Sibelius (scorewriter)
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 18 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 18 min
| Sibelius | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Original author(s) |
|
| Developer(s) | Avid |
| Initial release | April 1993 |
| Stable release | 2025.4 (14 April 2025) [±][1] |
| Written in | C++ |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows, macOS, RISC OS |
| Available in | 9 languages |
List of languages
| |
| Type | Scorewriter |
| License | Proprietary Freeware, Proprietary software |
| Website | www |

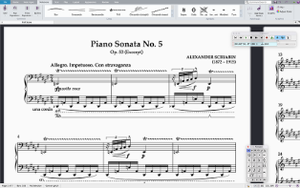
Sibelius is a scorewriter program developed and released by Sibelius Software (now part of Avid). Beyond creating, editing and printing music scores, it can also play the music back using sampled or synthesised sounds. It produces printed scores, and can also publish them via the Internet for others to access. Less advanced versions of Sibelius at lower prices have been released, as have various add-ons for the software.
Named after the Finnish composer Jean Sibelius, the company was founded in April 1993 by twin brothers Ben and Jonathan Finn to market the eponymous music notation program they had created.[2] It went on to develop and distribute various other music software products, particularly for education. In addition to its head office in Cambridge and subsequently London, Sibelius Software opened offices in the US, Australia and Japan, with distributors and dealers in many other countries worldwide. The company won numerous awards, including the Queen's Award for Innovation in 2005.
In August 2006 the company was acquired by Avid, to become part of its Digidesign division, which also manufactures the digital audio workstation Pro Tools. In July 2012, Avid announced plans to divest its consumer businesses, closed the Sibelius London office, and removed the original development team,[3][4][5] despite a 11,590-strong 'Save Sibelius' petition spearheading a campaign led by Derek Williams that included extensive protests on Facebook and elsewhere.[6][7][8][9] Avid subsequently recruited new programmers to continue the development of Sibelius, and Steinberg hired most of the former Sibelius team to create a competing software, Dorico.
History
[edit]Origins
[edit]Sibelius was originally developed by British twins Jonathan and Ben Finn for the Acorn Archimedes computer under the name 'Sibelius 7', not as a version number, but reminiscent of Sibelius' Symphony No 7.[2] The Finns said they could not remember why they used Jean Sibelius' name, but it was probably because he was also 'a Finn' (i.e. Finnish), as well as being one of their favourite composers. They started developing the software (entirely in assembly language) in the summer of 1986, just after they left school, and continued while studying at Oxford and Cambridge universities, respectively. Both brothers were composers, and wrote the program to automate the laborious process of writing music out by hand.[10]
The program was released to the public in April 1993 on 3.5-inch floppy disk. It required considerably less than 1 MB of memory (as its files only occupied a few KB per page of music), and the combination of assembly language and the Archimedes' ARM processor meant that it ran very quickly. No matter how long the score, changes were displayed almost instantly. A unique feature of the Sibelius GUI at that time was the ability it gave the user to drag the entire score around with the mouse, offering a bird's eye of the score, as distinct from having to use the QWERTY input keyboard arrow keys, or equivalent, to scroll the page.
The first ever user of Sibelius was the composer and engraver Richard Emsley, who provided advice on music engraving prior to the start of development, and beta tested the software before its release. The first concert performance from a Sibelius score was the premiere of Plus Loin for chamber orchestra by David Robert Coleman, copied by Emsley. The first score published using Sibelius was Antara by George Benjamin, also copied by Emsley, and published by Faber Music. Other early adopters included composer John Rutter, conductor Michael Tilson Thomas, and publisher Music Sales.
As a killer application for the niche Acorn platform, Sibelius rapidly dominated the UK market.[11] It also sold in smaller numbers in a few other countries, restricted by the availability of Acorn computers. 'Lite' versions were subsequently released, and these were successful in UK schools, where Acorns were widely used.[12]
Expansion
[edit]In September 1998, the first version for Windows was released as 'Sibelius', with the version number reset to 1.0.[13] A Mac version 1.2 was released a few months later, and the company thereafter used conventional version numbers for both platforms across subsequent upgrades. The Windows and Mac versions were essentially identical, and scores created on one platform could be opened on the other. To produce these versions, the software was completely rewritten from scratch in C++, while retaining most of the original Acorn version's functionality and user interface, plus numerous enhancements. The original Acorn names 'Sibelius 6' and 'Sibelius 7' were later re-used to denote versions 6 and 7 of Sibelius for Windows/Mac.
Releasing Sibelius for more widely available computers brought it to a worldwide market, particularly the US, where Sibelius Software had opened an office in late 1996. Following the break-up of Acorn Computers[14][15] shortly after Sibelius' Windows release, no further Acorn versions were developed. Sibelius Software later opened an office in Australia, also serving New Zealand, where Sibelius was widely used.
In August 2006, Sibelius Software Ltd was acquired by Avid Technology, an American manufacturer of software and hardware for audio and video production. Avid continued publishing Sibelius as a stand-alone notation product, as well as integrating it with some of its existing software products.
In July 2012, Avid announced plans to divest itself of its other consumer businesses, closed the Sibelius London office, and laid off the original development team,[4][16] amid an outpouring of user protest, then recruited a new team of programmers to continue Sibelius development in Montreal, Canada and Kyiv, Ukraine.
Timeline
[edit]- 1986: Founders Jonathan and Ben Finn start developing Sibelius 7 for Acorn computers.
- 1993: Sibelius Software founded to sell Sibelius 7 and related computer hardware/software in the UK. Early customers include Europe's largest publisher Music Sales, choral composer John Rutter, and the Royal Academy of Music. Sibelius 6 (educational version) also launched.
- 1994: Distribution in Europe, Australia and New Zealand commences. Sibelius 7 Student (educational version) launched.
- 1995: German versions of Sibelius launched.
- 1996: US office opened in California. Junior Sibelius (primary school program) launched.
- 1998: Sibelius for Windows launched worldwide. Company ceases selling hardware to concentrate on core software business.[17]
- 1999: Sibelius for Mac, PhotoScore and Scorch launched. Sibelius forms US subsidiary, creating the Sibelius Group, which now has 25 employees. Quester VCT invests.[18]
- 2000: Sibelius Internet Edition launched, and adopted for Internet publishing by leading European publishers Music Sales and Boosey & Hawkes. SibeliusMusic.com and Sibelius Notes (initially called Teaching Tools) launched.[19]
- 2001: World's largest sheet music publisher Hal Leonard also adopts Sibelius Internet Edition. Sibelius Group reaches 50 employees.
- 2002: Sibelius is first major music program for Mac OS X. Company acquires music software company MIDIworks.[20]
- 2003: Starclass, Instruments, G7 and G7music.net launched. Sibelius Group commences distributing Musition and Auralia. Sibelius in Japanese launched, distributed by Yamaha.
- 2004: Compass, Kontakt Gold, Sibelius Student Edition, Sibelius in French and Spanish launched. Company acquires SequenceXtra. Sibelius software used in more than 50% of UK secondary schools.
- 2005: Australian subsidiary formed after acquiring Australian distributor. Company reaches 75 employees. Wins Queen's Award for Enterprise.[21] Releases Rock & Pop Collection of sounds. Commences distributing O-Generator.
- 2006: Groovy Music and Coloured Keyboard launched. Sibelius Software bought by Avid Technology.
- 2007: Japanese office opened.
- 2012: Avid closes Sibelius' London office and lays off original development team, sparking the 'Save Sibelius' campaign.[7]
- 2014: First release of a Sibelius version (7.5) by the new development team.[22]
- 2018: Sibelius First (free, entry-level product), Sibelius (formerly Sibelius First) and Sibelius Ultimate (formerly Sibelius) launched together with a new year-based versioning system.
- 2021: Sibelius for iPad and iPhone is released.[23][24]
Features
[edit]Core functionality
[edit]Sibelius' main function is to help create, edit and print musical scores. It supports virtually all music notations, enabling even the most complex of modern orchestral, choral, jazz, pop, folk, rock and chamber music scores to be engraved to publication quality. Further, it allows scores to be played back or turned into MIDI or audio files, e.g. to create a CD. A built-in sample player and a large range of sampled sounds are included.[25] It supports any MIDI device, and allows Virtual Studio Technology (VST) and Audio Units plug-ins to be used as playback instruments, giving users access to third-party sample libraries.[26] Score playback can also be synchronised to video, or to DAW software via the ReWire standard.
