Caesium Chromate
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Dicaesium dioxido(dioxo)chromium
| |
| Other names
Dicaesium chromate
| |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties[1] | |
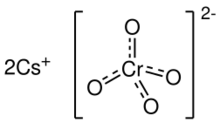
Chemical formula
|
Cs2CrO4 |
| Appearance | Yellow crystalline solid |
| Density | 4.237 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 954 to 961 °C (1,749 to 1,762 °F; 1,227 to 1,234 K) |
Solubility in water
|
45.50 g/100 g (25 °C) |
| Structure | |
Crystal structure
|
orthorhombic |
Space group
|
Pnma (№ 62) |
Lattice constant
|
a = 8.368 Å, b = 6.226 Å, c = 11.135 Å
|
Formula units (Z)
|
4 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | highly toxic, carcinogenic, oxidiser, environmental hazard |
| GHS pictograms |    
|
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Caesium sulfate |
Other cations
|
Sodium chromate Potassium chromate Ammonium chromate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Caesium chromate or cesium chromate is an inorganic compound with the formula Cs2CrO4. It is a yellow crystalline solid that is the caesium salt of chromic acid, and it crystallises in the orthorhombic system.
Its major application in the past was for the production of caesium vapour during vacuum tube manufacture.[2] Currently it is only used as the precursor for other compounds of academic interest.[3][4]
Preparation
Caesium chromate is mainly obtained from the reaction of chromium(VI) oxide with caesium carbonate, wherein carbon dioxide gas is evolved:[3]
- CrO3(aq) + Cs2CO3(aq) → Cs2CrO4(aq) + CO2(g)
Alternatively, salt metathesis between potassium chromate and caesium chloride can be performed:[4]
- K2CrO4(aq) + 2 CsCl(aq) → Cs2CrO4(aq) + 2 KCl(aq)
Finally, caesium dichromate (itself derived via salt metathesis from ammonium dichromate) yields the chromate following alkalinisation with caesium hydroxide:[2]
- Cs2Cr2O7(aq) + 2 CsOH(aq) → 2 Cs2CrO4(aq) + H2O(ℓ)
Applications
Caesium chromate was formerly used in the final stages of creating vacuum tubes. Therein, caesium vapour was produced by reaction of caesium chromate with silicon, boron, or titanium as reducing agents. The vapour was then added to the tube to react with and remove remaining gases, including nitrogen and oxygen.[5]
References
- ↑ Weast, Robert C., ed (1981). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (62nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. B-91. ISBN 0-8493-0462-8..
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Liebhafsky, H. A.; Winslow, A. F. (1947), "Cesium Chromate Photo‐Tube Pellets", Journal of Applied Physics (Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 18, No. 12) 18 (12): 1128, doi:10.1063/1.1697594, Bibcode: 1947JAP....18.1128L
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Pejov, Ljupčo; Petruševski, Vladimir M (2003-08-01). "Latent symmetry versus accidental degeneracy effects in the vibrational spectra of dopant chromate anions in M2CrxS1−xO4 solid solutions (M∈{K, Rb, Cs})" (in en). Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids 64 (8): 1353–1363. doi:10.1016/S0022-3697(03)00160-4. ISSN 0022-3697. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022369703001604.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Bender, Johannes; Wohlfarth, Andreas; Hoch, Constantin (2010-12-01). "Crystal Structures of New Alkali Metal-rich Oxometallates: Rubidium Aluminate Tetrahydroxide, Rb9(AlO4)(OH)4, Rubidium Orthogallate, Rb5GaO4, Cesiumbis-Chromate(IV) Oxide, Cs10(CrO4)2O, and Cesium Diindate, Cs8In2O7" (in en). Zeitschrift für Naturforschung B 65 (12): 1416–1426. doi:10.1515/znb-2010-1202. ISSN 1865-7117.
- ↑ Emsley, John (2001), Nature's Building Blocks: An A-Z Guide to the Elements, Oxford University Press, p. 81, ISBN 0-19-850340-7, https://books.google.com/books?id=j-Xu07p3cKwC&q="Caesium+chromate"+date:1950-2007&pg=RA1-PA81.
 |
Categories: [Caesium compounds] [Chromates]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 10/31/2023 01:03:33 | 9 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Caesium_chromate | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed:
 KSF
KSF