World War Ii
 From Nwe
From Nwe World War II, also WWII, or the Second World War, was a global military conflict that took place between 1939 and 1945. It was the largest and deadliest war in history. The date commonly given for the start of the war is September 1, 1939, when Nazi Germany invaded Poland. Within two days the United Kingdom and France declared war on Germany, although the only European battles remained in Poland. Pursuant to a then-secret provision of its non-aggression Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact, the Soviet Union joined with Germany on September 17, 1939, to conquer Poland and to divide Eastern Europe.
The Allies were initially made up of Poland, the British Empire, France, and others. In May, 1940, Germany invaded western Europe. Six weeks later, France surrendered to Germany. Three months after that, Germany, Italy, and Japan signed a mutual defense agreement, the Tripartite Pact, and were known as the Axis Powers. Then, nine months later, in June 1941, Germany betrayed and invaded the Soviet Union, forcing the Soviets into the Allied camp (although they continued their non-aggression treaty with Japan). In December 1941, Japan attacked the United States bringing it into the war on the Allied side. China also joined the Allies, as eventually did most of the rest of the world. From the beginning of 1942 through August 1945, battles raged across all of Europe, in the North Atlantic Ocean, across North Africa, throughout Southeast Asia, and China, across the Pacific Ocean and in the air over Germany and Japan.
After World War II, Europe was split into western and Soviet spheres of influence. Western Europe later aligned as NATO and Eastern Europe as the Warsaw Pact. There was a shift in power from Western Europe and the British Empire to the two post-war superpowers, the United States and the Soviet Union. These two rivals would later face off in the Cold War. In Asia, Japan's defeat led to its democratization. China's civil war continued into the 1950s, resulting eventually in the establishment of the People's Republic of China. European colonies began their road to independence. Disgusted at the human cost of war, as people had been after World War I, a commitment to diplomacy to resolve differences was written into the charter of the new international body that replaced the failed League of Nations, the United Nations, which this time attracted U.S. support. The real effectiveness of this body has been subsequently compromised because member states act when it suits them, and sometimes by-pass it altogether. The victory, though, of the Allies over the Axis powers is usually regarded as having safeguarded democracy and freedom. The Holocaust represented one of the the most evil incidents in human history. Even still, the Allies cannot be said to have conducted the war according to the highest standards of combat, using mass bombings that provoked one leading British Bishop, George Bell (1883-1958) to withdraw his support for the just cause of the war.
Causes
Commonly held general causes for WWII are the rise of nationalism, militarism, and unresolved territorial issues. In Germany, resentment of the harsh Treaty of Versailles—specifically article 231 (the "Guilt Clause"), the belief in the Dolchstosslegende (that treachery had cost them WWI), and the onset of the Great Depression—fueled the rise to power of Adolf Hitler's militarist National Socialist German Workers Party (the Nazi Party). Meanwhile, the treaty's provisions were laxly enforced due to fear of another war. Closely related is the failure of the British and French policy of appeasement, which sought to avoid war but actually gave Hitler time to re-arm. The League of Nations proved to be ineffective.
Japan, ruled by a militarist clique devoted to becoming a world power invaded China to bolster its meager stock of natural resources. This angered the United States, which reacted by making loans to China, providing covert military assistance, and instituting increasingly broad embargoes of raw materials against Japan. These embargoes would have eventually wrecked Japan's economy; Japan was faced with the choice of withdrawing from China or going to war in order to conquer the oil resources of the Dutch East Indies (Indonesia). It chose to proceed with plans for the Greater East Asia War in the Pacific.
War breaks out in Europe: 1939
- Pre-war alliances
In March 1939, when German armies entered Prague then occupied the remainder of Czechoslovakia, the Munich Agreement—which required Germany to peacefully resolve its claim to the Czech territory—collapsed. On May 19, Poland and France pledged to provide each other with military assistance in the event either was attacked. The British had already offered support to the Poles in March; then, on August 23, Germany and the Soviet Union signed the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact. The pact included a secret protocol which would divide eastern Europe into German and Soviet areas of interest. Each country agreed to allow the other a free hand in its area of influence, including military occupation. Hitler was now ready to go to war in order to conquer Poland. The signing of a new alliance between Britain and Poland on August 25, deterred him for only a few days.
- Invasion of Poland
On September 1, Germany invaded Poland. Two days later, Britain and France declared war on Germany. The French mobilized slowly, then mounted a token offensive in the Saar, which they soon abandoned, while the British could not take any direct action in support of the Poles in the time available. Meanwhile, on September 9, the Germans reached Warsaw, having slashed through the Polish defenses.
On September 17, Soviet troops occupied the eastern Poland, taking control of territory that Germany had agreed was in the Soviet sphere of influence. A day later the Polish president and commander-in-chief both fled to Romania. The last Polish units surrendered on October 6. Some Polish troops evacuated to neighboring countries. In the aftermath of the September Campaign, occupied Poland managed to create a powerful resistance movement and Poles made a significant contribution to the Allies' cause for the duration of World War II.
After Poland fell, Germany paused to regroup during the winter of 1939-1940 until April 1940, while the British and French stayed on the defensive. The period was referred to by journalists as "the Phony War," or the "Sitzkrieg," because so little ground combat took place.
- Battle of the Atlantic
Meanwhile in the North Atlantic, German U-boats operated against Allied shipping. The submarines made up in skill, luck, and daring what they lacked in numbers. One U-boat sank the British aircraft carrier HMS Courageous, while another managed to sink the battleship HMS Royal Oak in its home anchorage of Scapa Flow. Altogether, U-boats sank more than 110 vessels in the first four months of the war.
In the South Atlantic, the German pocket battleship Admiral Graf Spee raided Allied shipping, then was scuttled after the battle of the River Plate. About a year and a half later, another German raider, the battleship Bismarck, suffered a similar fate in the North Atlantic. Unlike the U-boat threat, which had a serious impact later in the war, German surface raiders had little impact because their numbers were so small.
War spreads: 1940
- Soviet-Finnish War
The Soviet Union attacked Finland on November 30, 1939, starting the Winter War. Finland surrendered to the Soviet Union in March 1940 and signed the Moscow Peace Treaty (1940) in which the Finns made territorial concessions. Later that year, in June the Soviet Union occupied Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia, and annexed Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina from Romania.
- Invasion of Denmark and Norway
Germany invaded Denmark and Norway on April 9, 1940, in part to counter the threat of an impending Allied invasion of Norway. Denmark did not resist, but Norway fought back, assisted by British, French, and Polish (exile) forces landing in support of the Norwegians at Namsos, Åndalsnes, and Narvik. By late June, the Allies were defeated, German forces were in control of most of Norway, and what remained of the Norwegian Army had surrendered.
- Invasion of France and the Low Countries
On May 10, 1940, the Germans invaded Luxembourg, Belgium, the Netherlands, and France, ending the "Phony War." The British Expeditionary Force (BEF) and the French Army advanced into northern Belgium, planning to fight a mobile war in the north while maintaining a static continuous front along the Maginot Line, built after World War I, further south.
In the first phase of the invasion, Fall Gelb (CACA), the Wehrmacht's Panzergruppe von Kleist raced through the Ardennes, broke the French line at Sedan, then slashed across northern France to the English Channel, splitting the Allies in two. Meanwhile Belgium, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands fell quickly against the attack of German Army Group B. The BEF, encircled in the north, was evacuated from Dunkirk in Operation Dynamo. On June 10, Italy joined the war, attacking France in the south. German forces then continued the conquest of France with Fall Rot (Case Red), advancing behind the Maginot Line and near the coast. France signed an armistice with Germany on June 22, 1940, leading to the establishment of the Vichy France puppet government in the unoccupied part of France.
Following the defeat of France, Britain chose to fight on, so Germany began preparations in summer of 1940 to invade Britain (Operation Sea Lion), while Britain made anti-invasion preparations. Germany's initial goal was to gain air control over Britain by defeating the Royal Air Force (RAF). The war between the two air forces became known as the Battle of Britain. The Luftwaffe initially targeted RAF Fighter Command. The results were not as expected, so the Luftwaffe later turned to terror bombing London. The Germans failed to defeat the Royal Air Force, thus Operation Sea Lion was postponed and eventually canceled.
- North African Campaign
Italy declared war in June 1940, which challenged British supremacy of the Mediterranean, hinged on Gibraltar, Malta, and Alexandria. Italian troops invaded and captured British Somaliland in August. In September, the North African Campaign began when Italian forces in Libya attacked British forces in Egypt. The aim was to make Egypt an Italian possession, especially the vital Suez Canal east of Egypt. British, Indian, and Australian forces counter-attacked in Operation Compass, but this offensive stopped in 1941 when much of the Commonwealth forces were transferred to Greece to defend it from German attack. However, German forces (known later as the Afrika Korps) under General Erwin Rommel landed in Libya and renewed the assault on Egypt.
- Invasion of Greece
Italy invaded Greece on October 28, 1940, from bases in Albania after the Greek Premier John Metaxas rejected an ultimatum to hand over Greek territory. Despite the enormous superiority of the Italian forces, the Greek army forced the Italians into a massive retreat deep into Albania. By mid-December, the Greeks occupied one-fourth of Albania. The Greek army had inflicted upon the Axis Powers their first defeat in the war, and Nazi Germany would soon be forced to intervene.
War becomes global: 1941
European theater
- Lend-Lease
U.S. President Franklin Delano Roosevelt signed the Lend-Lease Act on March 11. This program was the first large step away from American isolationism, providing for substantial assistance to the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, and other countries.
- Invasion of Greece and Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia's government succumbed to the pressure of the Axis and signed the Tripartite Treaty on March 25, but the government was overthrown in a coup which replaced it with a pro-Allied government. This prompted the Germans to invade Yugoslavia on April 6. In the early morning, Germans bombarded Belgrade with an estimated 450 aircraft. Yugoslavia was occupied in a matter of days, and the army surrendered on April 17, but the partisan resistance lasted throughout the war. The rapid downfall of Yugoslavia, however, allowed German forces to enter Greek territory through the Yugoslav frontier. The 58,000 British and Commonwealth troops who had been sent to help the Greeks were driven back and soon forced to evacuate. On April 27, German forces entered Athens which was followed by the end of organized Greek resistance. The occupation of Greece proved costly, as guerilla warfare continually plagued the Axis occupiers.
- Invasion of Soviet Union
Operation Barbarossa, the largest invasion in history, began June 22, 1941. An Axis force of over four million soldiers advanced rapidly deep into the Soviet Union, destroying almost the entire western Soviet army in huge battles of encirclement. The Soviets dismantled as much industry as possible ahead of the advancing forces, moving it to the Ural Mountains for reassembly. By late November, the Axis had reached a line at the gates of Leningrad, Moscow, and Rostov, at the cost of about 23 percent casualties. Their advance then ground to a halt. The German General Staff had underestimated the size of the Soviet army and its ability to draft new troops. They were now dismayed by the presence of new forces, including fresh Siberian troops under General Zhukov, and by the onset of a particularly cold winter. German forward units had advanced within distant sight of the golden onion domes of Moscow's Saint Basil's Cathedral, but then on December 5, the Soviets counter-attacked and pushed the Axis back some 150-250 kilometers (100-150 mi), which became the first major German defeat of World War II.
The Continuation War between Finland and the Soviet Union began on June 25, with Soviet air attacks shortly after the beginning of Operation Barbarossa.
- Allied conferences
The Atlantic Charter was a joint declaration by Churchill and Roosevelt, August 14, 1941.
In late December 1941, Churchill met Roosevelt again at the Arcadia Conference. They agreed that defeating Germany had priority over defeating Japan. The Americans proposed a 1942 cross-channel invasion of France which the British strongly opposed, suggesting instead a small invasion in Norway or landings in French North Africa.
- Mediterranean
Rommel's forces advanced rapidly eastward, laying siege to the vital seaport of Tobruk. Two Allied attempts to relieve Tobruk were defeated, but a larger offensive at the end of the year drove Rommel back after heavy fighting.
On May 20, the Battle of Crete began when elite German parachute and glider-borne mountain troops launched a massive airborne invasion of the Greek island. Crete was defended by Greek and Commonwealth troops. The Germans attacked the island's three airfields simultaneously. Their invasion on two airfields failed, but they successfully captured one, which allowed them to reinforce their position and capture the island in a little over one week.
In June 1941, Allied forces invaded Syria and Lebanon, capturing Damascus on June 17. In August, British and Soviet troops occupied neutral Iran to secure its oil and a southern supply line to Russia.
Pacific theater
- Sino-Japanese war
A war had begun in East Asia before World War II started in Europe. On July 7, 1937, Japan, after occupying Manchuria in 1931, launched another attack against China near Beijing. The Japanese made initial advances but were stalled at Shanghai. The city eventually fell to the Japanese and in December 1937, the capital city Nanking (now Nanjing) fell. As a result, the Chinese government moved its seat to Chongqing for the rest of the war. The Japanese forces committed brutal atrocities against civilians and prisoners of war when Nanking was occupied, slaughtering as many as 300,000 civilians within a month. The war by 1940 had reached a stalemate with both sides making minimal gains. The Chinese had successfully defended their land from oncoming Japanese on several occasions while strong resistance in areas occupied by the Japanese made a victory seem impossible to the Japanese.
- Japan and the United States
In the summer of 1941, the United States began an oil embargo against Japan, which was a protest to Japan's incursion into French Indo-China and the continued invasion of China. Japan planned an attack on Pearl Harbor to cripple the U.S. Pacific Fleet before consolidating oil fields in the Dutch East Indies. On December 7, a Japanese carrier fleet launched a surprise air attack on Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. The raid resulted in two U.S. battleships sunk, and six damaged but later repaired and returned to service. The raid failed to find any aircraft carriers and did not damage Pearl Harbor's usefulness as a naval base. The attack strongly united public opinion in the United States against Japan. The following day, December 8, the United States declared war on Japan. On the same day, China officially declared war against Japan. Germany declared war on the United States on December 11, even though it was not obliged to do so under the Tripartite Pact. Hitler hoped that Japan would support Germany by attacking the Soviet Union. Japan did not oblige, and this diplomatic move by Hitler proved a catastrophic blunder which unified the American public's support for the war.
- Japanese offensive
Japan soon invaded the Philippines and the British colonies of Hong Kong, Peninsular Malaysia, Borneo, and Burma, with the intention of seizing the oilfields of the Dutch East Indies. Despite fierce resistance by American, Philippine, British, Canadian, and Indian forces, all these territories capitulated to the Japanese in a matter of months. The British island fortress of Singapore was captured in what Churchill considered one of the most humiliating British defeats of all time.
Deadlock: 1942
European theater
- Western and Central Europe
In May, top Nazi leader Reinhard Heydrich was assassinated by Allied agents in Operation Anthropoid. Hitler ordered severe reprisals.
On August 19, British and Canadian forces launched the Dieppe Raid (codenamed Operation Jubilee) on the German occupied port of Dieppe, France. The attack was a disaster but provided critical information utilized later in Operation Torch and Operation Overlord.
- Soviet winter and early spring offensive
In the north, Soviets launched the Toropets-Kholm Operation January 9 to February 6 1942, trapping a German force near Andreapol. The Soviets also surrounded a German garrison in the Demyansk Pocket which held out with air supply for four months (February 8 until April 21), and established themselves in front of Kholm, Velizh and Velikie Luki.
In the south, Soviet forces launched an offensive in May against the German Sixth Army, initiating a bloody 17 day battle around Kharkov, which resulted in the loss of over 200,000 Red Army personnel.
- Axis summer offensive
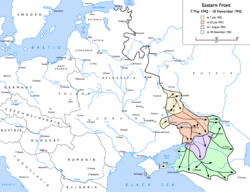
On June 28, the Axis began their summer offensive. German Army Group B planned to capture the city of Stalingrad, which would secure the German left while Army Group A planned to capture the southern oil fields. In the Battle of the Caucasus, fought in the late summer and fall of 1942, the Axis forces captured the oil fields.
- Stalingrad
After bitter street fighting which lasted for months, the Germans captured 90 percent of Stalingrad by November. The Soviets, however, had been building up massive forces on the flanks of Stalingrad. They launched Operation Uranus on November 19, with twin attacks that met at Kalach four days later and trapped the Sixth Army in Stalingrad. The Germans requested permission to attempt a break-out, which was refused by Hitler, who ordered Sixth Army to remain in Stalingrad where he promised they would be supplied by air until rescued. About the same time, the Soviets launched Operation Mars in a salient near the vicinity of Moscow. Its objective was to tie down Army Group Center and to prevent it from reinforcing Army Group South at Stalingrad.
In December, German relief forces got within 50 kilometers (30 mi) of the trapped Sixth Army before they were turned back by the Soviets. By the end of the year, the Sixth Army was in desperate condition, as the Luftwaffe was only able to supply about a sixth of the provisions needed. The battle ended in February 1943, when the Soviet forces succeeded in over-running the German positions.
The Battle of Stalingrad was a turning point in World War II and is considered the bloodiest battle in human history, with more combined casualties suffered than in any battle before. The battle was marked by brutality and disregard for military and civilian casualties on both sides. Total deaths are estimated to have approached 2.5 million. When it was over, the Axis powers had lost one fourth of their strength on that front.
- Eastern North Africa
At the beginning of 1942, the Allied forces in North Africa were weakened by detachments to the Far East. Rommel once again attacked and recaptured Benghazi. Then he defeated the Allies at the Battle of Gazala, and captured Tobruk with several thousand prisoners and large quantities of supplies. Following up, he drove deep into Egypt but with overstretched forces.
The First Battle of El Alamein took place in July 1942. Allied forces had retreated to the last defensible point before Alexandria and the Suez Canal. The Afrika Korps, however, had outrun its supplies, and the defenders stopped its thrusts. The Second Battle of El Alamein occurred between October 23 and November 3. Lieutenant-General Bernard Montgomery was in command of the Commonwealth forces, now known as the British Eighth Army. The Eighth Army took the offensive and was ultimately triumphant. After the German defeat at El Alamein, the Axis forces made a successful strategic withdrawal to Tunisia.
- Western North Africa
Operation Torch, launched on November 8, 1942, aimed to gain control of Morocco and Algiers through simultaneous landings at Casablanca, Oran, and Algiers, followed a few days later with a landing at Bône, the gateway to Tunisia. It was hoped that the local forces of Vichy France (the puppet government in France under the Nazis) would put up no resistance and submit to the authority of Free French General Henri Giraud. In response, Hitler invaded and occupied Vichy France and Tunisia, but the German and Italian forces were caught in the pincers of a twin advance from Algeria and Libya. Rommel's victory against American forces at the Battle of the Kasserine Pass could only hold off the inevitable.
Pacific theater
- Central and South West Pacific
On February 19, 1942, Roosevelt signed United States Executive Order 9066, leading to the internment of approximately 110,000 Japanese-Americans for the duration of the war.
In April, the Doolittle Raid, the first U.S. air raid on Tokyo, boosted morale in the U.S. and caused Japan to shift resources to homeland defense, but did little actual damage.
In early May, a Japanese naval invasion of Port Moresby, New Guinea, was thwarted by Allied navies in the Battle of the Coral Sea. This was both the first successful opposition to a Japanese attack and the first battle fought between aircraft carriers.
On June 5, American carrier-based dive-bombers sank four of Japan's best aircraft carriers in the Battle of Midway. Historians mark this battle as a turning point and the end of Japanese expansion in the Pacific. Cryptography played an important part in the battle, as the United States had broken the Japanese naval codes and knew the Japanese plan of attack.
In July, a Japanese overland attack on Port Moresby was led along the rugged Kokoda Track. An outnumbered and untrained Australian battalion defeated the 5,000-strong Japanese force, the first land defeat of Japan in the war and one of the most significant victories in Australian military history.
On August 7, United States Marines began the Battle of Guadalcanal. For the next six months, U.S. forces fought Japanese forces for control of the island. Meanwhile, several naval encounters raged in the nearby waters, including the Battle of Savo Island, Battle of Cape Esperance, Naval Battle of Guadalcanal, and Battle of Tassafaronga. In late August and early September, while battle raged on Guadalcanal, an amphibious Japanese attack on the eastern tip of New Guinea was met by Australian forces in the Battle of Milne Bay.
- Sino-Japanese War
Japan launched a major offensive in China following the attack on Pearl Harbor. The aim of the offensive was to take the strategically important city of Changsha which the Japanese had failed to capture on two previous occasions. For the attack, the Japanese massed 120,000 soldiers under 4 divisions. The Chinese responded with 300,000 men, and soon the Japanese army was encircled and had to retreat.
War turns: 1943
European theater
- German and Soviet spring offensives
After the surrender of the German Sixth Army at Stalingrad on February 2, 1943, the Red Army launched eight offensives during the winter. Many were concentrated along the Don basin near Stalingrad, which resulted in initial gains until German forces were able to take advantage of the weakened condition of the Red Army and regain the territory it lost.
- Operation Citadel
On July 4, the Wehrmacht launched a much-delayed offensive against the Soviet Union at the Kursk salient. Their intentions were known by the Soviets, and they hastened to defend the salient with an enormous system of earthwork defenses. Both sides massed their armor for what became a decisive military engagement. The Germans attacked from both the north and south of the salient and hoped to meet in the middle, cutting off the salient and trapping 60 Soviet divisions. The German offensive was ground down as little progress was made through the Soviet defenses. The Soviets then brought up their reserves, and the largest tank battle of the war occurred near the city of Prokhorovka. The Germans had exhausted their armored forces and could not stop the Soviet counter-offensive that threw them back across their starting positions.
- Soviet fall and winter offensives
In August, Hitler agreed to a general withdrawal to the Dnieper line, and as September proceeded into October, the Germans found the Dnieper line impossible to hold as the Soviet bridgeheads grew. Important Dnieper towns started to fall, with Zaporozhye the first to go, followed by Dnepropetrovsk.
Early in November the Soviets broke out of their bridgeheads on either side of Kiev and recaptured the Ukrainian capital.
The First Ukrainian Front attacked at Korosten on Christmas Eve. The Soviet advance continued along the railway line until the 1939 Polish-Soviet border was reached.
- Italy
The surrender of Axis forces in Tunisia on May 13, 1943 yielded some 250,000 prisoners. The North African war proved to be a disaster for Italy, and when the Allies invaded Sicily on July 10, in Operation Husky, capturing the island in a little over a month, the regime of Benito Mussolini collapsed. On July 25, he was removed from office by the King of Italy, and arrested with the positive consent of the Great Fascist Council. A new government, led by Pietro Badoglio, took power but declared that Italy would stay in the war. Badoglio actually had begun secret peace negotiations with the Allies.
The Allies invaded mainland Italy on September 3, 1943. Italy surrendered to the Allies on September 8, as had been agreed in negotiations. The royal family and Badoglio government escaped to the south, leaving the Italian army without orders, while the Germans took over the fight, forcing the Allies to a complete halt in the winter of 1943-44 at the Gustav Line south of Rome.
In the north, the Nazis let Mussolini create what was effectively a puppet state, the Italian Social Republic or "Republic of Salò," named after the new capital of Salò on Lake Garda.
Mid-1943 brought the fifth and final German Sutjeska offensive against the Yugoslav Partisans.
Pacific theater
- Central and South West Pacific

On January 2, Buna, New Guinea was captured by the Allies. This ended the threat to Port Moresby. By January 22, 1943, the Allied forces had achieved their objective of isolating Japanese forces in eastern New Guinea and cutting off their main line of supply.
American authorities declared Guadalcanal secure on February 9. Australian and U.S. forces undertook the prolonged campaign to retake the occupied parts of the Solomon Islands, New Guinea, and the Dutch East Indies, experiencing some of the toughest resistance of the war. The rest of the Solomon Islands were retaken in 1943.
In November, U.S. Marines won the Battle of Tarawa. This was the first heavily opposed amphibious assault in the Pacific theater. The high casualties taken by the Marines sparked off a storm of protest in the United States, where the large losses could not be understood for such a tiny and seemingly unimportant island.
- Sino-Japanese War
A vigorous, fluctuating battle for Changde in China's Hunan province began on November 2, 1943. The Japanese threw over 100,000 men into the attack on the city, which changed hands several times in a few days but ended up still held by the Chinese. Overall, the Chinese ground forces were compelled to fight a war of defense and attrition while they built up their armies and awaited an Allied counteroffensive.
- South East Asia
The Nationalist Kuomintang Army, under Chiang Kai-shek, and the Communist Chinese Army, under Mao Zedong, both opposed the Japanese occupation of China but never truly allied against the Japanese. Conflict between Nationalist and Communist forces emerged long before the war; it continued after and, to an extent, even during the war, though more implicitly. The Japanese and its auxiliary Indian National Army had captured most of Burma, severing the Burma Road by which the Western Allies had been supplying the Chinese Nationalists. This forced the Allies to create a large sustained airlift, known as "flying the Hump." U.S.-led and trained Chinese divisions, a British division and a few thousand U.S. ground troops cleared the Japanese forces from northern Burma so that the Ledo Road could be built to replace the Burma Road.
Beginning of the end: 1944
European theater
- Soviet winter and spring offensives
In the north, a Soviet offensive in January 1944, had relieved the siege of Leningrad. The Germans conducted an orderly retreat from the Leningrad area to a shorter line based on the lakes to the south.
In the south, in March, two Soviet fronts encircled Generaloberst Hans-Valentin Hube's German First Panzer Army north of the Dniestr river. The Germans escaped the pocket in April, saving most of their men but losing their heavy equipment.
In early May, the Red Army's 3rd Ukrainian Front engaged German Seventeenth Army of Army Group South which had been left behind after the German retreat from the Ukraine. The battle was a complete victory for the Red Army, and a botched evacuation effort across the Black Sea led to over 250,000 German and Romanian casualties.
During April 1944, a series of attacks by the Red Army near the city of Iaşi, Romania was aiming at capturing the strategically important sector. The German-Romanian forces successfully defended the sector throughout the month of April. The attack aiming at Târgul Frumos was the final attempt by the Red Army to achieve its goal of having a spring-board into Romania for a summer offensive.
With Soviet forces approaching, German troops occupied Hungary on March 20, as Hitler thought that the Hungarian leader, Admiral Miklós Horthy, might no longer be a reliable ally.
Finland sought a separate peace with Stalin in February 1944, but the terms offered were unacceptable. On June 9, the Soviet Union began the Fourth strategic offensive on the Karelian Isthmus that after three months would force Finland to accept an armistice.
- Soviet summer offensive
Operation Bagration, a Soviet offensive involving 2.5 million men and 6,000 tanks, was launched on June 22, and was intended to clear German troops from Belarus. The subsequent battle resulted in the destruction of German Army Group Center and over 800,000 German casualties, the greatest defeat for the Wehrmacht during the war. The Soviets swept forward, reaching the outskirts of Warsaw on July 31.
- Soviet fall and winter offensives
After the destruction of Army Group Center, the Soviets attacked German forces in the South in mid-July 1944 and in a month's time cleared the Ukraine of German presence.