By default, Sibelius plays a brief passage from a Jean Sibelius symphony as it launches, a feature that can be disabled in the application's Preferences if desired. Each version has used a different excerpt; e.g. Sibelius 7 appropriately uses the main theme from Sibelius' 7th Symphony.
In Version 7.0, Avid Technology rebuilt Sibelius as a 64-bit application, replacing the menu navigation system of previous versions with a Ribbon interface in the process. This met with considerable user resistance,[27] however the Ribbon remains integral to the current GUI.
Add-ons
[edit]Add-ons for Sibelius that are currently or have previously been available include:
- Sound libraries such as Note Performer,[28][29] Vienna Symphonic Library,[30][31] Spitfire Audio (samples of BBC Symphony Orchestra),[32] Kontakt,[33] Garritan,[34] and Mark of the Unicorn's (MOTU) Symphonic Instrument,[35][36] which can be added as Manual Sound Sets in the Playback Devices options from the Sibelius Play tab.[37]
- Extra plug-in features.[38] These are usually free of charge, and often created by Sibelius users, the most prolific of whom has been Bob Zawalich.[39]
- Myriad's PDF to MusicXML transcribing application PDFtoMusic.[40][41]
- Neuratron's Music OCR program PhotoScore (scanning),[42][43] which can be used to scan and create a Sibelius score from printed music and PDF documents. A lite version is bundled with Sibelius.
- Neuratron's AudioScore,[44] also bundled in a lite version, which claims to be able to turn singing or an acoustic instrument performance into a score,[45] though many users have complained that this does not work.[46][47] AudioScore currently holds a two-star rating on cnet.com.[48]
- QWERTY Keyboards such as Logic Keyboard.[49]
- Keyboard covers such as KB Covers.[50]
- Mobile device VNC controllers such as iPad Sibelius Wizard[51][52] and Sibelius Control for iPad,[53][54] allowing the user to control Sibelius wirelessly via shortcuts set up within the Preferences.
Cloud publishing
[edit]Sibelius users can publish their scores directly from the software via the Internet using desktops, laptops or iPads. Anyone else using software called Sibelius Scorch[55] (free for web browsers, charged for on iPads) can then view these scores, play them back, transpose them, change instruments, or print them from the web browser version. ScoreExchange.com is a website where any Sibelius user can upload scores they have composed, arranged or transcribed with Sibelius, so that anyone can access the music. The site began in 2001 as SibeliusMusic.com, and by June 2011 had amassed nearly 100,000 scores. The iPad version of Scorch also includes a store containing over 250,000 scores from publishers Music Sales, Hal Leonard, and Sibelius Scorch is used in the websites of various music publishers and individual musicians. Publishers can licence the Sibelius Internet Edition for commercial online publishing.
In October 2017, Scorch was replaced by Sibelius Cloud Publishing, providing publishers with an API to automate the publishing and selling of digital sheet Music.[56] It uses the same technology as Scorch to allow Sibelius users to share music online directly from within the program, and addresses compatibility issues.[57]
Education
[edit]There are various education-specific features for Sibelius' large market of schools and universities. The Sibelius Educational Suite[58] includes extensive built-in music teaching materials, and the ability to run and manage multiple copies of the software on a network at discounted educational pricing.
In 2012, Sibelius Student was replaced by a new version of Sibelius First.
Lite notation based on Sibelius is included in Avid's Pro Tools audio editing software.
