Triband (flag)
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 18 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 18 min
A triband is a vexillological style which consists of three stripes arranged to form a flag. These stripes may be two or three colours, and may be charged with an emblem in the middle stripe.[1] Not all tribands are tricolour flags, which requires three unique colours.
Design
[edit]Outside of the name, which requires three bands of colour, there are no other requirements for what a triband must look like, so there are many flags that look very different from each other but are all considered tribands.
Some triband flags (e.g. those of Germany, Russia and the Netherlands) have their stripes positioned horizontally, while others (e.g. that of Italy) position the stripes vertically. Often the stripes on a triband are of equal length and width, though this is not always the case, as can be seen in the flags of Colombia and Canada. Symbols on tribands may be seals, such as on the Belizean flag, or any manner of emblems of significance to the area the flag represents, such as in the flags of Argentina, India and Lebanon.
Tricolour
[edit]A tricolour (BE) or tricolor (AE) is a type of triband design which originated in the 16th century as a symbol of republicanism, liberty, or revolution. The oldest tricolour flag originates from the Netherlands, whose successor’s design later inspired the French and Russian flags.[2][3]
The flags of France, Italy, Romania, Mexico, Ireland and Paraguay[4] were all adopted with the formation of an independent republic in the period of the French Revolution to the Revolutions of 1848, with the exception of the Irish tricolour, which dates from 1848 but was not popularised until the Easter Rising in 1916 and adopted in 1919.[5]
History
[edit]The first association of the tricolour with republicanism is the orange-white-blue design of the Prince's Flag (Prinsenvlag, precursor of the flags of the Netherlands), first depicted 1575 and used by William I of Orange-Nassau in the Eighty Years' War, establishing the independence of the Dutch Republic from the Spanish Empire. Its red-white-blue successor is the oldest tricolour flag still in use. The flag of the Netherlands inspired both the French and Russian flags, which in turn further inspired many tricolour flags in other countries.[2][3]
Though not the first tricolour flag, one of the most famous, known as Le Tricolore, is the blue, white and red (whence also called Le Bleu-Blanc-Rouge) flag of France adopted in 1790 during the French Revolution. Based on a 1789 design of the Cockade of France, it was easy to construct and also stood in a visual opposition to complicated royal banners of the Ancien Regime.
With the formation of French client republics after 1795, the revolutionary tricolour was exported and adopted more widely in Europe, by the Republic of Alba 1796 (red-blue-yellow), the Cisalpine Republic 1797 (Transpadane Republic, green-white-red), the Cisrhenian Republic 1797 (green-white-red), the Anconine Republic 1797 (blue-yellow-red), the Roman Republic 1798 (black-white-red), the Helvetic Republic 1798 (green-red-yellow; canton of Neuchatel 1848), the Parthenopean Republic 1799 (blue-yellow-red), and the Principality of Lucca and Piombino 1805 (blue-white-red). Thus providing the format for many of modern Europe's national flags, from the flag of Italy, to the flag of Germany, flag of Ireland, flag of Belgium, flag of Romania, flag of Bulgaria, flag of Moldova, and others around the world such as the flag of India, flag of Cameroon, flag of Chad, flag of Ivory Coast, flag of Gabon, flag of Guinea, flag of Mali, and flag of Nigeria.
The green-white-red tricolour remained a symbol of republicanism throughout the 19th century and was adopted as national flag by a number of states following the Revolutions of 1848. It was also adopted by the Kingdom of Sardinia (inherited by the Kingdom of Italy 1861).
The flag of Germany (black-red-gold) originates from the uniform colours of the Lützow Free Corps during the Napoleonic Wars, which contained volunteers from many German states and became famous through propaganda. Prominent veterans and later students became the core of the republican movement of early 1800s which adopted the colours. At the time the flag was known as Dreifarb, a German calque of Tricolore. It was a symbol of opposition against the German Kleinstaaterei and the desire for German Unification. It was at first illegal in the German Confederation, but was adopted as the national flag at the Frankfurt Parliament of 1848/9. The flag of Belgium was introduced in a similar context, in 1831, its colours taken from the flag used in the Brabant Revolution of 1789. The first national flag of the New World inspired by this symbolism was the flag of Mexico, adopted when the First Mexican Empire gained independence from Spain in 1821.
