Immune system
 From Wikiversity - Reading time: 3 min
From Wikiversity - Reading time: 3 min
An immune system is a system of resistance to a particular infection or toxin owing to the presence of specific antibodies or sensitized white blood cells.
T-cell
[edit | edit source]- Divide when comes in contact with antigens.
- Signals B cells about the kind of antigens.
- Killer T-cells (CD8+ T cells) destroy infected cells and viruses.
- Helper T-cells (CD4+ T cells) alert B cells to start making antibodies; they can also activate other T-cells and immune system scavenger cells called macrophages (described @ bottom) and influence which type of antibody is produced.
B-cell
[edit | edit source]- Produces antibodies.
- Can produce ≈ 2,000 antibody molecules/second.
- Are matured in bone marrow.
- Gets info about antigens from T-cells.
Antigen
[edit | edit source]- Molecular structure (and, by extension, cell organelle, cell, organ or individual body) able to be recognized within the Immune System through interaction with an Idiotype Receptor (or Receptor for Antigen, that is either a TCR - T Cell Receptor for Antigen, a BCR - B Cell Receptor for Antigen, or the soluble, effector form of the last idiotype receptor: a soluble Antibody).
- For a given immunological host, a given antigen may qualify as Self Antigen (typically either not target of an counteracting type immune response, or target of a tolerizing type immune response), or as a Foreign Antigen (inducing either a counteracting immune response and thus called Immunogen, or a tolerogenic reaction and thus called Tolerogen, or not inducing immune responses and thus called Ignored antigen).
Antibody
[edit | edit source]Genetic term for a group of molecules, members of the Idiotype Receptor family, that identify either the membrane-bound, recognition subunit within the BCR (B Cell Receptor for Anteagen), or the solluble, efector, relesed form of the B lymphcyte iditype receptor.
- As other receptors, Antibodies are polar molecules: one end functioning as target ligand binding (that is serving for epitope surface / antigen recognition), while the other end is serving for deploying counteracting functions (as submembranar signaling, binding to various Fc Receptors, binding to some Complement System commoners).
- Are proteins made by the body's immune system.
- Reacts with specific antigens to remove them from body.
- All have different shape and sizes.
Macrophage
[edit | edit source]- Slower to respond to invaders than Granulocytes (white blood cell with secretory granules in its cytoplasm), but are larger, live longer, and have far greater capacities.
- Play a key part in alerting the rest of the immune system of invaders.

Steps of a macrophage ingesting a pathogen:
a. Ingestion through phagocytosis, a phagosome is formed
b. The fusion of lysosomes with the phagosome creates a phagolysosome; the pathogen is broken down by enzymes
c. Waste material is expelled or assimilated (the latter not pictured)
Parts:
1. Pathogens
2. Phagosome
3. Lysosomes
4. Waste material
5. Cytoplasm
6. Cell membrane
- Start out as a white blood cell. They leave the blood stream; they turn into macrophages.
- Destroy the virus.
Pathogen
[edit | edit source]- A type of bacteria, virus, or fungi which causes disease.
- Can only be killed or blocked by the human immune system.
- Anything that can cause any type of disease is a pathogen.
Lymph
[edit | edit source]- A clear liquid that bathes the cells with water and nutrients.
- Carries away any bacteria it finds.
Lymph nodes
[edit | edit source]- Filter lymph which later returns back to the blood stream.
- located along lymphatic vessels.
- stroma - supporting connective tissue
- stroma consist of capsule, trabeculae, reticular fibers and fibroblast.
- parenchyma - functional part
Lymph vessels
[edit | edit source]- Carry lymph.
Lymphocytes
[edit | edit source]- Cells that allow the body to remember and recognize previous invaders and help the body destroy them.
- Make antibodies to destroy foreign pathogens.
Vaccine and vaccination
[edit | edit source]- Used to establish immunity to a disease.
- The immune system recognizes vaccine agents as foreign, destroys them, and “remembers” them.
- Prepares the body for certain viruses.
- Injects some form of a pathogen into your body.
- Adaptive and Passive Immunity.
- Adaptive Immunity is achieved by stimulating the body to produce its own antibodies.
- Passive Immunity is when antibodies that are injected into the body are made by another organism.
Appendix
[edit | edit source]- A 2” by 4” pouch in the intestines. It has unknown reason in the immune system. It helps digest food.
Spleen
[edit | edit source]- A organ located in the abdomen of the human body. It is regarded as one of the centers of activity of the immune system.
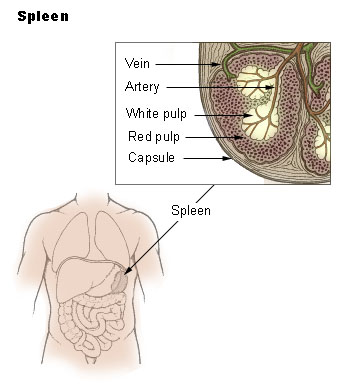
Spleen 
Laparoscopic view of a horse's spleen (the purple and gray mottled organ)
Thymus
[edit | edit source]- Produces T-cells.
Tonsils
[edit | edit source]- Two filters in the back of the mouth that trap germs. Although when kids are young they get their tonsils taking out to keep from getting sick all the time. When they get this done they are usually taken out at the earliest age of about 2 or maybe even younger but you will not see to many adults getting their tonsils taken out. They do that when they are at their earliest ages.
External links
[edit | edit source]Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://en.wikiversity.org/wiki/Immune_system26 views | Status: cached on July 16 2025 03:06:24↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF