(Cyclopentadiényl)vanadium tétracarbonyle
 From Wikipedia (Fr) - Reading time: 2 min
From Wikipedia (Fr) - Reading time: 2 min
| (Cyclopentadiényl)vanadium tétracarbonyle | |||
| |||
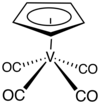
| Structure du (cyclopentadiényl)vanadium tétracarbonyle | |||
| Identification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | Tétracarbonyl(η5-cyclopenta-2,4-dién-1-yl)vanadium | ||
| No CAS | |||
| No ECHA | 100.031.955 | ||
| No CE | 235-163-9 | ||
| PubChem | 498652 | ||
| SMILES | |||
| InChI | |||
| Apparence | solide orange[1] | ||
| Propriétés chimiques | |||
| Formule | C9H5O4V |
||
| Masse molaire[2] | 228,075 1 ± 0,008 9 g/mol C 47,4 %, H 2,21 %, O 28,06 %, V 22,34 %, |
||
| Propriétés physiques | |||
| T° fusion | 138 °C[1] | ||
| Précautions | |||
| SGH[1] | |||
| H315, H319, H330, H335, P280, P310, P302+P352, P304+P340, P332+P313 et P337+P313 |
|||
| NFPA 704[1] | |||
| Transport[1] | |||
|
|||
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |||
| modifier |
|||
Le (cyclopentadiényl)vanadium tétracarbonyle est un complexe organovanadium (en) de formule chimique (η5-C5H5)V(CO)4. Il s'agit d'un solide diamagnétique orange, soluble dans les solvants organiques usuels[3], dont la molécule adopte une géométrie en tabouret de piano[4]. On peut l'obtenir en traitant du vanadocène (η5-C5H5)2V par une pression élevée de monoxyde de carbone CO.
Le (cyclopentadiényl)vanadium tétracarbonyle donne le dianion du tricarbonyle par réduction à l'amalgame de sodium Na(Hg) :
La protonation de ce sel donne le composé Cp2V2(CO)5[5].
Un mélange de cycloheptatriène C7H8 et de (cyclopentadiényl)vanadium tétracarbonyle peut former par chauffage du (cycloheptatriényl)(cyclopentadiényl)vanadium (η7-C7H7)(η5-C5H5)V[6], ou trovacène.
Notes et références
[modifier | modifier le code]- « Fiche du composé Cyclopentadienylvanadium tetracarbonyl, 97+% », sur Alfa Aesar (consulté le ).
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) R. B. King, F. G. A. Stone, William L. Jolly, Gordon Austin, William Covey, David Rabinovich, Henry Steinberg et Roy Tsugawa, « Cyclopentadienyl Metal Carbonyls and Some Derivatives », Inorganic Syntheses, vol. 7, (DOI 10.1002/9780470132388.ch31, lire en ligne)
- (en) J. B. Wilford, A. Whitla et H. M. Powell, « The crystal and molecular structure of π-cyclopentadienylvanadium tetracarbonyl », Journal of Organometallic Chemistry, vol. 8, no 3, , p. 495-502 (DOI 10.1016/S0022-328X(00)83671-2, lire en ligne)
- (de) Ernst Otto Fischer et Robert J. J. Schneider, « Über Aromatenkomplexe von Metallen, CXIV. Darstellung und Reaktionen von Dicyclopentadienyl-divanadin-pentacarbonyl, (C5H5)2V2(CO)5 », Chemische Berichte, vol. 103, no 11, , p. 3684-3695 (DOI 10.1002/cber.19701031133, lire en ligne)
- (en) R. B. King et F. G. A. Stone, « π-Cyclopentadienyl-π-cycloheptatrienyl vanadium », Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 81, no 19, , p. 5263-5264 (DOI 10.1021/ja01528a063, lire en ligne)
 KSF
KSF