After 1848, the young republican nation states continued to pick triband designs, but now more prevalently expressing the sentiment of nationalism or ethnic identity than anti-monarchism, the flag of Hungary (1848), the flag of Romania (1848), the flag of Ireland (1848), the flag of Estonia (1880s), the flag of Lithuania (1905), and the flag of Armenia (1918). By contrast, the flag of Russia was adopted by the Tsardom of Russia in the late 17th century and while it may or may not have been inspired by the Dutch tricolour, it never had any republican implications.
The political ideology of the unification of an ethnic nation state associated with tricolour flags since the 19th century has resulted in the design of new "tricolours" expressing specific nationalisms in the 20th century, the Pan-African colours adopted in the 1920s for Pan-Africanism, chosen in numerous African flags during decolonisation (green-yellow-red, taken from the triband design used by the Solomonic dynasty for the Ethiopian Empire since 1897). The Pan-Arab colours adopted in Arab nationalism 1916 are a comparable concept, even though they combine four, not three, colours. Also in the 20th century, Pan-Iranian colours for Iranian nationalism and Pan-Slavic colours for Slavic nationalism were adopted based on the triband design of the flags used during the 19th century by the Qajar dynasty and the Russian Empire, respectively.
During the brief Second Spanish Republic, a red-yellow-purple tricolour was adopted as its official flag. Today, it is still used by Spanish republicans.
The Indian independence movement in 1931 also adopted a tricolour (loan-translated as Hindi, तिरंगा Tiraṅgā) in the traditional symbolism of "national unification" and republican "self-rule" (Purna Swaraj), adopted as the flag of the India in 1947.[6]
In 1999, a red, green, and blue tricolour was proposed as the Flag of Mars. The design symbolises liberty, and also the terraforming of Mars by humanity from a red planet to a green one, and eventually an Earth-like blue one.
Gallery
[edit]-
The flag of Afghanistan (2013–2021), a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Afghanistan (1929), a charged vertical triband.
-
Variant of the flag of Afghanistan (1928–1929), a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Afghanistan (1928–1929), a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Afghanistan (1928), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The Alamo Flag, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of the Republic of Alba (1796), a simple vertical triband.
-
Variant flag of the Republic of Alba (1796), a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of the Italian National Liberation Committee (1944), a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Albany, New York, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Anaheim, California (2018–2019), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Andorra, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of the Arabian Republican movement, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of the Republic of Ararat, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Argentina, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Armenia, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Austria, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of the Federal State of Austria, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Azerbaijan, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Barbados, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Belgium, a simple vertical triband.
-
The flag of Belize, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Biafra, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Birmingham, Alabama, a charged vertical triband.
-
The bisexual pride flag, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Bolivia, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of The Bronx, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Bulgaria, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Cabinda Province, Angola, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Cambodia, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Cameroon, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Canada, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Chad, a simple vertical triband.
-
The flag of the Cispadane Republic, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Coahuila y Tejas, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Coclé Province, Panama, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Colombia, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Colorado, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Colorado (1911–1964), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Conway, Arkansas, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Crimea, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Croatia, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of SR Croatia, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Curaçao, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Dallas, Texas, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The Dodson Flag, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of the Durrani Empire, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of the Dutch West India Company, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of East Germany, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Ecuador, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Egypt, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of El Salvador, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Estonia, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Ethiopia, a charged horizontal triband.
-
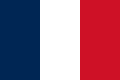
The flag of France, a simple vertical triband.
-
Variant of the flag of France, a simple vertical triband.
-
The flag of Free France, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of French Polynesia, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of French Sudan, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Gabon, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Gagauzia, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The genderqueer pride flag, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of the German Empire, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Germany, a simple horizontal triband.
-
Variant of the flag of Germany, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Ghana, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Ghana (1964–1966), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Gran Colombia (1819–1820), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Gran Colombia (1820–1821), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Gran Colombia (1821–1830), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Guatemala, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Guinea, a simple vertical triband.
-
The flag of Honduras, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Hungary, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The Illinois centennial flag, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The Indiana centennial flag, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of India, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Iowa, a charged vertical triband.
-
Variant flag of Iowa, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Iran, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Pahlavi Iran, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Iraq, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Iraq (2004–2008), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Iraq (1991–2004), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Iraq (1963–1991), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Iraq (1959–1963), a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Ireland, a simple vertical triband.
-
The flag of Italy, a simple vertical triband.