Network
[edit]A network licence is available for schools, colleges, universities and other multi-client situations.[59]
Version history
[edit]| Version | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2025.4 | 14 April 2025 | Implementing score subsets, dynamic parts and some useful fixes and improvements.[60] |
| 2025.3 | 13 March 2025 | UI improvements to staff filters, pitch correction tool, copying and pasting bar rests containing fermatas and other fixes.[61] |
| 2025.2 | 6 February 2025 | Automatic decondensing parts.[62] |
| 2024.10 | 24 October 2024 | MusicXML improvements, supported with macOS Sequoia.[63] |
| 2024.8 | 20 August 2024 | Update only for iOS, Android and Sibelius Cloud.[64] |
| 2024.6.1 | 17 July 2024 | Bug fixes and improvements, particularly for MusicXML import and MIDI handling.[65] |
| 2024.6 | 20 June 2024 | Native support for Apple silicon processors on Mac computers.[65] |
| 2024.3 | 7 March 2024 | MIDI copy and paste, remote connection and resizeable Keypad.[66] |
| 2023.11 | 30 November 2023 | Supported with macOS Sonoma.[67] |
| 2023.8 | 31 August 2023 | Enhanced redo, auto-completing chord symbols using AI.[68] |
| 2023.6.1 | July 2023 | Last version to support macOS High Sierra.[69] |
| 2023.6 | 22 June 2023 | Implementing AI for chord symbols.[70] |
| 2023.5 | 4 May 2023 | Added hiding options for individual voiced parts.[71] |
| 2022.3 | 17 March 2022 | Supported with Windows 11 and macOS Monterey.[72] |
| 2021.12 | 16 December 2021 | Introduced Avid Cloud Licensing,[73] last version to support macOS Sierra.[74] |
| 2021.9 | 27 September 2021 | [75] |
| 2021.2 | 25 February 2021 | Commands implemented in search bar, supported with Apple M1 processor under Rosetta.[76] |
| 2020.9 | 17 September 2020 | [77] |
| 2020.6 | 3 June 2020 | Improved MusicXML import and colour options for accessibility.[78] |
| 2020.3 | 26 March 2020 | Implementing laissez vibrer ties.[79] |
| 2020.1 | 16 January 2020 | Auto-Optimize staff spacing, added Dashed and Dotted and Tie-into Ties, added three house styles and manuscript papers, implementing wild-cards and large film-score time signatures.[80] |
| 2019.12 | 5 December 2019 | [81] |
| 2019.9 | September 2019 | Last version to support Mac OS X Yosemite and OS X El Capitan.[81] |
| 2019.4 | 6 April 2019 | Some bug fixes.[82] |
| 2019.1 | 1 January 2019 | [83] |
| 2018.12 | 17 December 2018 | [84] |
| 2018.11 | November 2018 | Recoded in Qt 5.[85] |
| 2018.7 | 11 July 2018 | MusicXML improvements, bug fixes.[86] |
| 2018.6 | 26 June 2018 | Free tier available, with all three tiers combined into one installer. Improvements in note spacing, grace notes, multi-text entry, tied notes and others.[87] |
| 2018.5 | 17 May 2018 | Maintenance release to fix an issue where running some plug-ins would cause a memory leak that slowed Sibelius down until it was relaunched.[88] |
| 2018.4 | April 2018 | Multi-edits for text, improved note spacing and rebranded as Sibelius Ultimate.[89] |
| 2018.1 | January 2018 | New versioning scheme, improved workflow enhancements.[90] |
| 8.7.2 | 16 November 2017 | [91] |
| 8.7 | 28 September 2017 | Cloud sharing support.[92] |
| 8.5.1 | 19 January 2017 | [93] |
| 8.5 | 1 December 2016 | Added staff sizes on a per-system basis.[94] |
| 8.4.2 | 24 August 2016 | [95] |
| 8.4 | 27 June 2016 | Custom staff size, updated Scorch for iPad.[96] |
| 8.3 | 5 May 2016 | Added individual note colors.[97] |
| 8.2 | 25 March 2016 | [98] |
| 8.1.1 | 8 February 2016 | [99] |
| 8.1 | 21 January 2016 | [100] |
| 8.0.1 | 29 September 2015 | [101] |
| 8.0 | 18 June 2015 | [102] |
| 7.5.1 | 3 July 2014 | Fixed issues with audio and video export, playback, localization, and the Timeline.[103] |
| 7.5 | 28 February 2014 | Support for score sharing, improved playback and notation interpretation, Timeline window and other features.[104][105] |
| 7.1.3 | 26 September 2012 | [106] |
| 7.1.2 | 20 March 2012 | [107] |
| 7.1 | 19 December 2011 | [108] |
| 7.0.3 | 20 October 2011 | [109] |
| 7.0.2 | 23 August 2011 | [110] |
| 7.0.1 | 15 August 2011 | [111] |
| 7.0 | 27 July 2011 | New ribbon-based user interface.[112] This version of Sibelius (and all future versions) is no longer supported on Mac OS X v10.5 or earlier, and Mac computers with PowerPC processors; the last version with this support is Sibelius 6.2.[113][114] |
| 6.2 | 29 April 2010 | [115] |
| 6.1 | 28 September 2009 | [116] |
| 6.0 | 19 May 2009 | [117] |
| 5.1 | 24 October 2007 | [118] |
| 5.0 | 7 June 2007 | [119] |
| 4.0 | 5 July 2005 | [120] |
| 3.0 | 23 September 2003 | [121] |
| 2.0 | 12 November 2001 | First released on Windows,[122] then followed by Mac OS X released on March 2002.[123][124] |
| 1.2 | 1 June 1999 | Macintosh version released.[125][126] |
| 1.0 | 3 September 1998 | Windows version released.[127] |
| Sibelius 7 | April 1993 | Initial release for RISC OS.[128] |
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "What's New in Sibelius". Avid. 14 April 2025. Retrieved 14 April 2025.
- ^ a b "An interview with Ben Finn, co-founder of Sibelius [Part 1 of 2] - Scoring Notes". 23 June 2015. Archived from the original on 5 September 2015. Retrieved 9 September 2015.
- ^ "Sibelius software's London offices to close". Rhinegold.co.uk. 4 July 2012. Archived from the original on 7 December 2017. Retrieved 4 June 2025.
- ^ a b "Avid Divests Consumer Businesses and Streamlines Operations". Business Wire. 2 July 2012. Archived from the original on 26 July 2012. Retrieved 4 June 2025.
- ^ "Of Note: Finale and Sibelius tips and tutorials by musician, arranger and music notation expert Robert Puff". Rpmseattle.com. 16 July 2012. Archived from the original on 4 March 2014. Retrieved 4 June 2025.
- ^ Banks, Adam. (17 August 2012). "Avid hits bum note with Sibelius", MacUser. p.14. Publisher: Dennis Publishing (London, England)
- ^ a b Schofield, Jack (7 August 2012). "Users petition Avid to sell Sibelius music software arm". ZDNet. Retrieved 4 June 2025.
- ^ "Save Sibelius". Facebook. Archived from the original on 16 March 2021. Retrieved 4 June 2025.
- ^ "Sibelius is in crisis!". Archived from the original on 16 March 2021. Retrieved 29 July 2012.
- ^ 'Sibelius' Archived 12 May 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Music Printing History.
- ^ Bourgeois, Derek (1 November 2001). "Score yourself an orchestra". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 10 May 2014. Retrieved 10 May 2011.
Many composers bought an Archimedes simply to have access to the program.
- ^ Arthur, Charles. (10 January 2012). 'How the BBC Micro started a computing revolution' Archived 16 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine. The Guardian. (United Kingdom)
- ^ "Sibelius Corporate Information". Sibelius Software. Archived from the original on 27 May 2007. Retrieved 21 May 2007.
- ^ (6 January 2011). ‘History of ARM: from Acorn to Apple’ Archived 16 March 2018 at the Wayback Machine. The Daily Telegraph. (United Kingdom).
- ^ Seymour, Elle. (28 February 2012). ‘The Day Olivetti Stitched up Acorn Computers’ Archived 23 March 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Huffington Post. (United Kingdom).
- ^ "Sibelius UK Office Closes : Avid Selling Consumer Businesses – OF NOTE". www.rpmseattle.com. 2 July 2012. Archived from the original on 16 March 2021. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- ^ [https://musicprintinghistory.org/sibelius/ Sibelius (1993). History of music publishing. musicprintinghistory.org website.
- ^ Cohen, Peter. (10 March 2002). 'Sibelius 2 music software released for OS X'. Macworld.
- ^ 'Internet publishing with Sibelius'. secure.sibelius.com website.
- ^ Cohen, Peter. (10 March 2002). Sibelius 2 music software released for OS X. Macworld.
- ^ Rothman, Philip. (25 June 2015). An interview with Ben Finn, co-founder of Sibelius [Part 2 of 2]. Scoring Notes.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (23 January 2014). "Sibelius 7.5 announced: An evolutionary, not revolutionary upgrade" Archived 16 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine. Scoring Notes. (Netherlands).
- ^ Rothman, Philip (29 July 2021). "Sibelius arrives on iPad". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 24 February 2022.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (26 October 2021). "Sibelius comes to the iPhone". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 24 February 2022.
- ^ "'Professional sound library—only in Sibelius'". Archived from the original on 19 May 2018. Retrieved 14 May 2018.
- ^ "VST play back in Sibelius 5". Sibelius Software. Archived from the original on 12 November 2013. Retrieved 9 June 2007.
- ^ 'Sib. 7.0: The blasted Ribbon!' Archived 13 May 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Sibelius Help Center. Avid (company).
- ^ NotePerformer Reviews. Slashdot website.
- ^ ‘Note Performer features’ Archived 11 May 2018 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Bourgeois, Derek. (31 October 2012).How to Use External VSTs with Sibelius 7. IMDb.
- ^ ‘Vienna Symphonic Library: Products’ Archived 14 May 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Vienna Symphonic Library.
- ^ Burt, Warren. (March 2020). Review – BBC Symphony Orchestra from Spitfire Audio[usurped]. soundbytesmag.net website.
- ^ Hinchey, John. (8 December 2021). Using Kontakt and other third party virtual instruments in Sibelius Ultimate. Tutorials: scoringnotes.com website.
- ^ ‘Configuring Garritan libraries for use in Sibelius’ Archived 15 May 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Finale (software)#Alfred Music involvement.
- ^ MOTU Symphonic Instrument review. Future Music, 8 November 2007. musicradar.com website.
- ^ 'MOTU Symphonic Instrument Overview' Archived 15 May 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Mark of the Unicorn.
- ^ ‘631: How to play back through a different device’ Archived 24 May 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Help Center. Avid (company).
- ^ ‘Extra plug-ins for Sibelius’ Archived 14 May 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Avid (company)
- ^ ‘WRITTEN BY BOB ZAWALICH’ Archived 16 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine. Scoring Notes.
- ^ Hinchey, John. (12 January 2021). A review of optical music recognition software. scoringnotes.com website.
- ^ ‘PDF to Music’ Archived 14 May 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Myriad.
- ^ PhotoScore and NotateMe Ultimate Review . Matt Vanacoro. macprovideo.com website.
- ^ ‘PhotoScore and NotateMe’ Archived 6 September 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Neuratron.
- ^ ‘AudioScore’ Archived 19 May 2018 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ ‘Create scores from a variety of sources’ Archived 13 May 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Avid (company).
- ^ ‘Neuratron Audioscore Ultimate 8 - Customer reviews’ Archived 16 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine. Amazon (company).
- ^ ‘Neuratron Audioscore Ultimate 7 - Customer reviews’ Archived 7 August 2020 at the Wayback Machine. Amazon (company).
- ^ "CNET AudioScore reviews". cnet.com. Archived from the original on 24 May 2014. Retrieved 23 May 2014.
- ^ Avid Sibelius - Advance Line Keyboard Archived 14 May 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Logic Keyboards.
- ^ ‘Sibelius Keyboard Cover’ Archived 14 May 2018 at the Wayback Machine. KB Covers.
- ^ Puff, Robert. (28 July 2012). iPad Sibelius Wizard : Control Surface for Sibelius. Of Note rpmseattle.com/ website.
- ^ Williams, Derek. ‘iPad Sibelius Wizard’ Archived 14 May 2018 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Spreadbury, Daniel (4 August 2011). Use your iPad as a Sibelius control surface. Scoring Notes.
- ^ Escher, Tobias. ‘Sibelius Control for iPad’ Archived 15 May 2018 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ ‘Sibelius Scorch’ Archived 16 May 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Avid (company).
- ^ ‘Sibelius - Cloud Sharing and Publishing’ Archived 14 May 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Avid (company).
- ^ Avid Knowledge Base: Sibelius Scorch plug-in compatibility Archived 17 August 2019 at the Wayback Machine. Avid (company).
- ^ "'Sibelius Ultimate in the classroom'". Archived from the original on 14 May 2018. Retrieved 14 May 2018.
- ^ 'Network License Server' Archived 14 May 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Avid (company).
- ^ Rothman, Philip (16 April 2025). "Sibelius 2025.4 released". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 17 April 2025.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (13 March 2025). "Sibelius 2025.3 released". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 21 March 2025.
- ^ Trefler, Joseph (10 February 2025). "Sibelius 2025.2 introduces decondensing parts with staff filters". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 12 March 2025.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (24 October 2024). "Sibelius 2024.10 targets MusicXML import, Sequoia support". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (20 August 2024). "Sibelius 2024.8 updated for mobile and cloud". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ a b Rothman, Philip (20 June 2024). "Sibelius is now native on Apple silicon with the 2024.6 update". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (7 March 2024). "Sibelius 2024.3: MIDI copy and paste, remote connection, resizeable Keypad". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (30 November 2023). "Sibelius 2023.11: Sonoma support, more system object positions, better Keypad". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (31 August 2023). "Sibelius 2023.8 released". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ "Sibelius 2023.6.1 on macOS 10.13 High Sierra". avidtech.my.salesforce-sites.com. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ "Introducing AI Model for Chord Auto-Complete". Avid. 22 June 2023. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (4 May 2023). "Sibelius 2023.5: New hiding options make individually voiced parts possible from a condensed score". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (17 March 2022). "Sibelius 2022.3 adds Windows 11, Monterey support". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (16 December 2021). "Avid introduces new license activation system alongside Sibelius 2021.12 update". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ "Sibelius 2021.12 on macOS 10.12 Sierra". Avid Knowledge Base.
- ^ "Avid Sibelius 2021.9 Software Update now available". Avid. 27 September 2021. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (25 February 2021). "Your search is a command in the Sibelius 2021.2 update; M1 Mac support under Rosetta [updated]". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (17 September 2020). "The focus is on staves with the Sibelius 2020.9 update". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (3 June 2020). "Sibelius 2020.6 brings better MusicXML import, color options". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (26 March 2020). "Sibelius 2020.3 released with laissez vibrer ties, other fixes". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (16 January 2020). "NAMM 2020: Sibelius 2020.1 brings automatic staff spacing, tie improvements, and more". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ a b "Sibelius 2019 Product Releases". Avid. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ "What's New in Sibelius 2019.4". Avid Blogs. 6 April 2019. Retrieved 16 May 2019.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (24 January 2019). "NAMM 2019: Sibelius 2019.1 released with Review Mode, Avid Link". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 12 February 2019.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (17 December 2018). "Sibelius 2018.12 update released". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 2 January 2019.
- ^ Rothman, Philip. (29 November 2018). 'Sibelius 2018.11 makes the infrastructure investment'. Scoring Notes. (Netherlands).
- ^ Rothman, Philip. (26 July 2018). 'Sibelius 2018.7 released with bug fixes'. Scoring Notes. (Netherlands).
- ^ Rothman, Philip. (26 June 2018). 'Free Sibelius First now available; other improvements in 2018.6 release'. Scoring Notes. (Netherlands).
- ^ Rothman, Philip. (17 May 2018). 'Sibelius 2018.5 released with one fix pertaining to plug-ins'. Scoring Notes. (Netherlands).
- ^ Rothman, Philip. (7 April 2018). 'Sibelius 2018.4 released with multi-edits for text, better note spacing, much more; re-brands as “Ultimate”'. Scoring Notes. (Netherlands)
- ^ "Supercharge Your Workflow with Avid Sibelius 2018—What's New". 25 January 2018.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (16 November 2017). "Sibelius 8.7.2 update available; instrument changes improved". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (28 September 2017). "Sibelius 8.7 released with Cloud Sharing, other fixes". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (19 January 2017). "Sibelius 8.5.1 update available". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (1 December 2016). "Sibelius 8.5 introduces staff sizes on a per-system basis". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (24 August 2016). "Sibelius 8.4.2 update available". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (27 June 2016). "Sibelius 8.4 released with more custom staff sizes; Scorch for iPad updated". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (5 May 2016). "Sibelius 8.3 released with individual note colors, other fixes". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (25 March 2016). "Sibelius 8.2 features start appearing on web sites". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (8 February 2016). "Sibelius 8.1.1 update available". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (21 January 2016). "Sibelius 8.1 released; rest placement, ending lines, MP3 export among improvements". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (29 September 2015). "Sibelius 8.0.1 update available". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (18 June 2015). "Sibelius 8 is here: The new Sibelius looks a lot like the old one". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Rothman, Philip (3 July 2014). "Sibelius 7.5.1 update released with many improvements". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ "Avid Continues Innovation of Proven and Trusted Music Notation Solutions with Sibelius 7.5 Software" (Press release). Avid. 23 January 2014. Retrieved 23 January 2014.
- ^ "Avid Sibelius 7.5 -". www.soundonsound.com.
- ^ Spreadbury, Daniel (26 September 2012). "Sibelius 7.1.3 update now available". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Spreadbury, Daniel (30 March 2012). "Sibelius 7.1.2 update now available". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Spreadbury, Daniel (19 December 2011). "Sibelius 7.1 update now available". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Spreadbury, Daniel (20 October 2011). "Sibelius 7.0.3 update now available". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Spreadbury, Daniel (23 August 2011). "Sibelius 7.0.2 update now available". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Spreadbury, Daniel (15 August 2011). "Sibelius 7.0.1 update now available". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ "Sibelius 7: Task-oriented user interface". Avid Technology. Retrieved 2 August 2011.
- ^ "Avid end of support announcement: Sibelius on Windows XP, Mac OS X 10.5 or earlier and Mac computers with PowerPC processors". Avid Technology, Inc. Archived from the original on 1 July 2012. Retrieved 5 November 2011.
- ^ Spreadbury, Daniel (27 July 2011). "Sibelius 7 is here!". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Spreadbury, Daniel (29 April 2010). "Sibelius 6.2 update now available". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ Spreadbury, Daniel (28 September 2009). "Sibelius 6.1 update now available". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ "Avid's Sibelius 6 Software Advances Music Notation by Cutting Score Preparation Time in Half". Sibelius Software. 19 May 2009. Archived from the original on 22 September 2009. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ "Sibelius 5.1 Released". Sibelius Software. 24 October 2007. Archived from the original on 25 March 2008. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ "Sibelius launches Sibelius 5". Sibelius Software. 7 June 2007. Archived from the original on 10 June 2007. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- ^ "Sibelius launches Sibelius 4". Sibelius Software. 5 July 2005. Archived from the original on 23 December 2005. Retrieved 10 November 2024.
- ^ "Sibelius 3 leaps forward with 170 new features". Sibelius Software. 23 September 2003. Archived from the original on 1 October 2003. Retrieved 10 November 2024.
- ^ "Sibelius scores again". Sibelius Software. 12 November 2001. Archived from the original on 11 January 2002. Retrieved 10 November 2024.
- ^ Cohen, Peter. "Sibelius 2 music software released for OS X". Macworld. Retrieved 10 November 2024.
- ^ "Revolutionary new Sibelius 2 music notation software is launched for Mac OS X". Sibelius Software. 13 March 2002. Archived from the original on 6 June 2002. Retrieved 10 November 2024.
- ^ "Sibelius® for Macintosh®". Sibelius Software. 1 June 1999. Archived from the original on 15 February 2001. Retrieved 10 November 2024.
- ^ Spreadbury, Daniel (14 October 2008). "A brief history of computer music". Scoring Notes. Retrieved 10 November 2024.
- ^ "Sibelius opens a window to music". Sibelius Software. Archived from the original on 15 February 2001. Retrieved 10 November 2024.
- ^ Halliburton, Rachel (27 August 1995). "Sibelius scores with the keyboard composers". The Independent. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
 KSF
KSF