V2 word order
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 35 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 35 min
| Linguistic typology |
|---|
| Morphological |
| Morphosyntactic |
| Word order |
| Lexicon |
In syntax, verb-second (V2) word order[1] is a sentence structure in which the finite verb of a sentence or a clause is placed in the clause's second position, so that the verb is preceded by a single word or group of words (a single constituent).
Examples of V2 in English include (brackets indicating a single constituent):
- "Neither do I", "[Never in my life] have I seen such things"
If English used V2 in all situations, then it would feature such sentences as:
V2 word order is common in the Germanic languages and is also found in Northeast Caucasian Ingush, Uto-Aztecan O'odham, and fragmentarily in Romance Sursilvan (a Rhaeto-Romansh variety) and Finno-Ugric Estonian.[2] Of the Germanic family, English is exceptional in having predominantly SVO order instead of V2, although there are vestiges of the V2 phenomenon.
Most Germanic languages do not normally use V2 order in embedded clauses, with a few exceptions. In particular, German, Dutch, and Afrikaans revert to VF (verb final) word order after a complementizer; Yiddish and Icelandic do, however, allow V2 in all declarative clauses: main, embedded, and subordinate. Kashmiri (an Indo-Aryan language) has V2 in 'declarative content clauses' but VF order in relative clauses.
Examples
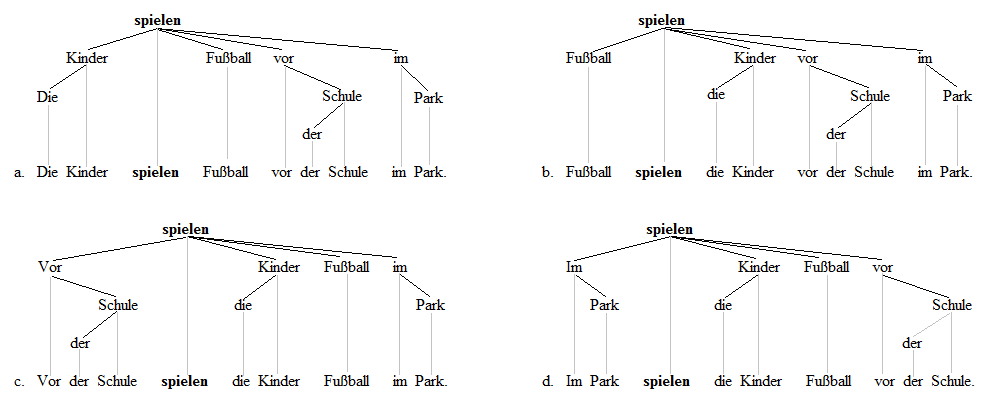
[edit]The example sentences in (1) from German illustrate the V2 principle, which allows any constituent to occupy the first position as long as the second position is occupied by the finite verb. Sentences (1a) through to (1d) have the finite verb spielten 'played' in second position, with various constituents occupying the first position: in (1a) the subject is in first position; in (1b) the object is; in (1c) the temporal modifier is in first position; and in (1d) the locative modifier is in first position.
Die
The-NOM-PL
Kinder
child-NOM-PL
spielten
play-PRET-3PL
vor
before
der
the-DAT-SG
Schule
school-DAT-SG
im
in the-DAT-SG
Park
park-DAT-SG
Fußball.
football/soccer-ACC-SG.
The children played football/soccer in the park before school.
Fußball
Football/soccer-ACC-SG
spielten
play-PRET-3PL
die
the-NOM-PL
Kinder
child-NOM-PL
vor
before
der
the-DAT-SG
Schule
school-DAT-SG
im
in the-DAT-SG
Park.
park-DAT-SG.
The children played football/soccer in the park before school.
Vor
Before
der
the-DAT-SG
Schule
school-DAT-SG
spielten
play-PRET-3PL
die
the-NOM-PL
Kinder
child-NOM-PL
im
in the-DAT-SG
Park
park-DAT-SG
Fußball.
football/soccer-ACC-SG.
The children played football/soccer in the park before school.
Im
In the-DAT-SG
Park
park-DAT-SG
spielten
play-PRET-3PL
die
the-NOM-PL
Kinder
child-NOM-PL
vor
before
der
Schule
school-DAT-SG
Fußball.
football/soccer-ACC-SG.
The children played football/soccer in the park before school.
In this example, English is more straightforward to compare to a North Germanic language: The same inversions occur regularly in the North Germanic languages, and in Dutch, for that matter, but English uses the North Germanic word order apart from having lost the inversions in common use. If the same example in Norwegian were translated to English with the inversions intact:
Barna
child-DEF-PL
spilte
play-PRET
fotball
football/soccer
i
in
parken
park-DEF-SG
før
before
skoletid.
schooltime-SG.
The children played football/soccer in the park before schooltime.
Fotball
football/soccer
spilte
play-PRET
barna
child-DEF-PL
i
in
parken
park-DEF-SG
før
before
skoletid.
schooltime-SG.
Football/soccer played the children in the park before schooltime.
Før
Before
skoletid
schooltime
spilte
play-PRET
barna
child-DEF-PL
fotball
football/soccer
i
in
parken.
park-DEF-SG.
Before schooltime played the children football/soccer in the park.
I
in
parken
park-DEF-SG
spilte
play-PRET
barna
child-DEF-PL
fotball
football/soccer
før
before
skoletid.
schooltime.
In the park played the children football/soccer before schooltime.
The caveat here (unlike in German) is that in languages without grammatical case, the form with the object first (2b) can only be used unambiguously when the object is unmistakable from the subject, such as if it is a personal pronoun, or as in this example, cannot meaningfully be the subject. In speech, such inversions are usually marked with emphasis: Apart from inversions that are obligatory in their grammatical context, such as "jeg tenker, derfor er jeg" (I think, therefore am I), when an inversion occurs for no other reason than emphasis, which is what opens up for possible ambiguity, the word in the emphasized position before the verb is usually also emphasized in speech.
Classical accounts
[edit]In major theoretical research on V2 properties, researchers discussed that verb-final orders found in German and Dutch embedded clauses suggest an underlying SOV order with specific syntactic movement rules which change the underlying SOV order, deriving a surface form where the finite verb is in the second position of the clause.[3]
We first see a "verb preposing" rule, which moves the finite verb to the left-most position in the sentence, then a "constituent preposing" rule, which moves a constituent in front of the finite verb. Following these two rules will always result with the finite verb in second position. "I like the man":
Ich
I
den
the-ACC-SG
Mann
man-ACC-SG
mag.
like-PRES-1SG.
I like the man.
→ Underlying form in modern German
Mag
Like-PRES-1SG
ich
I
den
the-ACC-SG
Mann.
man-ACC-SG.
I like the man.
→ Verb movement to left edge
Den
The-ACC-SG
Mann
man-ACC-SG
mag
like-PRES-1SG
ich.
I.
I like the man.
→ Constituent moved to left edge
Non-finite verbs and embedded clauses
[edit]Non-finite verbs
[edit]The V2 principle regulates the position of finite verbs only; its influence on non-finite verbs (infinitives, participles, etc.) is indirect. Non-finite verbs in V2 languages appear in varying positions depending on the language. In German and Dutch, for instance, non-finite verbs appear after the object (if one is present) in clause final position in main clauses (OV order). Swedish and Icelandic, in contrast, position non-finite verbs after the finite verb but before the object (if one is present) (VO order). That is, V2 operates on only the finite verb.
Embedded clauses
[edit](In the following examples, finite verb forms are in bold, non-finite verb forms are in italics and subjects are underlined.)
Germanic languages vary in the application of V2 order in embedded clauses. They fall into three groups.
Swedish, Danish, Norwegian, Faroese
[edit]In these languages, the word order of clauses is generally fixed in two patterns of conventionally numbered positions.[4] Both end with positions for (5) non-finite verb forms, (6) objects, and (7), adverbials.
In main clauses, the V2 constraint holds. The finite verb must be in position (2) and sentence adverbs in position (4). The latter include words with meanings such as 'not' and 'always'. The subject may be position (1), but when a topical expression occupies the position, the subject is in position (3).
In embedded clauses, the V2 constraint is absent. After the conjunction, the subject must immediately follow; it cannot be replaced by a topical expression. Thus, the first four positions are in the fixed order (1) conjunction, (2) subject, (3) sentence adverb, (4) finite verb
The position of the sentence adverbs is important to those theorists who see them as marking the start of a large constituent within the clause. Thus the finite verb is seen as inside that constituent in embedded clauses, but outside that constituent in V2 main clauses.
Swedish
main clause
embedded clauseFront
—Finite verb
ConjunctionSubject
SubjectSentence adverb
Sentence adverb—
Finite verbNon-finite verb
Non-finite verbObject
ObjectAdverbial
Adverbialmain clause a. I dag ville Lotte inte läsa tidningen 1 2 3 4 5 6 today wanted Lotte not read the newspaper ... 'Lotte didn't want to read the paper today.' embedded clause b. att Lotte inte ville koka kaffe i dag 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 that Lotte not wanted brew coffee today ... 'that Lotte didn't want to make coffee today'
Main clause Front Finite verb Subject Sentence adverb __ Non-finite verb Object Adverbial
Embedded clause __ Conjunction Subject Sentence adverb Finite verb Non-finite verb Object Adverbial
Main clause (a) I dag ville Lotte inte läsa tidningen
today wanted Lotte not read the newspaper
"Lotte didn't want to read the paper today."
Embedded clause (b) att Lotte inte ville koka kaffe i dag
that Lotte not wanted brew coffee today
"that Lotte didn't want to make coffee today."
Danish
main clause
embedded clauseFront
—Finite verb
ConjunctionSubject
SubjectSentence adverb
Sentence adverb—
Finite verbNon-finite verb
Non-finite verbObject
ObjectAdverbial
Adverbialmain clause a. Klaus er ikke kommet 1 2 4 5 Klaus is not come ...'Klaus hasn't come.' embedded clause b. når Klaus ikke er kommet 1 2 3 4 5 when Klaus not is come ...'when Klaus hasn't come'
So-called Perkerdansk is an example of a variety that does not follow the above.
Norwegian
(with multiple adverbials and multiple non-finite forms, in two varieties of the language)
main
embeddedFront
—Finite verb
ConjunctionSubject
SubjectSentence adverb
Sentence adverb—
Finite verbNon-finite verb
Non-finite verbObject
ObjectAdverbial
Adverbialmain clause a. Den gangen hadde han dessverre ikke villet sende sakspapirene før møtet. (Bokmål variety) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 that time had he unfortunately not wanted to send the documents before the meeting ... 'This time he had unfortunately not wanted
to send the documents before the meeting.'embedded clause b. av di han denne gongen diverre ikkje hadde vilja senda sakspapira føre møtet. (Nynorsk variety) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 because he this time unfortunately not had wanted to send the documents before the meeting ... 'because this time he had unfortunately not wanted
to send the documents before the meeting.'
Faroese
Unlike continental Scandinavian languages, the sentence adverb may either precede or follow the finite verb in embedded clauses. A (3a) slot is inserted here for the following sentence adverb alternative.
main clause
embedded clauseFront
—Finite verb
ConjunctionSubject
SubjectSentence adverb
Sentence adverb—
Finite verb—
Sentence adverbNon-finite verb
Non-finite verbObject
ObjectAdverbial
Adverbialmain clause a. Her man fólk ongantíð hava fingið fisk fyrr 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 here must people never have caught fish before ... 'People have surely never caught fish here before.' embedded clause b. hóast fólk ongantíð hevur fingið fisk her 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 although people never have caught fish here c. hóast fólk hevur ongantíð fingið fisk her 1 2 4 (3a) 5 6 7 although people have never caught fish here ... 'although people have never caught fish here'
German
[edit]In main clauses, the V2 constraint holds. As with other Germanic languages, the finite verb must be in the second position. However, any non-finite forms must be in final position. The subject may be in the first position, but when a topical expression occupies the position, the subject follows the finite verb.
In embedded clauses, the V2 constraint does not hold. The finite verb form must be adjacent to any non-finite at the end of the clause.
German grammarians traditionally divide sentences into fields. Subordinate clauses preceding the main clause are said to be in the first field (Vorfeld), clauses following the main clause in the final field (Nachfeld).
The central field (Mittelfeld) contains most or all of a clause, and is bounded by left bracket (Linke Satzklammer) and right bracket (Rechte Satzklammer) positions.
In main clauses, the initial element (subject or topical expression) is said to be located in the first field, the V2 finite verb form in the left bracket, and any non-finite verb forms in the right bracket.
In embedded clauses, the conjunction is said to be located in the left bracket, and the verb forms in the right bracket. In German embedded clauses, a finite verb form follows any non-finite forms.
German[5]
First field Left bracket Central field Right bracket Final field Main clause a. Er hat dich gestern nicht angerufen weil er dich nicht stören wollte. he has you yesterday not rung ... 'He didn't ring you yesterday because he didn't want to disturb you.' b. Sobald er Zeit hat wird er dich anrufen As soon as he has time will he you ring ...'When he has time he will ring you.' Embedded clause c. dass er dich gestern nicht angerufen hat that he you yesterday not rung has ...'that he didn't ring you yesterday'
Dutch and Afrikaans
[edit]V2 word order is used in main clauses; the finite verb must be in the second position. However, in subordinate clauses two word orders are possible for the verb clusters.