-
The civil ensign of Italy, a charged vertical triband.
-
The state ensign of Italy, a charged vertical triband.
-
The naval ensign of Italy, a charged vertical triband.
-
The war flag of Italy, a simple vertical triband.
-
The flag of the Kingdom of Italy, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Ivory Coast, a simple vertical triband.
-
The flag of the Kazakh SSR, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Kyiv Oblast, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Laos, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Latvia, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Lebanon, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Lesotho, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Libya, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of the Lybian Arab Republic (1972–1977), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of the Lybian Arab Republic (1969–1972), a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Lithuania, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of the Lithuanian SSR, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Luxembourg, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Malawi, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Mali, a simple vertical triband.
-
The flag of Manhattan, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Mauritania, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The maverique pride flag, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Mexico, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Missouri, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Moldova, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of the Moldavian SSR, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Mongolia, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Monseñor Nouel Province, Dominican Republic, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Myanmar, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Nauru, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of the Netherlands, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of New York City, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Nicaragua, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Niger, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Nigeria, a simple vertical triband.
-
The flag of North Caribbean Coast, Nicaragua, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Ossetia, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The Pan-African flag, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The pansexual flag, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Paraguay, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The state flag of Peru, a simple vertical triband.
-
The polyamory pride flag (original 1995 design by Jim Evans), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The polysexual pride flag, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The Prince's Flag, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Príncipe, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Prussia (1892–1918), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Prussia (1918–1933), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The service flag of Prussia (1933–1935), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of the Republic of the Congo, a simple diagonal triband.
-
The flag of the Roman Republic (1849), a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Romania, a simple vertical triband.
-
The flag of Russia, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Russia (1991–1993), a simple horizontal triband.
-
The black-yellow-white flag of the Russian Empire, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Rwanda, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The 1962–2001 flag of Rwanda, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Santa Cruz Department, Bolivia, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Schenectady County, New York, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Senegal, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of Serbia, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of SR Serbia, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Sierra Leone, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Slovakia, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Slovenia, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of SR Slovenia, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Somaliland, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of South Africa (1928–1994), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Spain, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Francoist Spain (1945–1977), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Francoist Spain (1938–1945), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Francoist Spain (1936-1938), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of the Second Spanish Republic, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of the First Spanish Republic, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The Statenvlag, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Sudan (1956–1970), a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Syria (previously the flag of the Syrian opposition to Bashar al-Assad), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of the Syrian Salvation Government, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Tajikistan, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The civil ensign of the Republic of Texas, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Transnistria, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Ulster County, New York, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of the Union of African States (1958–1961), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of the Union of African States (1961–1963), a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Utah, a horizontal triband charged with a beehive.
-
The flag of the United Team of Germany, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Venezuela, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Yemen, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of the Yemen Arab Republic, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Serbia and Montenegro, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Yugoslavia, a charged horizontal triband.
-
The flag of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, a simple horizontal triband.
-
The flag of Yukon, a charged vertical triband.
-
The flag of SR Zanzibar, a simple horizontal triband.
See also
[edit]- Flag families
- List of flags by design
- List of national flags by design
- Gallery of sovereign state flags
- Gallery of flags of dependent territories
- Fin flash on military aircraft, sometimes in a "tricolour" form
References
[edit]- ^ Smith, Whitney (2003). Flag Lore of All Nations. Brookfield, Connecticut: The Millbrook Press. ISBN 0-7613-1753-8.
- ^ a b "Flags That Look Alike". Britannica. Retrieved 2023-04-23.
- ^ a b Hylland Eriksen, Thomas; Jenkins, Richard (2007). Flag, nation and symbolism in Europe and America. London: Routledge. pp. 23 and 27. ISBN 978-0-203-93496-8. OCLC 182759362.
- ^ "Las Banderas del Paraguay y su Historia: el Ministerio del Interior cuenta con una Galería". mdi.gov.py. May 20, 2017. Archived from the original on Oct 7, 2016.
- ^ "tricolor - definition of tricolor". Oxford Dictionaries | English. Archived from the original on 1 November 2016. Retrieved 2016-10-31.
- ^ Roy, Srirupa (August 2006). "A Symbol of Freedom: The Indian Flag and the Transformations of Nationalism, 1906–". Journal of Asian Studies. 65 (3): 508. ISSN 0021-9118. OCLC 37893507.
 KSF
KSF