Influenza
 From Mdwiki
From Mdwiki
| Influenza | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Flu, the flu, Grippe | |
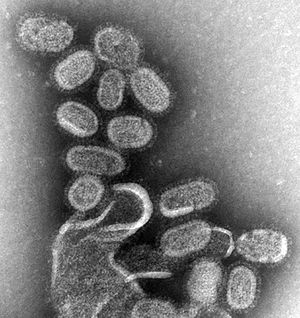 | |
| Influenza virus, magnified approximately 100,000 times | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle and joint pain, headache, coughing, feeling tired[1] |
| Usual onset | 1–4 days after exposure[1] |
| Duration | ~1 week[1] |
| Causes | Influenza viruses[2] |
| Prevention | Hand washing, influenza vaccine, surgical masks[1][3] |
| Medication | Antiviral medications such as oseltamivir[1] |
| Frequency | 3–5 million severe cases per year[1] |
| Deaths | Up to 650,000 respiratory deaths per year[1][4] |
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by an influenza virus.[1] Symptoms can be mild to severe.[5] The most common symptoms include: high fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle and joint pain, headache, coughing, and feeling tired.[1] These symptoms typically begin two days after exposure to the virus and most last less than a week.[1] The cough, however, may last for more than two weeks.[1] In children, there may be diarrhea and vomiting, but these are not common in adults.[6] Diarrhea and vomiting occur more commonly in gastroenteritis, which is an unrelated disease and sometimes inaccurately referred to as "stomach flu" or the "24-hour flu".[6] Complications of influenza may include viral pneumonia, secondary bacterial pneumonia, sinus infections, and worsening of previous health problems such as asthma or heart failure.[2][5]
Three of the four types of influenza viruses affect humans: Type A, Type B, and Type C.[2][7] Type D has not been known to infect humans, but is believed to have the potential to do so.[7][8] Usually, the virus is spread through the air from coughs or sneezes.[1] This is believed to occur mostly over relatively short distances.[9] It can also be spread by touching surfaces contaminated by the virus and then touching the eyes, nose, or mouth.[5][9][10] A person may be infectious to others both before and during the time they are showing symptoms.[5] The infection may be confirmed by testing the throat, sputum, or nose for the virus.[2] A number of rapid tests are available; however, people may still have the infection even if the results are negative.[2] A type of polymerase chain reaction that detects the virus's RNA is more accurate.[2]
Frequent hand washing reduces the risk of viral spread, as does wearing a surgical mask.[3] Yearly vaccinations against influenza are recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) for those at high risk,[1] and by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for those six months of age and older.[11] The vaccine is usually effective against three or four types of influenza.[1] It is usually well tolerated.[1] A vaccine made for one year may not be useful in the following year, since the virus evolves rapidly.[1] Antiviral medications such as the neuraminidase inhibitor oseltamivir, among others, have been used to treat influenza.[1] The benefit of antiviral medications in those who are otherwise healthy do not appear to be greater than their risks.[12] No benefit has been found in those with other health problems.[12][13]
Influenza spreads around the world in yearly outbreaks, resulting in about three to five million cases of severe illness and about 290,000 to 650,000 deaths.[1][4] About 20% of unvaccinated children and 10% of unvaccinated adults are infected each year.[14] In the northern and southern parts of the world, outbreaks occur mainly in the winter, while around the equator, outbreaks may occur at any time of the year.[1] Death occurs mostly in high risk groups—the young, the old, and those with other health problems.[1] Larger outbreaks known as pandemics are less frequent.[2] In the 20th century, three influenza pandemics occurred: Spanish influenza in 1918 (17–100 million deaths), Asian influenza in 1957 (two million deaths), and Hong Kong influenza in 1968 (one million deaths).[15][16][17] The World Health Organization declared an outbreak of a new type of influenza A/H1N1 to be a pandemic in June 2009.[18] Influenza may also affect other animals, including pigs, horses, and birds.[19]
Signs and symptoms[edit | edit source]
| Symptom: | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|
| Fever | 68–86% | 25–73% |
| Cough | 84–98% | 7–29% |
| Nasal congestion | 68–91% | 19–41% |
|
| ||
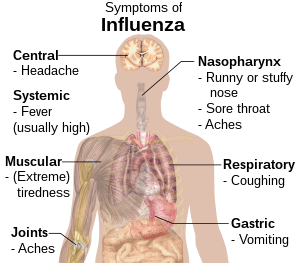
The time between exposure to the virus and development of symptoms, called the incubation period, is 1–4 days, most commonly 1–2 days. Many infections, however, are asymptomatic.[23] The onset of symptoms is sudden, and initial symptoms are predominately non-specific, including fever, chills, headaches, muscle pain or aching, a feeling of discomfort, loss of appetite, lack of energy/fatigue, and confusion. These symptoms are usually accompanied by respiratory symptoms such as a dry cough, sore or dry throat, hoarse voice, and a stuffy or runny nose. Coughing is the most common symptom.[24] Gastrointestinal symptoms may also occur, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea,[25] and gastroenteritis,[26] especially in children. The standard influenza symptoms typically last for 2–8 days.[27] A 2021 study suggests influenza can cause long lasting symptoms in a similar way to long COVID.[28]
Symptomatic infections are usually mild and limited to the upper respiratory tract, but progression to pneumonia is relatively common. Pneumonia may be caused by the primary viral infection or by a secondary bacterial infection. Primary pneumonia is characterized by rapid progression of fever, cough, labored breathing, and low oxygen levels that cause bluish skin. It is especially common among those who have an underlying cardiovascular disease such as rheumatic heart disease. Secondary pneumonia typically has a period of improvement in symptoms for 1–3 weeks[29] followed by recurrent fever, sputum production, and fluid buildup in the lungs,[24] but can also occur just a few days after influenza symptoms appear.[29] About a third of primary pneumonia cases are followed by secondary pneumonia, which is most frequently caused by the bacteria Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus.[23][24]
Virology[edit | edit source]
Types of virus[edit | edit source]
In virus classification, influenza viruses are RNA viruses that make up four of the seven genera of the family Orthomyxoviridae:[30]
These viruses are only distantly related to the human parainfluenza viruses, which are RNA viruses belonging to the paramyxovirus family that are a common cause of respiratory infections in children such as croup,[31] but can also cause a disease similar to influenza in adults.[32]
The fourth family of influenza viruses – Influenza D – was identified in 2016.[33][34][35][36][37][38][39] The type species for this family is Influenza D virus, which was first isolated in 2011.[8]
Influenzavirus A[edit | edit source]
.jpg)
This genus has one species, influenza A virus. Wild aquatic birds are the natural hosts for a large variety of influenza A.[40] Occasionally, viruses are transmitted to other species and may then cause devastating outbreaks in domestic poultry or give rise to human influenza pandemics.[40] The influenza A virus can be subdivided into different serotypes based on the antibody response to these viruses.[41] The serotypes that have been confirmed in humans are:
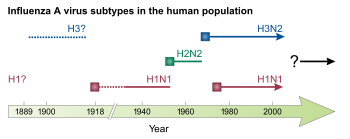
- H1N1, which caused Spanish flu in 1918, and Swine Flu in 2009
- H2N2, which caused Asian Flu in 1957
- H3N2, which caused Hong Kong Flu in 1968
- H5N1, which caused Bird Flu in 2004[42][43]
- H7N7, which has unusual zoonotic potential[44]
- H1N2, endemic in humans, pigs and birds
- H9N2
- H7N2
- H7N3
- H10N7
- H7N9, rated in 2018 as having the greatest pandemic potential among the Type A subtypes[45]
- H6N1, which only infected one person, who recovered[46]
Influenzavirus B[edit | edit source]

This genus has one species, influenza B virus. Influenza B almost exclusively infects humans[41] and is less common than influenza A. The only other animals known to be susceptible to influenza B infection are seals[47] and ferrets.[48] This type of influenza mutates at a rate 2–3 times slower than type A[49] and consequently is less genetically diverse, with only one influenza B serotype.[41] As a result of this lack of antigenic diversity, a degree of immunity to influenza B is usually acquired at an early age. However, influenza B mutates enough that lasting immunity is not possible.[50] This reduced rate of antigenic change, combined with its limited host range (inhibiting cross species antigenic shift), ensures that pandemics of influenza B do not occur.[51]
Influenzavirus C[edit | edit source]
This genus has one species, influenza C virus, which infects humans, dogs and pigs, sometimes causing both severe illness and local epidemics.[52][53] However, influenza C is less common than the other types and usually only causes mild disease in children.[54][55]
Influenzavirus D[edit | edit source]
This genus has only one species, influenza D virus, which infects pigs and cattle. The virus has the potential to infect humans, although no such cases have been observed.[8]
Structure, properties, and subtype nomenclature[edit | edit source]
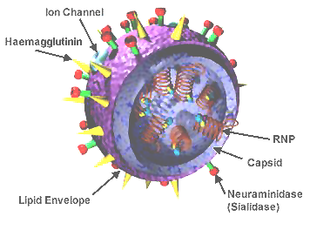
Influenzaviruses A, B, C, and D are very similar in overall structure.[8][56][57] The virus particle (also called the virion) is 80–120 nanometers in diameter such that the smallest virions adopt an elliptical shape.[58] The length of each particle varies considerably, owing to the fact that influenza is pleomorphic, and can be in excess of many tens of micrometers, producing filamentous virions.[59] However, despite these varied shapes, the viral particles of all influenza viruses are similar in composition.[60] These are made of a viral envelope containing the glycoproteins hemagglutinin and neuraminidase wrapped around a central core. The central core contains the viral RNA genome and other viral proteins that package and protect this RNA. RNA tends to be single stranded but in special cases it is double.[61] Unusually for a virus, its genome is not a single piece of nucleic acid; instead, it contains seven or eight pieces of segmented negative-sense RNA, each piece of RNA containing either one or two genes, which code for a gene product (protein).[60] For example, the influenza A genome contains 11 genes on eight pieces of RNA, encoding for 11 proteins: hemagglutinin (HA), neuraminidase (NA), nucleoprotein (NP), M1 (matrix 1 protein), M2, NS1 (non-structural protein 1), NS2 (other name is NEP, nuclear export protein), PA, PB1 (polymerase basic 1), PB1-F2 and PB2.[62]
Hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) are the two large glycoproteins on the outside of the viral particles. HA is a lectin that mediates binding of the virus to target cells and entry of the viral genome into the target cell, while NA is involved in the release of progeny virus from infected cells, by cleaving sugars that bind the mature viral particles.[63] Thus, these proteins are targets for antiviral medications.[64] Furthermore, they are antigens to which antibodies can be raised. Influenza A viruses are classified into subtypes based on antibody responses to HA and NA. These different types of HA and NA form the basis of the H and N distinctions in, for example, H5N1.[65] There are 18 H and 11 N subtypes known, but only H 1, 2 and 3, and N 1 and 2 are commonly found in humans.[66][67]
Replication[edit | edit source]
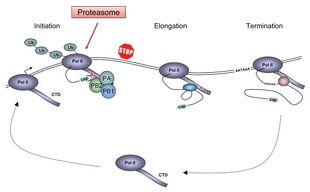
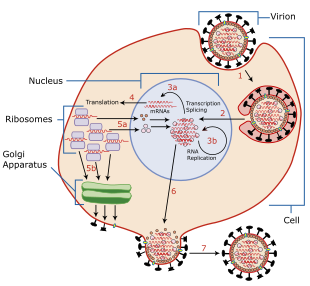
Viruses can replicate only in living cells.[69] Influenza infection and replication is a multi-step process: First, the virus has to bind to and enter the cell, then deliver its genome to a site where it can produce new copies of viral proteins and RNA, assemble these components into new viral particles, and, last, exit the host cell.[60]
Influenza viruses bind through hemagglutinin onto sialic acid sugars on the surfaces of epithelial cells, typically in the nose, throat, and lungs of mammals, and intestines of birds (Stage 1 in infection figure).[70] After the hemagglutinin is cleaved by a protease, the cell imports the virus by endocytosis.[71]
The intracellular details are still being elucidated. It is known that virions converge to the microtubule organizing center, interact with acidic endosomes and finally enter the target endosomes for genome release.[72]
Once inside the cell, the acidic conditions in the endosome cause two events to happen: First, part of the hemagglutinin protein fuses the viral envelope with the vacuole's membrane, then the M2 ion channel allows protons to move through the viral envelope and acidify the core of the virus, which causes the core to disassemble and release the viral RNA and core proteins.[60] The viral RNA (vRNA) molecules, accessory proteins and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase are then released into the cytoplasm (Stage 2).[73] The M2 ion channel is blocked by amantadine drugs, preventing infection.[74]
These core proteins and vRNA form a complex that is transported into the cell nucleus, where the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase begins transcribing complementary positive-sense vRNA (Steps 3a and b).[75] The vRNA either is exported into the cytoplasm and translated (step 4) or remains in the nucleus. Newly synthesized viral proteins are either secreted through the Golgi apparatus onto the cell surface (in the case of neuraminidase and hemagglutinin, step 5b) or transported back into the nucleus to bind vRNA and form new viral genome particles (step 5a). Other viral proteins have multiple actions in the host cell, including degrading cellular mRNA and using the released nucleotides for vRNA synthesis and also inhibiting translation of host-cell mRNAs.[76]
Negative-sense vRNAs that form the genomes of future viruses, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, and other viral proteins are assembled into a virion. Hemagglutinin and neuraminidase molecules cluster into a bulge in the cell membrane. The vRNA and viral core proteins leave the nucleus and enter this membrane protrusion (step 6). The mature virus buds off from the cell in a sphere of host phospholipid membrane, acquiring hemagglutinin and neuraminidase with this membrane coat (step 7).[77] As before, the viruses adhere to the cell through hemagglutinin; the mature viruses detach once their neuraminidase has cleaved sialic acid residues from the host cell.[70] After the release of new influenza viruses, the host cell dies.
