Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki | Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging | |
|---|---|
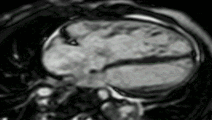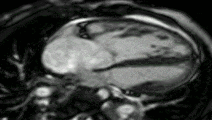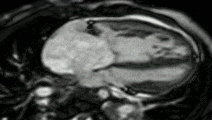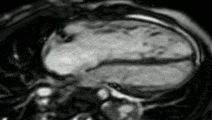
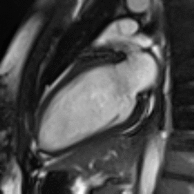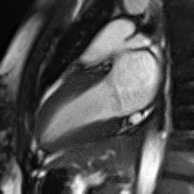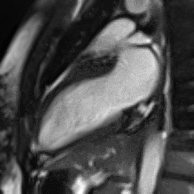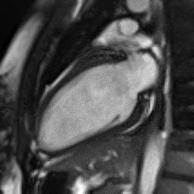
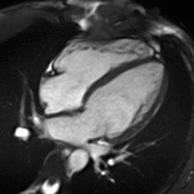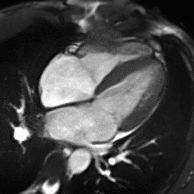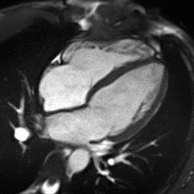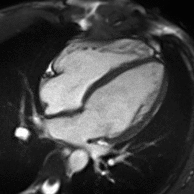
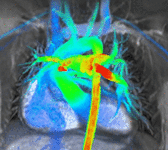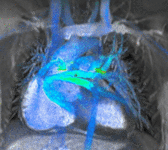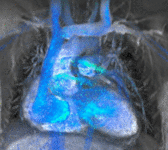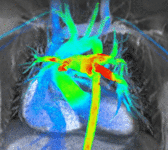
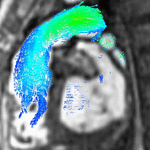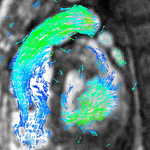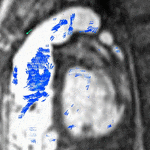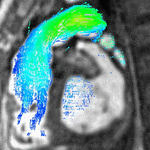
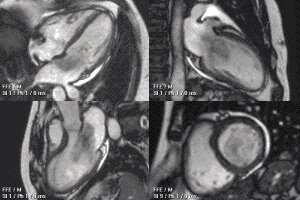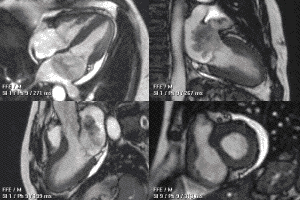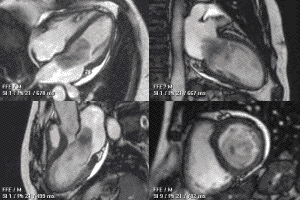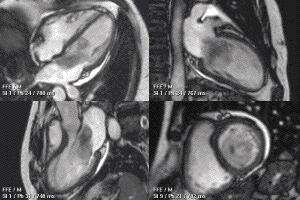 MRI sequences of a cardiac myxoma (a benign tumor)[1] | |
| ICD-10-PCS | B23 |
| ICD-9-CM | 88.92 |
| OPS-301 code | 3-803, 3-824 |
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (cardiac MRI, CMR), also known as cardiovascular MRI, is a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology used for non-invasive assessment of the function and structure of the cardiovascular system.[2] Conditions in which it is performed include congenital heart disease, cardiomyopathies and valvular heart disease, diseases of the aorta such as dissection, aneurysm and coarctation, coronary heart disease. It can also be used to look at pulmonary veins.[3] Patient information may be found here.
It is contraindicated if there are some implanted metal or electronic devices such as some intracerebral clips or claustrophobia.[3] These can be looked up to see if they are MRI conditional. For pacemaker or defibrillator patients, almost all can be scanned but special protocols are needed.
Conventional MRI sequences are adapted for cardiac imaging by using ECG gating and high temporal resolution protocols. The development of cardiac MRI is an active field of research and continues to see a rapid expansion of new and emerging techniques.[2]
Uses
Cardiovascular MRI is complementary to other imaging techniques, such as echocardiography, cardiac CT, and nuclear medicine. The technique has a key role in evidence-based diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular disease.[4] Its applications include assessment of myocardial ischemia and viability, cardiomyopathies, myocarditis, iron overload, vascular diseases, and congenital heart disease.[5] It is the reference standard for the assessment of cardiac structure and function,[6] and is valuable for diagnosis and surgical planning in complex congenital heart disease.[7]
Combined with vasodilator stress, it has a role in detecting and characterizing myocardial ischemia due to disease affecting the epicardial vessels and microvasculature. Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) and T1 mapping allow infarction and fibrosis to be identified for characterizing cardiomyopathy and assessing viability.[8] Magnetic resonance angiography may be performed with or without contrast medium and is used to assess congenital or acquired abnormalities of the coronary arteries and great vessels.[9]
Obstacles to its wider application include limited access to scanners, lack of technologists and skilled clinicians, relatively high costs, and competing diagnostic modalities.[4] Some organizations are working on solutions to reduce these obstacles so that more clinics can adopt CMR into their practices. These solutions are often software platforms that provide clinical decision support and improve the efficiency of the procedures.[10]
Risks
Cardiac MRI does not pose any specific risks compared to other indications for imaging.[11] Gadolinium based contrast medium is frequently used in CMR and has been associated with nephrogenic systemic fibrosis, predominantly using linear compounds in patients with renal disease. More recently evidence of intra-cranial deposition of gadolinium has been shown - although no neurological effects have been reported.[12] Genotoxic effects of cardiac MRI have been reported in vivo and in vitro,[13][14][15][16] but these findings have not been replicated by more recent studies,[17] and are unlikely to produce the complex DNA damage associated with ionizing radiation.[18]
Physics
CMR uses the same basic principles as other MRI techniques. Imaging of the cardiovascular system is usually performed with cardiac gating using an adaptation of conventional ECG techniques.[19] Cine sequences of the heart are acquired using balanced steady state free precession (bSSFP) which has good temporal resolution and intrinsic image contrast. T1-weighted sequences are used to visualize anatomy and detect the presence of intra-myocardial fat. T1 mapping has also been developed to quantify diffuse myocardial fibrosis.[20] T2-weighted imaging is mainly used to detect myocardial edema which may develop in acute myocarditis or infarction. Phase-contrast imaging uses bipolar gradients to encode velocity in a given direction and is used to assess valve disease and quantify shunts.
Techniques
A CMR study typically comprises a set of sequences in a protocol tailored to the specific indication for the exam.[21] A study begins with localisers to assist with image planning, and then a set of retrospectively-gated cine sequences to assess biventricular function in standard orientations. Contrast medium is given intravenously to assess myocardial perfusion and LGE. Phase contrast imaging may be used to quantify valvular regurgitant fraction and shunt volume. Additional sequences may include T1 and T2-weighted imaging and MR angiography. Examples are below:
Heart function using cine imaging
Functional and structural information is acquired using bSSFP cine sequences. These are usually retrospectively-gated and have intrinsically high contrast in cardiac imaging due to the relatively high T2:T1 ratio of blood compared to myocardium. Images are typically planned sequentially to achieve the standard cardiac planes used for assessment. Turbulent flow causes dephasing and signal loss allowing valvular disease to be qualitatively appreciated. The left ventricular short axis cines are acquired from base to apex and are used for quantifying end-diastolic and end-systolic volumes, as well as myocardial mass. Tagging sequences excite a grid pattern that deforms with cardiac contraction allowing strain to be assessed.
Late gadolinium enhancement
Gadolinium-based contrast agents are administered intravenously and delayed imaging is performed at least 10 minutes later to achieve optimum contrast between normal and infarcted myocardium. An inversion recovery (IR) sequence is used to null the signal from normal myocardium. Myocardial viability can be assessed by the degree of transmural enhancement. Cardiomyopathic, inflammatory and infiltrative diseases may also have distinctive patterns of non-ischemic LGE.[22][23]
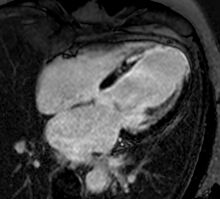
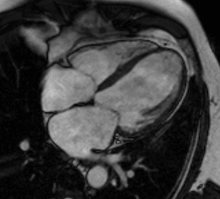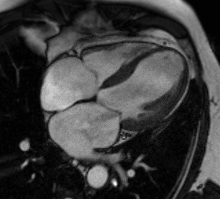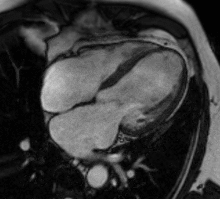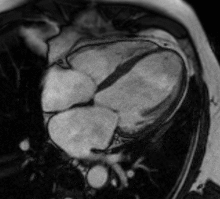
Perfusion
Adenosine is used as a vasodilator, via the A2A receptor, to increase the difference in perfusion between myocardial territories supplied by normal and stenosed coronary arteries. A continuous intravenous infusion is administered for a few minutes until there are hemodynamic signs of vasodilatation, then a bolus of contrast medium is administered while acquiring saturation recovery images of the heart with a high temporal resolution readout. A positive result is evident from an inducible myocardial perfusion defect. Cost and availability mean that its use is often confined to patients with intermediate pre-test probability,[24] but it has been shown to reduce unnecessary angiography compared with guidelines-directed care.[25]
4D flow CMR
Conventional phase contrast imaging can be extended by applying flow-sensitive gradients in 3 orthogonal planes within a 3D volume throughout the cardiac cycle. Such 4D imaging encodes the velocity of flowing blood at each voxel in the volume enabling fluid dynamics to be visualised using specialist software. Applications are in complex congenital heart disease and for research into cardiovascular flow characteristics - however it is not in routine clinical use due to the complexity of post-processing and relatively long acquisition times.[26]
Children and congenital heart disease
Congenital heart defects are the most common type of major birth defect. Accurate diagnosis is essential for the development of appropriate treatment plans. CMR can provide comprehensive information about the nature of congenital hearts defects in a safe fashion without using x-rays or entering the body. It is rarely used as the first or sole diagnostic test for congenital heart disease.
Rather, it is typically used in concert with other diagnostic techniques. In general, the clinical reasons for a CMR examination fall into one or more of the following categories: (1) when echocardiography (cardiac ultrasound) cannot provide sufficient diagnostic information, (2) as an alternative to diagnostic cardiac catheterization which involve risks including x-ray radiation exposure, (3) to obtain diagnostic information for which CMR offers unique advantages such as blood flow measurement or identification of cardiac masses, and (4) when clinical assessment and other diagnostic tests are inconsistent. Examples of conditions in which CMR is often used include tetralogy of Fallot, transposition of the great arteries, coarctation of the aorta, single ventricle heart disease, abnormalities of the pulmonary veins, atrial septal defect, connective tissue diseases such as Marfan syndrome, vascular rings, abnormal origins of the coronary arteries, and cardiac tumors.
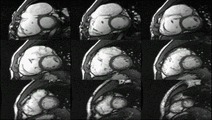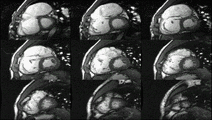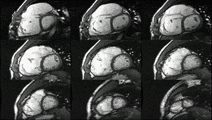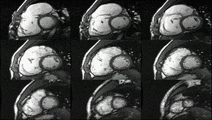
Atrial septal defect with dilation of the right ventricle by CMR

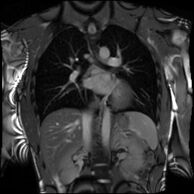
Partial Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Drainage by CMR
CMR examinations in children typically last 15 to 60 minutes. In order to avoid blurry images the child must remain very still during the examination. Different institutions have different protocols for pediatric CMR, but most children 7 years of age and older can cooperate sufficiently for a good quality examination. Providing an age-appropriate explanation of the procedure to the child in advance will increase the likelihood of a successful study. After proper safety screening, parents can be allowed into the MRI scanner room to help their child complete the examination. Some centers allow children to listen to music or watch movies through a specialized MRI-compatible audiovisual system to reduce anxiety and improve cooperation. However, the presence of a calm, encouraging, supportive parent generally produces better results in terms of pediatric cooperation than any distraction or entertainment strategy short of sedation. If the child cannot cooperate sufficiently, sedation with intravenous medications or general anesthesia may be necessary. In very young babies, it may be possible to perform the examination while they are in a natural sleep. New image capture techniques such as 4D flow require a shorter scan and can lead to reduced needs for sedation.
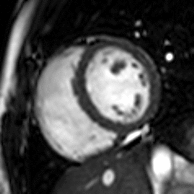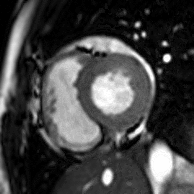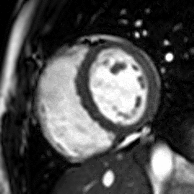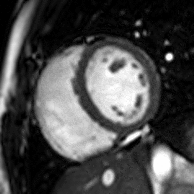
Enlarged right ventricle with poor function in a patient with repaired tetralogy of Fallot by CMR
Different cardiac-capable magnet types
The majority of CMR is performed on conventional superconducting MRI systems at either 1.5T or 3T.[27] Imaging at 3T field strength offers greater signal to noise ratio which can be traded for improved temporal or spatial resolution – which is of greatest utility in first-pass perfusion studies.[28] However, greater capital costs and effects of off-resonance artefact on image quality mean that many studies are routinely performed at 1.5T.[29] Imaging at 7T field strength is a growing area of research, but is not widely available.[30]
Current manufacturers of cardiac-capable MRI scanners include Philips, Siemens, Hitachi, Toshiba, GE.
History
The phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) was first described in molecular beams (1938) and bulk matter (1946), work later acknowledged by the award of a joint Nobel prize in 1952. Further investigation laid out the principles of relaxation times leading to nuclear spectroscopy. In 1971, there was the first report of the difference of the relaxation times for water in myocardium and pure water in spin-echo NMR by Hazlewood and Chang.[31] This difference forms the physical basis of the image contrast between cells and extracellular fluid. In 1973, the first simple NMR image was published and the first medical imaging in 1977, entering the clinical arena in the early 1980s. In 1984, NMR medical imaging was renamed MRI. Initial attempts to image the heart were confounded by respiratory and cardiac motion, solved by using cardiac ECG gating, faster scan techniques and breath hold imaging. Increasingly sophisticated techniques were developed including cine imaging and techniques to characterise heart muscle as normal or abnormal (fat infiltration, oedematous, iron loaded, acutely infarcted or fibrosed).
As MRI became more complex and application to cardiovascular imaging became more sophisticated, the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (SCMR) was set up (1996) with an academic journal, Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (JCMR) in 1999. In a move analogous to the development of 'echocardiography' from cardiac ultrasound, the term 'cardiovascular magnetic resonance' (CMR) was proposed and has gained acceptance as the name for the field.
CMR is increasingly recognized as a quantitative imaging modality for evaluation of the heart. The reporting of CMR exams involves manual work and visual assessment. In recent years, with the development of artificial intelligence techniques, the reporting and analysis of cardiac MRI are expected to be more efficient, facilitated by automatic deep learning tools.[32]
Training
Certification of competency in CMR can be obtained at three levels, with different requirements for each. Level 3 requires 50 hours of approved courses, at least 300 studies performed, sitting a written examination and recommendation by a supervisor.[33]
References
- ↑ "Case of the Week Number 06-01. Left Atrial Myxoma". 2016-10-21. http://www.scmr.org/caseoftheweek/case06-01.cfm.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Lee, Daniel C.; Markl, Michael; Dall’Armellina, Erica; Han, Yuchi; Kozerke, Sebastian; Kuehne, Titus; Nielles-Vallespin, Sonia; Messroghli, Daniel et al. (December 2018). "The growth and evolution of cardiovascular magnetic resonance: a 20-year history of the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (SCMR) annual scientific sessions". Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 20 (1): 8. doi:10.1186/s12968-018-0429-z. PMID 29386064.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Bunce, Nicholas H.; Ray, Robin; Patel, Hitesh (2020). "30. Cardiology". in Feather, Adam; Randall, David; Waterhouse, Mona (in en). Kumar and Clark's Clinical Medicine (10th ed.). Elsevier. pp. 1042–1044. ISBN 978-0-7020-7870-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=sl3sDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA1042.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 von Knobelsdorff-Brenkenhoff, Florian; Pilz, Guenter; Schulz-Menger, Jeanette (December 2017). "Representation of cardiovascular magnetic resonance in the AHA / ACC guidelines". Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 19 (1): 70. doi:10.1186/s12968-017-0385-z. PMID 28942735.
- ↑ von Knobelsdorff-Brenkenhoff, Florian; Schulz-Menger, Jeanette (December 2015). "Role of cardiovascular magnetic resonance in the guidelines of the European Society of Cardiology". Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 18 (1): 6. doi:10.1186/s12968-016-0225-6. PMID 26800662.
- ↑ Petersen, Steffen E.; Aung, Nay; Sanghvi, Mihir M.; Zemrak, Filip; Fung, Kenneth; Paiva, Jose Miguel; Francis, Jane M.; Khanji, Mohammed Y. et al. (December 2017). "Reference ranges for cardiac structure and function using cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) in Caucasians from the UK Biobank population cohort". Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 19 (1): 18. doi:10.1186/s12968-017-0327-9. PMID 28178995.
- ↑ Babu-Narayan, Sonya V.; Giannakoulas, George; Valente, Anne Marie; Li, Wei; Gatzoulis, Michael A. (14 April 2016). "Imaging of congenital heart disease in adults". European Heart Journal 37 (15): 1182–1195. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehv519. PMID 26424866.
- ↑ Captur, Gabriella; Manisty, Charlotte; Moon, James C (15 September 2016). "Cardiac MRI evaluation of myocardial disease". Heart 102 (18): 1429–1435. doi:10.1136/heartjnl-2015-309077. PMID 27354273. https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/1502457/.
- ↑ Carr, James C.; Carroll, Timothy J. (2016). Magnetic Resonance Angiography: Principles and Applications. Springer New York. ISBN 978-1-4939-4057-8. OCLC 1019592102.[page needed]
- ↑ "Cohesic cardioDI MR". https://cohesic.com/products/cardio-di/cmr.
- ↑ Kim, Soo Jung; Kim, Kyung Ah (2017). "Safety issues and updates under MR environments". European Journal of Radiology 89: 7–13. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.01.010. PMID 28267552.
- ↑ Gulani, Vikas; Calamante, Fernando; Shellock, Frank G; Kanal, Emanuel; Reeder, Scott B (2017). "Gadolinium deposition in the brain: summary of evidence and recommendations". The Lancet Neurology 16 (7): 564–570. doi:10.1016/s1474-4422(17)30158-8. PMID 28653648.
- ↑ "Impact of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging on human lymphocyte DNA integrity". European Heart Journal 34 (30): 2340–5. 2013. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/eht184. PMID 23793096.
- ↑ "Genotoxic effects of 3 T magnetic resonance imaging in cultured human lymphocytes". Bioelectromagnetics 32 (7): 535–42. 2011. doi:10.1002/bem.20664. PMID 21412810.
- ↑ "Is the genotoxic effect of magnetic resonance negligible? Low persistence of micronucleus frequency in lymphocytes of individuals after cardiac scan". Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagenesis 645 (1–2): 39–43. 2008. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2008.08.011. PMID 18804118.
- ↑ Suzuki, Y; Ikehata, M; Nakamura, K; Nishioka, M; Asanuma, K; Koana, T; Shimizu, H (November 2001). "Induction of micronuclei in mice exposed to static magnetic fields.". Mutagenesis 16 (6): 499–501. doi:10.1093/mutage/16.6.499. PMID 11682641.
- ↑ Critchley, William R; Reid, Anna; Morris, Julie; Naish, Josephine H; Stone, John P; Ball, Alexandra L; Major, Triin; Clark, David et al. (21 January 2018). "The effect of 1.5 T cardiac magnetic resonance on human circulating leucocytes". European Heart Journal 39 (4): 305–312. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehx646. PMID 29165554.
- ↑ Hill, Mark A (21 January 2018). "Cardiac MR imaging genotoxicity?". European Heart Journal 39 (4): 313–315. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehx719. PMID 29281062.
- ↑ Nacif, Marcelo Souto; Zavodni, Anna; Kawel, Nadine; Choi, Eui-Young; Lima, João A. C.; Bluemke, David A. (August 2012). "Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging and its electrocardiographs (ECG): tips and tricks". The International Journal of Cardiovascular Imaging 28 (6): 1465–1475. doi:10.1007/s10554-011-9957-4. PMID 22033762.
- ↑ Haaf, Philip; Garg, Pankaj; Messroghli, Daniel R.; Broadbent, David A.; Greenwood, John P.; Plein, Sven (January 2017). "Cardiac T1 Mapping and Extracellular Volume (ECV) in clinical practice: a comprehensive review". Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 18 (1): 89. doi:10.1186/s12968-016-0308-4. PMID 27899132.
- ↑ Kramer, Christopher M; Barkhausen, Jörg; Flamm, Scott D; Kim, Raymond J; Nagel, Eike; Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Board of Trustees Task Force on Standardized, Protocols. (December 2013). "Standardized cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) protocols 2013 update". Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 15 (1): 91. doi:10.1186/1532-429X-15-91. PMID 24103764.
- ↑ Doltra, Adelina; Amundsen, Brage Hoyem; Gebker, Rolf; Fleck, Eckart; Kelle, Sebastian (2013). "Emerging Concepts for Myocardial Late Gadolinium Enhancement MRI". Current Cardiology Reviews 9 (3): 185–190. doi:10.2174/1573403x113099990030. PMID 23909638.
- ↑ Eijgenraam, Tim R.; Silljé, Herman H.W.; de Boer, Rudolf A. (August 2020). "Current understanding of fibrosis in genetic cardiomyopathies". Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine 30 (6): 353–361. doi:10.1016/j.tcm.2019.09.003. PMID 31585768.
- ↑ "Chest pain of recent onset: assessment and diagnosis". 24 March 2010. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg95.
- ↑ Greenwood, John P.; Ripley, David P.; Berry, Colin; McCann, Gerry P.; Plein, Sven; Bucciarelli-Ducci, Chiara; Dall’Armellina, Erica; Prasad, Abhiram et al. (13 September 2016). "Effect of Care Guided by Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, Myocardial Perfusion Scintigraphy, or NICE Guidelines on Subsequent Unnecessary Angiography Rates: The CE-MARC 2 Randomized Clinical Trial". JAMA 316 (10): 1051–1060. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.12680. PMID 27570866.
- ↑ Dyverfeldt, Petter; Bissell, Malenka; Barker, Alex J.; Bolger, Ann F.; Carlhäll, Carl-Johan; Ebbers, Tino; Francios, Christopher J.; Frydrychowicz, Alex et al. (December 2015). "4D flow cardiovascular magnetic resonance consensus statement". Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 17 (1): 72. doi:10.1186/s12968-015-0174-5. PMID 26257141.
- ↑ "Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Equipment, Operations and Planning in the NHS". 2017-04-01. https://www.rcr.ac.uk/sites/default/files/cib_mri_equipment_report.pdf.
- ↑ Ripley, David P.; Brown, Julia M.; Everett, Colin C.; Bijsterveld, Petra; Walker, Simon; Sculpher, Mark; McCann, Gerry P.; Berry, Colin et al. (2015). "Rationale and design of the Clinical Evaluation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Coronary heart disease 2 trial (CE-MARC 2): A prospective, multicenter, randomized trial of diagnostic strategies in suspected coronary heart disease". American Heart Journal 169 (1): 17–24.e1. doi:10.1016/j.ahj.2014.10.008. PMID 25497243.
- ↑ Rajiah, Prabhakar; Bolen, Michael A. (October 2014). "Cardiovascular MR Imaging at 3 T: Opportunities, Challenges, and Solutions". RadioGraphics 34 (6): 1612–1635. doi:10.1148/rg.346140048. PMID 25310420.
- ↑ Niendorf, Thoralf; Sodickson, Daniel K.; Krombach, Gabriele A.; Schulz-Menger, Jeanette (December 2010). "Toward cardiovascular MRI at 7 T: clinical needs, technical solutions and research promises". European Radiology 20 (12): 2806–2816. doi:10.1007/s00330-010-1902-8. PMID 20676653.
- ↑ Hazlewood, C. F.; Chang, D. C.; Nichols, B. L.; Rorschach, H. E. (March 1971). "Interaction of water molecules with macromolecular structures in cardiac muscle". Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology 2 (1): 51–53. doi:10.1016/0022-2828(71)90078-2. PMID 5110317.
- ↑ Tao, Qian; Lelieveldt, Boudewijn P. F.; van der Geest, Rob J. (March 2020). "Deep Learning for Quantitative Cardiac MRI". American Journal of Roentgenology 214 (3): 529–535. doi:10.2214/AJR.19.21927. PMID 31670597.
- ↑ Petersen, S. E.; Almeida, A. G.; Alpendurada, F.; Boubertakh, R.; Bucciarelli-Ducci, C.; Cosyns, B.; Greil, G. F.; Karamitsos, T. D. et al. (1 July 2014). "Update of the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI) Core Syllabus for the European Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Certification Exam". European Heart Journal - Cardiovascular Imaging 15 (7): 728–729. doi:10.1093/ehjci/jeu076. PMID 24855220.
External links
- The Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
- The Journal for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
- An Atlas of normal cardiac structure and function by CMR
- Having a CMR scan
- Cardiac MRI, Technical Aspects Primer at eMedicine
- the basics of MRI
- MRI tutor
 |
Categories: [Cardiac imaging] [Magnetic resonance imaging]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 06/18/2024 21:54:19 | 14 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Physics:Cardiac_magnetic_resonance_imaging | License: CC BY-SA 3.0



 KSF
KSF