The Red Army's 2nd and 3rd Ukrainian Fronts engaged German Heeresgruppe Südukraine, which consisted of German and Romanian formations, in an operation to occupy Romania and destroy the German formations in the sector. The result of the battle was complete victory for the Red Army, and a switch of Romania from the Axis to the Allied camp.
In October 1944 General der Artillerie Maximilian Fretter-Pico's Sixth Army encircled and destroyed three corps of Marshal Rodion Yakovlevich Malinovsky's Group Pliyev near Debrecen, Hungary. This was to be the last German victory in the Eastern front.
The Red Army's 1st, 2nd, and 3rd Baltic Fronts engaged German Army Group Center and Army Group North to capture the Baltic region from the Germans. The result of the series of battles was a permanent loss of contact between Army Groups North and Center, and the creation of the Courland Pocket in Latvia.
From December 29, 1944, to February 13, 1945, Soviet forces laid siege to Budapest, which was defended by German Waffen-SS and Hungarian forces. It was one of the bloodiest sieges of the war.
- Warsaw uprising
The proximity of the Red Army led the Poles in Warsaw to believe they would soon be liberated. On August 1, they rose in revolt as part of the wider Operation Tempest. Nearly 40,000 Polish resistance fighters seized control of the city. The Soviets however stopped outside the city and gave the Poles no assistance, as German army units moved into the city to put down the revolt. The resistance ended on October 2. German units then destroyed most of what was left of the city.
- Allied invasion of Western Europe
On "D-Day" (June 6, 1944) the western Allies of mainly Britain, Canada and America invaded German-held Normandy. German resistance was stubborn and during the first month, the Allies measured progress in hundreds of yards and bloody rifle fights in the Bocage. An Allied breakout was effected at St.-Lô, and German forces were almost completely destroyed in the Falaise pocket while counter-attacking. Allied forces stationed in Italy invaded the French Riviera on August 15, and linked up with forces from Normandy. The clandestine French Resistance in Paris rose against the Germans on August 19, and a French division under General Jacques Leclerc, pressing forward from Normandy, received the surrender of the German forces there and liberated the city on August 25.
- Operation Market Garden
Allied paratroopers attempted a fast advance into the Netherlands with Operation Market Garden in September but were repulsed. Logistical problems were starting to plague the Allies' advance west as the supply lines still ran back to the beaches of Normandy. A decisive victory by the Canadian First Army in the Battle of the Scheldt secured the entrance to the port of Antwerp, freeing it to receive supplies by late November 1944.
- German winter offensive
In December 1944, the German Army made its last major offensive in the West, known as the Battle of the Bulge. Hitler sought to drive a wedge between the western Allies, causing them to agree to a favorable armistice, after which Germany could concentrate all its efforts on the Eastern front and have a chance to defeat the Soviets. The mission was doomed to failure, since the Allies had no intention of granting an armistice under any conditions. At first, the Germans scored successes against the unprepared Allied forces. Poor weather during the initial days of the offensive favored the Germans because it grounded Allied aircraft. However, with clearing skies allowing Allied air supremacy to resume, the German failure to capture Bastogne, and with the arrival of the United States Third Army, the Germans were forced to retreat back into Germany. The offensive was defeated but was the bloodiest battle in U.S. military history.
- Italy and the Balkans
During the winter the Allies tried to force the Gustav line on the southern Apennines of Italy but they could not break enemy lines until the landing of Anzio on January 22, 1944, on the southern coast of Latium, named Operation Shingle. Only after some months was the Gustav line broken and the Allies marched towards the north of the peninsula. On June 4, Rome fell to Allies, and the Allied army reached Florence in August, then stopped along the Gothic Line on the Tuscan Apennines during the winter.
Germany withdrew from the Balkans and held Hungary until February 1945.
Romania turned against Germany in August 1944 and Bulgaria surrendered in September.
Pacific theater
- Central and South West Pacific
The American advance continued in the southwest Pacific with the capture of the Marshall Islands before the end of February. 42,000 U.S. Army soldiers and Marines landed on Kwajalein atoll on January 31. Fierce fighting occurred and the island was taken on February 6. U.S. Marines next defeated the Japanese in the Battle of Eniwetok.
The main objective was the Marianas, especially Saipan and to a lessor extent, Guam. The Japanese in both places were strongly entrenched. On June 11, Saipan was bombarded from the sea and a landing made four days later; it was captured by July 9. The Japanese committed much of their declining naval strength in the Battle of the Philippine Sea but suffered severe losses in both ships and aircraft and after the battle the Japanese aircraft carrier force was no longer militarily effective. With the capture of Saipan, Japan was finally within range of B-29 bombers.
Guam was invaded on July 21, and taken on August 10, but Japanese fought fanatically and mopping up operations continued long after the Battle of Guam was officially over. The island of Tinian was invaded on July 24, and saw the first usage of napalm. The island fell on August 1. General MacArthur's troops invaded the Philippines, landing on the island of Leyte on October 20. The Japanese had prepared a rigorous defense and then used the last of their naval forces in an attempt to destroy the invasion force in the Battle of Leyte Gulf, October 23 through October 26, 1944, arguably the largest naval battle in history. The battle saw the first use of kamikaze (suicide) attacks.
Throughout 1944 American submarines and aircraft attacked Japanese merchant shipping, depriving Japan's industry of the raw materials it had gone to war to obtain. The effectiveness of this stranglehold increased as U.S. Marines captured islands closer to the Japanese mainland. In 1944 submarines sank three million tons of shipping while the Japanese were only able to replace less than one million tons.
- Sino-Japanese War
In April 1944, the Japanese launched Operation Ichigo whose aim was to secure the railway route across Japanese occupied territories of North East China and Korea and those in South East Asia and to destroy airbases in the area which serviced USAAF aircraft. In June 1944, the Japanese deployed 360,000 troops to invade Changsha for the fourth time. The Operation involved more Japanese troops than any other campaign in the Sino-Japanese war and after 47 days of bitter fighting, the city was taken but at a very high cost. By November, the Japanese had taken the cities of Guilin and Liuzhou which served as USAAF airbases from which it conducted bombing raids on Japan. However, despite having destroyed the airbases in this region, the USAAF could still strike at the Japanese main islands from newly acquired bases in the Pacific. By December, the Japanese forces reached French Indochina and achieved the purpose of the operation but only after incurring heavy losses.
- South East Asia
In March 1944, the Japanese began their "march to Delhi" by crossing the border from Burma into India. On March 30, they attacked the town of Imphal which involved some of the most ferocious fighting of the war. The Japanese soon ran out of supplies and withdrew resulting in a loss of 85,000 men, one of the largest Japanese defeats of the war. The Anglo-Indian forces were constantly re-supplied by the RAF.
End of the war: 1945
European theater
- Soviet winter offensive
On January 12, the Red Army was ready for its next big offensive. Konev's armies attacked the Germans in southern Poland, expanding out from their Vistula River bridgehead near Sandomierz. January 14, Rokossovsky's armies attacked from the Narew River north of Warsaw. They broke the defenses covering East Prussia. Zhukov's armies in the center attacked from their bridgeheads near Warsaw. The German front was now in shambles.
Zhukov took Zhukov took Warsaw on January 17, and Lódz on the 19th. The same day, his forces reached the German pre-war border. At the end of the first week of the offensive the Soviets had penetrated 100 miles deep on a front that was 400 miles wide. By February 13, the Soviets took Budapest. The Soviet onslaught finally halted at the end of January only 40 miles from Berlin, on the Oder river.
- Yalta Conference
At the Yalta Conference (February 1945), Churchill, Stalin, and Roosevelt made arrangements for post-war Europe. Many important resolutions were made:
- An April meeting would be held to form the United Nations;
- Poland would have free elections (though in fact they were heavily rigged by Soviets);
- Soviet nationals were to be repatriated;
- The Soviet Union was to attack Japan within three months of Germany's surrender.
- Soviet spring offensive
The Red Army (including 78,556 soldiers of the 1st Polish Army) began its final assault on Berlin on April 16. By this point, the German Army was in full retreat and Berlin had already been battered due to preliminary air bombings.
By April 24, the three Soviet army groups had completed the encirclement of the city. Hitler had sent the main German forces which were supposed to defend the city to the south as he believed that was the region where the Soviets would launch their spring offensive and not in Berlin. As a final resistance effort, Hitler called for civilians, including teenagers, to fight the oncoming Red Army in the Volkssturm militia. Those forces were augmented by the battered German remnants that had fought the Soviets in Seelow Heights. But even then the fighting was heavy, with house-to-house and hand-to-hand combat. The Soviets sustained 305,000 dead; the Germans sustained as many as 325,000, including civilians. Hitler and his staff moved into the Führerbunker, a concrete bunker beneath the Chancellery, where on April 30, 1945, he committed suicide, along with his bride, Eva Braun.
- Western Europe
The Allies resumed their advance into Germany once the Battle of the Bulge officially ended on January 27, 1945. The final obstacle to the Allies was the river Rhine which was crossed in late March 1945.
Once the Allies had crossed the Rhine, the British fanned out northeast towards Hamburg crossing the river Elbe and on towards Denmark and the Baltic. The U.S. Ninth Army went south as the northern pincer of the Ruhr encirclement and the U.S. First Army went north as the southern pincer of the Ruhr encirclement. On April 4 the encirclement was completed and the German Army Group B commanded by Field Marshal Walther Model was trapped in the Ruhr Pocket and 300,000 soldiers became POWs. The Ninth and First U.S. armies then turned east and then halted their advance at the Elbe river where they met up with the Soviet forces in mid-April, letting them take Berlin.
- Italy
Allied advances in the winter of 1944-45 up the Italian peninsula had been slow due the troop re-deployments to France. But by April 9, the British/American 15th Army Group which was composed of the U.S. Fifth Army and the British Eighth Army broke through the Gothic Line and attacked the Po Valley, gradually enclosing the main German forces. Milan was taken by the end of April and the U.S. 5th Army continued to move west and linked up with French units while the British 8th Army advanced towards Trieste and made contact with the Yugoslav partisans.
A few days before the surrender of German troops in Italy, Italian partisans intercepted a party of Fascists trying to make their escape to Switzerland. Hiding underneath a pile of coats was Mussolini. The whole party, including Mussolini's mistress, Clara Petacci, were summarily shot on April 28, 1945. Their bodies were taken to Milan and hung up on public display, upside down.
- Germany surrenders
Admiral Karl Dönitz became leader of the German government after the death of Hitler, but the German war effort quickly disintegrated. German forces in Berlin surrendered the city to the Soviet troops on May 2, 1945.
German forces in Italy surrendered May 2, 1945 at General Alexander's headquarters and German forces in northern Germany, Denmark, and the Netherlands surrendered on May 4; and the German High Command under Generaloberst Alfred Jodl surrendered unconditionally all remaining German forces on May 7 in Reims, France. The western Allies celebrated "V-E Day" on May 8.
The Soviet Union celebrated "Victory Day" on May 9. Some remnants of German Army Group Center continued resistance until May 11 or 12.
- Potsdam
The last Allied conference of World War II was held at the suburb of Potsdam, outside Berlin, from July 17 to August 2. The Potsdam Conference saw agreements reached between the Allies on policies for occupied Germany. An ultimatum was issued calling for the unconditional surrender of Japan.
Pacific theater
- Central and South West Pacific
In January the U.S. Sixth Army landed on Luzon, the main island of the Philippines. Manila was re-captured by March. U.S. capture of islands such as Iwo Jima in February and Okinawa (April through June) brought the Japanese homeland within easier range of naval and air attack. Amongst dozens of other cities, Tokyo was firebombed, and about 90,000 people died from the initial attack. The dense living conditions around production centers and the wooden residential constructions contributed to the large loss of life. In addition, the ports and major waterways of Japan were extensively mined by air in Operation Starvation which seriously disrupted the logistics of the island nation.
The last major offensive in the South West Pacific Area was the Borneo campaign of mid-1945, which was aimed at further isolating the remaining Japanese forces in South East Asia and securing the release of Allied prisoners of war.
- South East Asia
In South-East Asia, from August 1944, to November 1944, British 14th Army pursued the Japanese to the Chindwin River in Burma after their failed attack on India. The British Commonwealth forces launched a series of offensive operations back into Burma during late 1944 and the first half of 1945. On May 2, 1945, Rangoon, the capital city of Myanmar (Burma) was taken in Operation Dracula. The planned amphibious assault on the western side of Malaya was canceled after the dropping of the atomic bombs and Japanese forces in South-East Asia surrendered soon afterwards.
- Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
The U.S. military and political chiefs had decided to use their new super-weapon to bring the war to a speedy end. The battle for Okinawa had shown that an invasion of the Japanese mainland (planned for November), seen as an Okinawa type operation on a far larger scale, would result in more casualties than the United States had suffered so far in all theaters since the war began.
On August 6, 1945, the B-29 Superfortress Enola Gay, piloted by Col. Paul Tibbets, dropped a nuclear weapon named "Little Boy" on Hiroshima, destroying the city. After the destruction of Hiroshima, the United States again called upon Japan to surrender. No response was made, and accordingly on August 9, the B-29 BOCKS CAR, piloted by Maj. Charles Sweeney, dropped a second atomic bomb named "Fat Man" on Nagasaki.
- Soviet invasion of Manchuria
On August 8, two days after the atomic bomb was dropped on Hiroshima, the Soviet Union, having renounced its nonaggression pact with Japan, attacked the Japanese in Manchuria, fulfilling its Yalta pledge to attack the Japanese within three months after the end of the war in Europe. The attack was made by three Soviet army groups. In less than two weeks the Japanese army in Manchuria consisting of over a million men had been destroyed by the Soviets. The Red Army moved into North Korea on August 18. Korea was subsequently divided at the 38th parallel into Soviet and U.S. zones.
- Japan Surrenders
The American use of atomic weapons against Japan prompted Emperor Hirohito to bypass the existing government and intervene to end the war. The entry of the Soviet Union to the war may have also played a part, but in his radio address to the nation Emperor Hirohito did not mention it as a major reason for his country's surrender.
The Japanese surrendered on August 15, 1945 (V-J day), signing the Japanese Instrument of Surrender on September 2, 1945, aboard the USS Missouri (BB-63) anchored in Tokyo Bay. The Japanese troops in China formally surrendered to the Chinese on September 9, 1945. This did not fully end the war, however, as Japan and the Soviet Union never signed a peace agreement. In the last days of the war, the Soviet Union occupied the southern Kuril Islands, an area claimed by the Soviets and still contested by Japan.
World War Two: Religious Aspects
World War II was declared to be a just war by many church leaders in the Allied nations. Support for the just cause of the war, though, was famously withdrawn by Church of England Bishop George Bell of Chichester following the mass bombing of Dresen. This is said to have cost him the most senior appointment in the Anglican Church, as Archbishop of Canterbury. It has even been suggested that World War II is the definitive example of a just war. In Germany, Hitler attempted to bring state and church policy together with his German Christian church, combining religious and Teutonic symbolism and deifying his concept of the superiority of the German race. Many supported this arguing that God spoke through Hitler and nature just as God speaks though scripture. A minority, the Confessing Church, led by Martin Niemoeller, opposed Hitler. Bishop Bell was very close to the Confessing Church and met with Dietrich Bonhoeffer one of its leading members, who was executed for plotting against Hitler. While the Confessing Church denounced what they saw as Hitler-worship they failed to condemn the "Final Solution" although they did protest against Hitler's Jewish policy. For many theologians, issues raised by some of the atrocities of World War II remain a matter of profound concern, since they illustrate the human potential for utter evil. The scale of involvement in mass murder begs the question whether many felt that they had no choice but to comply with orders, or whether they really believed that Jews should be exterminated. Jewish thought especially would be transformed in the post-Holocaust world, in which the questions "why" and "where was God" loom large.
Aftermath
- Europe in ruins
At the end of the war, millions of refugees were homeless, the European economy had collapsed, and 70 percent of the European industrial infrastructure was destroyed.
- Partitioning of Germany and Austria
Germany was partitioned into four zones of occupation. An Allied Control Council was created to co-ordinate the zones. The original divide of Germany was between America, Soviet Union, and Britain. Stalin agreed to give France a zone but it had to come from the American or British zones and not the Soviet zone. The American, British, and French zones joined in 1949 as the Federal Republic of Germany and the Soviet zone became the German Democratic Republic.
Austria was once again separated from Germany and it, too, was divided into four zones of occupation, which eventually reunited and became the Republic of Austria.
- Reparations
Germany paid reparations to France, Britain and Russia, in the form of dismantled factories, forced labor, and shipments of coal. The U.S. settled for confiscating German patents and German owned property in the U.S., mainly subsidiaries of German companies.
In accordance with the Paris Peace Treaties, 1947, payment of war reparations was assessed from the countries of Italy, Romania, Hungary, Bulgaria, and Finland.
- Morgenthau Plan
The initial occupation plans proposed by the United States were harsh. The Morgenthau Plan of 1944 called for dividing Germany into two independent nations and stripping her of the industrial resources required for war. All heavy industry was to be dismantled or destroyed, the main industrial areas (Upper Silesia, Saar, Ruhr, and the German speaking parts of Alsace-Lorraine), were to be annexed.
While the Morgenthau Plan itself was never implemented per se, its general economic philosophy did end up greatly influencing events. Most notable were the toned-down offshoots, including the Potsdam Conference, Joint Chiefs of Staff Directive 1067 (April 1945-July 1947), and the industrial plans for Germany.
- Marshall Plan
Germany had long been the industrial giant of Europe, and its poverty held back the general European recovery. The continued scarcity in Germany also led to considerable expenses for the occupying powers, which were obligated to try and make up the most important shortfalls. Learning a lesson from the aftermath of World War I when no effort was made to systematically rebuild Europe, and when Germany was treated as a pariah, the United States made a bold decision to help reconstruct Europe. Secretary of State George Marshall proposed the "European Recovery Program," better known as the Marshall Plan, which called for the U.S. Congress to allocate billions of dollars for the reconstruction of Europe. Also as part of the effort to rebuild global capitalism and spur post-war reconstruction, the Bretton Woods system for international money management was put into effect after the war.
- Border revisions and population shifts
As a result of the new borders drawn by the victorious nations, large populations suddenly found themselves in hostile territory. The main benefactor of these border revisions was the Soviet Union, which expanded its borders at the expense of Germany, Finland, Poland, and Japan. Poland was compensated for its losses to the Soviet Union by receiving most of Germany east of the Oder-Neisse line, including the industrial regions of Silesia. The German state of the Saar temporarily became a protectorate of France but it later returned to German administration.
The number of Germans expelled totaled roughly 15 million, including 11 million from Germany proper and 3,500,000 from the Sudetenland.
Germany officially states that 2,100,000 of these expelled lost their lives due to violence on the part of the Russians, Polish, and Czech, though Polish and Czech historians dispute this figure.
- United Nations

Because the League of Nations had failed to actively prevent the war, in 1945 a new international body was considered and then created: The United Nations.
The UN operates within the parameters of the United Nations Charter, and the reason for the UN’s formation is outlined in the Preamble to the United Nations Charter. Unlike its predecessor, the United Nations has taken a more active role in the world, such as fighting diseases and providing humanitarian aid to nations in distress. The UN also served as the diplomatic front line during the Cold War.
The UN also was responsible for the initial creation of the modern state of Israel in 1948, in part as a response to the Holocaust.
Casualties, civilian impact, and atrocities
- Casualties
Possibly 62 million people lost their lives in World War II—about 25 million soldiers and 37 million civilians, with estimates varying widely. This total includes the estimated 12 million lives lost due to The Holocaust. Of the total deaths in World War II, approximately 80 percent were on the Allied side and 20 percent on the Axis side.
Allied forces suffered approximately 17 million military deaths, of which about 10 million were Soviet and 4 million Chinese. Axis forces suffered about 8 million, of which more than 5 million were German. The Soviet Union suffered by far the largest death toll of any nation in the war; perhaps 23 million Soviets died in total, of which more than 12 million were civilians. The figures include deaths due to internal Soviet actions against its own people. The statistics available for Soviet and Chinese casualties are only rough guesses, as they are poorly documented. Some modern estimates double the amount of Chinese casualties.
- Genocide
The Holocaust was the organized murder of at least nine million people, about two-thirds of whom were Jewish. Originally, the Nazis used killing squads, Einsatzgruppen, to conduct massive open-air killings, shooting as many as 33,000 people in a single massacre, as in the case of Babi Yar. By 1942, the Nazi leadership decided to implement the Final Solution (Endlösung), the genocide of all Jews in Europe, and increase the pace of the Holocaust. The Nazis built six extermination camps specifically to kill Jews. Millions of Jews who had been confined to massively overcrowded Ghettos were transported to these "Death-camps" where they were gassed or shot, usually immediately after arriving.
- Concentration camps, labor camps and internment
In addition to the Nazi concentration camps, the Soviet Gulag or labor camps, led to the death of many citizens of occupied countries such as Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia, as well as German prisoners of war and even Soviet citizens themselves: opponents of Stalin's regime and large proportions of some ethnic groups (particularly Chechens). Japanese POW camps also had high death rates; many were used as labor camps, and starvation conditions among the mainly U.S. and Commonwealth prisoners were little better than many German concentration camps. Sixty percent (1,238,000) of Soviet POWs died during the war. Vadim Erlikman puts it at 2.6 million Soviet POWs that died in German Captivity.
Furthermore, hundreds of thousands of Japanese North Americans were interned by the U.S. and Canadian governments. Though these camps did not involve heavy labor, forced isolation and sub-standard living conditions were the norm.
- War crimes and attacks on civilians
From 1945 to 1951, German and Japanese officials and personnel were prosecuted for war crimes. Top German officials were tried at the Nuremberg Trials and many Japanese officials at the Tokyo War Crime Trial and other war crimes trials in the Asia-Pacific region.
None of the alleged Allied war crimes such as the bombing of Dresden, the nuclear bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, or the alleged Red Army atrocities on the Eastern front were ever prosecuted.
Resistance and collaboration
Resistance during World War II occurred in every occupied country by a variety of means, ranging from non-cooperation, disinformation, and propaganda to outright warfare.
Among the most notable resistance movements were the Polish Home Army, the French Maquis, and the Yugoslav Partisans. Germany itself also had an anti-Nazi movement. The Communist resistance was among the fiercest since they were already organized and militant even before the war and they were ideologically opposed to the Nazis.
Before D-Day there were also many operations performed by the French Resistance to help with the forthcoming invasion. Communications lines were cut, trains derailed, roads, water towers, and ammunition depots were destroyed and some German garrisons were attacked.
Although Great Britain did not suffer invasion in World War II, the British made preparations for a British resistance movement, called the Auxiliary Units. Various organizations were also formed to establish foreign resistance cells or support existing resistance movements, like the British SOE and the American OSS.
The home fronts
"Home front" is the name given to the activities of the civilians of a nation that is in a state of total war.
In the United Kingdom, women joined the work force doing jobs that were typically reserved for men. Food, clothing, petrol, and other items were rationed. Access to luxuries was severely restricted, though there was also a significant black market. Families grew small home vegetable gardens to supply themselves with food, and the Women's Land Army recruited or conscripted over 80,000 women to work on farms. Civilians also served as Air Raid Wardens, volunteer emergency services, and other critical functions. Schools and organizations held scrap drives and money collections to help the war effort. Many things were conserved to turn into weapons later, such as fat to turn into nitroglycerin.
In the United States and Canada women also joined the workforce. In the United States these women were called "Rosies" for Rosie the Riveter. President Roosevelt stated that the efforts of civilians at home to support the war through personal sacrifice were as critical to winning the war as the efforts of the soldiers themselves. In Canada, the government established three military compartments for women: the CWAAF (Canadian Women's Auxiliary Air Force), CWAC (Canadian Women's Army Corps) and WRCNS (Women's Royal Canadian Naval Services).
In Germany, until 1943 there were few restrictions on civilian activities. Most goods were freely available. This was due in large part to the reduced access to certain luxuries already experienced by German civilians prior to the beginning of hostilities; the war made some less available, but many were in short supply to begin with. It was not until comparatively late in the war that the civilian population was effectively organized to support the war effort. For example, women's labor was not mobilized as thoroughly as in the United Kingdom or the United States. Foreign slave labor substituted for the men who served in the armed forces.
American production was the major factor in keeping the Allies better supplied than the Axis. For example, in 1943 the United States produced 369 warships (1.01/day). In comparison, Japan produced 122 warships, and Germany only built three. The United States also succeeded in rebuilding the Merchant Marine, reducing the build time of a Liberty or Victory ship from 105 days to 56 days. Much of this improved efficiency came from technological advances in shipbuilding. Hull plates were being welded rather than bolted, plastics were beginning to take the place of certain metals, and modular construction was being used.
Technologies
Weapons and technology improved rapidly during World War II and played a crucial role in determining the outcome of the war. Many major technologies were used for the first time, including nuclear weapons, radar, jet engines, and electronic computers. Enormous advances were made in aircraft, and tank design such that models coming into use at the beginning of the war were long obsolete by its end.
More new inventions, as measured in the U.S. by numbers of patent applications and weapon contracts issued to private contractors, were deployed to the task of killing humans more effectively and to a lesser degree, avoiding being killed, than ever before.
The massive research and development demands of the war had a great impact on the growth of the scientific community. After the war ended, these developments led to new sciences like cybernetics and computer science, and created entire new institutions of weapons design.
References
ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Gilbert, Martin. 1995. Second World War. NY: Phoenix. ISBN 1857993462
- Keegan, John. 1989. The Second World War. London: Hutchinson. ISBN 0091740118
- Liddel, Basil Henry. 1970. History of the Second World War. London: Cassell. ISBN 0304935646.
- Murray, Williamson. 2000. A War to Be Won: Fighting the Second World War. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. ISBN 067400163X
- Overy, Richard. 1995 Why the Allies Won. Pimlico. NY: W W Norton. ISBN 0712674535.
- Smith, J. Douglas and Richard Jensen. 2003. World War II on the Web: A Guide to the Very Best Sites. Lanham, MD: S R Books. ISBN 0842050205
External links
All links retrieved October 10, 2020.
- Directory of Online World War II Indexes & Records.
- World War II Military Situation Maps. Library of Congress.
- US National Archives Photos.
- Multimedia map - Presentation that covers the war from the invasion of Russia to the fall of Berlin.
- Virtual Museum of World War II - pictures & info.
- WW2 People's War - A project by the BBC to gather the stories of ordinary people from World War II.
- Workers' War: Home Front Recalled - A project by London Metropolitan University, TUC and the National Pensioners Convention to document the history of workers during World War II.
- Memories of Leutnant d.R. Wilhelm Radkovsky 1940-1945 Experiences as a German soldier on the Eastern and Western Front.
- The World at War (1974) is a 36-part BBC series that covers most aspects of World War II from many points of view. It includes interviews with many key figures (Karl Dönitz, Albert Speer, Anthony Eden etc.) (Imdb link).
- The Second World War in Colour (1999) is a three episode documentary showing unique footage in color (Imdb link).
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 02/03/2023 19:43:09 | 430 views
☰ Source: https://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/World_War_II | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed:
























 KSF
KSF