Because of the absence of RNA proofreading enzymes, the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase that copies the viral genome makes an error roughly every 10 thousand nucleotides, which is the approximate length of the influenza vRNA. Hence, the majority of newly manufactured influenza viruses are mutants; this causes antigenic drift, which is a slow change in the antigens on the viral surface over time.[78] The separation of the genome into eight separate segments of vRNA allows mixing or reassortment of vRNAs if more than one type of influenza virus infects a single cell. The resulting rapid change in viral genetics produces antigenic shifts, which are sudden changes from one antigen to another. These sudden large changes allow the virus to infect new host species and quickly overcome protective immunity.[65] This is important in the emergence of pandemics, as discussed below in the section on epidemiology. Also, when two or more viruses infect a cell, genetic variation may be generated by homologous recombination.[79][80] Homologous recombination can arise during viral genome replication by the RNA polymerase switching from one template to another, a process known as copy choice.[80]
Mechanism[edit | edit source]
Transmission[edit | edit source]
When an infected person sneezes or coughs more than half a million virus particles can be spread to those close by.[81] In otherwise healthy adults, influenza virus shedding (the time during which a person might be infectious to another person) increases sharply one-half to one day after infection, peaks on day 2 and persists for an average total duration of 5 days—but can persist as long as 9 days.[82] In those who develop symptoms from experimental infection (only 67% of healthy experimentally infected individuals), symptoms and viral shedding show a similar pattern, but with viral shedding preceding illness by one day.[82] Children are much more infectious than adults and shed virus from just before they develop symptoms until two weeks after infection.[83] In immunocompromised people, viral shedding can continue for longer than two weeks.[84]
Influenza can be spread in three main ways:[85][86] by direct transmission (when an infected person sneezes mucus directly into the eyes, nose or mouth of another person); the airborne route (when someone inhales the aerosols produced by an infected person coughing, sneezing or spitting) and through hand-to-eye, hand-to-nose, or hand-to-mouth transmission, either from contaminated surfaces or from direct personal contact such as a handshake. The relative importance of these three modes of transmission is unclear, and they may all contribute to the spread of the virus.[9] In the airborne route, the droplets that are small enough for people to inhale are 0.5 to 5 μm in diameter and inhaling just one droplet might be enough to cause an infection.[85] Although a single sneeze releases up to 40,000 droplets,[87] most of these droplets are quite large and will quickly settle out of the air.[85] How long influenza survives in airborne droplets seems to be influenced by the levels of humidity and UV radiation, with low humidity and a lack of sunlight in winter aiding its survival;[85] ideal conditions can allow it to live for an hour in the atmosphere.[88]
As the influenza virus can persist outside of the body, it can also be transmitted by contaminated surfaces such as banknotes,[89] doorknobs, light switches and other household items.[90] The length of time the virus will persist on a surface varies, with the virus surviving for one to two days on hard, non-porous surfaces such as plastic or metal, for about fifteen minutes on dry paper tissues, and only five minutes on skin.[91] However, if the virus is present in mucus, this can protect it for longer periods (up to 17 days on banknotes).[85][89] Avian influenza viruses can survive indefinitely when frozen.[92] They are inactivated by heating to 56 °C (133 °F) for a minimum of 60 minutes, as well as by acids (at pH <2).[92]
Pathophysiology[edit | edit source]
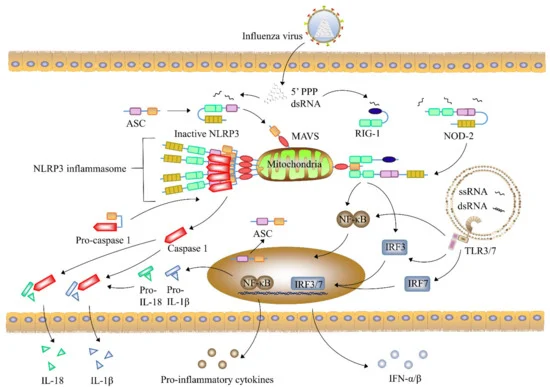
The mechanisms by which influenza infection causes symptoms in humans have been studied intensively. One of the mechanisms is believed to be the inhibition of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) resulting in lowered cortisol levels.[93] Knowing which genes are carried by a particular strain can help predict how well it will infect humans and how severe this infection will be (that is, predict the strain's pathophysiology).[53][94]
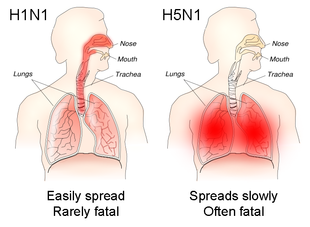
For instance, part of the process that allows influenza viruses to invade cells is the cleavage of the viral hemagglutinin protein by any one of several human proteases.[71] In mild and avirulent viruses, the structure of the hemagglutinin means that it can only be cleaved by proteases found in the throat and lungs, so these viruses cannot infect other tissues. However, in highly virulent strains, such as H5N1, the hemagglutinin can be cleaved by a wide variety of proteases, allowing the virus to spread throughout the body.[94]
The viral hemagglutinin protein is responsible for determining both which species a strain can infect and where in the human respiratory tract a strain of influenza will bind.[96] Strains that are easily transmitted between people have hemagglutinin proteins that bind to receptors in the upper part of the respiratory tract, such as in the nose, throat and mouth. In contrast, the highly lethal H5N1 strain binds to receptors that are mostly found deep in the lungs.[97] This difference in the site of infection may be part of the reason why the H5N1 strain causes severe viral pneumonia in the lungs, but is not easily transmitted by people coughing and sneezing.[98][99]
Common symptoms of the flu such as fever, headaches, and fatigue are the result of the huge amounts of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines (such as interferon or tumor necrosis factor) produced from influenza-infected cells.[100][101] In contrast to the rhinovirus that causes the common cold, influenza does cause tissue damage, so symptoms are not entirely due to the inflammatory response.[102] This massive immune response might produce a life-threatening cytokine storm. This effect has been proposed to be the cause of the unusual lethality of both the H5N1 avian influenza,[103] and the 1918 pandemic strain.[104][105] However, another possibility is that these large amounts of cytokines are just a result of the massive levels of viral replication produced by these strains, and the immune response does not itself contribute to the disease.[106] Influenza appears to trigger programmed cell death (apoptosis).[107]
Prevention[edit | edit source]
Vaccination[edit | edit source]

The influenza vaccine is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) for high-risk groups, such as pregnant women, children aged less than five years, the elderly, health care workers, and people who have chronic illnesses such as HIV/AIDS, asthma, diabetes, heart disease, or are immunocompromised among others.[108][109] The United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends the influenza vaccine for those aged six months or older who do not have contraindications.[110][11] In healthy adults it is modestly effective in decreasing the amount of influenza-like symptoms in a population.[111] In healthy children over the age of two years, the vaccine reduces the chances of getting influenza by around two-thirds, while it has not been well studied in children under two years.[112] In those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease vaccination reduces exacerbations,[113] it is not clear if it reduces asthma exacerbations.[114] Evidence supports a lower rate of influenza-like illness in many groups who are immunocompromised such as those with: HIV/AIDS, cancer, and post organ transplant.[115] In those at high risk immunization may reduce the risk of heart disease.[116] Whether immunizing health care workers affects patient outcomes is controversial with some reviews finding insufficient evidence[117][118] and others finding tentative evidence.[119][120]
Due to the high mutation rate of the virus, a particular influenza vaccine usually confers protection for no more than a few years. Each year, the World Health Organization predicts which strains of the virus are most likely to be circulating in the next year (see Historical annual reformulations of the influenza vaccine), allowing pharmaceutical companies to develop vaccines that will provide the best immunity against these strains.[121] The vaccine is reformulated each season for a few specific flu strains but does not include all the strains active in the world during that season. It takes about six months for the manufacturers to formulate and produce the millions of doses required to deal with the seasonal epidemics; occasionally, a new or overlooked strain becomes prominent during that time.[122] It is also possible to get infected just before vaccination and get sick with the strain that the vaccine is supposed to prevent, as the vaccine takes about two weeks to become effective.[123] Vaccines can cause the immune system to react as if the body were actually being infected, and general infection symptoms (many cold and flu symptoms are just general infection symptoms) can appear, though these symptoms are usually not as severe or long-lasting as influenza. The most dangerous adverse effect is a severe allergic reaction to either the virus material itself or residues from the hen eggs used to grow the influenza; however, these reactions are extremely rare.[124]
A 2018 Cochrane review of children in good general health found that the live immunization seemed to lower the risk of getting influenza for the season from 18% to 4%. The inactivated vaccine seemed to lower the risk of getting flu for the season from 30% to 11%. Not enough data was available to draw definite conclusions about serious complications such as pneumonia or hospitalization.[112]
For healthy adults, a 2018 Cochrane review showed that vaccines reduced the incidence of lab-confirmed influenza from 2.3% to 0.9%, which constitutes a reduction of risk of approximately 60%. However, for influenza-like illness which is defined as the same symptoms of cough, fever, headache, runny nose, and bodily aches and pains, vaccine reduced the risk from 21.5% to 18.1%. This constitutes a much more modest reduction of risk of approximately 16%. The difference is most probably explained by the fact that over 200 viruses cause the same or similar symptoms as the flu virus.[111] Another review looked at the effect of short and long term exercise before the vaccine, however, no benefits or harms were recorded.[125]
The cost-effectiveness of seasonal influenza vaccination has been widely evaluated for different groups and in different settings.[126] It has generally been found to be a cost-effective intervention, especially in children[127] and the elderly,[128] however the results of economic evaluations of influenza vaccination have often been found to be dependent on key assumptions.[129][130]
Infection control[edit | edit source]
These are the main ways that influenza spreads
- by direct transmission (when an infected person sneezes mucus directly into the eyes, nose or mouth of another person);
- the airborne route (when someone inhales the aerosols produced by an infected person coughing, sneezing or spitting);
- through hand-to-eye, hand-to-nose, or hand-to-mouth transmission, either from contaminated surfaces or from direct personal contact such as a hand-shake.
When vaccines and antiviral medications are limited, non-pharmaceutical interventions are essential to reduce transmission and spread. The lack of controlled studies and rigorous evidence of the effectiveness of some measures has hampered planning decisions and recommendations. Nevertheless, strategies endorsed by experts for all phases of flu outbreaks include hand and respiratory hygiene, self-isolation by symptomatic individuals and the use of face masks by them and their caregivers, surface disinfection, rapid testing and diagnosis, and contact tracing. In some cases, other forms of social distancing including school closures and travel restrictions are recommended.[131]
Reasonably effective ways to reduce the transmission of influenza include good personal health and hygiene habits such as: not touching the eyes, nose or mouth;[132] frequent hand washing (with soap and water, or with alcohol-based hand rubs);[133] covering coughs and sneezes with a tissue or sleeve; avoiding close contact with sick people; and staying home when sick. Avoiding spitting is also recommended.[131] Although face masks might help prevent transmission when caring for the sick,[134][135] there is mixed evidence on beneficial effects in the community.[131][136] Smoking raises the risk of contracting influenza, as well as producing more severe disease symptoms.[137][138]
Since influenza spreads through both aerosols and contact with contaminated surfaces, surface sanitizing may help prevent some infections.[139] Alcohol is an effective sanitizer against influenza viruses, while quaternary ammonium compounds can be used with alcohol so that the sanitizing effect lasts for longer.[140] In hospitals, quaternary ammonium compounds and bleach are used to sanitize rooms or equipment that have been occupied by people with influenza symptoms.[140] At home, this can be done effectively with a diluted chlorine bleach.[141]
Social distancing strategies used during past pandemics, such as quarantines, travel restrictions, and the closing of schools, churches and theaters, have been employed to slow the spread of influenza viruses. Researchers have estimated that such interventions during the 1918 Spanish flu pandemic in the US reduced the peak death rate by up to 50%, and the overall mortality by about 10–30%, in areas where multiple interventions were implemented. The more moderate effect on total deaths was attributed to the measures being employed too late, or lifted too early, most after six weeks or less.[142][143]
For typical flu outbreaks, routine cancellation of large gatherings or mandatory travel restrictions have received little agreement, particularly as they may be disruptive and unpopular. School closures have been found by most empirical studies to reduce community spread, but some findings have been contradictory. Recommendations for these community restrictions are usually on a case-by-case basis.[131]
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
There are a number of rapid tests for the flu. One is called a Rapid Molecular Assay, when an upper respiratory tract specimen (mucus) is taken using a nasal swab or a nasopharyngeal swab.[144] It should be done within 3–4 days of symptom onset, as upper respiratory viral shedding takes a downward spiral after that.[145]
Treatment[edit | edit source]
People with the flu are advised to get plenty of rest, drink plenty of liquids, avoid using alcohol and tobacco and, if necessary, take medications such as acetaminophen (paracetamol) to relieve the fever and muscle aches associated with the flu.[146][147] In contrast, there is not enough evidence to support corticosteroids as additional therapy for influenza.[148] It is advised to avoid close contact with others to prevent spread of infection.[146][147] Children and teenagers with flu symptoms (particularly fever) should avoid taking aspirin during an influenza infection (especially influenza type B), because doing so can lead to Reye's syndrome, a rare but potentially fatal disease of the liver.[149] Since influenza is caused by a virus, antibiotics have no effect on the infection; unless prescribed for secondary infections such as bacterial pneumonia. Antiviral medication may be effective, if given early (within 48 hours to first symptoms), but some strains of influenza can show resistance to the standard antiviral medications and there is concern about the quality of the research.[150] High-risk individuals such as young children, pregnant women, the elderly, and those with compromised immune systems should visit the doctor for antiviral medications. Those with the emergency warning signs should visit the emergency room at once.[151]
Antivirals[edit | edit source]
| Drug | Route of administration | Approved age of use |
|---|---|---|
| Oseltamivir | By mouth | At least two weeks old |
| Zanamivir | Inhalation | At least five years old |
| Peramivir | Intravenous | At least 18 years old |
| Laninamivir | Inhalation[24] | 40 milligrams (mg) dose for people at least 10 years old, 20 mg for those under 10[152] |
| Baloxavir marboxil | By mouth[153] | At least 12 years old[154] |
The two classes of antiviral medications used against influenza are neuraminidase inhibitors (oseltamivir, zanamivir, laninamivir and peramivir) and M2 protein inhibitors (adamantane derivatives).[155][156][157] In Russia, umifenovir is sold for treatment of influenza[158] and in the first quarter of 2020 had a 16 percent share in the antiviral market.[159]
Neuraminidase inhibitors[edit | edit source]
Overall the benefits of neuraminidase inhibitors in those who are otherwise healthy do not appear to be greater than the risks.[12] There does not appear to be any benefit in those with other health problems.[12] In those believed to have the flu, they decreased the length of time symptoms were present by slightly less than a day but did not appear to affect the risk of complications such as needing hospitalization or pneumonia.[13] Increasingly prevalent resistance to neuraminidase inhibitors has led researchers to seek alternative antiviral medications with different mechanisms of action.[160]
M2 inhibitors[edit | edit source]
The antiviral medications amantadine and rimantadine inhibit a viral ion channel (M2 protein), thus inhibiting replication of the influenza A virus.[74] These medications are sometimes effective against influenza A if given early in the infection but are ineffective against influenza B viruses, which lack the M2 drug target.[161] Measured resistance to amantadine and rimantadine in American isolates of H3N2 has increased to 91% in 2005.[162] This high level of resistance may be due to the easy availability of amantadines as part of over-the-counter cold remedies in countries such as China and Russia,[163] and their use to prevent outbreaks of influenza in farmed poultry.[164][165] The CDC recommended against using M2 inhibitors during the 2005–06 influenza season due to high levels of drug resistance.[166]
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
Influenza's effects are much more severe and last longer than those of the common cold. Most people will recover completely in about one to two weeks, but others will develop life-threatening complications (such as pneumonia). Thus, influenza can be deadly, especially for the weak, young and old, those with compromised immune systems, or the chronically ill.[65] People with a weak immune system, such as people with advanced HIV infection or transplant recipients (whose immune systems are medically suppressed to prevent transplant organ rejection), suffer from particularly severe disease.[167] Pregnant women and young children are also at a high risk for complications.[168]
The flu can worsen chronic health problems. People with emphysema, chronic bronchitis or asthma may experience shortness of breath while they have the flu, and influenza may cause worsening of coronary heart disease or congestive heart failure.[169] Smoking is another risk factor associated with more serious disease and increased mortality from influenza.[137]
Even healthy people can be affected, and serious problems from influenza can happen at any age. People over 65 years old, pregnant women, very young children and people of any age with chronic medical conditions are more likely to get complications from influenza, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, sinus, and ear infections.[170]
Neurological[edit | edit source]
In some cases, an autoimmune response to an influenza infection may contribute to the development of Guillain–Barré syndrome.[171] However, as many other infections can increase the risk of this disease, influenza may only be an important cause during epidemics.[171][172] This syndrome has been believed to also be a rare side effect of influenza vaccines. One review gives an incidence of about one case per million vaccinations.[173] Getting infected by influenza itself increases both the risk of death (up to 1 in 10,000) and increases the risk of developing GBS to a much higher level than the highest level of suspected vaccine involvement (approx. 10 times higher by recent estimates).[171][174]
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), "Children of any age with neurologic conditions are more likely than other children to become very sick if they get the flu. Flu complications may vary and for some children, can include pneumonia and even death."[175]
Neurological conditions can include:
- Disorders of the brain and spinal cord
- Cerebral palsy
- Epilepsy (seizure disorders)
- Stroke
- Intellectual disability
- Moderate to severe developmental delay
- Muscular dystrophy
- Spinal cord injury
These conditions can impair coughing, swallowing, clearing the airways, and in the worst cases, breathing. Therefore, they worsen the flu symptoms.[175]
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
Seasonal variations[edit | edit source]
Influenza reaches peak prevalence in winter, and because the Northern and Southern Hemispheres have winter at different times of the year, there are actually two different flu seasons each year. This is why the World Health Organization (assisted by the National Influenza Centers) makes recommendations for two different vaccine formulations every year; one for the Northern, and one for the Southern Hemisphere.[121]
A long-standing puzzle has been why outbreaks of the flu occur seasonally rather than uniformly throughout the year. One possible explanation is that, because people are indoors more often during the winter, they are in close contact more often, and this promotes transmission from person to person. Increased travel due to the Northern Hemisphere winter holiday season may also play a role.[176] Another factor is that cold temperatures lead to drier air, which may dehydrate mucus particles. Dry particles are lighter and can thus remain airborne for a longer period. The virus also survives longer on surfaces at colder temperatures and aerosol transmission of the virus is highest in cold environments (less than 5 °C) with low relative humidity.[177] The lower air humidity in winter seems to be the main cause of seasonal influenza transmission in temperate regions.[178][179]
However, seasonal changes in infection rates also occur in tropical regions, and in some countries these peaks of infection are seen mainly during the rainy season.[180] Seasonal changes in contact rates from school terms, which are a major factor in other childhood diseases such as measles and pertussis, may also play a role in the flu. A combination of these small seasonal effects may be amplified by dynamical resonance with the endogenous disease cycles.[181] H5N1 exhibits seasonality in both humans and birds.[182][183]
An alternative hypothesis to explain seasonality in influenza infections is an effect of vitamin D levels on immunity to the virus.[184] This idea was first proposed by Robert Edgar Hope-Simpson in 1981.[185] He proposed that the cause of influenza epidemics during winter may be connected to seasonal fluctuations of vitamin D, which is produced in the skin under the influence of solar (or artificial) UV radiation. This could explain why influenza occurs mostly in winter and during the tropical rainy season, when people stay indoors, away from the sun, and their vitamin D levels fall.
Mortality[edit | edit source]
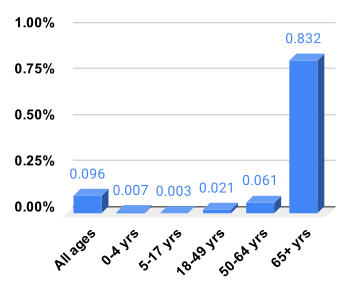
Every year about 290,000 to 650,000 people die due to influenza globally, with an average of 389,000.[187] In the developed world most of those who die are over the age of 65.[1] In the developing world the effects are less clear; however, it appears that children are affected to a greater degree.[1]
Although the number of cases of influenza can vary widely between years, approximately 36,000 deaths and more than 200,000 hospitalizations are directly associated with influenza a year in the United States.[188][189] One method of calculating influenza mortality produced an estimate of 41,400 average deaths per year in the United States between 1979 and 2001.[190] Different methods in 2010 by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported a range from a low of about 3,300 deaths to a high of 49,000 per year.[191]
Outbreaks[edit | edit source]
As influenza is caused by a variety of species and strains of viruses, in any given year some strains can die out while others create epidemics, while yet another strain can cause a pandemic. Typically, in a year's normal two flu seasons (one per hemisphere), there are between three and five million cases of severe illness,[1][4][192] which by some definitions is a yearly influenza epidemic.[1]
Roughly three times per century, a pandemic occurs, which infects a large proportion of the world's population and can kill tens of millions of people (see pandemics section). In 2006, a study estimated that if a strain with similar virulence to the 1918 influenza had emerged that year, it could have killed between 50 and 80 million people.[193]
New influenza viruses are constantly evolving by mutation or by reassortment.[41] Mutations can cause small changes in the hemagglutinin and neuraminidase antigens on the surface of the virus. This is called antigenic drift, which slowly creates an increasing variety of strains until one evolves that can infect people who are immune to the pre-existing strains. This new variant then replaces the older strains as it rapidly sweeps through the human population, often causing an epidemic.[194] However, since the strains produced by drift will still be reasonably similar to the older strains, some people will still be immune to them. In contrast, when influenza viruses reassort, they acquire completely new antigens—for example by reassortment between avian strains and human strains; this is called antigenic shift. If a human influenza virus is produced that has entirely new antigens, everybody will be susceptible, and the novel influenza will spread uncontrollably, causing a pandemic.[195] In contrast to this model of pandemics based on antigenic drift and shift, an alternative approach has been proposed where the periodic pandemics are produced by interactions of a fixed set of viral strains with a human population with a constantly changing set of immunities to different viral strains.[196]
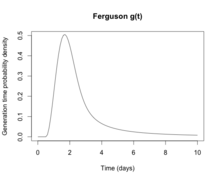
From a public health point of view, flu epidemics spread rapidly and are very difficult to control. Most influenza virus strains are not very infectious and each infected individual will only go on to infect one or two other individuals (the basic reproduction number for influenza is generally around 1.4). However, the generation time for influenza is extremely short: the time from a person becoming infected to when he infects the next person is only two days. The short generation time means that influenza epidemics generally peak at around 2 months and burn out after 3 months: the decision to intervene in an influenza epidemic, therefore, has to be taken early, and the decision is therefore often made on the back of incomplete data. Another problem is that individuals become infectious before they become symptomatic, which means that putting people in quarantine after they become ill is not an effective public health intervention.[197] For the average person, viral shedding tends to peak on day two, whereas symptoms peak on day three.[82]
History[edit | edit source]
Etymology[edit | edit source]
The word Influenza comes from the Italian language meaning "influence" and refers to the cause of the disease; initially, this ascribed illness to unfavorable astrological influences. It was introduced into English in the mid-eighteenth century during a pan-European epidemic.[198] Archaic terms for influenza include epidemic catarrh, la grippe (from the French, first used by Molyneaux in 1694; also used in German),[199] sweating sickness, and Spanish fever (particularly for the 1918 flu pandemic strain).[200]
Pandemics[edit | edit source]

An overall lack of data up until 1500 precludes meaningful search for the influenza outbreaks in the more distant past.[202] Possibly the first influenza pandemic occurred around 6000 BC in China.[202] The symptoms of human influenza were clearly described by Hippocrates roughly 2,400 years ago.[203][204] Although the virus seems to have caused epidemics throughout human history, historical data on influenza are difficult to interpret, because the symptoms can be similar to those of other respiratory diseases.[199][205] The disease may have spread from Europe to the Americas as early as the European colonization of the Americas, since almost the entire indigenous population of the Antilles was killed by an epidemic resembling influenza that broke out in 1493, after the arrival of Christopher Columbus.[206][207]
The first convincing record of an influenza pandemic was a minor pandemic chronicled in 1510, which began in East Asia before spreading to North Africa and then Europe. During this pandemic, influenza killed about 1% of its victims.[208][209] The first pandemic of influenza to be reliably recorded as spreading worldwide was the 1557 influenza pandemic,[210][211][212][213] in which a reoccurring wave likely killed Queen Mary I of England and the Archbishop of Canterbury within 12 hours of each other.[214][215] One of the most well-chronicled pandemics of influenza in the 16th Century occurred in 1580, beginning in East Asia and spreading to Europe through Africa, Russia, and the Spanish and Ottoman Empires. In Rome, over 8,000 people were killed. Several Spanish cities saw large scale deaths, among the fatalities the Queen of Spain, Anna of Austria. Pandemics continued sporadically throughout the 17th and 18th centuries, with the pandemic of 1830–1833 being particularly widespread; it infected approximately a quarter of the people exposed.[199]
The most famous and lethal outbreak was the 1918 flu pandemic (Spanish flu) (type A influenza, H1N1 subtype), which lasted into 1920. It is not known exactly how many it killed, but estimates range from 17 million to 100 million people.[15][201][216][217] This pandemic has been described as "the greatest medical holocaust in history" and may have killed as many people as the Black Death.[199] This huge death toll was caused by an extremely high infection rate of up to 50% and the extreme severity of the symptoms, suspected to be caused by cytokine storms.[217] Symptoms in 1918 were so unusual that initially influenza was misdiagnosed as dengue, cholera, or typhoid. One observer wrote, "One of the most striking of the complications was hemorrhage from mucous membranes, especially from the nose, stomach, and intestine. Bleeding from the ears and petechial hemorrhages in the skin also occurred."[216] The majority of deaths were from bacterial pneumonia, a secondary infection caused by influenza, but the virus also killed people directly, causing massive hemorrhages and edema in the lung.[218]
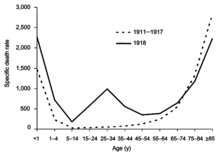
The 1918 flu pandemic was truly global, spreading even to the Arctic and remote Pacific islands. The unusually severe disease killed between two and twenty percent of those infected, as opposed to the more usual flu epidemic mortality rate of 0.1%.[201][216] Another unusual feature of this pandemic was that it mostly killed young adults, with 99% of pandemic influenza deaths occurring in people under 65, and more than half in young adults 20 to 40 years old.[219] This is unusual since influenza is normally most deadly to the very young (under age 2) and the very old (over age 70). The total mortality of the 1918–1919 pandemic is not known, but it is estimated that 2.5% to 5% of the world's population was killed. As many as 25 million may have been killed in the first 25 weeks; in contrast, HIV/AIDS has killed 25 million in its first 25 years.[216]
Later flu pandemics were not so devastating. They included the 1957 Asian flu (type A, H2N2 strain) and the 1968 Hong Kong flu (type A, H3N2 strain), but even these smaller outbreaks killed millions of people. In later pandemics antibiotics were available to control secondary infections and this may have helped reduce mortality compared to the Spanish flu of 1918.[201]
| Name | Date | World pop. | Subtype | Reproduction number | Infected (est.) | Deaths worldwide | Case fatality rate | Pandemic severity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1889–90 flu pandemic[222] | 1889–90 | 1.53 billion | Likely H3N8 or H2N2 | 2.10 (IQR, 1.9–2.4)[222] | 20–60%[222] (300–900 million) | 1 million[223] | 0.10–0.28%[222] | 2 |
| 1918 flu[224] | 1918–20 | 1.80 billion | H1N1 | 1.80 (IQR, 1.47–2.27)[225] | 33% (500 million)[226] or >56% (>1 billion)[227] | 17[228]–100[229][230] million | 2–3%,[227] or ~4%, or ~10%[231] | 5 |
| Asian flu[232] | 1957–58 | 2.90 billion | H2N2 | 1.65 (IQR, 1.53–1.70)[225] | >17% (>500 million)[227] | 1–4 million[227] | <0.2%[227] | 2 |
| Hong Kong flu[233] | 1968–69 | 3.53 billion | H3N2 | 1.80 (IQR, 1.56–1.85)[225] | >14% (>500 million)[227] | 1–4 million[227] | <0.1%[227][234] | 2 |
| 2009 flu pandemic[235][236] | 2009–10 | 6.85 billion | H1N1/09 | 1.46 (IQR, 1.30–1.70)[225] | 11–21% (0.7–1.4 billion)[237] | 151,700–575,400[238] | 0.01%[239][240] | 1 |
| Typical seasonal flu[t 1] | Every year | 7.75 billion | A/H3N2, A/H1N1, B, ... | 1.28 (IQR, 1.19–1.37)[225] | 5–15% (340 million – 1 billion)[241] 3–11% or 5–20%[242][243] (240 million – 1.6 billion) |
290,000–650,000/year[244] | <0.1%[245] | 1 |
Notes
| ||||||||
It was incorrectly assumed that the cause of influenza was bacterial in origin from 1892 (with Haemophilus influenzae being discovered by and suggested as the origin of influenza by R. F. J. Pfeiffer).[246] The first influenza virus to be isolated was from poultry, when in 1901, the agent causing a disease called "fowl plague" was passed through Chamberland filters, which have pores that are too small for bacteria to pass through.[247] However, the conceptual differences between viruses and bacteria as different entities was not fully understood for some time, complicating preventative measures taken during the 1918 influenza pandemic.[246] The etiological cause of influenza, the virus family Orthomyxoviridae, was first discovered in pigs by Richard Shope in 1931.[248] This discovery was shortly followed by the isolation of the virus from humans by a group headed by Patrick Laidlaw at the Medical Research Council of the United Kingdom in 1933.[249] However, it was not until Wendell Stanley first crystallized tobacco mosaic virus in 1935 that the non-cellular nature of viruses was appreciated.
The first significant step towards preventing influenza was the development in 1944 of a killed-virus vaccine for influenza by Thomas Francis, Jr. This built on work by Australian Frank Macfarlane Burnet, who showed that the virus lost virulence when it was cultured in fertilized hen's eggs.[251] Application of this observation by Francis allowed his group of researchers at the University of Michigan to develop the first influenza vaccine, with support from the U.S. Army.[252] The Army was deeply involved in this research due to its experience of influenza in World War I, when thousands of troops were killed by the virus in a matter of months.[216] In comparison to vaccines, the development of anti-influenza drugs has been slower, with amantadine being licensed in 1966 and, almost thirty years later, the next class of drugs (the neuraminidase inhibitors) being developed.[253]
Society and culture[edit | edit source]
Influenza produces direct costs due to lost productivity and associated medical treatment, as well as indirect costs of preventive measures. In the United States, seasonal influenza is estimated to result in a total average annual economic cost of over $11 billion, with direct medical costs estimated to be over $3 billion annually.[254] It has been estimated that a future pandemic could cause hundreds of billions of dollars in direct and indirect costs.[255] However, the economic impacts of past pandemics have not been intensively studied, and some authors have suggested that the Spanish influenza actually had a positive long-term effect on per-capita income growth, despite a large reduction in the working population and severe short-term depressive effects.[256] Other studies have attempted to predict the costs of a pandemic as serious as the 1918 Spanish flu on the U.S. economy, where 30% of all workers became ill, and 2.5% were killed. A 30% sickness rate and a three-week length of illness would decrease the gross domestic product by 5%. Additional costs would come from medical treatment of 18 million to 45 million people, and total economic costs would be approximately $700 billion.[257]
Preventive costs are also high. Governments worldwide have spent billions of U.S. dollars preparing and planning for a potential H5N1 avian influenza pandemic, with costs associated with purchasing drugs and vaccines as well as developing disaster drills and strategies for improved border controls.[258] On 1 November 2005, United States President George W. Bush unveiled the National Strategy to Safeguard Against the Danger of Pandemic Influenza[255] backed by a request to Congress for $7.1 billion to begin implementing the plan.[259] Internationally, on 18 January 2006, donor nations pledged US$2 billion to combat bird flu at the two-day International Pledging Conference on Avian and Human Influenza held in China.[260][261]
In an assessment of the 2009 H1N1 pandemic on selected countries in the Southern Hemisphere, data suggest that all countries experienced some time-limited and/or geographically isolated socioeconomic effects and a temporary decrease in tourism most likely due to fear of 2009 H1N1 disease. It is still too early to determine whether the H1N1 pandemic has had any long-term economic effects.[262][needs update]
Research[edit | edit source]
Research on influenza includes studies on molecular virology, how the virus produces disease (pathogenesis), host immune responses, viral genomics, and how the virus spreads (epidemiology). These studies help in developing influenza countermeasures; for example, a better understanding of the body's immune system response helps vaccine development, and a detailed picture of how influenza invades cells aids the development of antiviral drugs. One important basic research program is the Influenza Genome Sequencing Project, which was initiated in 2004 to create a library of influenza sequences and help clarify which factors make one strain more lethal than another, which genes most affect immunogenicity, and how the virus evolves over time.[263]
The sequencing of the influenza genome and recombinant DNA technology may accelerate the generation of new vaccine strains by allowing scientists to substitute new antigens into a previously developed vaccine strain.[264] Growing viruses in cell culture also promises higher yields, less cost, better quality and surge capacity.[265] Research on a universal influenza A vaccine, targeted against the external domain of the transmembrane viral M2 protein (M2e), is being done at the University of Ghent by Walter Fiers, Xavier Saelens and their team[266][267][268] and has now successfully concluded Phase I clinical trials. There has been some research success towards a "universal flu vaccine" that produces antibodies against proteins on the viral coat which mutate less rapidly, and thus a single shot could potentially provide longer-lasting protection.[269][270][271]
A number of biologics, therapeutic vaccines and immunobiologics are also being investigated for treatment of infection caused by viruses. Therapeutic biologics are designed to activate the immune response to virus or antigens. Typically, biologics do not target metabolic pathways like anti-viral drugs, but stimulate immune cells such as lymphocytes, macrophages, and/or antigen-presenting cells, in an effort to drive an immune response towards a cytotoxic effect against the virus. Influenza models, such as murine influenza, are convenient models to test the effects of prophylactic and therapeutic biologics. For example, lymphocyte T-cell immunomodulator inhibits viral growth in the murine model of influenza.[272]
-
Dr. Terrence Tumpey examining a laboratory-grown reconstruction of the 1918 Spanish flu virus in a biosafety level 3 environment.