Main clauses:
Dutch[6]
First field Left bracket Central field Right bracket Final field Main clause a. De Māori hebben Nieuw-Zeeland ontdekt The Māori have New Zealand discovered ...'The Māori have discovered New Zealand.' b. Tussen ongeveer 1250 en 1300 ontdekten de Māori Nieuw-Zeeland Between approximately 1250 and 1300 discovered the Māori New Zealand ...'Between about 1250 and 1300, the Māori discovered New Zealand.' c. Niemand had gedacht dat ook maar iets zou gebeuren. Nobody had thought ...'Nobody figured that anything would happen.' Embedded clause d. dat de Māori Nieuw-Zeeland hebben ontdekt that the Māori New Zealand have discovered ...'that the Māori have discovered New Zealand'
This analysis suggests a close parallel between the V2 finite form in main clauses and the conjunctions in embedded clauses. Each is seen as an introduction to its clause-type, a function which some modern scholars have equated with the notion of specifier. The analysis is supported in spoken Dutch by the placement of clitic pronoun subjects. Forms such as ze cannot stand alone, unlike the full-form equivalent zij. The words to which they may be attached are those same introduction words: the V2 form in a main clause, or the conjunction in an embedded clause.[7]
First field Left bracket Central field Right bracket Final field Main clause e. Tussen ongeveer 1250 en 1300 ontdekten-ze Nieuw-Zeeland between approximately 1250 and 1300 discovered-they New Zealand ...'Between about 1250 and 1300, they discovered New Zealand.' Embedded clause f. dat-ze tussen ongeveer 1250 en 1300 Nieuw-Zeeland hebben ontdekt that-they between approximately 1250 and 1300 New Zealand have discovered ...'that they have discovered New Zealand between about 1250 and 1300'
Subordinate clauses:
In Dutch subordinate clauses two word orders are possible for the verb clusters and are referred to as the "red": omdat ik heb gewerkt, "because I have worked": like in English, where the auxiliary verb precedes the past particle, and the "green": omdat ik gewerkt heb, where the past particle precedes the auxiliary verb, "because I worked have": like in German.[8] In Dutch, the green word order is the most used in speech, and the red is the most used in writing, particularly in journalistic texts, but the green is also used in writing as is the red in speech. Unlike in English however adjectives and adverbs must precede the verb: ''dat het boek groen is'', "that the book green is".
First field Left bracket Central field Right bracket Final field Embedded clause g. omdat ik het dan gezien zou hebben most common in the Netherlands because I it then seen would have h. omdat ik het dan zou gezien hebben most common in Belgium because I it then would seen have i. omdat ik het dan zou hebben gezien often used in writing in both countries, but common in speech as well, most common in Limburg because I it then would have seen j. omdat ik het dan gezien hebben zou used in Friesland, Groningen and Drenthe, least common but used as well because I it then seen have would ...'because then I would have seen it'
V2 in Icelandic and Yiddish
[edit]These languages freely allow V2 order in embedded clauses.
Icelandic
Two word-order patterns are largely similar to continental Scandinavian. However, in main clauses an extra slot is needed for when the front position is occupied by Það. In these clauses the subject follows any sentence adverbs. In embedded clauses, sentence adverbs follow the finite verb (an optional order in Faroese).[9]
main clause
embedded clauseFront
—Finite verb
ConjunctionSubject
Subject—
Finite verbSentence adverb
Sentence adverbSubject
—Non-finite verb
Non-finite verbObject
ObjectAdverbial
Adverbialmain clause a. Margir höfðu aldrei lokið verkefninu. Many had never finished the assignment ... 'Many had never finished the assignment.' b. Það höfðu aldrei margir lokið verkefninu. there have never many finished the assignment ... 'There were never many people who had finished the assignment.' c. Bókina hefur María ekki lesið. the book has Mary not read ... 'Mary hasn't read the book.' embedded clause d. hvort María hefur ekki lesið bokina. whether Mary has not read the book ... 'whether Mary hasn't read the book'
In more radical contrast with other Germanic languages, a third pattern exists for embedded clauses with the conjunction followed by the V2 order: front-finite verb-subject.[10]
Conjunction Front
(Topic adverbial)Finite verb Subject e. Jón efast um að á morgun fari María snemma á fætur. John doubts that tomorrow get Mary early up ... 'John doubts that Mary will get up early tomorrow.' Conjunction Front
(Object)Finite verb Subject f. Jón harmar að þessa bók skuli ég hafa lesið. John regrets that this book shall I have read ... 'John regrets that I have read this book.'
Yiddish
Unlike Standard German, Yiddish normally has verb forms before Objects (SVO order), and in embedded clauses has conjunction followed by V2 order.[11]
Front
(Subject)Finite verb Conjunction Front
(Subject)Finite verb a. ikh hob gezen mitvokh, az ikh vel nit kenen kumen donershtik I have seen Wednesday that I will not can come Thursday ... 'I saw on Wednesday that I wouldn't be able to come on Thursday.' Front
(Adverbial)Finite verb Subject Conjunction Front
(Adverbial)Finite verb Subject b. mitvokh hob ikh gezen, az donershtik vel ikh nit kenen kumen Wednesday have I seen that Thursday will I not can come ... On Wednesday I saw that on Thursday I wouldn't be able to come.'
Root clauses
[edit]One type of embedded clause with V2 following the conjunction is found throughout the Germanic languages, although it is more common in some than it is others. These are termed root clauses. They are declarative content clauses, the direct objects of so-called bridge verbs, which are understood to quote a statement. For that reason, they exhibit the V2 word order of the equivalent direct quotation.
Danish
Items other than the subject are allowed to appear in front position.
Conjunction Front
(Subject)Finite verb a. Vi ved at Bo ikke har læst denne bog We know that Bo not has read this book ... 'We know that Bo has not read this book.' Conjunction Front
(Object)Finite verb Subject b. Vi ved at denne bog har Bo ikke læst We know that this book has Bo not read ... 'We know that Bo has not read this book.'
Swedish
Items other than the subject are occasionally allowed to appear in front position. Generally, the statement must be one with which the speaker agrees.
Conjunction Front
(Adverbial)Finite verb Subject d. Jag tror att i det fallet har du rätt I think that in that respect have you right ... 'I think that in that respect you are right.'
This order is not possible with a statement with which the speaker does not agree.
Conjunction Front
(Adverbial)Finite verb Subject e. *Jag tror inte att i det fallet har du rätt (The asterisk signals that the sentence is not grammatically acceptable.) I think not that in that respect have you right ... 'I don't think that in that respect you are right.'
Norwegian
Conjunction Front
(Adverbial)Finite verb Subject f. hun fortalte at til fødselsdagen hadde hun fått kunstbok (Bokmål variety) she told that for her birthday had' she received art-book ... 'She said that for her birthday she had been given a book on art.'
German
Root clause V2 order is possible only when the conjunction dass is omitted. In such cases, formal usage also places the finite verb form into the present subjunctive (German Konjunktiv I) if the verb form is clearly distinguishable from the indicative; if not, the past subjunctive (German Konjunktiv II) is used.
By contrast, a form with an embedded first-person subject would usually use the past subjunctive here, since the present indicative and subjunctive appear identical: Er behauptet, ich hätte (instead of habe) es zur Post gebracht.Conjunction Front
(Subject)Finite verb g. *Er behauptet, dass er hat es zur Post gebracht (The asterisk signals that the sentence is not grammatically acceptable.) h. Er behauptet, er habe es zur Post gebracht he claims (that) he has it to the post office taken ... 'He claims that he took it to the post office.'
