Sierra Madre del Sur
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 11 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 11 min
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2011) |
| Sierra Madre del Sur | |
|---|---|
 Sierra Madre del Sur on the coast west of Playa Azul, in Michoacán. | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 3,720 m (12,200 ft) |
| Coordinates | 17°55′41″N 100°18′0″W / 17.92806°N 100.30000°W |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 1,000 km (620 mi) NW x SE[1] |
| Area | 143,447 km2 (55,385 sq mi) |
| Geography | |
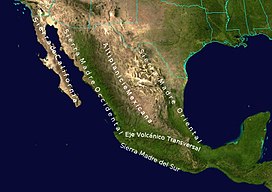 Sierra Madre del Sur, other major mountain ranges, and the Mexican Plateau | |
| Country | Mexico |
| States | Michoacán, Guerrero, Oaxaca |
The Sierra Madre del Sur is a mountain range in southern Mexico, extending 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) from southern Michoacán east through Guerrero, to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in eastern Oaxaca.
Geography
[edit]The Sierra Madre del Sur joins with the Eje Volcánico Transversal (Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt) of central Mexico in northern Oaxaca, but is separated from this range further west by the valley of the Balsas River and its tributary the Tepalcatepec River.
The mountains' highest point is Cerro Nube – 3,720 metres (12,200 ft), in southern Oaxaca. Just one major highway crossed the range between Acapulco and Mexico City until 2024, when two major highways, both in the state of Oaxaca, were inaugurated. [2]
Although separated from the main part of the Sierra Madre del Sur by the deep canyon of the lower Río Balsas, the mountains of southern Michoacán around Coalcomán are usually considered part of the Sierra Madre del Sur.
The eastern end of the Sierra Madre del Sur, in southern Oaxaca, is known as the Sierra Miahuatlán. It extends east–west for about 180 km parallel to the Pacific coast, with broad areas over 1,500 metres elevation, including Cerro Nube. It is bounded on the east and northeast by the valley of the Tehuantepec River and on the north by the Central Valleys of Oaxaca. The Pacific (southern) slope of the Sierra Miahuatlán is covered by humid broadleaf forests.[3]
Ecology
[edit]The range is noted for its very high biodiversity and large number of endemic species.
The Sierra Madre del Sur pine-oak forests ecoregion occupies the higher reaches of the range. These forests are part of a chain of Mesoamerican pine-oak forests that stretch from the Southwestern United States to Costa Rica along the American Cordillera.
Lower elevations of the range are covered by tropical dry forests. Tropical dry forests include closed-canopy forests, woodlands, and thorn scrub, and many trees and shrubs lose their leaves during the winter dry season. The Jalisco dry forests ecoregion occupies the western end of the range's Pacific slope. The Southern Pacific dry forests occupy most of the Pacific slope of the range, from Michoacan in the west through Guerrero and Oaxaca. The basin of the Balsas River, north of the Sierra, is home to the Balsas dry forests.
Protected areas
[edit]Protected areas in the Sierra include the Sierra de Manantlán, Zicuirán-Infiernillo, and Tehuacán-Cuicatlán biosphere reserves, General Juan Álvarez National Park, Boquerón de Tonalá Flora and Fauna Protection Area, Omiltemi Ecological State Park, Los Olivos and El Nanchal state reserves, and the Campo Verde, Iliatenco, Cafetal San Juanito (Pluma Hidalgo), Cafetal Soconusco, Cerro Azul, Concepción Vista Hermosa, El Corozal, and El Borbollón, La Pandura y La Yerbabuena voluntary conservation areas.[4]
References
[edit]- ^ "Sierra Madre del Sur". Peakbagger.com. Retrieved 17 March 2013.
- ^ Lee Stacy (October 2002). Mexico and the United States. Marshall Cavendish. p. 754. ISBN 978-0-7614-7402-9.
- ^ Campbell, J. A., Solano-Zavaleta, I., Flores-Villela, O., Caviedes-Solis, I. W., & Frost, D. R. (2016). A New Species of Abronia (Squamata: Anguidae) from the Sierra Madre del Sur of Oaxaca, Mexico. Journal of Herpetology, 50(1), 149–156. http://www.jstor.org/stable/44164651
- ^ "Sierra Madre del Sur pine-oak forests". DOPA Explorer. Accessed 15 September 2021. [1]
External links
[edit]- "Sierra Madre del Sur pine-oak forests". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund.
- World Wildlife Fund, ed. (2001). "Sierra Madre del Sur pine-oak forests". WildWorld Ecoregion Profile. National Geographic Society. Archived from the original on 2010-03-08.
 KSF
KSF