Other animals[edit | edit source]
 |
Influenza infects many animal species, and transfer of viral strains between species can occur. Birds are thought to be the main animal reservoirs of influenza viruses.[276] Most influenza strains are believed to have originated after humans began their intensive domestication of animals about 10,000 years ago.[277] Sixteen forms of hemagglutinin and nine forms of neuraminidase have been identified. All known subtypes (HxNy) are found in birds, but many subtypes are endemic in humans, dogs, horses, and pigs; populations of camels, ferrets, cats, seals, mink, and whales also show evidence of prior infection or exposure to influenza.[50] Variants of flu virus are sometimes named according to the species the strain is endemic in or adapted to. The main variants named using this convention are: bird flu, human flu, swine flu, horse flu and dog flu. (Cat flu generally refers to feline viral rhinotracheitis or feline calicivirus and not infection from an influenza virus.) In pigs, horses and dogs, influenza symptoms are similar to humans, with cough, fever and loss of appetite.[50] The frequency of animal diseases are not as well-studied as human infection, but an outbreak of influenza in harbor seals caused approximately 500 seal deaths off the New England coast in 1979–1980.[278] However, outbreaks in pigs are common and do not cause severe mortality.[50] Vaccines have also been developed to protect poultry from avian influenza. These vaccines can be effective against multiple strains and are used either as part of a preventive strategy, or combined with culling in attempts to eradicate outbreaks.[279]
Bird flu[edit | edit source]
Flu symptoms in birds are variable and can be unspecific.[280] The symptoms following infection with low-pathogenicity avian influenza may be as mild as ruffled feathers, a small reduction in egg production, or weight loss combined with minor respiratory disease.[281] Since these mild symptoms can make diagnosis in the field difficult, tracking the spread of avian influenza requires laboratory testing of samples from infected birds. Some strains such as Asian H9N2 are highly virulent to poultry and may cause more extreme symptoms and significant mortality.[282] In its most highly pathogenic form, influenza in chickens and turkeys produces a sudden appearance of severe symptoms and almost 100% mortality within two days.[283] As the virus spreads rapidly in the crowded conditions seen in the intensive farming of chickens and turkeys, these outbreaks can cause large economic losses to poultry farmers.[citation needed]
An avian-adapted, highly pathogenic strain of H5N1 (called HPAI A(H5N1), for "highly pathogenic avian influenza virus of type A of subtype H5N1") causes H5N1 flu, commonly known as "avian influenza" or simply "bird flu", and is endemic in many bird populations, especially in Southeast Asia. This Asian lineage strain of HPAI A(H5N1) is spreading globally. It is epizootic (an epidemic in non-humans) and panzootic (a disease affecting animals of many species, especially over a wide area), killing tens of millions of birds and spurring the culling of hundreds of millions of other birds in an attempt to control its spread. Most references in the media to "bird flu" and most references to H5N1 are about this specific strain.[284][285]
HPAI A(H5N1) is an avian disease and there is no evidence suggesting efficient human-to-human transmission of HPAI A(H5N1). In almost all cases, those infected have had extensive physical contact with infected birds.[286] H5N1 may mutate or reassort into a strain capable of efficient human-to-human transmission. The exact changes that are required for this to happen are not well understood.[287] Due to the high lethality and virulence of H5N1, its endemic presence, and its large and increasing biological host reservoir, the H5N1 virus was the world's major pandemic threat in the 2006–07 flu season, and billions of dollars are being raised and spent researching H5N1 and preparing for a potential influenza pandemic.[258]

In March 2013, the Chinese government reported three cases of H7N9 influenza infections in humans, two of whom had died and the third became critically ill. Although the strain of the virus is not thought to spread efficiently between humans,[288][289] by mid-April, at least 82 persons had become ill from H7N9, of which 17 had died. These cases include three small family clusters in Shanghai and one cluster between a neighboring girl and boy in Beijing, raising at least the possibility of human-to-human transmission. The WHO points out that one cluster did not have two of the cases lab confirmed and further points out, as a matter of baseline information, that some viruses are able to cause limited human-to-human transmission under conditions of close contact but are not transmissible enough to cause large community outbreaks.[290][291][292]
Swine flu[edit | edit source]
In pigs swine influenza produces fever, lethargy, sneezing, coughing, difficulty breathing and decreased appetite.[293] In some cases the infection can cause abortion. Although mortality is usually low, the virus can produce weight loss and poor growth, causing economic loss to farmers.[293] Infected pigs can lose up to 12 pounds of body weight over a three- to four-week period.[293] Direct transmission of an influenza virus from pigs to humans is occasionally possible (this is called zoonotic swine flu). In all, 50 human cases are known to have occurred since the virus was identified in the mid-20th century, which have resulted in six deaths.[294]
In 2009, a swine-origin H1N1 virus strain commonly referred to as "swine flu" caused the 2009 flu pandemic, but there is no evidence that it is endemic to pigs (i.e. actually a swine flu) or of transmission from pigs to people; instead, the virus spreads from person to person.[295][296] This strain is a reassortment of several strains of H1N1 that are usually found separately, in humans, birds, and pigs.[297]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 1.22 1.23 "Influenza (Seasonal)". World Health Organization (WHO). 6 November 2018. Archived from the original on 30 November 2019. Retrieved 30 November 2019.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Longo, Dan L. (2012). "Chapter 187: Influenza". Harrison's principles of internal medicine (18th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-174889-6.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Jefferson T, Del Mar CB, Dooley L, Ferroni E, Al-Ansary LA, Bawazeer GA, et al. (July 2011). "Physical interventions to interrupt or reduce the spread of respiratory viruses" (PDF). Cochrane Database Syst Rev (7): CD006207. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006207.pub4. PMC 6993921. PMID 21735402. Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "Up to 650 000 people die of respiratory diseases linked to seasonal flu each year". World Health Organization (WHO) (Press release). 14 December 2017. Archived from the original on 18 April 2019. Retrieved 24 September 2019.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 "Key Facts About Influenza (Flu)". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 9 September 2014. Archived from the original on 2 December 2014. Retrieved 26 November 2014.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Duben-Engelkirk, Paul G.; Engelkirk, Janet (2011). Burton's microbiology for the health sciences (9th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 314. ISBN 978-1-60547-673-5. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Types of Influenza Viruses Seasonal Influenza (Flu)". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 27 September 2017. Archived from the original on 21 January 2017. Retrieved 28 September 2018.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 Su S, Fu X, Li G, Kerlin F, Veit M (25 August 2017). "Novel Influenza D virus: Epidemiology, pathology, evolution and biological characteristics". Virulence. 8 (8): 1580–91. doi:10.1080/21505594.2017.1365216. PMC 5810478. PMID 28812422.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Brankston G, Gitterman L, Hirji Z, Lemieux C, Gardam M (April 2007). "Transmission of influenza A in human beings". Lancet Infect Dis. 7 (4): 257–65. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(07)70029-4. PMID 17376383.
- ↑ "Influenza in children". Paediatr Child Health. 10 (8): 485–7. October 2005. doi:10.1093/pch/10.8.485. PMC 2722601. PMID 19668662.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Grohskopf LA, Alyanak E, Broder KR, Walter EB, Fry AM, Jernigan DB (2019). "Prevention and Control of Seasonal Influenza with Vaccines: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices – United States, 2019–20 Influenza Season" (PDF). MMWR Recomm Rep. 68 (3): 1–21. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr6803a1. PMC 6713402. PMID 31441906. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 December 2020. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 Michiels B, Van Puyenbroeck K, Verhoeven V, Vermeire E, Coenen S (2013). "The value of neuraminidase inhibitors for the prevention and treatment of seasonal influenza: a systematic review of systematic reviews". PLOS One. 8 (4): e60348. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...860348M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0060348. PMC 3614893. PMID 23565231.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Ebell MH, Call M, Shinholser J (April 2013). "Effectiveness of oseltamivir in adults: a meta-analysis of published and unpublished clinical trials". Family Practice. 30 (2): 125–33. doi:10.1093/fampra/cms059. PMID 22997224.
- ↑ Somes MP, Turner RM, Dwyer LJ, Newall AT (May 2018). "Estimating the annual attack rate of seasonal influenza among unvaccinated individuals: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Vaccine. 36 (23): 3199–207. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.04.063. PMID 29716771.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Spreeuwenberg P, Kroneman M, Paget J (December 2018). "Reassessing the Global Mortality Burden of the 1918 Influenza Pandemic". American Journal of Epidemiology. 187 (12): 2561–67. doi:10.1093/aje/kwy191. PMID 30202996.
- ↑ World Health Organization (December 2005). "Ten things you need to know about pandemic influenza (update of 14 October 2005)". Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 80 (49–50): 428–31. hdl:10665/232955. PMID 16372665.
- ↑ Jilani TN, Jamil RT, Siddiqui AH (January 2020). "H1N1 Influenza (Swine Flu)". StatPearls. PMID 30020613.
- ↑ Chan, Margaret (11 June 2009). "World now at the start of 2009 influenza pandemic". World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 12 June 2009. Retrieved 12 June 2009.
- ↑ Palmer SR (2011). Oxford textbook of zoonoses : biology, clinical practice, and public health control (2. ed.). Oxford u.a.: Oxford Univ. Press. p. 332. ISBN 978-0-19-857002-8. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Call SA, Vollenweider MA, Hornung CA, Simel DL, McKinney WP (February 2005). "Does this patient have influenza?". JAMA. 293 (8): 987–97. doi:10.1001/jama.293.8.987. PMID 15728170.
- ↑ "Flu Symptoms & Diagnosis". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 10 July 2019. Archived from the original on 27 December 2019. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "Flu Symptoms & Complications". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 26 February 2019. Archived from the original on 1 August 2020. Retrieved 6 July 2019.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Dharmapalan D (October 2020). "Influenza". Indian Journal of Pediatrics. 87 (10): 828–832. doi:10.1007/s12098-020-03214-1. PMC 7091034. PMID 32048225.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 24.3 Krammer F, Smith GJ, Fouchier RA, Peiris M, Kedzierska K, Doherty PC, Palese P, Shaw ML, Treanor J, Webster RG, García-Sastre A (28 June 2018). "Influenza". Nature Reviews Disease Primers. 4 (1): 3. doi:10.1038/s41572-018-0002-y. PMC 7097467. PMID 29955068.
- ↑ Ghebrehewet S, MacPherson P, Ho A (7 December 2016). "Influenza". The BMJ. 355: i6258. doi:10.1136/bmj.i6258. PMC 5141587. PMID 27927672.
- ↑ Sederdahl BK, Williams JV (13 January 2020). "Epidemiology and Clinical Characteristics of Influenza C Virus". Viruses. 12 (1): 89. doi:10.3390/v12010089. PMC 7019359. PMID 31941041.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Peteranderl C, Herold S, Schmoldt C (August 2016). "Human Influenza Virus Infections". Seminars in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 37 (4): 487–500. doi:10.1055/s-0036-1584801. PMC 7174870. PMID 27486731.
- ↑ People also suffer 'long flu', study shows People also suffer 'long flu', study shows - BBC News at the Wayback Machine (archived 25 March 2022) BBC
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 Kalil AC, Thomas PG (19 July 2019). "Influenza virus-related critical illness: pathophysiology and epidemiology". Critical Care. 23 (1): 258. doi:10.1186/s13054-019-2539-x. PMC 6642581. PMID 31324202.
- ↑ Kawaoka Y, ed. (2006). Influenza Virology: Current Topics. Caister Academic Press. ISBN 978-1-904455-06-6. Archived from the original on 9 May 2008.
- ↑ Vainionpää R, Hyypiä T (April 1994). "Biology of parainfluenza viruses". Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 7 (2): 265–75. doi:10.1128/CMR.7.2.265. PMC 358320. PMID 8055470.
- ↑ Hall CB (June 2001). "Respiratory syncytial virus and parainfluenza virus". The New England Journal of Medicine. 344 (25): 1917–28. doi:10.1056/NEJM200106213442507. PMID 11419430.
- ↑ Hause BM, Collin EA, Liu R, Huang B, Sheng Z, Lu W, et al. (2014). "Characterization of a novel influenza virus in cattle and swine: proposal for a new genus in the Orthomyxoviridae family". mBio. 5 (2): e00031–14. doi:10.1128/mBio.00031-14. PMC 3958797. PMID 24595369.
- ↑ Collin EA, Sheng Z, Lang Y, Ma W, Hause BM, Li F (2015). "Cocirculation of two distinct genetic and antigenic lineages of proposed influenza D virus in cattle". J Virol. 89 (2): 1036–42. doi:10.1128/JVI.02718-14. PMC 4300623. PMID 25355894.
- ↑ Ducatez MF, Pelletier C, Meyer G (2015). "Influenza D virus in cattle, France, 2011–2014". Emerg Infect Dis. 21 (2): 368–71. doi:10.3201/eid2102.141449. PMC 4313661. PMID 25628038.
- ↑ Song H, Qi J, Khedri Z, Diaz S, Yu H, Chen X, et al. (2016). "An open receptor-binding cavity of hemagglutinin-esterase-fusion glycoprotein from newly-identified Influenza D Virus: Basis for its broad cell tropism". PLOS Pathog. 12 (1): e1005411. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1005411. PMC 4729479. PMID 26816272.
- ↑ Sheng Z, Ran Z, Wang D, Hoppe AD, Simonson R, Chakravarty S, et al. (2014). "Genomic and evolutionary characterization of a novel influenza-C-like virus from swine". Arch Virol. 159 (2): 249–55. doi:10.1007/s00705-013-1815-3. PMC 5714291. PMID 23942954.
- ↑ Quast M, Sreenivasan C, Sexton G, Nedland H, Singrey A, Fawcett L, et al. (2015). "Serological evidence for the presence of influenza D virus in small ruminants". Vet Microbiol. 180 (3–4): 281–85. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.09.005. PMC 4618254. PMID 26414999.
- ↑ Smith DB, Gaunt ER, Digard P, Templeton K, Simmonds P (2016). "Detection of influenza C virus but not influenza D virus in Scottish respiratory samples". J Clin Virol. 74: 50–53. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2015.11.036. PMC 4710576. PMID 26655269.
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 Klenk, Hans-Dieter; Matrosovich, Mikhail; Stech, Jürgen (2008). "Avian Influenza: Molecular Mechanisms of Pathogenesis and Host Range". Animal Viruses: Molecular Biology. Caister Academic Press. ISBN 978-1-904455-22-6. Archived from the original on 20 August 2016. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 41.2 41.3 Hay AJ, Gregory V, Douglas AR, Lin YP (December 2001). "The evolution of human influenza viruses". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 356 (1416): 1861–70. doi:10.1098/rstb.2001.0999. PMC 1088562. PMID 11779385.
- ↑ World Health Organization (30 June 2006). "Epidemiology of WHO-confirmed human cases of avian influenza A(H5N1) infection" (PDF). Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 81 (26): 249–57. hdl:10665/233137. PMID 16812929. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 July 2020. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ World Health Organization (November 2008). "Update: WHO-confirmed human cases of avian influenza A (H5N1) infection, November 2003-May 2008" (PDF). Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 83 (46): 415–20. hdl:10665/241238. PMID 19009716. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 August 2020. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ Fouchier RA, Schneeberger PM, Rozendaal FW, Broekman JM, Kemink SA, Munster V, et al. (February 2004). "Avian influenza A virus (H7N7) associated with human conjunctivitis and a fatal case of acute respiratory distress syndrome". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 101 (5): 1356–61. Bibcode:2004PNAS..101.1356F. doi:10.1073/pnas.0308352100. PMC 337057. PMID 14745020.
- ↑ "Asian Lineage Avian Influenza A(H7N9) Virus". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 7 December 2018. Archived from the original on 29 April 2013. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- ↑ Yuan J, Zhang L, Kan X, Jiang L, Yang J, Guo Z, Ren Q (November 2013). "Origin and Molecular Characteristics of a Novel 2013 Avian Influenza A(H6N1) Virus Causing Human Infection in Taiwan". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 57 (9): 1367–68. doi:10.1093/cid/cit479. ISSN 1537-6591. PMID 23881153.
- ↑ Osterhaus AD, Rimmelzwaan GF, Martina BE, Bestebroer TM, Fouchier RA (May 2000). "Influenza B virus in seals". Science. 288 (5468): 1051–53. Bibcode:2000Sci...288.1051O. doi:10.1126/science.288.5468.1051. PMID 10807575.
- ↑ Jakeman KJ, Tisdale M, Russell S, Leone A, Sweet C (August 1994). "Efficacy of 2'-deoxy-2'-fluororibosides against influenza A and B viruses in ferrets". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 38 (8): 1864–67. doi:10.1128/aac.38.8.1864. PMC 284652. PMID 7986023.
- ↑ Nobusawa E, Sato K (April 2006). "Comparison of the mutation rates of human influenza A and B viruses". Journal of Virology. 80 (7): 3675–78. doi:10.1128/JVI.80.7.3675-3678.2006. PMC 1440390. PMID 16537638.
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 50.2 50.3 Webster RG, Bean WJ, Gorman OT, Chambers TM, Kawaoka Y (March 1992). "Evolution and ecology of influenza A viruses". Microbiological Reviews. 56 (1): 152–79. doi:10.1128/MMBR.56.1.152-179.1992. PMC 372859. PMID 1579108.
- ↑ Zambon MC (November 1999). "Epidemiology and pathogenesis of influenza" (PDF). The Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 44 Suppl B (90002): 3–9. doi:10.1093/jac/44.suppl_2.3. PMID 10877456. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 March 2013.
- ↑ Matsuzaki Y, Sugawara K, Mizuta K, Tsuchiya E, Muraki Y, Hongo S, et al. (February 2002). "Antigenic and genetic characterization of influenza C viruses which caused two outbreaks in Yamagata City, Japan, in 1996 and 1998". Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 40 (2): 422–29. doi:10.1128/JCM.40.2.422-429.2002. PMC 153379. PMID 11825952.
- ↑ 53.0 53.1 Taubenberger JK, Morens DM (2008). "The pathology of influenza virus infections". Annual Review of Pathology. 3: 499–522. doi:10.1146/annurev.pathmechdis.3.121806.154316. PMC 2504709. PMID 18039138.
- ↑ Matsuzaki Y, Katsushima N, Nagai Y, Shoji M, Itagaki T, Sakamoto M, et al. (May 2006). "Clinical features of influenza C virus infection in children". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 193 (9): 1229–35. doi:10.1086/502973. PMID 16586359.
- ↑ Katagiri S, Ohizumi A, Homma M (July 1983). "An outbreak of type C influenza in a children's home". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 148 (1): 51–56. doi:10.1093/infdis/148.1.51. PMID 6309999.
- ↑ International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses descriptions of:Orthomyxoviridae, Influenzavirus B and Influenzavirus C
- ↑ Nakatsu S, Murakami S, Shindo K, Horimoto T, Sagara H, Noda T, et al. (March 2018). "Influenza C and D Viruses Package Eight Organized Ribonucleoprotein Complexes". Journal of Virology. 92 (6): e02084–17. doi:10.1128/jvi.02084-17. PMC 5827381. PMID 29321324.
- ↑ Sugita Y, Noda T, Sagara H, Kawaoka Y (November 2011). "Ultracentrifugation deforms unfixed influenza A virions". The Journal of General Virology. 92 (Pt 11): 2485–93. doi:10.1099/vir.0.036715-0. PMC 3352361. PMID 21795472.
- ↑ Dadonaite B, Vijayakrishnan S, Fodor E, Bhella D, Hutchinson EC (August 2016). "Filamentous influenza viruses". The Journal of General Virology. 97 (8): 1755–64. doi:10.1099/jgv.0.000535. PMC 5935222. PMID 27365089.
- ↑ 60.0 60.1 60.2 60.3 Bouvier NM, Palese P (September 2008). "The biology of influenza viruses". Vaccine. 26 Suppl 4: D49–53. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.07.039. PMC 3074182. PMID 19230160.
- ↑ Lamb RA, Choppin PW (1983). "The gene structure and replication of influenza virus". Annu. Rev. Biochem. 52: 467–506. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002343. PMID 6351727.
- ↑ Ghedin E, Sengamalay NA, Shumway M, Zaborsky J, Feldblyum T, Subbu V, et al. (October 2005). "Large-scale sequencing of human influenza reveals the dynamic nature of viral genome evolution". Nature. 437 (7062): 1162–66. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1162G. doi:10.1038/nature04239. PMID 16208317.
- ↑ Suzuki Y (March 2005). "Sialobiology of influenza: molecular mechanism of host range variation of influenza viruses". Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 28 (3): 399–408. doi:10.1248/bpb.28.399. PMID 15744059.
- ↑ Wilson JC, von Itzstein M (July 2003). "Recent strategies in the search for new anti-influenza therapies". Current Drug Targets. 4 (5): 389–408. doi:10.2174/1389450033491019. PMID 12816348.
- ↑ 65.0 65.1 65.2 Hilleman MR (August 2002). "Realities and enigmas of human viral influenza: pathogenesis, epidemiology and control". Vaccine. 20 (25–26): 3068–87. doi:10.1016/s0264-410x(02)00254-2. PMID 12163258.
- ↑ Tong S, Zhu X, Li Y, Shi M, Zhang J, Bourgeois M, et al. (10 October 2013). "New world bats harbor diverse influenza A viruses". PLOS Pathogens. 9 (10): e1003657. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1003657. PMC 3794996. PMID 24130481.
- ↑ Tong S, Li Y, Rivailler P, Conrardy C, Castillo DA, Chen LM, et al. (March 2012). "A distinct lineage of influenza A virus from bats". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 109 (11): 4269–74. Bibcode:2012PNAS..109.4269T. doi:10.1073/pnas.1116200109. PMC 3306675. PMID 22371588.
- ↑ Vreede, Frank T.; Fodor, Ervin (2010). "The role of the influenza virus RNA polymerase in host shut-off". Virulence. 1 (5): 436–439. doi:10.4161/viru.1.5.12967. ISSN 2150-5608. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- ↑ Smith AE, Helenius A (April 2004). "How viruses enter animal cells". Science. 304 (5668): 237–42. Bibcode:2004Sci...304..237S. doi:10.1126/science.1094823. PMID 15073366.
- ↑ 70.0 70.1 Wagner R, Matrosovich M, Klenk HD (May–June 2002). "Functional balance between haemagglutinin and neuraminidase in influenza virus infections". Reviews in Medical Virology. 12 (3): 159–66. doi:10.1002/rmv.352. PMID 11987141.
- ↑ 71.0 71.1 Steinhauer DA (May 1999). "Role of hemagglutinin cleavage for the pathogenicity of influenza virus". Virology. 258 (1): 1–20. doi:10.1006/viro.1999.9716. PMID 10329563.
- ↑ Liu SL, Zhang ZL, Tian ZQ, Zhao HS, Liu H, Sun EZ, Xiao GF, Zhang W, Wang HZ, Pang DW (2011) Effectively and efficiently dissecting the infection of influenza virus by quantum dot-based single-particle tracking. ACS Nano
- ↑ Lakadamyali M, Rust MJ, Babcock HP, Zhuang X (August 2003). "Visualizing infection of individual influenza viruses". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 100 (16): 9280–85. Bibcode:2003PNAS..100.9280L. doi:10.1073/pnas.0832269100. PMC 170909. PMID 12883000.
- ↑ 74.0 74.1 Pinto LH, Lamb RA (April 2006). "The M2 proton channels of influenza A and B viruses". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 281 (14): 8997–9000. doi:10.1074/jbc.R500020200. PMID 16407184.
- ↑ Cros JF, Palese P (September 2003). "Trafficking of viral genomic RNA into and out of the nucleus: influenza, Thogoto and Borna disease viruses". Virus Research. 95 (1–2): 3–12. doi:10.1016/S0168-1702(03)00159-X. PMID 12921991.
- ↑ Kash JC, Goodman AG, Korth MJ, Katze MG (July 2006). "Hijacking of the host-cell response and translational control during influenza virus infection". Virus Research. 119 (1): 111–20. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2005.10.013. PMID 16630668.
- ↑ Nayak DP, Hui EK, Barman S (December 2004). "Assembly and budding of influenza virus". Virus Research. 106 (2): 147–65. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2004.08.012. PMC 7172797. PMID 15567494.
- ↑ Drake JW (May 1993). "Rates of spontaneous mutation among RNA viruses". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 90 (9): 4171–75. Bibcode:1993PNAS...90.4171D. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.9.4171. PMC 46468. PMID 8387212.
- ↑ He CQ, Xie ZX, Han GZ, Dong JB, Wang D, Liu JB, Ma LY, Tang XF, Liu XP, Pang YS, Li GR (January 2009). "Homologous recombination as an evolutionary force in the avian influenza A virus". Mol Biol Evol. 26 (1): 177–87. doi:10.1093/molbev/msn238. PMID 18931384.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ 80.0 80.1 De A, Sarkar T, Nandy A (2016). "Bioinformatics studies of Influenza A hemagglutinin sequence data indicate recombination-like events leading to segment exchanges". BMC Res Notes. 9: 222. doi:10.1186/s13104-016-2017-3. PMC 4832483. PMID 27083561.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Sherman, Irwin W. (2007). Twelve diseases that changed our world. Washington, DC: ASM Press. p. 161. ISBN 978-1-55581-466-3.
- ↑ 82.0 82.1 82.2 Carrat F, Vergu E, Ferguson NM, Lemaitre M, Cauchemez S, Leach S, et al. (April 2008). "Time lines of infection and disease in human influenza: a review of volunteer challenge studies". American Journal of Epidemiology. 167 (7): 775–85. doi:10.1093/aje/kwm375. ISSN 1476-6256. PMID 18230677.
In almost all studies, participants were individually confined for 1 week
- ↑ Mitamura K, Sugaya N (June 2006). "[Diagnosis and Treatment of influenza – clinical investigation on viral shedding in children with influenza]". Uirusu. 56 (1): 109–16. doi:10.2222/jsv.56.109. PMID 17038819.
- ↑ Gooskens J, Jonges M, Claas EC, Meijer A, Kroes AC (May 2009). "Prolonged influenza virus infection during lymphocytopenia and frequent detection of drug-resistant viruses". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 199 (10): 1435–41. doi:10.1086/598684. PMID 19392620.
- ↑ 85.0 85.1 85.2 85.3 85.4 Weber TP, Stilianakis NI (November 2008). "Inactivation of influenza A viruses in the environment and modes of transmission: a critical review". The Journal of Infection. 57 (5): 361–73. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2008.08.013. PMC 7112701. PMID 18848358.
- ↑ Hall CB (August 2007). "The spread of influenza and other respiratory viruses: complexities and conjectures" (PDF). Clinical Infectious Diseases. 45 (3): 353–59. doi:10.1086/519433. PMC 7107900. PMID 17599315. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 January 2016.
- ↑ Cole EC, Cook CE (August 1998). "Characterization of infectious aerosols in health care facilities: an aid to effective engineering controls and preventive strategies". American Journal of Infection Control. 26 (4): 453–64. doi:10.1016/S0196-6553(98)70046-X. PMC 7132666. PMID 9721404.
- ↑ Kormuth KA, Lin K, Prussin AJ, Vejerano EP, Tiwari AJ, Cox SS, et al. (July 2018). "Influenza Virus Infectivity Is Retained in Aerosols and Droplets Independent of Relative Humidity". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 218 (5): 739–747. doi:10.1093/infdis/jiy221. PMC 6057527. PMID 29878137.
- ↑ 89.0 89.1 Thomas Y, Vogel G, Wunderli W, Suter P, Witschi M, Koch D, et al. (May 2008). "Survival of influenza virus on banknotes". Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 74 (10): 3002–07. doi:10.1128/AEM.00076-08. PMC 2394922. PMID 18359825.
- ↑ Tesini, Brenda L. (September 2018). "Influenza (Flu)". Merck. Archived from the original on 17 March 2008. Retrieved 15 March 2008.
- ↑ Bean B, Moore BM, Sterner B, Peterson LR, Gerding DN, Balfour HH (July 1982). "Survival of influenza viruses on environmental surfaces". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 146 (1): 47–51. doi:10.1093/infdis/146.1.47. PMID 6282993.
- ↑ 92.0 92.1 "Influenza Factsheet" (PDF). Center for Food Security and Public Health, Iowa State University. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 March 2009. p. 7
- ↑ Jefferies WM, Turner JC, Lobo M, Gwaltney JM (March 1998). "Low plasma levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone in patients with acute influenza". Clin Infect Dis. 26 (3): 708–10. doi:10.1086/514594. PMID 9524849.
- ↑ 94.0 94.1 Korteweg C, Gu J (May 2008). "Pathology, molecular biology, and pathogenesis of avian influenza A (H5N1) infection in humans". The American Journal of Pathology. 172 (5): 1155–70. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2008.070791. PMC 2329826. PMID 18403604.
- ↑ Gu, Yinuo; Zuo, Xu; Zhang, Siyu; Ouyang, Zhuoer; Jiang, Shengyu; Wang, Fang; Wang, Guoqiang (July 2021). "The Mechanism behind Influenza Virus Cytokine Storm". Viruses. 13 (7): 1362. doi:10.3390/v13071362. ISSN 1999-4915.
- ↑ Nicholls JM, Chan RW, Russell RJ, Air GM, Peiris JS (April 2008). "Evolving complexities of influenza virus and its receptors". Trends in Microbiology. 16 (4): 149–57. doi:10.1016/j.tim.2008.01.008. PMID 18375125.
- ↑ van Riel D, Munster VJ, de Wit E, Rimmelzwaan GF, Fouchier RA, Osterhaus AD, et al. (April 2006). "H5N1 Virus Attachment to Lower Respiratory Tract". Science. 312 (5772): 399. doi:10.1126/science.1125548. PMID 16556800.
- ↑ Shinya K, Ebina M, Yamada S, Ono M, Kasai N, Kawaoka Y (March 2006). "Avian flu: influenza virus receptors in the human airway". Nature. 440 (7083): 435–36. Bibcode:2006Natur.440..435S. doi:10.1038/440435a. PMID 16554799.
- ↑ van Riel D, Munster VJ, de Wit E, Rimmelzwaan GF, Fouchier RA, Osterhaus AD, et al. (October 2007). "Human and avian influenza viruses target different cells in the lower respiratory tract of humans and other mammals". The American Journal of Pathology. 171 (4): 1215–23. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2007.070248. PMC 1988871. PMID 17717141.
- ↑ Eccles R (November 2005). "Understanding the symptoms of the common cold and influenza". The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 5 (11): 718–25. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(05)70270-X. PMC 7185637. PMID 16253889.
- ↑ Schmitz N, Kurrer M, Bachmann MF, Kopf M (May 2005). "Interleukin-1 is responsible for acute lung immunopathology but increases survival of respiratory influenza virus infection". Journal of Virology. 79 (10): 6441–48. doi:10.1128/JVI.79.10.6441-6448.2005. PMC 1091664. PMID 15858027.
- ↑ Winther B, Gwaltney JM, Mygind N, Hendley JO (1998). "Viral-induced rhinitis". American Journal of Rhinology. 12 (1): 17–20. doi:10.2500/105065898782102954. PMID 9513654.
- ↑ Cheung CY, Poon LL, Lau AS, Luk W, Lau YL, Shortridge KF, et al. (December 2002). "Induction of proinflammatory cytokines in human macrophages by influenza A (H5N1) viruses: a mechanism for the unusual severity of human disease?". Lancet. 360 (9348): 1831–37. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11772-7. PMID 12480361.
- ↑ Kobasa D, Jones SM, Shinya K, Kash JC, Copps J, Ebihara H, et al. (January 2007). "Aberrant innate immune response in lethal infection of macaques with the 1918 influenza virus". Nature. 445 (7125): 319–23. Bibcode:2007Natur.445..319K. doi:10.1038/nature05495. PMID 17230189.
- ↑ Kash JC, Tumpey TM, Proll SC, Carter V, Perwitasari O, Thomas MJ, et al. (October 2006). "Genomic analysis of increased host immune and cell death responses induced by 1918 influenza virus". Nature. 443 (7111): 578–81. Bibcode:2006Natur.443..578K. doi:10.1038/nature05181. PMC 2615558. PMID 17006449.
- ↑ Beigel J, Bray M (April 2008). "Current and future antiviral therapy of severe seasonal and avian influenza". Antiviral Research. 78 (1): 91–102. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2008.01.003. PMC 2346583. PMID 18328578.
- ↑ Spiro, Stephen G.; Silvestri, Gerard A.; Agustí, Alvar (2012). Clinical Respiratory Medicine. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 311. ISBN 978-1-4557-2329-4. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ "Vaccine use". World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 15 December 2012. Retrieved 6 December 2012.
- ↑ "Vaccines against influenza WHO position paper". Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 87 (47): 461–76. November 2012. PMID 23210147. Archived from the original on 2 August 2020. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- Lay summary in: (PDF) https://www.who.int/immunization/position_papers/PP_influenza_november2012_summary.pdf.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help)
- Lay summary in: (PDF) https://www.who.int/immunization/position_papers/PP_influenza_november2012_summary.pdf.
- ↑ "CDC launches universal flu vaccination recommendation". Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy (CIDRAP). 29 July 2010. Archived from the original on 24 September 2019. Retrieved 24 September 2019.
- ↑ 111.0 111.1 Demicheli V, Jefferson T, Ferroni E, Rivetti A, Di Pietrantonj C (February 2018). "Vaccines for preventing influenza in healthy adults". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2: CD001269. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001269.pub6. PMC 6491184. PMID 29388196.
- ↑ 112.0 112.1 Jefferson T, Rivetti A, Di Pietrantonj C, Demicheli V (February 2018). "Vaccines for preventing influenza in healthy children". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2: CD004879. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004879.pub5. PMC 6491174. PMID 29388195.
- ↑ Kopsaftis Z, Wood-Baker R, Poole P (June 2018). "Influenza vaccine for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2: CD002733. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002733.pub3. PMC 6513384. PMID 29943802.
- ↑ Cates CJ, Rowe BH (February 2013). "Vaccines for preventing influenza in people with asthma". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2 (2): CD000364. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000364.pub4. PMC 6999427. PMID 23450529.
- ↑ Beck CR, McKenzie BC, Hashim AB, Harris RC, Nguyen-Van-Tam JS (October 2012). "Influenza vaccination for immunocompromised patients: systematic review and meta-analysis by etiology". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 206 (8): 1250–59. doi:10.1093/infdis/jis487. PMID 22904335.
- ↑ Udell JA, Zawi R, Bhatt DL, Keshtkar-Jahromi M, Gaughran F, Phrommintikul A, et al. (October 2013). "Association between influenza vaccination and cardiovascular outcomes in high-risk patients: a meta-analysis". JAMA. 310 (16): 1711–20. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.279206. PMID 24150467.
- ↑ Abramson ZH (2012). "What, in Fact, Is the Evidence That Vaccinating Healthcare Workers against Seasonal Influenza Protects Their Patients? A Critical Review". International Journal of Family Medicine. 2012: 205464. doi:10.1155/2012/205464. PMC 3502850. PMID 23209901.
- ↑ Thomas RE, Jefferson T, Lasserson TJ (June 2016). "Influenza vaccination for healthcare workers who care for people aged 60 or older living in long-term care institutions". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (6): CD005187. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005187.pub5. PMID 27251461.
- ↑ Ahmed F, Lindley MC, Allred N, Weinbaum CM, Grohskopf L (January 2014). "Effect of influenza vaccination of healthcare personnel on morbidity and mortality among patients: systematic review and grading of evidence". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 58 (1): 50–57. doi:10.1093/cid/cit580. PMID 24046301.
- ↑ Dolan GP, Harris RC, Clarkson M, Sokal R, Morgan G, Mukaigawara M, et al. (September 2013). "Vaccination of healthcare workers to protect patients at increased risk of acute respiratory disease: summary of a systematic review". Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses. 7 Suppl 2: 93–96. doi:10.1111/irv.12087. PMC 5909400. PMID 24034492.
- ↑ 121.0 121.1 "Recommended composition of influenza virus vaccines for use in the 2006–2007 influenza season" (PDF). WHO Report. 14 February 2006. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 April 2016. Retrieved 28 December 2016.
- ↑ Holmes EC, Ghedin E, Miller N, Taylor J, Bao Y, St George K, et al. (September 2005). "Whole-genome analysis of human influenza A virus reveals multiple persistent lineages and reassortment among recent H3N2 viruses". PLOS Biology. 3 (9): e300. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0030300. PMC 1180517. PMID 16026181.
- ↑ "Key Facts About Seasonal Flu Vaccine". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 6 September 2018. Archived from the original on 8 May 2019. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- ↑ "Seasonal Flu Shot". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 7 November 2019. Archived from the original on 2 December 2019. Retrieved 2 December 2019.
- ↑ Grande AJ, Reid H, Thomas EE, Nunan D, Foster C (August 2016). "Exercise prior to influenza vaccination for limiting influenza incidence and its related complications in adults" (PDF). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (8): CD011857. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011857.pub2. PMID 27545762. Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ Jit M, Newall AT, Beutels P (April 2013). "Key issues for estimating the impact and cost-effectiveness of seasonal influenza vaccination strategies". Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics. 9 (4): 834–40. doi:10.4161/hv.23637. PMC 3903903. PMID 23357859.
- ↑ Newall AT, Jit M, Beutels P (August 2012). "Economic evaluations of childhood influenza vaccination: a critical review". PharmacoEconomics. 30 (8): 647–60. doi:10.2165/11599130-000000000-00000. PMID 22788257.
- ↑ Postma MJ, Baltussen RP, Palache AM, Wilschut JC (April 2006). "Further evidence for favorable cost-effectiveness of elderly influenza vaccination". Expert Review of Pharmacoeconomics & Outcomes Research. 6 (2): 215–27. doi:10.1586/14737167.6.2.215. PMID 20528557.
- ↑ Newall AT, Dehollain JP, Creighton P, Beutels P, Wood JG (August 2013). "Understanding the cost-effectiveness of influenza vaccination in children: methodological choices and seasonal variability". PharmacoEconomics. 31 (8): 693–702. doi:10.1007/s40273-013-0060-7. PMID 23645539.
- ↑ Newall AT, Kelly H, Harsley S, Scuffham PA (1 June 2009). "Cost effectiveness of influenza vaccination in older adults: a critical review of economic evaluations for the 50- to 64-year age group". PharmacoEconomics. 27 (6): 439–50. doi:10.2165/00019053-200927060-00001. PMID 19640008.
- ↑ 131.0 131.1 131.2 131.3 Aledort JE, Lurie N, Wasserman J, Bozzette SA (August 2007). "Non-pharmaceutical public health interventions for pandemic influenza: an evaluation of the evidence base". BMC Public Health. 7: 208. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-7-208. PMC 2040158. PMID 17697389.
- ↑ "2009 H1N1 Flu ("Swine Flu") and You". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 10 February 2010. Archived from the original on 4 March 2010. Retrieved 2 December 2019.
- ↑ Grayson ML, Melvani S, Druce J, Barr IG, Ballard SA, Johnson PD, et al. (February 2009). "Efficacy of soap and water and alcohol-based hand-rub preparations against live H1N1 influenza virus on the hands of human volunteers". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 48 (3): 285–91. doi:10.1086/595845. PMID 19115974.
- ↑ MacIntyre CR, Cauchemez S, Dwyer DE, Seale H, Cheung P, Browne G, et al. (February 2009). "Face mask use and control of respiratory virus transmission in households". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 15 (2): 233–41. doi:10.3201/eid1502.081167. PMC 2662657. PMID 19193267.
- ↑ Bridges CB, Kuehnert MJ, Hall CB (October 2003). "Transmission of influenza: implications for control in health care settings". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 37 (8): 1094–101. doi:10.1086/378292. PMID 14523774.
- ↑ "Interim Guidance for the Use of Masks to Control Seasonal Influenza Virus Transmission". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 5 March 2019. Archived from the original on 2 December 2019. Retrieved 2 December 2019.
- ↑ 137.0 137.1 Murin S, Bilello KS (October 2005). "Respiratory tract infections: another reason not to smoke". Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine. 72 (10): 916–20. doi:10.3949/ccjm.72.10.916. PMID 16231688.
- ↑ Kark JD, Lebiush M, Rannon L (October 1982). "Cigarette smoking as a risk factor for epidemic a(h1n1) influenza in young men". New England Journal of Medicine. 307 (17): 1042–46. doi:10.1056/NEJM198210213071702. PMID 7121513.
- ↑ Hota B (October 2004). "Contamination, disinfection, and cross-colonization: are hospital surfaces reservoirs for nosocomial infection?". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 39 (8): 1182–89. doi:10.1086/424667. PMC 7107941. PMID 15486843.
- ↑ 140.0 140.1 McDonnell G, Russell AD (January 1999). "Antiseptics and disinfectants: activity, action, and resistance". Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 12 (1): 147–79. doi:10.1128/CMR.12.1.147. PMC 88911. PMID 9880479.
- ↑ "Chlorine Bleach: Helping to Manage the Flu Risk". Water Quality & Health Council. April 2009. Archived from the original on 7 June 2009. Retrieved 12 May 2009.
- ↑ Hatchett RJ, Mecher CE, Lipsitch M (May 2007). "Public health interventions and epidemic intensity during the 1918 influenza pandemic". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104 (18): 7582–87. Bibcode:2007PNAS..104.7582H. doi:10.1073/pnas.0610941104. PMC 1849867. PMID 17416679.
- ↑ Bootsma MC, Ferguson NM (May 2007). "The effect of public health measures on the 1918 influenza pandemic in U.S. cities". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104 (18): 7588–93. Bibcode:2007PNAS..104.7588B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0611071104. PMC 1849868. PMID 17416677.
- ↑ "Influenza Virus Testing Methods". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 26 March 2018. Archived from the original on 31 March 2018. Retrieved 30 March 2018.
- ↑ "Guide for considering influenza testing when influenza viruses are circulating in the community". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 20 February 2018. Archived from the original on 31 March 2018. Retrieved 30 March 2018.
- ↑ 146.0 146.1 "Wash your hands often and right way". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 5 January 2018. Archived from the original on 5 April 2019. Retrieved 29 March 2018.
- ↑ 147.0 147.1 "Flu: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 14 February 2010. Retrieved 7 February 2010.
- ↑ Lansbury L, Rodrigo C, Leonardi-Bee J, Nguyen-Van-Tam J, Lim WS (24 February 2019). "Corticosteroids as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of influenza". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2: CD010406. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010406.pub3. PMC 6387789. PMID 30798570.
- ↑ Glasgow JF, Middleton B (November 2001). "Reye syndrome – insights on causation and prognosis" (PDF). Archives of Disease in Childhood. 85 (5): 351–53. doi:10.1136/adc.85.5.351. PMC 1718987. PMID 11668090. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 July 2011.
- ↑ Hurt AC, Ho HT, Barr I (October 2006). "Resistance to anti-influenza drugs: adamantanes and neuraminidase inhibitors". Expert Review of Anti-Infective Therapy. 4 (5): 795–805. doi:10.1586/14787210.4.5.795. PMID 17140356.
- ↑ "The Flu: What To Do If You Get Sick". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 8 October 2019. Archived from the original on 24 January 2020. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "Laninamivir". National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 9 March 2021.
- ↑ Lampejo T (July 2020). "Influenza and antiviral resistance: an overview". European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases. 39 (7): 1201–1208. doi:10.1007/s10096-020-03840-9. PMC 7223162. PMID 32056049.
- ↑ Chow EJ, Doyle JD, Uyeki TM (12 June 2019). "Influenza virus-related critical illness: prevention, diagnosis, treatment". Critical Care. 23 (1): 214. doi:10.1186/s13054-019-2491-9. PMC 6563376. PMID 31189475.
- ↑ Allen UD, Aoki FY, Stiver HG (September 2006). "The use of antiviral drugs for influenza: recommended guidelines for practitioners". Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 17 (5): 273–84. doi:10.1155/2006/165940. PMC 2095091. PMID 18382639.
- ↑ Gubareva LV, Besselaar TG, Daniels RS, Fry A, Gregory V, Huang W, et al. (October 2017). "Global update on the susceptibility of human influenza viruses to neuraminidase inhibitors, 2015-2016". Antiviral Res. 146: 12–20. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2017.08.004. PMC 5667636. PMID 28802866.
- ↑ Mawatari M, Saito R, Hibino A, Kondo H, Yagami R, Odagiri T, et al. (November 2019). "Effectiveness of four types of neuraminidase inhibitors approved in Japan for the treatment of influenza". PLOS One. 14 (11): e0224683. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0224683. PMC 6837752. PMID 31697721.
- ↑ Lian, N.; Xie, H.; Lin, S.; Huang, J.; Zhao, J.; Lin, Q. (April 2020). "Umifenovir treatment is not associated with improved outcomes in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a retrospective study". Clinical Microbiology and Infection. doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.04.026. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 17 June 2020.
- ↑ "Most popular antiviral medication brands in the Russian pharmaceutical market in 1st quarter 2020 by sales value share". Statista. Archived from the original on 18 June 2020. Retrieved 17 June 2020.
- ↑ Moscona A (5 March 2009). "Global Transmission of Oseltamivir-Resistant Influenza". New England Journal of Medicine. 360 (10): 953–56. doi:10.1056/NEJMp0900648. ISSN 0028-4793. PMID 19258250.
- ↑ Stephenson I, Nicholson KG (July 1999). "Chemotherapeutic control of influenza". The Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 44 (1): 6–10. doi:10.1093/jac/44.1.6. PMID 10459804.
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control Prevention (CDC) (January 2006). "High levels of adamantane resistance among influenza A (H3N2) viruses and interim guidelines for use of antiviral agents – United States, 2005–06 influenza season" (PDF). MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 55 (2): 44–46. PMID 16424859. Archived (PDF) from the original on 29 June 2011.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ Bright RA, Medina MJ, Xu X, Perez-Oronoz G, Wallis TR, Davis XM, et al. (October 2005). "Incidence of adamantane resistance among influenza A (H3N2) viruses isolated worldwide from 1994 to 2005: a cause for concern". Lancet. 366 (9492): 1175–81. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67338-2. PMID 16198766.
- ↑ Ilyushina NA, Govorkova EA, Webster RG (October 2005). "Detection of amantadine-resistant variants among avian influenza viruses isolated in North America and Asia" (PDF). Virology. 341 (1): 102–06. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2005.07.003. PMID 16081121. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 July 2011.
- ↑ Parry J (July 2005). "Use of antiviral drug in poultry is blamed for drug resistant strains of avian flu". BMJ. 331 (7507): 10. doi:10.1136/bmj.331.7507.10. PMC 558527. PMID 15994677.
- ↑ "CDC Recommends against the Use of Amantadine and Rimantadine for the Treatment or Prophylaxis of Influenza in the United States during the 2005–06 Influenza Season". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 14 January 2006. Archived from the original on 19 June 2017. Retrieved 28 December 2016.
- ↑ Hayden FG (March 1997). "Prevention and treatment of influenza in immunocompromised patients". Am. J. Med. 102 (3A): 55–60, discussion 75–76. doi:10.1016/S0002-9343(97)80013-7. PMID 10868144.
- ↑ Whitley RJ, Monto AS (2006). "Prevention and treatment of influenza in high-risk groups: children, pregnant women, immunocompromised hosts, and nursing home residents" (PDF). J Infect Dis. 194 S2: S133–38. doi:10.1086/507548. PMID 17163386. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 January 2016.
- ↑ Angelo SJ, Marshall PS, Chrissoheris MP, Chaves AM (April 2004). "Clinical characteristics associated with poor outcome in patients acutely infected with Influenza A". Conn Med. 68 (4): 199–205. PMID 15095826.
- ↑ "People at High Risk For Flu Complications". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 26 August 2016. Archived from the original on 10 July 2017. Retrieved 20 March 2017.
- ↑ 171.0 171.1 171.2 Sivadon-Tardy V, Orlikowski D, Porcher R, Sharshar T, Durand MC, Enouf V, et al. (January 2009). "Guillain-Barré syndrome and influenza virus infection". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 48 (1): 48–56. doi:10.1086/594124. PMID 19025491.
- ↑ Jacobs BC, Rothbarth PH, van der Meché FG, Herbrink P, Schmitz PI, de Klerk MA, et al. (October 1998). "The spectrum of antecedent infections in Guillain-Barré syndrome: a case-control study". Neurology. 51 (4): 1110–15. doi:10.1212/wnl.51.4.1110. PMID 9781538.
- ↑ Vellozzi C, Burwen DR, Dobardzic A, Ball R, Walton K, Haber P (March 2009). "Safety of trivalent inactivated influenza vaccines in adults: background for pandemic influenza vaccine safety monitoring". Vaccine. 27 (15): 2114–20. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.01.125. PMID 19356614. Archived from the original on 1 August 2020. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ Stowe J, Andrews N, Wise L, Miller E (February 2009). "Investigation of the temporal association of Guillain-Barre syndrome with influenza vaccine and influenzalike illness using the United Kingdom General Practice Research Database" (PDF). American Journal of Epidemiology. 169 (3): 382–88. doi:10.1093/aje/kwn310. PMID 19033158.
- ↑ 175.0 175.1 "Children with Neurologic Conditions & Influenza (Flu)". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 5 February 2019. Archived from the original on 6 July 2019. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
Children of any age with neurologic conditions are more likely than other children to become very sick if they get flu. Flu complications may vary and for some children, can include pneumonia and even death.
- ↑ "Slate's Explainer: Weather and the Flu Season". NPR. 17 December 2003. Archived from the original on 15 November 2016. Retrieved 19 October 2006.
- ↑ Lowen AC, Mubareka S, Steel J, Palese P (October 2007). "Influenza virus transmission is dependent on relative humidity and temperature". PLOS Pathogens. 3 (10): 1470–76. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.0030151. PMC 2034399. PMID 17953482.
- ↑ Shaman J, Kohn M (March 2009). "Absolute humidity modulates influenza survival, transmission, and seasonality". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 106 (9): 3243–48. Bibcode:2009PNAS..106.3243S. doi:10.1073/pnas.0806852106. PMC 2651255. PMID 19204283.
- ↑ Shaman J, Pitzer VE, Viboud C, Grenfell BT, Lipsitch M (February 2010). Ferguson NM (ed.). "Absolute humidity and the seasonal onset of influenza in the continental United States". PLOS Biology. 8 (2): e1000316. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000316. PMC 2826374. PMID 20186267.
- ↑ Shek LP, Lee BW (June 2003). "Epidemiology and seasonality of respiratory tract virus infections in the tropics". Paediatric Respiratory Reviews. 4 (2): 105–11. doi:10.1016/S1526-0542(03)00024-1. PMID 12758047.
- ↑ Dushoff J, Plotkin JB, Levin SA, Earn DJ (November 2004). "Dynamical resonance can account for seasonality of influenza epidemics". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 101 (48): 16915–16. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10116915D. doi:10.1073/pnas.0407293101. PMC 534740. PMID 15557003.
- ↑ "WHO Confirmed Human Cases of H5N1". WHO Epidemic and Pandemic Alert and Response (EPR). Archived from the original on 16 November 2016. Retrieved 28 December 2016.
- ↑ World Health Organization (25 August 2006). "Antigenic and genetic characteristics of H5N1 viruses and candidate H5N1 vaccine viruses developed for potential use as pre-pandemic vaccines". Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 81 (34/35): 328–30. hdl:10665/233175. PMID 16933379. Archived from the original on 2 August 2020. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ Cannell JJ, Vieth R, Umhau JC, Holick MF, Grant WB, Madronich S, et al. (December 2006). "Epidemic influenza and vitamin D". Epidemiology and Infection. 134 (6): 1129–40. doi:10.1017/S0950268806007175. PMC 2870528. PMID 16959053.
- ↑ Hope-Simpson RE (February 1981). "The role of season in the epidemiology of influenza". The Journal of Hygiene. 86 (1): 35–47. doi:10.1017/s0022172400068728. PMC 2134066. PMID 7462597.
- ↑ "Estimated Influenza Illnesses, Medical visits, Hospitalizations, and Deaths in the United States – 2018–2019 influenza season". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 9 January 2020. Archived from the original on 26 August 2020. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- ↑ Paget J, Spreeuwenberg P, Charu V, Taylor RJ, Iuliano AD, Bresee J, et al. (December 2019). "Global mortality associated with seasonal influenza epidemics: New burden estimates and predictors from the GLaMOR Project" (PDF). Journal of Global Health. 9 (2): 020421. doi:10.7189/jogh.09.020421. PMC 6815659. PMID 31673337. Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 September 2020. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ Thompson WW, Shay DK, Weintraub E, Brammer L, Cox N, Anderson LJ, et al. (January 2003). "Mortality associated with influenza and respiratory syncytial virus in the United States". JAMA. 289 (2): 179–86. doi:10.1001/jama.289.2.179. PMID 12517228.
- ↑ Thompson WW, Shay DK, Weintraub E, Brammer L, Bridges CB, Cox NJ, et al. (September 2004). "Influenza-associated hospitalizations in the United States". JAMA. 292 (11): 1333–40. doi:10.1001/jama.292.11.1333. PMID 15367555.
- ↑ Dushoff J, Plotkin JB, Viboud C, Earn DJ, Simonsen L (January 2006). "Mortality due to influenza in the United States – an annualized regression approach using multiple-cause mortality data". American Journal of Epidemiology. 163 (2): 181–87. doi:10.1093/aje/kwj024. PMID 16319291. Archived from the original on 21 November 2009.
The regression model attributes an annual average of 41,400 (95% confidence interval: 27,100, 55,700) deaths to influenza over the period 1979–2001
- ↑ Steenhuysen, Julie (26 August 2010). "CDC backs away from decades-old flu death estimate". Reuters. Archived from the original on 31 August 2010. Retrieved 13 September 2010.
Instead of the estimated 36,000 annual flu deaths in the United States ... the actual number in the past 30 years has ranged from a low of about 3,300 deaths to a high of nearly 49,000…
- ↑ Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. (December 2012). "Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010" (PDF). Lancet. 380 (9859): 2095–128. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0. hdl:10536/DRO/DU:30050819. PMID 23245604. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 August 2020. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ Murray CJ, Lopez AD, Chin B, Feehan D, Hill KH (December 2006). "Estimation of potential global pandemic influenza mortality on the basis of vital registry data from the 1918–20 pandemic: a quantitative analysis". Lancet. 368 (9554): 2211–18. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69895-4. PMID 17189032.
- ↑ Wolf YI, Viboud C, Holmes EC, Koonin EV, Lipman DJ (October 2006). "Long intervals of stasis punctuated by bursts of positive selection in the seasonal evolution of influenza A virus". Biology Direct. 1 (1): 34. doi:10.1186/1745-6150-1-34. PMC 1647279. PMID 17067369.
- ↑ Parrish CR, Kawaoka Y (2005). "The origins of new pandemic viruses: the acquisition of new host ranges by canine parvovirus and influenza A viruses". Annual Review of Microbiology. 59: 553–86. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.59.030804.121059. PMID 16153179.
- ↑ Recker M, Pybus OG, Nee S, Gupta S (May 2007). "The generation of influenza outbreaks by a network of host immune responses against a limited set of antigenic types". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104 (18): 7711–16. Bibcode:2007PNAS..104.7711R. doi:10.1073/pnas.0702154104. PMC 1855915. PMID 17460037.
- ↑ 197.0 197.1 Ferguson NM, Cummings DA, Cauchemez S, Fraser C, Riley S, Meeyai A, et al. (September 2005). "Strategies for containing an emerging influenza pandemic in Southeast Asia". Nature. 437 (7056): 209–14. Bibcode:2005Natur.437..209F. doi:10.1038/nature04017. hdl:10722/54275. PMID 16079797.
- ↑ Influenza, The Oxford English Dictionary, second edition.
- ↑ 199.0 199.1 199.2 199.3 Potter CW (October 2001). "A history of influenza". Journal of Applied Microbiology. 91 (4): 572–79. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.2001.01492.x. PMID 11576290.
- ↑ Calisher CH (August 2009). "Swine flu". Croatian Medical Journal. 50 (4): 412–15. doi:10.3325/cmj.2009.50.412. PMC 2728380. PMID 19673043.
- ↑ 201.0 201.1 201.2 201.3 Taubenberger JK, Morens DM (January 2006). "1918 Influenza: the mother of all pandemics". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 12 (1): 15–22. doi:10.3201/eid1201.050979. PMC 3291398. PMID 16494711.
- ↑ 202.0 202.1 Mordini E, Green M, eds. (2013). Internet-Based Intelligence in Public Health Emergencies: Early Detection and Response in Disease Outbreak Crises. IOS Press. p. 67. ISBN 978-1614991755.
- ↑ Martin PM, Martin-Granel E (June 2006). "2,500-year evolution of the term epidemic". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 12 (6): 976–80. doi:10.3201/eid1206.051263. PMC 3373038. PMID 16707055.
- ↑ Hippocrates. "Of the Epidemics, c. 400 BCE". Adams, Francis (transl.). Archived from the original on 5 October 2006. Retrieved 18 October 2006.
- ↑ Beveridge WI (1991). "The chronicle of influenza epidemics". History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences. 13 (2): 223–34. PMID 1724803.
- ↑ Guerra F (1988). "The earliest American epidemic. The influenza of 1493". Social Science History. 12 (3): 305–25. doi:10.2307/1171451. JSTOR 1171451. PMID 11618144.
- ↑ Guerra F (1993). "The European-American exchange". History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences. 15 (3): 313–27. PMID 7529930.
- ↑ Morens DM, North M, Taubenberger JK (December 2010). "Eyewitness accounts of the 1510 influenza pandemic in Europe". Lancet. 376 (9756): 1894–5. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62204-0. PMC 3180818. PMID 21155080.
- ↑ Morens DM, Taubenberger JK, Folkers GK, Fauci AS (December 2010). "Pandemic influenza's 500th anniversary". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 51 (12): 1442–4. doi:10.1086/657429. PMC 3106245. PMID 21067353.
- ↑ Thompson, Theophilus (1852). Annals of Influenza Or Epidemic Catarrhal Fever in Great Britain from 1510 to 1837. Sydenham Society. p. 101. Archived from the original on 25 February 2021. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ Vaughan, M.D., Warren T. (July 1921). "Influenza - An Epidemiologic Study". The American Journal of Hygiene. 1: 19. Archived from the original on 3 August 2020. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ Dictionnaire encyclopédique des sciences médicales (in français). Paris: Asselin. 1877. p. 332. Archived from the original on 3 August 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2022.
- ↑ Pease, Franklin; Damas (1999). Historia general de América Latina: El primer contacto y la formación de nuevas sociedades (in español). Paris, France: UNESCO. p. 311. ISBN 978-92-3-303151-7. Archived from the original on 3 August 2020. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ Starky, David (2002). "Edward and Mary: The Unknown Tudors". Youtube. Event occurs at 46:20-46:25. Archived from the original on 18 June 2020.
- ↑ Mémorial de Chronologie, d'Histoire Industrielle, d'Èconomie Politique, de Biographie, etc (in français). Paris: Chez Verdière, Libraire. 1830. p. 863. Archived from the original on 3 August 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2022.
- ↑ 216.0 216.1 216.2 216.3 216.4 Institute of Medicine (US) Forum on Microbial Threats, Knobler SL, Mack A, Mahmoud A, Lemon SM (2005). "1: The Story of Influenza". In Knobler S, Mack A, Mahmoud A, Lemon S (eds.). The Threat of Pandemic Influenza: Are We Ready? Workshop Summary (2005). Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. pp. 60–61. doi:10.17226/11150. ISBN 978-0-309-09504-4. PMID 20669448. Archived from the original on 7 August 2009. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ 217.0 217.1 Patterson KD, Pyle GF (Spring 1991). "The geography and mortality of the 1918 influenza pandemic". Bulletin of the History of Medicine. 65 (1): 4–21. PMID 2021692.
- ↑ Taubenberger JK, Reid AH, Janczewski TA, Fanning TG (December 2001). "Integrating historical, clinical and molecular genetic data in order to explain the origin and virulence of the 1918 Spanish influenza virus". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 356 (1416): 1829–39. doi:10.1098/rstb.2001.1020. PMC 1088558. PMID 11779381.
- ↑ Simonsen L, Clarke MJ, Schonberger LB, Arden NH, Cox NJ, Fukuda K (July 1998). "Pandemic versus epidemic influenza mortality: a pattern of changing age distribution". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 178 (1): 53–60. doi:10.1086/515616. PMID 9652423.
- ↑ Hilleman MR (August 2002). "Realities and enigmas of human viral influenza: pathogenesis, epidemiology and control". Vaccine. 20 (25–26): 3068–87. doi:10.1016/S0264-410X(02)00254-2. PMID 12163258.
- ↑ Potter CW (October 2001). "A history of influenza". Journal of Applied Microbiology. 91 (4): 572–9. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.2001.01492.x. PMID 11576290.
- ↑ 222.0 222.1 222.2 222.3 Valleron AJ, Cori A, Valtat S, Meurisse S, Carrat F, Boëlle PY (May 2010). "Transmissibility and geographic spread of the 1889 influenza pandemic". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 107 (19): 8778–81. Bibcode:2010PNAS..107.8778V. doi:10.1073/pnas.1000886107. PMC 2889325. PMID 20421481.
- ↑ "The Russian Flu of 1889: The Deadly Pandemic Few Americans Took Seriously". HISTORY. 3 October 2023. Retrieved 28 February 2024.
- ↑ Mills CE, Robins JM, Lipsitch M (December 2004). "Transmissibility of 1918 pandemic influenza". Nature. 432 (7019): 904–6. Bibcode:2004Natur.432..904M. doi:10.1038/nature03063. PMC 7095078. PMID 15602562.
- ↑ 225.0 225.1 225.2 225.3 225.4 Biggerstaff M, Cauchemez S, Reed C, Gambhir M, Finelli L (September 2014). "Estimates of the reproduction number for seasonal, pandemic, and zoonotic influenza: a systematic review of the literature". BMC Infectious Diseases. 14 (1): 480. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-14-480. PMC 4169819. PMID 25186370.
- ↑ Taubenberger JK, Morens DM (January 2006). "1918 Influenza: the mother of all pandemics". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 12 (1): 15–22. doi:10.3201/eid1201.050979. PMC 3291398. PMID 16494711.
- ↑ 227.0 227.1 227.2 227.3 227.4 227.5 227.6 227.7 "Report of the Review Committee on the Functioning of the International Health Regulations (2005) in relation to Pandemic (H1N1) 2009" (PDF). 5 May 2011. p. 37. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 May 2015. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ↑ Spreeuwenberg P, Kroneman M, Paget J (December 2018). "Reassessing the Global Mortality Burden of the 1918 Influenza Pandemic". American Journal of Epidemiology. 187 (12): 2561–2567. doi:10.1093/aje/kwy191. PMID 30202996.
- ↑ Morens DM, Fauci AS (April 2007). "The 1918 influenza pandemic: insights for the 21st century". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 195 (7): 1018–28. doi:10.1086/511989. PMID 17330793.
- ↑ Johnson NP, Mueller J (2002). "Updating the accounts: global mortality of the 1918-1920 "Spanish" influenza pandemic". Bulletin of the History of Medicine. 76 (1): 105–15. doi:10.1353/bhm.2002.0022. PMID 11875246.
- ↑ "Why the coronavirus outbreak isn't likely to be a repeat of the 1918 Spanish flu". Los Angeles Times. 6 March 2020. Retrieved 17 February 2024.
- ↑ Jackson, Claire (1 August 2009). "History lessons: the Asian Flu pandemic". The British Journal of General Practice. 59 (565): 622–623. doi:10.3399/bjgp09X453882. ISSN 0960-1643. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ↑ Jester, Barbara J.; Uyeki, Timothy M.; Jernigan, Daniel B. (2020). "Fifty Years of Influenza A(H3N2) Following the Pandemic of 1968". American Journal of Public Health. 110 (5): 669–676. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2019.305557. ISSN 0090-0036.
- ↑ Schwarzmann, Stephen W. (1 June 1971). "Bacterial Pneumonia During the Hong Kong Influenza Epidemic of 1968-1969". Archives of Internal Medicine. 127 (6): 1037. doi:10.1001/archinte.1971.00310180053006. ISSN 0003-9926.
- ↑ Donaldson LJ, Rutter PD, Ellis BM, Greaves FE, Mytton OT, Pebody RG, Yardley IE (December 2009). "Mortality from pandemic A/H1N1 2009 influenza in England: public health surveillance study". BMJ. 339: b5213. doi:10.1136/bmj.b5213. PMC 2791802. PMID 20007665.
- ↑ "First Global Estimates of 2009 H1N1 Pandemic Mortality Released by CDC-Led Collaboration". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 25 June 2012. Retrieved 7 July 2012.
- ↑ Kelly H, Peck HA, Laurie KL, Wu P, Nishiura H, Cowling BJ (5 August 2011). "The age-specific cumulative incidence of infection with pandemic influenza H1N1 2009 was similar in various countries prior to vaccination". PLOS One. 6 (8): e21828. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...621828K. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021828. PMC 3151238. PMID 21850217.
- ↑ Dawood FS, Iuliano AD, Reed C, Meltzer MI, Shay DK, Cheng PY, et al. (September 2012). "Estimated global mortality associated with the first 12 months of 2009 pandemic influenza A H1N1 virus circulation: a modelling study". The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 12 (9): 687–95. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70121-4. PMID 22738893.
- ↑ Riley, Steven; Kwok, Kin O.; Wu, Kendra M.; Ning, Danny Y.; Cowling, Benjamin J.; Wu, Joseph T.; Ho, Lai-Ming; Tsang, Thomas; Lo, Su-Vui; Chu, Daniel K. W.; Ma, Edward S. K. (21 June 2011). "Epidemiological Characteristics of 2009 (H1N1) Pandemic Influenza Based on Paired Sera from a Longitudinal Community Cohort Study". PLOS Medicine. 8 (6): e1000442. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000442. ISSN 1549-1676. PMC 3119689. PMID 21713000.
- ↑ Wong, Jessica Y.; Kelly, Heath; Ip, Dennis K. M.; Wu, Joseph T.; Leung, Gabriel M.; Cowling, Benjamin J. (November 2013). "Case fatality risk of influenza A(H1N1pdm09): a systematic review". Epidemiology (Cambridge, Mass.). 24 (6). doi:10.1097/EDE.0b013e3182a67448. ISSN 1044-3983. PMC 3809029. PMID 24045719.
- ↑ "WHO Europe – Influenza". World Health Organization (WHO). June 2009. Archived from the original on 17 June 2009. Retrieved 12 June 2009.
- ↑ "Key Facts About Influenza (Flu)". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2 May 2023. Retrieved 17 February 2024.
- ↑ Tokars JI, Olsen SJ, Reed C (May 2018). "Seasonal Incidence of Symptomatic Influenza in the United States". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 66 (10): 1511–1518. doi:10.1093/cid/cix1060. PMC 5934309. PMID 29206909.
- ↑ "Influenza: Fact sheet". World Health Organization (WHO). 6 November 2018. Archived from the original on 17 December 2019. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "H1N1 fatality rates comparable to seasonal flu". The Malaysian Insider. Washington, D.C., USA. Reuters. 17 September 2009. Archived from the original on 20 October 2009. Retrieved 26 September 2009.
- ↑ 246.0 246.1 Taubenberger JK, Hultin JV, Morens DM (2007). "Discovery and characterization of the 1918 pandemic influenza virus in historical context". Antiviral Therapy. 12 (4 Pt B): 581–91. PMC 2391305. PMID 17944266.
- ↑ Heinen PP (15 September 2003). "Swine influenza: a zoonosis". Veterinary Sciences Tomorrow. ISSN 1569-0830. Archived from the original on 11 February 2007. Retrieved 28 December 2016.
- ↑ Shimizu K (October 1997). "[History of influenza epidemics and discovery of influenza virus]". Nihon Rinsho. Japanese Journal of Clinical Medicine. 55 (10): 2505–11. PMID 9360364.
- ↑ Smith W, Andrewes CH, Laidlaw PP (1933). "A virus obtained from influenza patients". Lancet. 2 (5732): 66–68. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)78541-2.
- ↑ Palese P (December 2004). "Influenza: old and new threats". Nature Medicine. 10 (12 Suppl): S82–87. doi:10.1038/nm1141. PMID 15577936.
- ↑ "Sir Frank Macfarlane Burnet Biographical". Nobel Foundation. 1960. Archived from the original on 26 January 2009. Retrieved 22 October 2006.
- ↑ Hoyt K (2006). "Vaccine Innovation: Lessons from World War II". Journal of Public Health Policy. 27 (1): 38–57. doi:10.1057/palgrave.jphp.3200064. PMID 16681187.
- ↑ Lynch JP, Walsh EE (April 2007). "Influenza: evolving strategies in treatment and prevention". Seminars in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 28 (2): 144–58. doi:10.1055/s-2007-976487. PMID 17458769.
- ↑ Putri WC, Muscatello DJ, Stockwell MS, Newall AT (June 2018). "Economic burden of seasonal influenza in the United States". Vaccine. 36 (27): 3960–66. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.05.057. PMID 29801998.
- ↑ 255.0 255.1 "Statement from President George W. Bush on Influenza". Archived from the original on 9 January 2009. Retrieved 26 October 2006.
- ↑ Brainerd, E. and M. Siegler (2003), "The Economic Effects of the 1918 Influenza Epidemic", CEPR Discussion Paper, no. 3791.
- ↑ Poland GA (March 2006). "Vaccines against avian influenza – a race against time". New England Journal of Medicine. 354 (13): 1411–13. doi:10.1056/NEJMe068047. PMID 16571885.
- ↑ 258.0 258.1 Rosenthal E, Bradsher K (16 March 2006). "Is Business Ready for a Flu Pandemic?". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 11 December 2008. Retrieved 17 April 2006.
- ↑ Bush Outlines $7 Billion Pandemic Flu Preparedness Plan US Mission to the EU. Retrieved 12 December 2009.
- ↑ "Donor Nations Pledge $1.85 Billion to Combat Bird Flu". ENS (Press release). 18 January 2006. Archived from the original on 27 January 2017. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- ↑ "Donors pledge nearly $2 billion to fight bird flu". The New York Times. Associated Press. 18 January 2006. Archived from the original on 5 June 2020. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- ↑ "Assessment of the 2009 Influenza A (H1N1) Outbreak on Selected Countries in the Southern Hemisphere". 2009. Archived from the original on 24 September 2009. Retrieved 21 September 2009.
- ↑ "Influenza A Virus Genome Project". Institute of Genomic Research. Archived from the original on 22 May 2006. Retrieved 19 October 2006.
- ↑ Subbarao K, Katz J (2004). Influenza vaccines generated by reverse genetics. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology. Vol. 283. pp. 313–42. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-06099-5_9. ISBN 978-3-642-07375-5. PMID 15298174.
- ↑ Bardiya N, Bae J (2005). "Influenza vaccines: recent advances in production technologies". Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 67 (3): 299–305. doi:10.1007/s00253-004-1874-1. PMID 15660212.
- ↑ Neirynck S, Deroo T, Saelens X, Vanlandschoot P, Jou WM, Fiers W (October 1999). "A universal influenza A vaccine based on the extracellular domain of the M2 protein". Nat. Med. 5 (10): 1157–63. doi:10.1038/13484. PMID 10502819.
- ↑ Fiers W, Neirynck S, Deroo T, Saelens X, Jou WM (December 2001). "Soluble recombinant influenza vaccines". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. 356 (1416): 1961–63. doi:10.1098/rstb.2001.0980. PMC 1088575. PMID 11779398.
- ↑ Fiers W, De Filette M, Birkett A, Neirynck S, Min Jou W (July 2004). "A "universal" human influenza A vaccine". Virus Res. 103 (1–2): 173–76. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2004.02.030. PMID 15163506.
- ↑ Petsch B, Schnee M, Vogel AB, Lange E, Hoffmann B, Voss D, et al. (November 2012). "Protective efficacy of in vitro synthesized, specific mRNA vaccines against influenza A virus infection". Nat. Biotechnol. 30 (12): 1210–16. doi:10.1038/nbt.2436. PMID 23159882. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ Adams, Stephen (8 July 2011). "Universal flu vaccine a step closer". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 14 July 2011.
- ↑ Ekiert DC, Friesen RH, Bhabha G, Kwaks T, Jongeneelen M, Yu W, et al. (August 2011). "A highly conserved neutralizing epitope on group 2 influenza A viruses". Science. 333 (6044): 843–50. Bibcode:2011Sci...333..843E. doi:10.1126/science.1204839. PMC 3210727. PMID 21737702.
- ↑ Gingerich, DA (2008). "Lymphocyte T-Cell Immunomodulator: Review of the ImmunoPharmacology of a new Veterinary Biologic" (PDF). Journal of Applied Research in Veterinary Medicine. 6 (2): 61–68. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 July 2011. Retrieved 5 December 2010.
- ↑ "Tetramer of the Influenza Neuraminidase Protein Bound by Variable Domains of Two New Human Antibodies". NIAID. Archived from the original on 5 April 2024. Retrieved 5 April 2024.
- ↑ "New Antibodies Target "Dark Side" of Influenza Virus Protein". NIH. Archived from the original on 20 March 2024. Retrieved 5 April 2024.
- ↑ Lederhofer, Julia; Tsybovsky, Yaroslav; Nguyen, Lam; Raab, Julie E.; Creanga, Adrian; Stephens, Tyler; Gillespie, Rebecca A.; Syeda, Hubza Z.; Fisher, Brian E.; Skertic, Michelle; Yap, Christina; Schaub, Andrew J.; Rawi, Reda; Kwong, Peter D.; Graham, Barney S.; McDermott, Adrian B.; Andrews, Sarah F.; King, Neil P.; Kanekiyo, Masaru (March 2024). "Protective human monoclonal antibodies target conserved sites of vulnerability on the underside of influenza virus neuraminidase". Immunity. 57 (3): 574–586.e7. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2024.02.003. Archived from the original on 9 April 2024. Retrieved 5 April 2024.
- ↑ Gorman OT, Bean WJ, Kawaoka Y, Webster RG (April 1990). "Evolution of the nucleoprotein gene of influenza A virus". Journal of Virology. 64 (4): 1487–97. doi:10.1128/JVI.64.4.1487-1497.1990. PMC 249282. PMID 2319644.
- ↑ Greger M (2007). "The Human/Animal Interface: Emergence and Resurgence of Zoonotic Infectious Diseases". Critical Reviews in Microbiology. 33 (4): 243–99. doi:10.1080/10408410701647594. PMID 18033595. Archived from the original on 1 August 2020. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ Hinshaw VS, Bean WJ, Webster RG, Rehg JE, Fiorelli P, Early G, et al. (September 1984). "Are seals frequently infected with avian influenza viruses?". Journal of Virology. 51 (3): 863–65. doi:10.1128/JVI.51.3.863-865.1984. PMC 255856. PMID 6471169.
- ↑ Capua I, Alexander DJ (June 2006). "The challenge of avian influenza to the veterinary community". Avian Pathology. 35 (3): 189–205. doi:10.1080/03079450600717174. PMID 16753610.
- ↑ Elbers A, Koch G, Bouma A (2005). "Performance of clinical signs in poultry for the detection of outbreaks during the avian influenza A (H7N7) epidemic in The Netherlands in 2003". Avian Pathol. 34 (3): 181–87. doi:10.1080/03079450500096497. PMID 16191700.
- ↑ Capua I, Mutinelli F (2001). "Low pathogenicity (LPAI) and highly pathogenic (HPAI) avian influenza in turkeys and chicken". A Colour Atlas and Text on Avian Influenza. Bologna: Papi Editore. pp. 13–20. ISBN 978-88-88369-00-6. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016.
- ↑ Bano S, Naeem K, Malik S (2003). "Evaluation of pathogenic potential of avian influenza virus serotype H9N2 in chickens". Avian Dis. 47 (3 Suppl): 817–22. doi:10.1637/0005-2086-47.s3.817. PMID 14575070.
- ↑ Swayne D, Suarez D (2000). "Highly pathogenic avian influenza". Rev Sci Tech. 19 (2): 463–82. doi:10.20506/rst.19.2.1230. PMID 10935274.
- ↑ Li KS, Guan Y, Wang J, Smith GJ, Xu KM, Duan L, et al. (July 2004). "Genesis of a highly pathogenic and potentially pandemic H5N1 influenza virus in eastern Asia". Nature. 430 (6996): 209–13. Bibcode:2004Natur.430..209L. doi:10.1038/nature02746. PMID 15241415. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ Li KS, Guan Y, Wang J, Smith GJ, Xu KM, Duan L, et al. (2005). Knobler SL, Mack A, Mahmoud A, Lemon SM (eds.). Today's Pandemic Threat: Genesis of a Highly Pathogenic and Potentially Pandemic H5N1 Influenza Virus in Eastern Asia. The Threat of Pandemic Influenza: Are We Ready? Workshop Summary. The National Academies Press. pp. 116–30. doi:10.17226/11150. ISBN 978-0-309-09504-4. PMID 20669448. Archived from the original on 5 August 2012. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ↑ Liu J (2006). "Avian influenza – a pandemic waiting to happen?". J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 39 (1): 4–10. PMID 16440117. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 July 2016. Retrieved 28 December 2016.
- ↑ Salomon R, Webster RG (February 2009). "The influenza virus enigma". Cell. 136 (3): 402–10. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.029. PMC 2971533. PMID 19203576.
- ↑ Barboza, David (31 March 2013). "Lesser-Known Strain of Bird Flu Kills 2 in China". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 27 June 2017.
- ↑ "Human infection with influenza A(H7N9) virus in China". World Health Organization (WHO). 1 April 2013. Archived from the original on 29 July 2016. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
So far no further cases have been identified among the 88 identified contacts under follow up.
- ↑ Moisse, Katie (18 April 2013). "Deadly Bird Flu Spreading in China, Unclear How". ABC News. Archived from the original on 5 November 2016.
- ↑ "Background and summary of human infection with influenza A(H7N9) virus – as of 5 April 2013" (PDF). World Health Organization (WHO). 5 April 2013. Archived from the original on 27 April 2013. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- ↑ "Analysis of recent scientific information on avian influenza A(H7N9) virus". World Health Organization. 10 February 2017. Archived from the original on 31 July 2020. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- ↑ 293.0 293.1 293.2 Kothalawala H, Toussaint MJ, Gruys E (June 2006). "An overview of swine influenza". Vet Q. 28 (2): 46–53. doi:10.1080/01652176.2006.9695207. PMID 16841566.
- ↑ Myers KP, Olsen CW, Gray GC (April 2007). "Cases of swine influenza in humans: a review of the literature". Clin. Infect. Dis. 44 (8): 1084–88. doi:10.1086/512813. PMC 1973337. PMID 17366454.
- ↑ Zampaglione, Maria (29 April 2009). "Press Release: A/H1N1 influenza like human illness in Mexico and the USA: OIE statement". World Organisation for Animal Health. Archived from the original on 30 April 2009. Retrieved 29 April 2009.
- ↑ Grady, Denise (30 April 2009). "W.H.O. Gives Swine Flu a Less Loaded, More Scientific Name". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 9 November 2012. Retrieved 31 March 2010.
- ↑ McNeil Jr, Donald G (1 May 2009). "Virus's Tangled Genes Straddle Continents, Raising a Mystery About Its Origins". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 7 May 2009. Retrieved 31 March 2010.
Further reading[edit | edit source]
|
General
History
Microbiology
|
Pathogenesis
Epidemiology
Treatment and prevention
Research
|
External links[edit | edit source]
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- "Seasonal Influenza". Centre for Health Protection. Hong Kong. Archived from the original on 2 August 2020. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- "What you need to know about influenza (flu) from CDC". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 7 February 2020. Archived from the original on 23 May 2019. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
Categories: [Influenza] [Animal viral diseases] [Healthcare-associated infections] [RTT] [RTTEM] [Vaccine-preventable diseases] [Airborne diseases] [RTTOSh]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 06/20/2024 06:12:16 | 95 views
☰ Source: https://mdwiki.org/wiki/Influenza | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
![Tetramer of influenza neuraminidase protein bound by variable domains of two new human antibodies targeting its dark side (1G01 and DA03E17)[273][274][275]](tmp/50nK4xcVk1Dj/data/media/images/456px-53567915080016dd03a56o.jpg)

 KSF
KSF