Compare the normal embed-clause order after dass
Left bracket
(Conjunction)Central field Right bracket
(Verb forms)i. Er behauptet, dass er es zur Post gebracht hat he claims that he it to the post office taken has
Perspective effects on embedded V2
[edit]There are a limited number of V2 languages that can allow for embedded verb movement for a specific pragmatic effect similar to that of English. This is due to the perspective of the speaker. Languages such as German and Swedish have embedded verb second. The embedded verb second in these kinds of languages usually occur after 'bridge verbs'.[12]
(Bridge verbs are common verbs of speech and thoughts such as "say", "think", and "know", and the word "that" is not needed after these verbs. For example: I think he is coming.)
Jag
I
ska
will
säga
say
dig
you
att
that
jag
I
är
am
inte
not
ett
a
dugg
dew
intresserad.
interested.
(Swedish)
"I tell you that I am not the least bit interested."
→ In this sentence, "tell" is the bridge verb and "am" is an embedded verb second.
Based on an assertion theory, the perspective of a speaker is reaffirmed in embedded V2 clauses. A speaker's sense of commitment to or responsibility for V2 in embedded clauses is greater than a non-V2 in embedded clause.[13] This is the result of V2 characteristics. As shown in the examples below, there is a greater commitment to the truth in the embedded clause when V2 is in place.
Maria
Maria-NOM-SG
denkt,
think-PRES-3SG,
dass
that
Peter
Peter-NOM-SG
glücklich
happy
ist.
be-PRES-3SG
→ In a non-V2 embedded clause, the speaker is only committed to the truth of the statement "Maria thinks ..."
Maria
Maria-NOM-SG
denkt,
think-PRES-3SG,
Peter
Peter-NOM-SG
ist
be-PRES-3SG
glücklich.
happy.
→ In a V2 embedded clause, the speaker is committed to the truth of the statement "Maria thinks ..." and also the proposition "Peter is happy".
Variations
[edit]Variations of V2 order such as V1 (verb-initial word order), V3 and V4 orders are widely attested in many Early Germanic and Medieval Romance languages. These variations are possible in the languages however it is severely restricted to specific contexts.
V1 word order
[edit]V1 (verb-initial word order) is a type of structure that contains the finite verb as the initial clause element. In other words the verb appears before the subject and the object of the sentence.
(a) Max y-il [s no' tx;i;] [o naq Lwin]. (Mayan)
PFV A3-see CLF dog CLF Pedro
'The dog saw Pedro.'
V3 word order
[edit]V3 (verb-third word order) is a variation of V2 in which the finite verb is in third position with two constituents preceding it. In V3, like in V2 word order, the constituents preceding the finite verb are not categorically restricted, as the constituents can be a DP, a PP, a CP and so on.[14]
[DP
Jedes
every
jahr]
year
[Pn
ich]
I
kauf
buy-PRES-1SG
mir
me-DAT-SG
bei
at
Deichmann
Deichmann-DAT-SG
(substandard German, „Kiezdeutsch“)
"Every year I buy (shoes) at Deichmann's"
[PP
ab
from
jetzt]
now
[Pn
ich]
I
krieg
get-PRES-SG
immer
always
zwanzig
twenty
Euro
euro-ACC-PL
(substandard German)
"From now on, I always get twenty euros"
Left edge filling trigger (LEFT)
[edit]V2 is fundamentally derived from a morphological obligatory exponence effect at sentence level. The left edge filling trigger (LEFT) effects are usually seen in classical V2 languages such as Germanic languages and Old Romance languages. The left edge filling trigger is independently active in morphology as EPP effects are found in word-internal levels. The obligatory exponence derives from absolute displacement, ergative displacement and ergative doubling in inflectional morphology. In addition, second position rules in clitic second languages demonstrate post-syntactic rules of LEFT movement. Using the language Breton as an example, absence of a pre-tense expletive will allow for the LEFT to occur to avoid tense-first. The LEFT movement is free from syntactic rules which is evidence for a post-syntactic phenomenon. With the LEFT movement, V2 word order can be obtained as seen in the example below.[15]
Bez
EXPL
'nevo
Fin.[will.have]
hennex
he
traou
things
(in Breton)
"He will have goods"
In this Breton example, the finite head is phonetically realized and agrees with the category of the preceding element. The pre-tense "Bez" is used in front of the finite verb to obtain the V2 word order. (finite verb "nevo" is bolded).
Syntactic verb second
[edit]It is said that V2 patterns are a syntactic phenomenon and therefore have certain environments where it can and cannot be tolerated. Syntactically, V2 requires a left-peripheral head (usually C) with an occupied specifier and paired with raising the highest verb-auxiliary to that head. V2 is usually analyzed as the co-occurrence of these requirements, which can also be referred to as "triggers". The left-peripheral head, which is a requirement that causes the effect of V2, sets further requirements on a phrase XP that occupies the initial position, so that this phrase XP may always have specific featural characteristics. [16]
English
[edit]Modern English differs greatly in word order from other modern Germanic languages, but earlier English shared many similarities. For this reason, some scholars propose a description of Old English with V2 constraint as the norm. The history of English syntax is thus seen as a process of losing the constraint.[17]
Old English
[edit]In these examples, finite verb forms are in green, non-finite verb forms are in orange and subjects are blue.
Main clauses
[edit]Se
the
mæssepreost
masspriest
sceal
shall
manum
people
bodian
preach
þone
the
soþan
true
geleafan
faith
'The mass priest shall preach the true faith to the people.'
Hwi
Why
wolde
would
God
God
swa
so
lytles
small
þinges
thing
him
him
forwyrman
deny
'Why would God deny him such a small thing?'
on
in
twam
two
þingum
things
hæfde
has
God
God
þæs
the
mannes
man's
sawle
soul
geododod
endowed
'With two things God had endowed man's soul.'
þa
then
wæs
was
þæt
the
folc
people
þæs
of-the
micclan
great
welan
prosperity
ungemetlice
excessively
brucende
partaking
'Then the people were partaking excessively of the great prosperity.'
Ne
not
sceal
shall
he
he
naht
nothing
unaliefedes
unlawful
don
do
'He shall not do anything unlawful.'
Ðas
these
ðreo
three
ðing
things
forgifð
gives
God
God
he
his
gecorenum
chosen
'These three things God gives to his chosen
Position of object
[edit]In examples b, c and d, the object of the clause precedes a non-finite verb form. Superficially, the structure is verb-subject-object- verb. To capture generalities, scholars of syntax and linguistic typology treat them as basically subject-object-verb (SOV) structure, modified by the V2 constraint. Thus Old English is classified, to some extent, as an SOV language. However, example a represents a number of Old English clauses with object following a non-finite verb form, with the superficial structure verb-subject-verb object. A more substantial number of clauses contain a single finite verb form followed by an object, superficially verb-subject-object. Again, a generalisation is captured by describing these as subject–verb–object (SVO) modified by V2. Thus Old English can be described as intermediate between SOV languages (like German and Dutch) and SVO languages (like Swedish and Icelandic).
Effect of subject pronouns
[edit]When the subject of a clause was a personal pronoun, V2 did not always operate.
forðon
therefore
we
we
sceolan
must
mid
with
ealle
all
mod
mind
&
and
mægene
power
to
to
Gode
God
gecyrran
turn
'Therefore, we must turn to God with all our mind and power
This section's factual accuracy is disputed. (May 2022) |
However, V2 verb-subject inversion occurred without exception after a question word or the negative ne, and with few exceptions after þa even with pronominal subjects.
for
for
hwam
what
noldest
not-wanted
þu
you
ðe sylfe
yourself
me
me
gecyðan
make-known
þæt...
that...
'wherefore would you not want to make known to me yourself that...'
Ne
not
sceal
shall
he
he
naht
nothing
unaliefedes
unlawful
don
do
'He shall not do anything unlawful.'
þa
then
foron
sailed
hie
they
mid
with
þrim
three
scipum
ships
ut
out
'Then they sailed out with three ships.'
Inversion of a subject pronoun also occurred regularly after a direct quotation.[18]
"Me
to me
is,"
is
cwæð
said
hēo
she
Þīn
your
cyme
coming
on
in
miclum
much
ðonce"
thankfulness
'"Your coming," she said, "is very gratifying to me".'
Embedded clauses
[edit]Embedded clauses with pronoun subjects were not subject to V2. Even with noun subjects, V2 inversion did not occur.
...þa ða
...when
his
his
leorningcnichtas
disciples
hine
him
axodon
asked
for
for
hwæs
whose
synnum
sins
se
the
man
man
wurde
became
swa
thus
blind
blind
acenned
'...when his disciples asked him for whose sins the man was thus born blind'
Yes–no questions
[edit]In a similar clause pattern, the finite verb form of a yes–no question occupied the first position
Truwast
trust
ðu
you
nu
now
þe
you
selfum
self
and
and
þinum
your
geferum
companions
bet
better
þonne
than
ðam
the
apostolum...?
apostles
'Do you now trust yourself and your companions better than the apostles...?'
Middle English
[edit]Continuity
[edit]Early Middle English generally preserved V2 structure in clauses with nominal subjects.
On
in
þis
this
gær
year
wolde
wanted
þe
the
king
king
Stephne
Stephen
tæcen
seize
Rodbert
Robert
'During this year King Stephen wanted to seize Robert.'
Nu
now
loke
look
euerich
every
man
man
toward
to
himseleun
himself
'Now it's for every man to look to himself.'
As in Old English, V2 inversion did not apply to clauses with pronoun subjects.
bi
by
þis
this
ȝe
you
mahen
may
seon
see
ant
and
witen...
know
alle
all
ðese
those
bebodes
commandments
ic
I
habbe
have
ihealde
kept
fram
from
childhade
childhood
Change
[edit]Late Middle English texts of the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries show increasing incidence of clauses without the inversion associated with V2.
sothely
Truly
se
the
ryghtwyse
righteous
sekys
seeks
þe
the
loye
joy
and...
and...
And
And
by
by
þis
this
same
same
skyle
skill
hop
hope
and
and
sore
sorrow
shulle
shall
jugen
judge
us
us
Negative clauses were no longer formed with ne (or na) as the first element. Inversion in negative clauses was attributable to other causes.
why
why
ordeyned
ordained
God
God
not
not
such
such
ordre
order
'Why did God not ordain such an order?' (not follows noun phrase subject)
why
why
shulde
should
he
he
not...
not
(not precedes pronoun subject)
Ther
there
nys
not-is
nat
not
oon
one
kan
can
war
aware
by
by
other
other
be
be
'There is not a single person who learns from the mistakes of others'
He
He
was
was
despeyred;
in despair;
no thyng
nothing
dorste
dared
he
he
seye
say
Vestiges in Modern English
[edit]As in earlier periods, Modern English normally has subject-verb order in declarative clauses and inverted verb-subject order[19] in interrogative clauses. However these norms are observed irrespective of the number of clause elements preceding the verb.
Classes of verbs in Modern English: auxiliary and lexical
[edit]Inversion in Old English sentences with a combination of two verbs could be described in terms of their finite and non-finite forms. The word which participated in inversion was the finite verb; the verb which retained its position relative to the object was the non-finite verb. In most types of Modern English clause, there are two verb forms, but the verbs are considered to belong to different syntactic classes. The verbs which participated in inversion have evolved to form a class of auxiliary verbs which may mark tense, aspect and mood; the remaining majority of verbs with full semantic value are said to constitute the class of lexical verbs. The exceptional type of clause is that of declarative clause with a lexical verb in a present simple or past simple form.
Questions
[edit]Like Yes/No questions, interrogative Wh- questions are regularly formed with inversion of subject and auxiliary. Present Simple and Past Simple questions are formed with the auxiliary do, a process known as do-support.
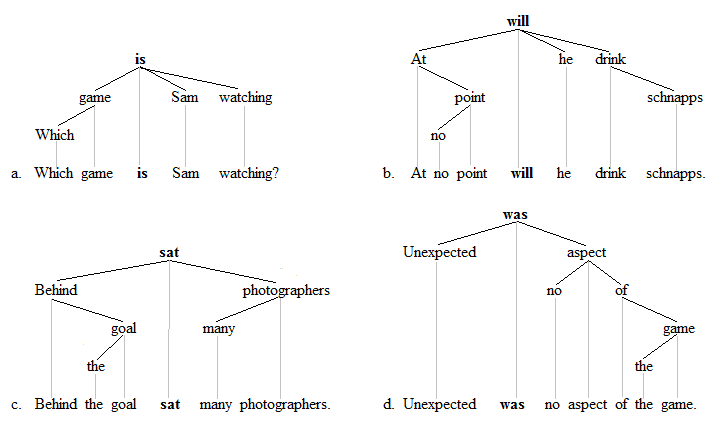
a. Which game is Sam watching? b. Where does she live?
With topic adverbs and adverbial phrases
[edit]In certain patterns similar to Old and Middle English, inversion is possible. However, this is a matter of stylistic choice, unlike the constraint on interrogative clauses.
negative or restrictive adverbial first
c. At no point will he drink Schnapps. d. No sooner had she arrived than she started to make demands.
- (see negative inversion)
comparative adverb or adjective first
e. So keenly did the children miss their parents, they cried themselves to sleep. f. Such was their sadness, they could never enjoy going out.
After the preceding classes of adverbial, only auxiliary verbs, not lexical verbs, participate in inversion
locative or temporal adverb first
g. Here comes the bus. h. Now is the hour when we must say goodbye.
prepositional phrase first
i. Behind the goal sat many photographers. j. Down the road came the person we were waiting for.
After the two latter types of adverbial, only one-word lexical verb forms (Present Simple or Past Simple), not auxiliary verbs, participate in inversion, and only with noun-phrase subjects, not pronominal subjects.
Direct quotations
[edit]When the object of a verb is a verbatim quotation, it may precede the verb, with a result similar to Old English V2. Such clauses are found in storytelling and in news reports.
k. "Wolf! Wolf!" cried the boy. l. "The unrest is spreading throughout the country," writes our Jakarta correspondent.
