Carboxamide
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 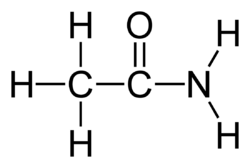
Acetamide, a simple carboxamide
In organic chemistry carboxamides (or amino carbonyls) are functional groups with the general structure R-CO-NR'R′′ with R, R', and R′′ as organic substituents, or hydrogen.[1]
Two amino acids, asparagine and glutamine, have a carboxamide group in them. The properties and reactivity of the carboxamide group arise from the hydrogen bonding capabilities of the -NH2 group as well as the carbonyl oxygen. Furthermore, the carbon atom in a carboxamide has a low-lying LUMO that is capable of accepting electron density from the nonbonding lone pair on the nitrogen, weakening the carbon-oxygen bond.
Examples of simple carboxamides include:
- Acetamide
- Benzamide
See also
- Amide
References
- ↑ "Chapter 21: Amides and Imides". Nomenclature of Organic Compounds. Volume 126. pp. 166–173. doi:10.1021/ba-1974-0126.ch021. ISBN 9780841201910. https://archive.org/details/nomenclatureofor0000flet/page/166.
Categories: [Carboxamides] [Functional groups]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 07/24/2024 06:51:36 | 9 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Carboxamide | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
✘
ZWI is not signed. [what is this?]

 KSF
KSF