress. For the most part, they tend to follow European practices closely, usually identical to United Kingdom or the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals. However yellow rectangular signs that do carry such messages like "Be gentle on my curves" and "Danger creeps when safety sleeps" are present nationwide.[1]
The official typeface for road signs in India is Transport and Arial.[2] The Official typeface for Highway shields is Highway Gothic.[2] Though sometimes, road signs may use hand-painted fonts.[3][4] Most urban roads and state highways have signs in the state language and English. National highways have signs in the state language, Hindi and English.
History
[edit]From 1963, a circle with a red diagonal slash shows prohibited activities and circles without slashes show rules, blue circles indicate compulsory instructions and triangles with red borders indicate cautions and dangers. Road signs with imperial measures were fully replaced with their metric counterparts.
Prior to 1963, street signs with imperial measurements were used, the warning signage used was triangle above a rectangle which showed dangers and warnings similar to the pre-worboys design used in the United Kingdom and the mandatory signs used were red circles, some with a with band such as No Parking and Closed, but some with a rectangular plates that would give written warnings.
Mandatory/Regulatory signs
[edit]The mandatory/regulatory signs in India as per the IRC-67 (2022) Guidelines are as follows:
-
Give Way
-
Give Way to Buses (Exiting the Bus Bay)
-
Stop
-
Stop (in major Indian languages)
-
No entry
-
Priority for oncoming vehicles
-
One-way traffic
-
One-way traffic
-
No vehicles in both directions
-
Cycles prohibited
-
Trucks prohibited
-
Pedestrians prohibited
-
Tongas prohibited
-
Bullock carts prohibited
-
Hand carts prohibited
-
Bullock cart and hand carts prohibited
-
All motor vehicles prohibited
-
Buses Prohibited
-
Height limit
-
Width limit
-
Load limit
-
Axle load limit
-
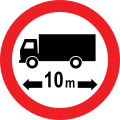
Length limit
-
Left turn prohibited
-
Right turn prohibited
-
Overtaking prohibited
-
U-Turn Prohibited
-
Maximum Speed Limit
-
Stop For Police Check
-
Horns prohibited
-
Restriction Ends
-
No Parking
-
No Standing
-
No Stopping
-
Parking Not Allowed On Footpath
-
Parking Not Allowed On Half of Footpath
Compulsory signs
[edit]The compulsory signs in India as per the IRC-67 (2022) Guidelines are as follows:
-
Compulsory Ahead
-
Compulsory Turn Left
-
Compulsory Turn Right
-
Compulsory turn left (In advance of a Junction)
-
Compulsory turn right (In advance of a Junction)
-
Compulsory Ahead or turn Right
-
Compulsory Ahead or turn Left
-
Compulsory Keep Left
-
Compulsory Keep Right
-
Pass Either Side
-
Mini Roundabout
-
Compulsory Cycle track/Cycle Only
-
Compulsory Cyclist and Pedestrian Route
-
Pedestrian Only
-
Bus Way/Buses Only
-
Compulsory Snow Chain
-
Compulsory Sound Horn
-
Minimum Speed Limit
Cautionary/Warning signs
[edit]The cautionary/ warning signs in India as per the IRC-67 (2022) Guidelines are as follows:
-
Left curve
-
Right curve
-
Right hairpin bend
-
Left hairpin bend
-
Right reverse bend
-
Left reverse bend
-
Series of Bends
-
270 Degree Loop
-
Side road to right
-
Side road to left
-
Y-Intersection (Left)
-
Y-Intersection (Right)
-
Y-Intersection
-
Crossroads
-
Roundabout
-
Traffic Signals
-
T-junction
-
T-junction major road ahead
-
Major road ahead
-
Staggered junction
-
Merging Traffic ahead from Right
-
Merging Traffic ahead from Left
-
Road Narrows Ahead
-
Road widens
-
Narrow Bridge Ahead
-
Steep ascent
-
Steep descent
-
Reduced Carriageway Left Lane(s) Reduced
-
Reduced Carriageway Right Lane(s) Reduced
-
Start of dual carriageway
-
End of dual carriageway
-
Gap in median
-
Pedestrian crossing
-
School Ahead
-
Built-up area
-
Two Way Operation
-
Two way Traffic on crossroads Ahead Warning
-
People at Work
-
Supplementary plate ''END'' at the leaving side of work zone
-
Danger warning
-
Differently Abled Persons Ahead
-
Deaf Persons Ahead
-
Blind Persons Ahead
-
Cycle crossing
-
Cycle Route Ahead
-
Dangerous Dip
-
Speed Breaker
-
Rumble strip
-
Rough road
-
Soft verges
-
Loose gravel
-
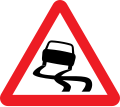
Slippery road
-
Slippery road because of Ice
-
Opening or Swing Bridge
-
Overhead cables
-
Quayside or riverbank
-
Barrier
-
Sudden Side Winds
-
Tunnel ahead
-
Ferry
-
Trams crossing
-
Falling rocks
-
Cattle crossing
-
Wild Animals
-
Queues likely ahead
-
Low-flying aircraft
-
Unguarded railway crossing
-
Unguarded railway crossing (50 - 100 Metres Ahead)
-
Unguarded railway crossing (200 metres ahead)
-
Guarded railway crossing
-
Guarded railway crossing (50-100 metres ahead)
-
Guarded railway crossing (200 metres ahead)
-
U-Turn Ahead
-
Single Chevron
-
Double chevron
-
Triple chevron
-
Object Hazard (Left)
-
Object Hazard (Right)
-
Two Way Object Hazard Marker
Informatory signs
[edit]The informatory signs in India as per the IRC-67 (2022) Guidelines are as follows:
-
Stack-type advance direction sign
-
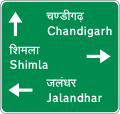
Map-type advance direction sign
-
Roundabout
-
Flag-type direction sign
-
Confirmatory sign
-
Place identification sign
-
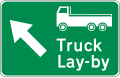
Truck-lay by
-
Weigh bridge ahead
-
Gantry-mounted advance direction sign ahead of a grade-separated junction
-
Gantry-mounted advance direction ahead of an at-grade junction
-
Lane dedicated gantry sign
-
Shoulder-mounted sign in advance of grade-separated junction
-
Expressway Ahead
-
Gantry-mounted advance direction sign ahead of a flyover in urban/city roads
-
Supplementary road sign ''No parking''
-
Supplementary road sign ''No stopping No standing''
-
Crash Prone Area
Facility informatory signs
[edit]The facility information signs in India as per the IRC-67 (2022) Guidelines are as follows:
-
Eating Place
-
Light Refreshment
-
Resting Place
-
First Aid Post
-
Toilet
-
Filling Station (Fuel Pump)
-
Hospital
-
Emergency SOS Facility
-
U-Turn Ahead
-
Pedestrian Subway
-
Foot Over Bridge
-
Chair Lift
-
Police Station
-
Repair Facility
-
Railway Station/Metro Station/Monorail Station
-
Cycle Rickshaw Stand
-
Taxi Stand
-
Auto-rickshaw Stand
-
Shared Taxi/Share Auto Stand
-
Home Zone
-
Camp Site
-
Airport
-
Golf Course
-
National Heritage
-
No Through Road
-
No Through Side Road
-
Toll Road Ahead
-
ETC Lane Guide
-
Country Border
-
Entry Ramp for Expressway
-
Exit Ramp for Expressway
-
Expressway Symbol
-
End of Expressway
-
Bus Stop
-
Bus Lane
-
Contra Flow Bus Lane
-
Cycle Lane
-
Contra Flow Cycle Lane
-
Holiday Chalets
-
Emergency Exit (a)
-
Emergency Exit (b)
-
Emergency Helpline Number (a)
-
Emergency Helpline Number (b)
-
Emergency Lay-by
-
Fire Extinguisher
-
Rest and Service Area (a)
-
Rest and Service Area (b)
-
Pedestrian Crossing
-
Speed Breaker
-
Electric Vehicle Charging Station
Parking signs
[edit]The parking signs in India as per the IRC-67 (2022) Guidelines are as follows:
-
Parking
-
Auto Rickshaw Parking
-
Cycle Parking
-
Cycle Rickshaw Parking
-
Scooter and Motorcycle Parking
-
Taxi Parking
-
Car Parking
-
Park and Ride (By Metro)
-
Park and Ride (By Bus)
-
Pick Up & Drop Point
-
Parking Restriction Sign for Traffic Management (a)
-
Parking Restriction Sign for Traffic Management (b)
-
Parking Restriction Sign for Traffic Management (c)
-
Flood Gauge
Route Marker signs
[edit]The Route Marker signs in India as per the IRC-67 (2022) Guidelines are as follows:
-
State Highway Route Marker
-
National Highway Route Marker
-
Asian Highway Route Marker
-
National Expressway Route Marker
Retired road signs
[edit]-
School
-
Roadworks
-
Deaf persons likely on road ahead
-
Blind persons likely on road ahead
1950 road signs
[edit]-
Speed limit
-
Weight limit
-
Road closed
-
Mandatory direction
-
No parking
-
Overtaking prohibited
-
Horns prohibited
-
Slow down, main road ahead
-
Bumpy road
-
Right reverse bend
-
Left reverse bend
-
Crossroads
-
Guarded railway crossing
-
Unguarded railway crossing
-
Right curve
-
Left curve
-
School
-
T-junction
-
Side road to right
-
Side road to left
-
Steep descent
-
Ferry
-
Right hairpin bend
-
Left hairpin bend
-
Narrow bridge
-
Bumpy road
-
Right reverse bend
-
Left reverse bend
-
Crossroads
-
Guarded railway crossing
-
Unguarded railway crossing
-
Right curve
-
Left curve
-
School
-
T-junction
-
Side road to right
-
Side road to left
-
Steep descent
-
Ferry
-
Right hairpin bend
-
Left hairpin bend
-
Narrow bridge
References
[edit]- ^ "Unusual road signs in Northern India". arrivealive.co.za. Retrieved 2022-09-10.
- ^ a b IRC 67-2022-Code of Practice For Road Signs (4th ed.). Dehli: Indian Roads Congress (published June 2022). 2022. p. 24.
- ^ "Hand-painted Signs: Forgotten Markers of the City Space". Sahapedia. Retrieved 2025-04-03.
- ^ "Hand painted Indian typography". Richard Frazer blog. Retrieved 2025-04-03.
 KSF
KSF