Fillings
 From Wikiversity - Reading time: 2 min
From Wikiversity - Reading time: 2 min
 |
| Click to return to School of Dentistry |
This is a learning resource about dental fillings.
Caries diagnosis
- Clean tooth (water + air)
- Dry (air)
- Bright light
- Magnification?
- Sharp / Blunt probe (international variation). Better tactile feedback with sharp probe, but more likely to cause cavitation of lesions which were not cavitated before.
- Trans-illumination (caries shows up as shadow)
- X-ray
- Clinical experience. Not an exact science, much variation with regards caries diagnosis from one clinician to the next
Management algorithm[1]
- Active or inactive caries? Soft, sticky – active, hard, smooth – arrested
- Cavitated or non-cavitated? Probe “catching” - cavity
| No carious lesion | No treatment | ||
| Carious lesion | Inactive lesion | No treatment | |
| Active lesion | Non-cavitated lesion | Non-operative treatment | |
| Cavitated lesion | Operative treatment | ||
| Existing filling | No defect | No replacement | |
| Defective filling | Ditching, overhang | No replacement | |
| Fracture or food impaction | Repair or replacement of filling | ||
| Inactive lesion | No treatment | ||
| Active lesion | Non-cavitated lesion | Non-operative treatment | |
| Cavitated lesion | Repair or replacement of filling |
- Non-operative treatment: requires patient education and motivation, fluoride (toothpaste, mouthrinse, topical), plaque control, dietary modification (decrease frequency of sugar)
- If non-operative management is not working, caries will progress
- Dentin cannot remineralize if enamel is present over the dentin
- In the real world, patient's cosmetic concerns often demand restoration even if a cavity is arrested
GV Black classification
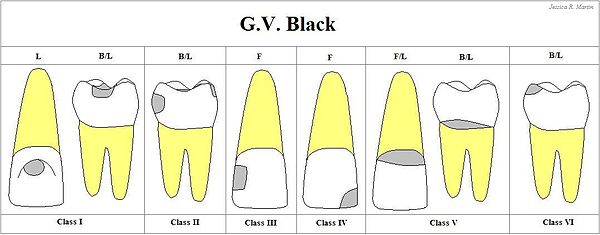
- Class I - pit and fissure caries (anterior or posterior teeth)
- Class II - approximal surfaces of posterior teeth
- Class III - approximal surfaces of anterior teeth without incisal edge involvement
- Class IV - approximal surfaces of anterior teeth with incisal edge involvement
- Class V - gingival/cervical surfaces on the lingual or facial aspect (anterior or posterior)
- Class VI - incisal edge of anterior teeth or cusp heights of posterior teeth
Class I
[edit | edit source]Minimally invasive operative intervention
- Enamel biopsy (start cavity, if no caries in fissure, abort and fill with fissure sealant)
- Preventative resin restoration (remove enamel caries in fissures, fill with fissure sealant alone, or with glass ionomer/composite then fissure sealant)

References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ Ole Fejerskov, Edwina Kidd (2004). Dental caries : the disease and its clinical management. Copenhagen [u.a.]: Blackwell Munksgaard. ISBN 9781405107181.
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://en.wikiversity.org/wiki/Fillings17 views | Status: cached on April 27 2025 01:37:39↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF