Lake Burley Griffin
 From Nwe
From Nwe | Lake Burley Griffin | |
|---|---|
| Location | Canberra, Australia |
| Coordinates | |
| Lake type | artificial lake |
| Primary sources | Molonglo River |
| Primary outflows | Molonglo River |
| Basin countries | Australia |
| Max length | 11 km (7 mi) |
| Max width | 1.2 km (0.75 mi) |
| Surface area | 6.64 km² (2.56 sq mi) |
| Water volume | 33 mio m³ |
| Surface elevation | 556 m (1824 ft) |
| Islands | 6 (Aspen, Springbank, Spinnaker, others unnamed) |
| Settlements | Canberra |
Lake Burley Griffin is the centerpiece of Canberra, an entirely purpose-built, planned city which serves as Australia's federal capital city. Canberra was designed by Chicago architects Walter Burley Griffin, for whom the lake is named, and his wife Marion Mahony Griffin.
The Griffins incorporated town planning and urban design with landscape architecture. Their planning went beyond functionality to include art and aesthetics. While natural vegetation was an important feature of the design plan, the most important aspect was a central lake around which was built parks, and toward which city streets flowed.
Numerous institutions, such as the National Gallery of Australia, National Museum of Australia, National Library of Australia, and the High Court of Australia line its periphery. The Parliament House is a short distance away. Surrounding the lake are popular recreational areas and public parks. There are bicycle and walking paths as well as opportunities for water sports, such as swimming, canoeing, sailing, windsurfing, and sport fishing.
Canberra provides a balanced environment, which supplies for physical needs and nurtures human internal aspects. In that regard Canberra may be considered a model city. Lake Burley Griffin was designed into the city as an integral element.
Background
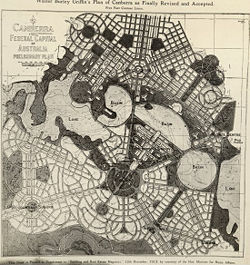
In April 1911, the Australian Government held an international competition to produce a design for its new capital city, Canberra. Walter Burley Griffin of Chicago produced a design with impressive watercolor renderings of the plan produced by his wife, Marion Mahony Griffin. On May 23, 1912, Griffin's design was selected as the winner from among 137 entries. The win created significant press coverage at the time and brought Griffin professional and public recognition. Of his plan, he famously remarked:
I have planned a city that is not like any other in the world. I have planned it not in a way that I expected any government authorities in the world would accept. I have planned an ideal city—a city that meets my ideal of the city of the future.
In 1913, Griffin was invited to inspect the site. In 1914, he and his wife moved to Australia to oversee the design of the new capital. He was appointed the Federal Capital Director of Design and Construction. In this role, Griffin oversaw the design of North and South Canberra, though he struggled with political and bureaucratic obstacles. With the outbreak of World War I, Griffin was under pressure to reduce the scope and scale of his plans due to the need to divert funds toward the war effort. Ultimately, Griffin resigned from the Canberra design project in December 1920, due to conflicts with the bureaucracy.
Much of Griffin's design was used in the building of Canberra, though there were a few adaptations. The original design involved the city being built around a lake. It took several decades, but eventually Lake Burley Griffin was built into the city according to design.
Design
Charles Scrivener (1855-1923) recommended the site for Canberra in 1909, and his detailed survey plans of the area were supplied to the architects who entered the Canberra design competition. Later, Scrivener, as part of a design committee, was responsible for modifying Griffin's winning design. He recommended changing the shape of the lake from Griffin's very geometric shapes to a much more organic one using a single dam, unlike Griffin's series of weirs. The new design included elements from several of the best design submissions and was widely criticized. The new plan for the lake retained Griffin's three formal basins: east, central, and west, though in a more relaxed form. The plans were varied again in the following years with the return of Griffin, but the design of Lake Burley Griffin remains based largely on the original committee's plan.
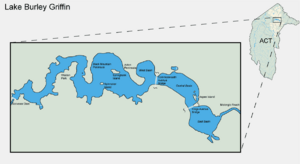
The lake contains 33 million cubic meters of water with a surface area of 6.64 square kilometers (2.56 sq mi). It is 11 kilometers (7 mi) long, 1.2 kilometers (0.75 mi) wide at its widest point, has a shoreline of 40.5 kilometers (25.2 mi) and a water level of 556 meters (1824 ft) above sea level. Lake Burley Griffin contains six islands, three unnamed small islands and three larger named islands. Of the larger islands, Aspen Island is located in Central Basin while Springbank and Spinnaker Islands are located in the West Lake. Aspen Island is connected to dry land by a footbridge and is the site of the Australian National Carillon.
Construction
Excavation
Construction of Lake Burley Griffin was begun in 1960 and progressed well due to drought having greatly reduced the water flow of the Molonglo River. Since critics believed that the lake would act as a breeding ground for mosquitoes, care was taken to excavate the lake to a depth of over two meters. In addition to preventing mosquitoes from breeding, that depth would also allow clearance for boat keels. The lake varies in depth from around 2 meters at the eastern end, to 18 meters at the dam wall. The mean depth is 4 meters.
Dam
The dam used to create Lake Burley Griffin was named Scrivener Dam in honor of Charles Scrivener. The dam is 33 meters high and 319 meters long with a five bay spillway controlled by 30.5 meter wide, hydraulically operated fish-belly flap gates. The fish-belly gates allow for a precise control of water level, reducing the dead area on the banks between high and low water levels. The dam is designed to handle a once in 5,000 year flood event. It contains 55,000 cubic meters of concrete with a maximum wall thickness of 19.7 meters. A roadway atop the dam wall provides a third road crossing for the lake.
Filling
The drought that had made construction easy also meant that when the valves were closed on September 20, 1963, the lake was very slow to fill. After seven months there was still only a trickle of water and some mosquito-infested pools. Eventually, when the drought broke the lake was filled after only several days of heavy rain.
On October 17, 1964, Robert Menzies commemorated the filling of the lake and the completion of stage one with an opening ceremony. The minister for the Interior, Gordon Freeth suggested that Menzies had "been in a material sense the father of the lake" and that the lake should be named Lake Menzies. Menzies insisted that the lake should be named after Walter Burley Griffin—Canberra's designer responsible for the concept of the lake—who had no existing monument in Canberra. (Griffin usually referred to himself as Walter Griffin, but the form "Walter Burley Griffin" has become established in Australia.)
Lake levels in times of severe drought can sometimes fall below the desired level. This can be compensated for by the release of water from Googong Dam on the Queanbeyan River, a tributary of the Molonglo. Googong Dam was built in 1979, to cope with Canberra and Queanbeyan's growing water supply needs, and can contain up to 124,500 million liters of water.
Bridges
Lake Burley Griffin is crossed by Commonwealth Avenue Bridge (310 m), Kings Avenue Bridge (270 m) and a roadway over Scrivener Dam. The two bridges were constructed before the lake was filled and are designed to allow the passage of recreational sailing boats with tall masts. Both bridges are dual-carriageway. Commonwealth Avenue has three lanes in each direction while Kings Avenue has two. Site testing for both the Commonwealth Avenue Bridge and the Kings Avenue Bridge took place during late 1959 to early 1960. Scrivener Dam is crossed by Lady Denman Drive, a narrow two lane roadway, and a bicycle path.
Water quality
Toxic blue-green algae blooms are a reasonably common occurrence in the lake. Warnings about coming into contact with the water are released when an algal bloom is detected. Attempts are being made to limit the amount of phosphates entering the lake in the hope of improving its water quality.
Blue-green algae produce toxins, which can be harmful for humans and any other animals that come in contact with the contaminated water. Several cases of dogs being adversely affected after playing in and drinking the lake water have been recorded.
The water also appears murky due to a high level of turbidity, possibly a result of the bottom feeding of large numbers of introduced carp in the lake.
Landmarks
National Carillon
The National Carillon, situated on Aspen Island in Lake Burley Griffin is a large carillon managed and maintained by the National Capital Authority on behalf of the Commonwealth of Australia.
The carillon was a gift from the British government to the people of Australia to commemorate the 50th anniversary of the National Capital, Canberra. Queen Elizabeth II officially opened the National Carillon on April 26, 1970. The 50 meter tall National Carillon tower was designed by Western Australian architects Cameron, Chisholm & Nicol.
In 2004, the carillon underwent refurbishment including renovations of interior function facilities and the addition of two extra bells.
Carillons must have at least 23 bells to be considered as such, and the National Carillon has 55. Each bell weighs between seven kilograms and six tonnes. The bells span four and a half octaves chromatically.
Although not large, the carillon features function facilities for small gatherings, offering views over the lake and central Canberra.
The carillon is in regular use, chiming every quarter hour and playing a short tune on the hour along with tours and recitals on many days. The sound can usually be heard much further away in the Parliamentary Triangle, Kingston, and Civic.
Captain Cook Memorial
The Captain James Cook Memorial was built by the Commonwealth Government to commemorate the Bicentenary of Captain James Cook's first sighting of the east coast of Australia. The memorial includes a water jet located in the central basin and a skeleton globe sculpture at Regatta Point showing the paths of Cook's expeditions. On April 25, 1970, Queen Elizabeth II officially inaugurated the memorial.
The water jet is powered by two 560 kilowatt electric motors driving four stage centrifugal pumps capable of pumping up to 250 liters per second against a head of 183 meters. The water velocity at the water nozzle is 260 km/h. While running both pumps simultaneously the main jet throws approximately six tons of water into the air at any instant, reaching a maximum height of 147 meters. Alternatively the jet can be run on a single pump reaching a lower height of 110 meters. During special occasions it is often illuminated, many times with colored lights.
The water jet operates from 10–11.45 am and 2–3.45 pm. During summer it operates for an extra period from 7-9 pm. In periods of high wind the jet is automatically disabled as water landing on the nearby Commonwealth Avenue Bridge can be a hazard to traffic. The water jet must also be occasionally shut down when drought lowers the water level of the lake.
Lakeside recreation
The surrounds of Lake Burley Griffin are very popular recreational areas, especially in the warmer months. Public parks exist along most of the shoreline. A bike path also surrounds the lake with riding, walking or jogging around the lake being a popular activity. Fireworks displays are often held over the lake on New Years Eve, and there has been an annual large fireworks show called Skyfire run at the lake since 1988.
- Water sports
In addition to being ornamental, the Lake is used for many recreational activities. Canoeing, sailing, and windsurfing are popular all year round. A rowing course is set up at the western end of the lake. Molonglo Reach, an area of the Molonglo River just before it enters the east basin is set aside for water skiing. Powerboats may be used in this limited area. Swimming is becoming less common due partly to concerns about water quality and generally cold water temperature. During summer, the lake is used for the swim leg of numerous triathlon and aquathlon events including the Sri Chinmoy Triathlon Festival.
- Fishing
Fishing is quite popular in the lake with the most common species being the illegally introduced carp. The lake has been stocked annually with a variety of introduced and native species and over 1.26 million fish have been released since 1964. Annual monitoring is carried out to determine fish populations. The 2001 survey only returned carp and redfin perch, both introduced species, and native golden perch. However a number of less common species also inhabit the lake, including native Murray cod, western carp gudgeon and silver perch, as well as introduced goldfish, Gambusia, rainbow trout, and brown trout.
There have been many changes to the fish populations in the lake as well as stocking practices since it was first filled. Stockings of introduced trout have been abandoned as the lake has proved to be a warm, eutrophic habitat that is not suited to the survival of introduced trout species.
Regular stocking since the beginning of the 1980s have re-established reasonable populations of golden perch and highly elusive Murray cod; native fish that were indigenous to the Molonglo River before the lake was built, but had been lost to mining pollution of the Molonglo in the 1930s and 1940s. Today golden perch and Murray cod are the only fish stocked in the lake. Murray cod are remarkable as freshwater fish for the extreme sizes they achieve. This is particularly the case for Lake Burley Griffin; specimens to approximately 38 kg have been recorded.
Images
References
ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Australia. 1972. Lake Burley Griffin. Canberra: Australian Government Pub. Service. ISBN 9780642001085.
- Forge, Samantha. 2019. Lonely Planet Pocket Canberra. Lonely Planet. ISBN 978-1788682718
- Hendry, Margaret J. 1975. Commonwealth Gardens, Canberra, A.C.T.
External links
All links retrieved October 21, 2022.
- 15 Top-Rated Tourist Attractions in Canberra & Easy Day Trips
- Lake Burley Griffin - Canberra Sweet Water Fishing
- Lake Burley Griffin Visit Canberra
- Lake Burley Griffin Attractions and Memorials, National Capital Authority
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 02/04/2023 00:55:49 | 8 views
☰ Source: https://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Lake_Burley_Griffin | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed:










 KSF
KSF