Spadix (zoology)
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 5 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 5 min

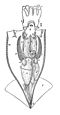
In the field of zoology, a spadix (pl.: spadices) is a secondary sexual organ found in some cephalopods and hydrozoans. In the genus Nautilus, the spadix is a composite erectile organ in the male located in the oral region which is composed of four highly modified tentacles and which is paired with a somewhat smaller antispadix that is also composed of four tentacles. The spadix is normally a concealed organ but quickly becomes distended upon the animal's death. The exact function of the spadix and antispadix in Nautilus is not yet known.[1]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Arthur Giese (2 December 2012). Reproduction of Marine Invertebrates V4: Molluscs: Gastropods and Cephalopods. Elsevier Science. p. 233. ISBN 978-0-323-15305-8.
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spadix_(zoology)39 views | Status: cached on August 16 2025 08:44:16↧ Download as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF