Ḥanina (Hananiah; Ḥinena) B. Adda (Idda)
 From Jewish Encyclopedia (1906)
From Jewish Encyclopedia (1906) Ḥanina (Hananiah; Ḥinena) B. Adda (Idda):
By: Joseph Jacobs , S. Mendelsohn
Babylonian scholar of the third century. He was skilled in both Halakah and Haggadah;
Adda B. Ahabah
appears to have beenhis teacher in the former (Pes. 75a; 'Ab. Zarah 40a); in the latter he seems to have been a pupil of Tanḥum b. Ḥiyya. From Tanḥum, Ḥanina received the following illustration of the relative positions of the prophet and the elder (teacher, sage): "A king delegated two commissioners; with respect to one he wrote, 'Unless he exhibits to you my signature and my seal, credit him not'; with reference to the other he wrote, 'Even if he shows you neither my signature nor my seal, credit him.' So it is said regarding the prophet: '. . . and giveth thee a sign or a wonder' [Deut. xiii. 2 (A.V. 1)]: while of the sages it is said: 'According to the sentence of the law which they shall teach thee, and according to the judgment which they shall tell thee, thou shalt do'" (Deut. xvii. 11; Yer. Ber. i. 3b; Yer. Sanh. xi. 30b; Yer. 'Ab. Zarah ii. 41c; Cant. R. i. 2). In the Book of Isaiah
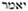 (the future: "will say"), instead of the usual
(the future: "will say"), instead of the usual
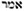 ("saith"), is used eight times (i. 11, 18; xxxiii. 10; xl. 1, 25; xli. 21, twice; lxvi. 9). This peculiarity, according to Ḥanina, contains an allusion to the corresponding number of prophets that were to appear after the destruction of the (first) Temple: Joel, Amos, Zephaniah, Haggai, Zechariah, Malachi, Ezekiel, and Jeremiah (Pesiḳ. xvi. 128b; see Buber
ad loc.
). An elder namesake of Ḥanina was a tanna, contemporary of AḤai b. Josiah, with whom he discussed a halakic midrash (Mek., Mishpaṭim, v.; comp. Sifra, Ḳedoshim, ix. 6, 14).
("saith"), is used eight times (i. 11, 18; xxxiii. 10; xl. 1, 25; xli. 21, twice; lxvi. 9). This peculiarity, according to Ḥanina, contains an allusion to the corresponding number of prophets that were to appear after the destruction of the (first) Temple: Joel, Amos, Zephaniah, Haggai, Zechariah, Malachi, Ezekiel, and Jeremiah (Pesiḳ. xvi. 128b; see Buber
ad loc.
). An elder namesake of Ḥanina was a tanna, contemporary of AḤai b. Josiah, with whom he discussed a halakic midrash (Mek., Mishpaṭim, v.; comp. Sifra, Ḳedoshim, ix. 6, 14).
- Bacher, Ag. Pal. Amor. iii. 553;
- idem, Ag. Tan. ii. 553;
- Frankel, Mebo, p. 89a;
- Heilprin, Seder ha-Dorot, ii. 143a, 148b, Warsaw, 1897.
Categories: [Jewish encyclopedia 1906]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 09/04/2022 19:00:57 | 56 views
☰ Source: https://www.jewishencyclopedia.com/articles/7204-hanina-hananiah-hinena-b-adda-idda.html | License: Public domain
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed: KSF
KSF