- (see quotative inversion)
Declarative clauses without inversion
[edit]Corresponding to the above examples, the following clauses show the normal Modern English subject-verb order.
Declarative equivalents
a′. Sam is watching the Cup games. b′. She lives in the country.
Equivalents without topic fronting
c′. He will at no point drink Schnapps. d′. She had no sooner arrived than she started to make demands. e′. The children missed their parents so keenly that they cried themselves to sleep. g′. The bus is coming here. h′. The hour when we must say goodbye is now. i′. Many photographers sat behind the goal. j′. The person we were waiting for came down the road. k′. The boy cried "Wolf! Wolf!" l′. Our Jakarta correspondent writes, "The unrest is spreading throughout the country" .
French
[edit]Modern French is a subject-verb-object (SVO) language like other Romance languages (though Latin was a subject-object-verb language). However, V2 constructions existed in Old French and were more common than in other early Romance language texts. It has been suggested that this may be due to influence from the Germanic Frankish language.[20] Modern French has vestiges of the V2 system similar to those found in modern English.
The following sentences have been identified as possible examples of V2 syntax in Old French:[21]
a. Old French Longetemps fu ly roys Elinas en la montaigne Modern French Longtemps fut le roi Elinas dans la montagne .... 'Pendant longtemps le roi Elinas a été dans les montagnes.' English For a long time was the king Elinas in the mountain ... 'King Elinas was in the mountains for a long time.'
b. Old French Iteuses paroles distrent li frere de Lancelot Modern French Telles paroles dirent les frères de Lancelot .... 'Les frères de Lancelot ont dit ces paroles' English Such words uttered the brothers of Lancelot .... 'Lancelot's brothers spoke these words.'
c. Old French Atant regarda contreval la mer Modern French Alors regarda en bas la mer .... 'Alors Il a regardé la mer plus bas.' English Then looked at downward the sea .... 'Then he looked down at the sea.' (Elision of subject pronoun, contrary to the general rule in other Old French clause structures.)
Old French
[edit]Similarly to Modern French, Old French allows a range of constituents to precede the finite verb in the V2 position.
Il
He
oste
removes.3sg
ses
his
armes
weapons
'He removes his weapons'
Old Occitan
[edit]A language that is compared to Old French is Old Occitan, which is said to be the sister of Old French. Although the two languages are thought to be sister languages, Old Occitan exhibits a relaxed V2 whereas Old French has a much more strict V2. However, the differences between the two languages extend past V2 and also differ in a variation of V2, which is V3. In both language varieties, occurrence of V3 can be triggered by the presence of an initial frame-setting clause or adverbial (1).
Car
For
s'il
if-he
ne
NEG
me
me.CL=
garde
look.3SG
de
of
pres,
close
je
I
ne
NEG
dout
doubt.1SG
mie
NEG
'Since he watches me so closely, I do not doubt'
Other languages
[edit]Kotgarhi and Kochi
[edit]In his 1976 three-volume study of two languages of Himachal Pradesh, Hendriksen reports on two intermediate cases: Kotgarhi and Kochi. Although neither language shows a regular V 2 pattern, they have evolved to the point that main and subordinate clauses differ in word order and auxiliaries may separate from other parts of the verb:
hyunda-baassie
winter-after
jaa
goes
gõrmi
summer
hõ-i
become-GER
(in Kotgarhi)
"After winter comes summer." (Hendriksen III:186)
Hendriksen reports that relative clauses in Kochi show a greater tendency to have the finite verbal element in clause-final position than matrix clauses do (III:188).
Ingush
[edit]In Ingush, "for main clauses, other than episode-initial and other all-new ones, verb-second order is most common. The verb, or the finite part of a compound verb or analytic tense form (i.e. the light verb or the auxiliary), follows the first word or phrase in the clause."[22]
muusaa
Musa
vy
V.PROG
hwuona
2sg.DAT
telefon
telephone
jettazh
striking
'Musa is telephoning you.'
O'odham
[edit]O'odham has relatively free V2 word order within clauses; for example, all of the following sentences mean "the boy brands the pig":[23]
ceoj ʼo g ko:jĭ ceposid
ko:jĭ ʼo g ceoj ceposid
ceoj ʼo ceposid g ko:jĭ
ko:jĭ ʼo ceposid g ceoj
ceposid ʼo g ceoj g ko:jĭ
ceposid ʼo g ko:jĭ g ceoj
The finite verb is "'o" and appears after a constituent in the second position.
Despite the general freedom of sentence word order, O'odham is fairly strictly V2 in its placement of the auxiliary verb (in the sentences above, it is ʼo; in the sentences below, it is ʼañ):
Affirmative: cipkan ʼañ = "I am working"
Negative: pi ʼañ cipkan = "I am not working" [not *pi cipkan ʼañ]
Sursilvan
[edit]Among dialects of the Romansh, V2 word order is limited to Sursilvan, the insertion of entire phrases between auxiliary verbs and participles occurs, as in 'Cun Mariano Tschuor ha Augustin Beeli discurriu ' ('Mariano Tschuor has spoken with Augustin Beeli'), as compared to Engadinese 'Cun Rudolf Gasser ha discurrü Gion Peider Mischol' ('Rudolf Gasser has spoken with Gion Peider Mischol'.)[24]
The constituent that is bounded by the auxiliary, ha, and the participle, discurriu, is known as a Satzklammer or 'verbal bracket'.
Estonian
[edit]In Estonian, V2 is very frequent in the literate register but less frequent in the spoken register. When V2 occurs, it is found in main clauses as illustrated in (1).
Kiiresti
quickly
lahku-s-id
leave-PST-3PL
õpilase-d
student-NOM.PL
koolimaja-st.
schoolhouse-ELA
'The students departed quickly from the schoolhouse.'
Unlike Germanic V2 languages, Estonian has several instances where V2 word order is not attested in embedded clauses, such as wh-interrogatives (2), exclamatives (3), and non-subject-initial clauses (4).[25]
Kes
who.NOM
mei-le
we-ALL
täna
today
külla
village/visit.ILL
tule-b?
come-PRS.3SG
'Who will visit us today?'
Küll
EMP
ta
s/he.NOM
täna
today
tule-b.
come-PRS.3SG
'S/he's sure to come today!'
Täna
today
ta
s/he.NOM
mei-le
we-ALL
külla
village/visit.ILL
ei
not
tule.
come
'Today s/he won't come to visit us.'
Welsh
[edit]In Welsh, V2 word order is found in Middle Welsh but not in Old and Modern Welsh, which have only verb-initial order.[26] Middle Welsh displays three characteristics of V2 grammar:
(1) A finite verb in the C-domain
(2) The constituent preceding the verb can be any constituent (often driven by pragmatic features).
(3) Only one constituent preceding the verb in subject position
As can be seen in the following examples of V2 in Welsh, there is only one constituent preceding the finite verb, but any kind of constituent (such as a noun phrase NP, adverb phrase AP and preposition phrase PP) can occur in this position.
[DP
'r
the
guyrda
nobles
a]
PRT
doethant
came
y gyt.
together.
"The nobles came together"
→ This sentence has a constituent with a subject, followed by the verb in second position.
[DP
deu
two
drws
door
a]
PRT
welynt
saw
yn
PRED
agoret.
open.
"They saw two doors that were open"
→ This sentence has a constituent with a object, followed by the verb in second position.
[AdvP
yn
PRED
diannot
immediate
y]
PRT
doeth
came
tan
fire
o
from
r
the
nef.
heaven.
"Immediately there came fire from the heavens"
→ This sentence has a constituent that is an adverb phrase, followed by the verb in second position.
[PP
y
to
r
the
neuad
hall
y]
PRT
kyrchyssant.
went.
"They made for the hall"
→ This sentence has a constituent that is a preposition phrase, followed by the verb in second position.
Middle Welsh can also exhibit variations of V2 such as cases of V1 (verb-initial word order) and V3 orders. However, these variations are restricted to specific contexts, such as in sentences with impersonal verbs, imperatives, answers or direct responses to questions or commands and idiomatic sayings. A preverbal particle can also precede the verb in V2, but such sentences are limited as well.
Wymysorys
[edit]Wymysory is classified as a West Germanic language but can exhibit various Slavonic characteristics. It is argued that Wymysorys enables its speaker to operate between two word order system, which represent both forces driving its grammar: Germanic and Slavonic. The Germanic system is not as flexible and allows for V2 to exist in it form, but the Slavonic system is relatively free. The rigid word order in the Germanic system causes the placement of the verb to be determined by syntactic rules in which V2 is commonly respected.[27]
Wymysory, like with other languages that exhibit V2, has the finite verb in second position, and a constituent of any category precedes the verb such as DP, PP, AP and so on.
[DP
Der
The
klop]
man
kuzt
speaks
wymyioerys.
Wymysorys.
"The man speaks Wymysorys"
→ This sentence has a constituent with a subject, followed by the verb in second position.
[DP
Dos
This
bihɫa]
book
hot
had
yh
I
gyśrejwa.
written.
"I had written that book"
→ This sentence has a constituent with an object, followed by the verb in second position.
[PP
Fjyr
For
ejn]
him
ej
is
do.
this.
"This is for him"
→ This sentence has a preposition phrase, followed by the verb in second position.
Classical Portuguese
[edit]V2 word order existed in Classical Portuguese much longer than in other Romance languages. Although Classical Portuguese was a V2 language, V1 occurred more frequently and so it is argued whether or not Classical Portuguese really is a V2-like language. However, Classical Portuguese was a relaxed V2 language, and V2 co-exist with its variations: V1 and V3. Classical Portuguese had a strong relationship between V1 and V2 since V2 clauses were derived from V1 clauses.
In languages where both V1 and V2 exist, both patterns depend on the movement of the verb to a high position of the CP layer. The difference is whether or not a phrase is moved to a preverbal position.[28]
Although V1 occurred more frequently in Classical Portuguese, V2 was more frequently found in matrix clauses. Post-verbal subjects could also occupy a high position in the clause and precede VP adverbs. In (1) and (2), it can be seen that the adverb 'bem' could be before or after the post-verbal subject.
E
and
nos
in-the
gasalhados
welcome
e
and
abraços
greetings
mostraram
showed
os
the
cardeais
cardinals
legados
delegates
'In the welcome and greetings the cardinal delegates showed this satisfaction well.'
E
and
quadra-lhe
fits-CL.3.DAT
bem
well
o
the
nome
name
de
of
Piemonte...
Piemonte
'And the name of Piemonte fits it well...'
In (2), the post-verbal subject is understood as an informational focus, but the same cannot be said for (1) because the different positions determine how the subject is interpreted.
Structural analysis
[edit]Various structural analyses of V2 have been developed, including within the model of dependency grammar and generative grammar.
Dependency grammar
[edit]Dependency grammar (DG) can accommodate the V2 phenomenon simply by stipulating that one and only one constituent must be a predependent of the finite verb (i.e. a dependent which precedes its head) in declarative (matrix) clauses (in this, Dependency Grammar assumes only one clausal level and one position of the verb, instead of a distinction between a VP-internal and a higher clausal position of the verb as in Generative Grammar, cf. the next section).[29] On this account, the V2 principle is violated if the finite verb has more than one predependent or no predependent at all. The following DG structures of the first four German sentences above illustrate the analysis (the sentence means 'The kids play soccer in the park before school'):
The finite verb spielen is the root of all clause structure. The V2 principle requires that this root have a single predependent, which it does in each of the four sentences.
The four English sentences above involving the V2 phenomenon receive the following analyses:
Generative grammar
[edit]In the theory of Generative Grammar, the verb second phenomenon has been described as an application of X-bar theory. The combination of a first position for a phrase and a second position for a single verb has been identified as the combination of specifier and head of a phrase. The part after the finite verb is then the complement. While the sentence structure of English is usually analysed in terms of three levels, CP, IP, and VP, in German linguistics the consensus has emerged that there is no IP in German.[30]

The VP (verb phrase) structure assigns position and functions to the arguments of the verb. Hence, this structure is shaped by the grammatical properties of the V (verb) which heads the structure. The CP (complementizer phrase) structure incorporates the grammatical information which identifies the clause as declarative or interrogative, main or embedded. The structure is shaped by the abstract C (complementiser) which is considered the head of the structure. In embedded clauses the C position accommodates complementizers. In German declarative main clauses, C hosts the finite verb. Thus the V2 structure is analysed as
- 1 Topic element (specifier of CP)
- 2 Finite-verb form (C=head of CP) i.e. verb-second
- 3 Remainder of the clause
In embedded clauses, the C position is occupied by a complementizer. In most Germanic languages (but not in Icelandic or Yiddish), this generally prevents the finite verb from moving to C.
- The structure is analysed as
- 1 Complementizer (C=head of CP)
- 2 Bulk of clause (VP), including, in German, the subject.
- 3 Finite verb (V position)
This analysis does not provide a structure for the instances in some language of root clauses after bridge verbs.
- Example: Danish Vi ved at denne bog har Bo ikke læst with the object of the embedded clause fronted.
- (Literally 'We know that this book has Bo not read')
The solution is to allow verbs such as ved to accept a clause with a second (recursive) CP.[31]
- The complementizer occupies C position in the upper CP.
- The finite verb moves to the C position in the lower CP.
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ For discussions of the V2 principle, see Borsley (1996:220f.), Ouhalla (1994:284ff.), Fromkin et al. (2000:341ff.), Adger (2003:329ff.), Carnie (2007:281f.).
- ^ Ehalka, Martin (2006), "The Word Order of Estonian: Implications to Universal Language", Journal of Universal Language, 7: 49–89, doi:10.22425/jul.2006.7.1.49, S2CID 52222499, Corpus ID: 52222499
- ^ Woods, Rebecca; Wolf, Sam (2020). Rethinking Verb Second. Oxford University Press.
- ^ The examples are discussed in König and van der Auwera (1994) in the chapters devoted to each language.
- ^ These and other examples are discussed in Fagan (2009)
- ^ Similar examples to these and others are discussed in Zwart (2011)
- ^ Zwart (2011) p. 35.
- ^ "Colloquium Neerlandicum 16 (2006) · DBNL".
- ^ See Thráinsson (2007) p.19.
- ^ Examples from Fischer et al (2000) p.112
- ^ see König & van der Auwera (1994) p.410
- ^ Woods, Rebecca (March 25, 2020), "A different perspective on embedded Verb Second", Rethinking Verb Second, Oxford University Press, pp. 297–322, doi:10.1093/oso/9780198844303.003.0013, ISBN 978-0-19-884430-3, retrieved April 30, 2021
- ^ Woods, Rebecca (March 25, 2020), "A different perspective on embedded Verb Second", Rethinking Verb Second, Oxford University Press, pp. 297–322, doi:10.1093/oso/9780198844303.003.0013, ISBN 978-0-19-884430-3, retrieved April 30, 2021
- ^ Walkden, George (February 16, 2017). "Language contact and V3 in Germanic varieties new and old". The Journal of Comparative Germanic Linguistics. 20 (1): 49–81. doi:10.1007/s10828-017-9084-2. ISSN 1383-4924.
- ^ Jouitteau, Mélanie (March 25, 2020), "Verb Second and the Left Edge Filling Trigger", Rethinking Verb Second, Oxford University Press, pp. 455–481, doi:10.1093/oso/9780198844303.003.0019, ISBN 978-0-19-884430-3, retrieved April 30, 2021
- ^ Urk, Coppe van (March 25, 2020), "Verb Second is syntactic", Rethinking Verb Second, Oxford University Press, pp. 623–641, doi:10.1093/oso/9780198844303.003.0026, ISBN 978-0-19-884430-3, retrieved April 30, 2021
- ^ See Fischer et al. (2000: 114ff.) for discussion of these and other examples from Old English and Middle English.
- ^ Harbert (2007) p. 414
- ^ Inversion is discussed in Peters (2013)
- ^ see Rowlett (2007:4)
- ^ see Posner (1996:248)
- ^ Nichols, Johanna. (2011). Ingush Grammar. Berkeley: The University of California Press. Pp. 678ff.
- ^ Zepeda, Ofelia. (1983). A Tohono O'odham Grammar. Tucson, AZ: The University of Arizona Press.
- ^ Liver 2009, pp. 138
- ^ Vihman, Virve-Anneli; Walkden, George (2021). "Verb-second in spoken and written Estonian". Glossa: A Journal of General Linguistics. 6 (1). doi:10.5334/gjgl.1404. ISSN 2397-1835.
- ^ Meelen, Marieke (March 25, 2020), "Reconstructing the rise of Verb Second in Welsh", Rethinking Verb Second, Oxford University Press, pp. 426–454, doi:10.1093/oso/9780198844303.003.0018, ISBN 978-0-19-884430-3, retrieved April 29, 2021
- ^ Andrason, Alexander (March 25, 2020), "Verb Second in Wymysorys", Rethinking Verb Second, Oxford University Press, pp. 700–722, doi:10.1093/oso/9780198844303.003.0030, ISBN 978-0-19-884430-3, retrieved April 29, 2021
- ^ Galves, Charlotte (March 25, 2020), "Relaxed Verb Second in Classical Portuguese", Rethinking Verb Second, Oxford University Press, pp. 368–395, doi:10.1093/oso/9780198844303.003.0016, ISBN 978-0-19-884430-3, retrieved April 29, 2021
- ^ For an example of a DG analysis of the V2 principle, see Osborne (2005:260). That DG denies the existence of a finite VP constituent is apparent with most any DG representation of sentence structure; finite VP is never shown as a complete subtree (=constituent). See for instance the trees in the essays on DG in Ágel et al. (2003/2006) in this regard. Concerning the strict denial of a finite VP constituent, see especially Tesnière (1959:103-105).
- ^ See especially: Hubert Haider, The syntax of German, Cambridge University Press, 2010
- ^ Sten Vikner: Sten Vikner: Verb movement and expletive subjects in the Germanic languages. Oxford University Press, 1995.
Literature
[edit]- Adger, D. 2003. Core syntax: A minimalist approach. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
- Ágel, V., L. Eichinger, H.-W. Eroms, P. Hellwig, H. Heringer, and H. Lobin (eds.) 2003/6. Dependency and valency: An international handbook of contemporary research. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter.
- Andrason, A. (2020). Verb second in Wymysorys. Oxford University Press.
- Borsley, R. 1996. Modern phrase structure grammar. Cambridge, MA: Blackwell Publishers.
- Carnie, A. 2007. Syntax: A generative introduction, 2nd edition. Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishing.
- Emonds, J. 1976. A transformational approach to English syntax: Root, structure-preserving, and local transformations. New York: Academic Press.
- Fagan, S. M. B. 2009. German: A linguistic introduction. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
- Fischer, O., A. van Kermenade, W. Koopman, and W. van der Wurff. 2000. The Syntax of Early English. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Fromkin, V. et al. 2000. Linguistics: An introduction to linguistic theory. Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers.
- Harbert, Wayne. 2007. The Germanic Languages. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Hook, P. E. 1976. Is Kashmiri an SVO Language? Indian Linguistics 37: 133–142.
- Jouitteau, M. (2020). Verb second and the left edge filling trigger. Oxford University
- Liver, Ricarda. 2009. Deutsche Einflüsse im Bündnerromanischen. In Elmentaler, Michael (Hrsg.) Deutsch und seine Nachbarn. Peter Lang. ISBN 978-3-631-58885-7
- König, E. and J. van der Auwera (eds.). 1994. The Germanic Languages. London and New York: Routledge.
- Liver, Ricarda. 2009. Deutsche Einflüsse im Bündnerromanischen. In Elmentaler, Michael (Hrsg.) Deutsch und seine Nachbarn. Frankfurt am Main: Peter Lang.
- Meelen, M. (2020). Reconstructing the rise of verb second in Welsh. Oxford University Press.
- Nichols, Johanna. 2011. Ingush Grammar. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Osborne T. 2005. Coherence: A dependency grammar analysis. SKY Journal of Linguistics 18, 223–286.
- Ouhalla, J. 1994. Transformational grammar: From rules to principles and parameters. London: Edward Arnold.
- Peters, P. 2013. The Cambridge Dictionary of English Grammar. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Posner, R. 1996. The Romance languages. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Rowlett, P. 2007. The Syntax of French. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- van Riemsdijk, H. and E. Williams. 1986. Introduction to the theory of grammar. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press.
- Tesnière, L. 1959. Éleménts de syntaxe structurale. Paris: Klincksieck.
- Thráinsson, H. 2007. The Syntax of Icelandic. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Walkden, G. (2017). Language contact and V3 in germanic varieties new and old. The Journal of Comparative Germanic Linguistics, 20(1), 49-81.
- Woods, R. (2020). A different perspective on embedded verb second. Oxford University Press.
- Woods, R., Wolfe, s., & UPSO eCollections. (2020). Rethinking verb second (First ed.). Oxford University Press.
- Zwart, J-W. 2011. The Syntax of Dutch. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
 KSF
KSF