Foodborne Illness
 From Mdwiki
From Mdwiki
| Foodborne illness | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Foodborne disease[1] | |
| |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Nausea, Vomiting[2] |
| Causes | Bacillus cereus, Escherichia coli, Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus[3] |
| Risk factors | Improper handling, or food storage[4] |
| Diagnostic method | Stool test, sigmoidoscopy[5] |
| Differential diagnosis | Acute hepatitis,acute cholecystitis,mesenteric ischemia[5] |
| Prevention | Consists of good food safety practices,such as via cooking food sufficiently[6] [7] |
| Treatment | Antiemetics, antibiotic therapy[5] |
| Frequency | 600 million cases of foodborne diseases (and 420,000 deaths)[8] |
Foodborne illness (also foodborne disease or food poisoning)[9] is any illness resulting from the spoilage of contaminated food by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, or parasites that contaminate food,[6] as well as prions (the agents of mad cow disease), and toxins such as aflatoxins in peanuts, poisonous mushrooms[10]
Symptoms vary depending on the cause but often include vomiting, fever, and aches, and may include diarrhea. Bouts of vomiting can be repeated with an extended delay in between, because even if infected food was eliminated from the stomach in the first bout, microbes, like bacteria, can pass through the stomach into the intestine and begin to multiply. Some types of microbes stay in the intestine.[11][10][12]
For contaminants requiring an incubation period, symptoms may not manifest for hours to days, depending on the cause and on quantity of consumption. Longer incubation periods tend to cause those affected to not associate the symptoms with the item consumed.[13]
Signs and symptoms[edit | edit source]
In terms of the presentation of Foodborne illness we find the following, though this is not an exaustive list:[2]
Causes[edit | edit source]
Foodborne illness usually arises from improper handling, preparation, or food storage. Good hygiene practices before, during, and after food preparation can reduce the chances of contracting an illness. There is a consensus in the public health community that regular hand-washing is one of the most effective defenses against the spread of foodborne illness. The action of monitoring food to ensure that it will not cause foodborne illness is known as food safety. Foodborne disease can also be caused by a large variety of toxins that affect the environment.[4][14]
Furthermore, foodborne illness can be caused by a number of chemicals, such as pesticides, medicines, and natural toxic substances such as vomitoxin, poisonous mushrooms or reef fish.[15]
Bacteria[edit | edit source]
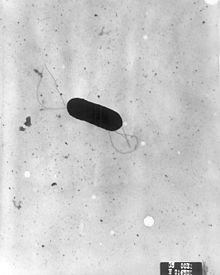
Bacteria are a common cause of foodborne illness. The United Kingdom, in 2000, reported the individual bacteria involved as the following: Campylobacter jejuni 77.3%, Salmonella 20.9%, Escherichia coli O157:H7 1.4%, and all others less than 0.56%.[16] In the past, bacterial infections were thought to be more prevalent because few places had the capability to test for norovirus and no active surveillance was being done for this particular agent. Toxins from bacterial infections are delayed because the bacteria need time to multiply. As a result, symptoms associated with intoxication are usually not seen until 12–72 hours or more after eating contaminated food. However, in some cases, such as Staphylococcal food poisoning, the onset of illness can be as soon as 30 minutes after ingesting contaminated food.[17]
Most common bacterial foodborne pathogens are:
- Campylobacter jejuni which can lead to secondary Guillain–Barré syndrome and periodontitis[18]
- Clostridium perfringens, the "cafeteria germ"[19][20]
- Salmonella spp. – its S. typhimurium infection is caused by consumption of eggs or poultry that are not adequately cooked or by other interactive human-animal pathogens[21][22][23]
- Escherichia coli O157:H7 enterohemorrhagic (EHEC) which can cause hemolytic-uremic syndrome[24][25]
Other common bacterial foodborne pathogens are:[3]
- Bacillus cereus
- Escherichia coli, other virulence properties, such as enteroinvasive (EIEC), enteropathogenic (EPEC), enterotoxigenic (ETEC), enteroaggregative (EAEC or EAgEC)
- Listeria monocytogenes
- Shigella spp.
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Staphylococcal enteritis
- Streptococcus
- Vibrio cholerae, including O1 and non-O1
- Vibrio parahaemolyticus
- Vibrio vulnificus
- Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis
Less common bacterial agents:
- Brucella spp.[26]
- Coxiella burnetii or Q fever[27]
Enterotoxins[edit | edit source]
In addition to disease caused by direct bacterial infection, some foodborne illnesses are caused by enterotoxins (exotoxins targeting the intestines). Enterotoxins can produce illness even when the microbes that produced them have been killed. Symptom appearance varies with the toxin but may be rapid in onset, as in the case of enterotoxins of Staphylococcus aureus in which symptoms appear in one to six hours.[28] This causes intense vomiting including or not including diarrhea (resulting in staphylococcal enteritis), and staphylococcal enterotoxins (most commonly staphylococcal enterotoxin A but also including staphylococcal enterotoxin B) are the most commonly reported enterotoxins although cases of poisoning are likely underestimated.[29] It occurs mainly in cooked and processed foods due to competition with other biota in raw foods, and humans are the main cause of contamination as a substantial percentage of humans are persistent carriers of S. aureus.[29] The CDC has estimated about 240,000 cases per year in the United States.[30]
Enterotoxins include the following:[31]
The rare but potentially deadly disease botulism occurs when the anaerobic bacterium Clostridium botulinum grows in improperly canned low-acid foods and produces botulin, a powerful paralytic toxin.[32]
Pseudoalteromonas tetraodonis, certain species of Pseudomonas and Vibrio, and some other bacteria, produce the lethal tetrodotoxin.[33][34]
Emerging foodborne pathogens[edit | edit source]
- Aeromonas hydrophila, Aeromonas caviae, Aeromonas sobria[35]
- Yersinia enterocolitica have recently increased to an annual basis (Scandinavian outbreaks), connected to the non-canonical contamination of pre-washed salad.[36]
Mycotoxins and alimentary mycotoxicoses[edit | edit source]
The term alimentary mycotoxicosis refers to the effect of poisoning by mycotoxins through food consumption. The term mycotoxin is usually reserved for the toxic chemical products produced by fungi that readily colonize crops. Mycotoxins sometimes have important effects on human and animal health. For example, an outbreak which occurred in the UK in 1960 caused the death of 100,000 turkeys which had consumed aflatoxin-contaminated peanut meal. In the USSR in World War II, 5,000 people died due to alimentary toxic aleukia (ALA).[37] [38]The common foodborne Mycotoxins include:
- Aflatoxins – originating from Aspergillus parasiticus and Aspergillus flavus. They are frequently found in tree nuts, peanuts, maize, sorghum and other oilseeds, including corn and cottonseeds. The pronounced forms of Aflatoxins are those of B1, B2, G1, and G2, amongst which Aflatoxin B1 predominantly targets the liver, which will result in necrosis, cirrhosis, and carcinoma.[39][40] In the US, the acceptable level of total aflatoxins in foods is less than 20 μg/kg, except for Aflatoxin M1 in milk, which should be less than 0.5 μg/kg.[41] The official document can be found at FDA's website.[42][43]
- Altertoxins – are those of alternariol (AOH), alternariol methyl ether (AME), altenuene (ALT), altertoxin-1 (ATX-1), tenuazonic acid (TeA), and radicinin (RAD), originating from Alternaria spp. Some of the toxins can be present in sorghum, ragi, wheat and tomatoes.[44][45][46] Some research has shown that the toxins can be easily cross-contaminated between grain commodities, suggesting that manufacturing and storage of grain commodities is a critical practice.[47]
- Citrinin[48]
- Citreoviridin[49]
- Cyclopiazonic acid[50]
- Ergot alkaloids [51]
- Fumonisins – crop corn can be easily contaminated by the fungi Fusarium moniliforme, and its fumonisin B1 will cause leukoencephalomalacia (LEM) in horses, pulmonary edema syndrome (PES) in pigs, liver cancer in rats and esophageal cancer in humans.[52][53] For human and animal health, both the FDA and the EC have regulated the content levels of toxins in food and animal feed.[54][55]
- Fusaric acid[56]
- Kojic acid[57](does not present health concern)
- Moniliformin[58]
- 3-Nitropropionic acid[59]
- Nivalenol[60]
- Ochratoxins – in Australia, The Limit of Reporting (LOR) level for ochratoxin A (OTA) analyses in 20th Australian Total Diet Survey was 1 µg/kg,[61] whereas the EC restricts the content of OTA to 5 µg/kg in cereal commodities, 3 µg/kg in processed products and 10 µg/kg in dried vine fruits.[62]
- Patulin – currently, this toxin has been advisably regulated on fruit products. The EC and the FDA have limited it to under 50 µg/kg for fruit juice and fruit nectar, while limits of 25 µg/kg for solid-contained fruit products and 10 µg/kg for baby foods were specified by the EC.[62][63]
- Sporidesmin A[64]
- Sterigmatocystin[65]
- Tremorgenic mycotoxins – five of them have been reported to be associated with molds found in fermented meats. These are fumitremorgen B, paxilline, penitrem A, verrucosidin, and verruculogen.[66]
- Trichothecenes – sourced from Cephalosporium, Fusarium, Myrothecium, Stachybotrys, and Trichoderma. The toxins are usually found in molded maize, wheat, corn, peanuts and rice, or animal feed of hay and straw.[67][68] Four trichothecenes, T-2 toxin, HT-2 toxin, diacetoxyscirpenol (DAS), and deoxynivalenol (DON) have been most commonly encountered by humans and animals. The consequences of oral intake of, or dermal exposure to, the toxins will result in alimentary toxic aleukia, neutropenia, aplastic anemia, thrombocytopenia and/or skin irritation.[69][70][71] In 1993, the FDA issued a document for the content limits of DON in food and animal feed at an advisory level.[72] In 2003, US published a patent that is very promising for farmers to produce a trichothecene-resistant crop.[73]
- Zearalenone[74]
- Zearalenols[75]
Viruses[edit | edit source]
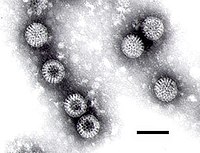
Viral infections make up perhaps one third of cases of food poisoning in developed countries. In the US, more than 50% of cases are viral and noroviruses are the most common foodborne illness. Foodborne viral infection are usually of intermediate, 1–3 days incubation period, causing illnesses which are self-limited in otherwise healthy individuals[76][77]
These are viral foodborne infections:
- Enterovirus[78]
- Hepatitis A is distinguished from other viral causes by its prolonged (2–6 week) incubation period and its ability to spread beyond the stomach and intestines into the liver. It often results in jaundice, or yellowing of the skin, but rarely leads to chronic liver dysfunction. The virus has been found to cause infection due to the consumption of fresh-cut produce which has fecal contamination.[79][80]
- Hepatitis E[81]
- Norovirus[82]
- Rotavirus[83]
Parasites[edit | edit source]
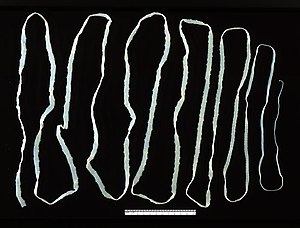
Most foodborne parasites are zoonoses.[84]
- Platyhelminthes:[85][86]
- Diphyllobothrium sp.
- Nanophyetus sp.
- Taenia saginata
- Taenia solium
- Fasciola hepatica
- Nematode:[87]
- Protozoa:[88]
- Acanthamoeba and other free-living amoebae
- Cryptosporidiosis
- Cyclospora cayetanensis
- Entamoeba histolytica
- Giardia lamblia
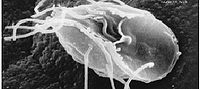
Giardia lamblia - Sarcocystis hominis
- Sarcocystis suihominis
- Toxoplasma
Natural toxins[edit | edit source]
Several foods can naturally contain toxins, many of which are not produced by bacteria, plants in particular may be toxic. In evolutionary terms, animals, for example, can escape being eaten by fleeing; plants can use only passive defenses such as poisons and distasteful substances, for example capsaicin in chili peppers and pungent sulfur compounds in garlic and onions. [89]
These are the following:
- Ciguatera poisoning[90]
- Grayanotoxin [91]
- Hormones from the thyroid glands of slaughtered animals (especially Triiodothyronine in cases of hamburger thyrotoxicosis or alimentary thyrotoxicosis)[92][93][94][95][96]
- Mushroom toxins[97]
- Phytohaemagglutinin[98]
- Pyrrolizidine alkaloids[99]
- Shellfish toxin, including paralytic shellfish poisoning, diarrhetic shellfish poisoning, neurotoxic shellfish poisoning[100][101][102]
- Scombrotoxin[103]
- Tetrodotoxin (fugu fish poisoning)[104]
Some plants contain substances which are toxic in large doses, but have therapeutic properties in appropriate dosages.[105][106]
- Foxglove contains cardiac glycosides.
- Poisonous hemlock (conium) has medicinal uses.
Other pathogenic agents[edit | edit source]
- Prions, resulting in Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD) and its variant (vCJD)[107]
"Ptomaine poisoning" [edit | edit source]
Ptomaine poisoning was a myth that persisted in the public consciousness, in newspaper headlines, and legal cases as an official diagnosis, decades after it had been disproven scientifically in the 1910s.[108]
In the 19th century, the Italian chemist Francesco Selmi, of Bologna, introduced the generic name ptomaine (from Greek ptōma, "fall, fallen body, corpse") for alkaloids found in decaying animal and vegetable matter, especially (as reflected in their names) putrescine and cadaverine.[109] The 1892 Merck's Bulletin stated, "We name such products of bacterial origin ptomaines; and the special alkaloid produced by the comma bacillus is variously named Cadaverine, Putrescine, etc."[110] While The Lancet stated, "The chemical ferments produced in the system, the... ptomaines which may exercise so disastrous an influence"[111].
Tainted potato salad sickening hundreds at a Communist political convention in Massillon, Ohio,[112] and aboard a Washington DC cruise boat in separate incidents during a single week in 1932 drew national attention to the dangers of so-called "ptomaine poisoning" in the pages of the American news weekly, Time.[113] Another newspaper article from 1944 told of more than 150 persons being hospitalized in Chicago with ptomaine poisoning apparently from rice pudding served by a chain of restaurants.[114]
Mechanism[edit | edit source]
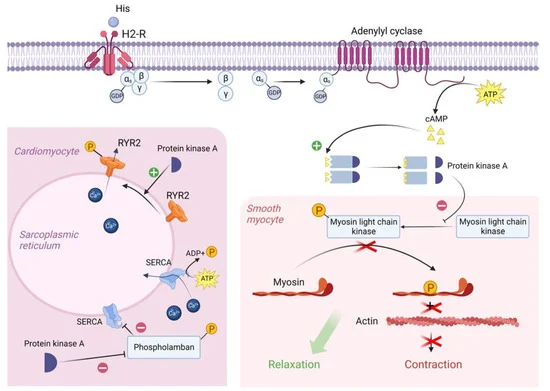
Incubation period[edit | edit source]
The delay between the consumption of contaminated food and the appearance of the first symptoms of illness is called the incubation period. This ranges from hours to days , depending on the agent, and on how much was consumed. If symptoms occur within one to six hours after eating the food, it suggests that it is caused by a bacterial toxin.[116][13][117][1]
The long incubation period of many foodborne illnesses tends to cause those affected to attribute their symptoms to gastroenteritis.[118]
During the incubation period, microbes pass through the stomach into the intestine, attach to the cells lining the intestinal walls, and begin to multiply there. Some types of microbes stay in the intestine, some produce a toxin that is absorbed into the bloodstream, and some can directly invade the deeper body tissues. The symptoms produced depend on the type of microbe.[119]
Infectious dose[edit | edit source]
The infectious dose is the amount of agent that must be consumed to give rise to symptoms of foodborne illness, and varies according to the agent and the consumer's age and overall health. Pathogens vary in minimum infectious dose; for example, Shigella sonnei has a low estimated minimum dose of < 500 colony-forming units (CFU) while Staphylococcus aureus has a relatively high estimate.[120]
In the case of Salmonella a relatively large inoculum of >50,000 organisms is necessary to produce symptoms in healthy human volunteers, as Salmonellae are very sensitive to acid. An unusually high stomach pH level greatly reduces the number of bacteria required to cause symptoms.[121][122]
Unaccustomed to organisms[edit | edit source]
Foodborne illness often occurs as travelers' diarrhea in persons whose gut microbiota is unaccustomed to organisms endemic to the visited region, this effect of microbiologic naivete is compounded by any food safety lapses in the food's preparation.[123]
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
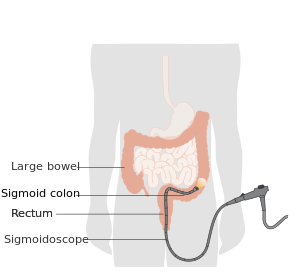
In terms of the diagnosis of foodborne illness we find that a physical exam and a review of certain factors that may cause the symptoms being experienced are done, as well as:[5][124]
- Complete blood count
- Stool test
- Sigmoidoscopy
Differential diagnosis[edit | edit source]
The DDx of Foodborne illness is as follows:[5]
- Acute hepatitis
- Acute cholecystitis
- Mesenteric ischemia
Prevention[edit | edit source]
Prevention is mainly the role of the state, through the definition of strict rules of hygiene and a public services of veterinary surveying of animal products in the food chain, from farming to the transformation industry and delivery (shops and restaurants). This regulation includes:[6] [7][125][126]
- Traceability: in a final product, it must be possible to know the origin of the ingredients (originating farm, identification of the harvesting or of the animal) and where and when it was processed; the origin of the illness can thus be tracked and solved (and possibly penalized), and the final products can be removed from the sale if a problem is detected;
- Enforcement of hygiene procedures ;
- Power of control and of law enforcement of veterinarians.
In August 2006, the United States Food and Drug Administration approved phage therapy which involves spraying meat with viruses that infect bacteria, and thus preventing infection. This has raised concerns, because without mandatory labelling consumers would not be aware that meat and poultry products have been treated with the spray.[127]
At home, prevention mainly consists of good food safety practices. Many forms of bacterial poisoning can be prevented by cooking food sufficiently, and either eating it quickly or refrigerating it effectively.[6]
Techniques that help prevent food borne illness in the kitchen are hand washing, rinsing produce,[128] preventing cross-contamination, proper storage, and maintaining cooking temperatures. In general, freezing or refrigerating prevents virtually all bacteria from growing, and heating food sufficiently kills parasites, viruses, and most bacteria. Bacteria grow most rapidly at the range of temperatures between 40 and 140 °F (4 and 60 °C), called the "danger zone". Storing food below or above the "danger zone" can effectively limit the production of toxins. For storing leftovers, the food must be put in shallow containers for quick cooling and must be refrigerated within two hours. When food is reheated, it must reach an internal temperature of 165 °F (74 °C) or until hot or steaming to kill bacteria.[129]
Treatment[edit | edit source]
The management of Foodborne illness in an affected individual, is done via the following:[5]
- Antiemetics
- Antibiotic therapy
- Rehydration therapy
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
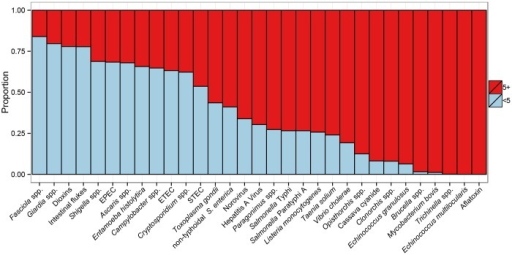
Asymptomatic subclinical infection may help spread these diseases, particularly Staphylococcus aureus, Campylobacter, Salmonella, Shigella, Enterobacter, Vibrio cholerae, and Yersinia.[120] For example, as of 1984 it was estimated that in the United States, 200,000 people were asymptomatic carriers of Salmonella.[120]
Infants[edit | edit source]
Globally, infants are a group that is especially vulnerable to foodborne disease. The World Health Organization has issued recommendations for the preparation, use and storage of prepared formulas. Breastfeeding remains the best preventive measure for protection from foodborne infections in infants.[130]
United States[edit | edit source]
In the United States, using FoodNet data from 2000 to 2007, the CDC estimated there were 47.8 million foodborne illnesses per year (16,000 cases for 100,000 inhabitants)[131] with 9.4 million of these caused by 31 known identified pathogens.[132]
- 127,839 were hospitalized (43 per 100,000 inhabitants per year).[133][134][135]
- 3,037 people died (1.0 per 100,000 inhabitants per year).[134][135]
|
|
United Kingdom[edit | edit source]
According to a 2012 report from the Food Standards Agency, there were around a million cases of foodborne illness per year.[136]
- 20,000 were hospitalized (32 per 100,000 inhabitants);[136][137]
- 500 people died (0.80 per 100,000 inhabitants).[136][137]
France[edit | edit source]
This data pertains to reported medical cases of 23 specific pathogens, as opposed to total population estimates of all foodborne illness for the United States.In France, for 750,000 cases :[138][139][140]
- 70,000 people consulted in the emergency department of a hospital (113 per 100,000 inhabitants);
- 113,000 people were hospitalized (182 per 100,000 inhabitants);
- 460 people died (0.75 per 100,000 inhabitants).
|
|
Australia[edit | edit source]
A study by the Australian National University, published in November 2014, found in 2010 that there were an estimated 4.1 million cases of foodborne gastroenteritis acquired in Australia on average each year, along with 5,140 cases of non-gastrointestinal illness. The study was funded by the Australian Department of Health, Food Standards Australia New Zealand and the NSW Food Authority.[142]
The main causes are Norovirus, pathogenic Escherichia coli, Campylobacter spp. and non-typhoidal Salmonella spp., although the causes of approximately 80% of illnesses were unknown. Approximately 25% of the 15.9 million episodes of gastroenteritis that occur in Australia were estimated to be transmitted by contaminated food. This equates to an average of approximately one episode of foodborne gastroenteritis every five years per person. Data on the number of hospitalisations and deaths represent the occurrence of serious foodborne illness. Including gastroenteritis, non-gastroenteritis and sequelae, there were an estimated annual 31,920 hospitalisations due to foodborne illness and 86 deaths due to foodborne illness circa 2010.A main aim of this study was to compare if foodborne illness incidence had increased over time. In this study, similar methods of assessment were applied to data from circa 2000, which showed that the rate of foodborne gastroenteritis had not changed significantly over time. Two key estimates were the total number of gastroenteritis episodes each year, and the proportion considered foodborne. In circa 2010, it was estimated that 25% of all episodes of gastroenteritis were foodborne. By applying this proportion of episodes due to food to the incidence of gastroenteritis circa 2000, there were an estimated 4.3 million episodes of foodborne gastroenteritis circa 2000, although credible intervals overlap with 2010.[142][143]
This study replaces a previous estimate of 5.4 million cases of foodborne illness in Australia every year, causing:[144]
- 18,000 hospitalizations
- 120 deaths (0.5 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants)
- 2.1 million lost days off work
- 1.2 million doctor consultations
- 300,000 prescriptions for antibiotics.
Most foodborne disease outbreaks in Australia have been linked to raw or minimally cooked eggs or poultry.[145] The Australian Food Safety Information Council estimates that one third of cases of food poisoning occur in the home.[146]
Outbreaks[edit | edit source]
The vast majority of reported cases of foodborne illness occur as individual or sporadic cases. The origin of most sporadic cases is undetermined. In the United States, where people eat outside the home frequently, the majority of cases originate from commercial food facilities. An outbreak is defined as occurring when two or more people experience similar illness after consuming food from a common source.Often, a combination of events contributes to an outbreak, for example, food might be left at room temperature for many hours, allowing bacteria to multiply which is compounded by inadequate cooking which results in a failure to kill the dangerously elevated bacterial levels.Outbreaks are usually identified when those affected know each other. Outbreaks can also be identified by public health staff when there are unexpected increases in laboratory results for certain strains of bacteria. Outbreak detection and investigation in the United States is primarily handled by local health jurisdictions and is different from district to district. It is estimated that a low percentage of outbreaks are detected.[147][10][148]
Society and culture[edit | edit source]
United Kingdom[edit | edit source]
In postwar Aberdeen (1964) a large-scale (>400 cases) outbreak of typhoid occurred, caused by contaminated corned beef which had been imported from Argentina. The corned beef was placed in cans and because the cooling plant had failed, cold river water from the Plate estuary was used to cool the cans. One of the cans had a defect and the meat inside was contaminated. This meat was then sliced using a meat slicer in a shop in Aberdeen, and a lack of cleaning the machinery led to spreading the contamination to other meats cut in the slicer. These meats were then eaten by the people of Aberdeen who then became ill.[149][150]
Serious outbreaks of foodborne illness since the 1970s prompted key changes in UK food safety law. These included the death of 19 patients in the Stanley Royd Hospital outbreak[151] and the bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE, mad cow disease) outbreak identified in the 1980s. The death of 21 people in the 1996 Wishaw outbreak of E. coli O157[152][153] was a precursor to the establishment of the Food Standards Agency which, according to Tony Blair in the 1998 white paper A Force for Change Cm 3830, "would be powerful, open and dedicated to the interests of consumers".[154]
In May 2015, for the second year running, England's Food Standards Agency devoted its annual Food Safety Week to – "The Chicken Challenge". The focus was on the handling of raw chicken in the home and in catering facilities in a drive to reduce the high levels of food poisoning from the campylobacter bacterium. Anne Hardy argues that widespread public education of food hygiene can be useful, particularly through media (TV cookery programmes) and advertisement. She points to the examples set by Scandinavian societies.[155]
United States[edit | edit source]
.jpg)
In 2001, the Center for Science in the Public Interest petitioned the United States Department of Agriculture to require meat packers to remove spinal cords before processing cattle carcasses for human consumption, a measure designed to lessen the risk of infection by variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease. The petition was supported by the American Public Health Association, the Consumer Federation of America, the Government Accountability Project, the National Consumers League, and Safe Tables Our Priority.[156]
None of the US Department of Health and Human Services targets[157] regarding incidence of foodborne infections were reached in 2007.[158]
A report issued in June 2018 by NBC's Minneapolis station using research by both the CDC and the Minnesota Department of Health concluded that foodborne illness is on the rise in the U.S.[159]
Organizations[edit | edit source]
The World Health Organization Department of Food Safety and Zoonoses (FOS) provides scientific advice for organizations and the public on issues concerning the safety of food. Its mission is to lower the burden of foodborne disease, thereby strengthening the health security and sustainable development of Member States. Foodborne and waterborne diarrheal diseases kill millions of people annually, most of whom are children. WHO works closely with the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) to address food safety issues along the entire food production chain—from production to consumption—using new methods of risk analysis. These methods provide efficient, science-based tools to improve food safety, thereby benefiting both public health and economic development.[160][161]
International Food Safety Authorities Network (INFOSAN)[edit | edit source]
The International Food Safety Authorities Network (INFOSAN) is a joint program of the WHO and FAO. INFOSAN has been connecting national authorities from around the globe since 2004, with the goal of preventing the international spread of contaminated food and foodborne disease and strengthening food safety systems globally. [162]
Prioritisation of foodborne pathogens[edit | edit source]
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and The World Health Organization have published a global ranking of foodborne parasites using a multicriteria ranking tool concluding that Taenia solium was the most relevant, followed by Echinococcus granulosus, Echinococcus multilocularis, and Toxoplasma gondii.[163] The same method was used regionally to rank the most important foodborne parasites in Europe ranking Echinococcus multilocularis of highest relevance, followed by Toxoplasma gondii and Trichinella spiralis.[164]
Regulatory steps[edit | edit source]
Food may be contaminated during all stages of food production and retailing, in order to prevent viral contamination, regulatory authorities in Europe have enacted several measures:
- European Commission Regulation (EC) No 2073/2005 of November 15, 2005[165]
- European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Standard method for the detection of norovirus and hepatitis A virus in food products [166]
- CODEX Committee on Food Hygiene (CCFH): Guideline for the application of general principles of food hygiene for the control of viruses in food[167]
See also[edit | edit source]
- American Public Health Association v. Butz
- Food allergy
- Food microbiology
- Food quality
- Food safety
- Food spoilage
- Food testing strips
- Gastroenteritis
- List of foodborne illness outbreaks by country
- List of food contamination incidents
- Mycotoxicology
- STOP Foodborne Illness
- United States Disease Control and Prevention
- Zoonotic pathogens
Notes[edit | edit source]
- 1.^ NIH news has been used for this source, due to its useful text
- 2.^ It should be noted that this list indicates figures from more that one particular year
References[edit | edit source]
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- ↑ "Foodborne diseases". www.who.int. Archived from the original on March 12, 2024. Retrieved April 18, 2024.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Food Poisoning Symptoms". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. October 24, 2023. Archived from the original on March 20, 2024. Retrieved March 31, 2024.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 CDC (March 18, 2020). "Foodborne Germs and Illnesses". Archived from the original on September 5, 2015. Retrieved August 9, 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - ↑ 4.0 4.1 "10 Dangerous Food Safety Mistakes". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. October 24, 2023. Archived from the original on March 31, 2024. Retrieved March 31, 2024.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Switaj, Timothy L.; Winter, Kelly J.; Christensen, Scott R. (September 1, 2015). "Diagnosis and Management of Foodborne Illness". American Family Physician. pp. 358–365. Archived from the original on August 18, 2022. Retrieved March 31, 2024.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 "Foodborne Illness - Frequently Asked Questions". US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Archived from the original on March 3, 2011. Retrieved July 3, 2016.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Todd, E (July 16, 2020). "Food-Borne Disease Prevention and Risk Assessment". International journal of environmental research and public health. 17 (14). doi:10.3390/ijerph17145129. PMID 32708573. Archived from the original on May 14, 2023. Retrieved April 1, 2024.
- ↑ "Estimating the burden of foodborne diseases". www.who.int. Archived from the original on January 9, 2024. Retrieved March 31, 2024.
- ↑ "food poisoning" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Bintsis, T (2017). "Foodborne pathogens". AIMS microbiology. 3 (3): 529–563. doi:10.3934/microbiol.2017.3.529. PMID 31294175. Archived from the original on October 28, 2023. Retrieved April 5, 2024.
- ↑ Bold, J; Rostami, K (2011). "Foodborne, food related illness and role of the healthcare professionals". Gastroenterology and hepatology from bed to bench. 4 (1): 1–2. PMID 24834147. Archived from the original on April 5, 2024. Retrieved April 2, 2024.
- ↑ "Food Poisoning - NIDDK". National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Archived from the original on February 13, 2024. Retrieved April 11, 2024.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Chai, S. J.; Gu, W.; O'Connor, K. A.; Richardson, L. C.; Tauxe, R. V. (2019). "Incubation periods of enteric illnesses in foodborne outbreaks, United States, 1998–2013". Epidemiology and Infection. 147. doi:10.1017/S0950268819001651. PMID 31587689. Archived from the original on April 9, 2024. Retrieved April 8, 2024.
- ↑ "NCEZID: Foodborne Disease (Food Poisoning) | What We Do | NCEZID | CDC". www.cdc.gov. December 18, 2019. Archived from the original on October 23, 2023. Retrieved April 3, 2024.
- ↑ U.S. Food and Drug (2021). "Chemicals, Metals & Pesticides in Food". Food and Drug Administration. Archived from the original on July 28, 2022. Retrieved August 9, 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - ↑ "Reducing the risk from E. coli 0157 – controlling cross-contamination". Food Standards Agency, United Kingdom. February 2011. Archived from the original on April 16, 2014. Retrieved 14 August 2016.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ↑ "Staphylococcal Food Poisoning". U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Archived from the original on February 8, 2016. Retrieved July 3, 2016.
- ↑ Humphrey T, O'Brien S, Madsen M (July 2007). "Campylobacters as zoonotic pathogens: a food production perspective". International Journal of Food Microbiology. 117 (3): 237–57. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.01.006. PMID 17368847.
- ↑ "Foodborne Illness: What Consumers Need to Know". USDA.gov. Archived from the original on March 2, 2021. Retrieved August 14, 2016.
- ↑ Kiu R, Caim S, Painset A, Pickard D, Swift C, Dougan G, et al. (October 2019). "Clostridium perfringens in England and Wales over a 7-year period indicates distribution of clonal toxigenic strains in multiple outbreaks and extensive involvement of enterotoxin-encoding (CPE) plasmids". Microbial Genomics. 5 (10): e000297. doi:10.1099/mgen.0.000297. PMC 6861862. PMID 31553300.
- ↑ Tribe IG, Cowell D, Cameron P, Cameron S (2002). "An outbreak of Salmonella typhimurium phage type 135 infection linked to the consumption of raw shell eggs in an aged care facility". Communicable Diseases Intelligence Quarterly Report. 26 (1): 38–9. PMID 11950200. Archived from the original on February 17, 2014.
- ↑ "Salmonella Infection (salmonellosis) and Animals". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Archived from the original on July 4, 2007. Retrieved August 12, 2007.
- ↑ Doyle MP, Erickson MC (June 2006). "Reducing the carriage of foodborne pathogens in livestock and poultry". Poultry Science. 85 (6): 960–73. doi:10.1093/ps/85.6.960. PMID 16776463.
- ↑ Gally DL, Stevens MP (January 2017). "Microbe Profile: Escherichia coli O157:H7 - notorious relative of the microbiologist's workhorse" (PDF). Microbiology. 163 (1): 1–3. doi:10.1099/mic.0.000387. PMID 28218576. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 31, 2020. Retrieved October 10, 2022.
- ↑ Karch H, Tarr PI, Bielaszewska M (October 2005). "Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli in human medicine". International Journal of Medical Microbiology. 295 (6–7): 405–18. doi:10.1016/j.ijmm.2005.06.009. PMID 16238016.
- ↑ Béjaoui, A; Ben Abdallah, I; Maaroufi, A (July 29, 2022). "Brucella spp. Contamination in Artisanal Unpasteurized Dairy Products: An Emerging Foodborne Threat in Tunisia". Foods (Basel, Switzerland). 11 (15). doi:10.3390/foods11152269. PMID 35954037. Archived from the original on April 24, 2024. Retrieved April 22, 2024.
- ↑ "Q fever". www.ecdc.europa.eu. July 8, 2010. Archived from the original on February 25, 2024. Retrieved April 22, 2024.
- ↑ Food poisoning: Causes Archived December 27, 2012, at the Wayback Machine. Mayo Clinic.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 Argudín MÁ, Mendoza MC, Rodicio MR (July 2010). "Food poisoning and Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins". Toxins. 2 (7): 1751–73. doi:10.3390/toxins2071751. PMC 3153270. PMID 22069659.
- ↑ Staphylococcus aureus: A Problem When Food Is Left Out Too Long Archived November 23, 2015, at the Wayback Machine. Ohio State University Extension HYG-5564-11].
- ↑ Stiles, Bradley G.; Pradhan, Kisha; Fleming, Jodie M.; Samy, Ramar Perumal; Barth, Holger; Popoff, Michel R. (September 2014). "Clostridium and Bacillus Binary Enterotoxins: Bad for the Bowels, and Eukaryotic Being". Toxins. 6 (9): 2626–2656. doi:10.3390/toxins6092626. ISSN 2072-6651. Archived from the original on November 23, 2023. Retrieved April 4, 2024.
- ↑ Jarosz, Aleksandra; Grenda, Tomasz; Goldsztejn, Magdalena; Kozak, Beata; Kwiatek, Krzysztof (November 7, 2022). "Potential risk of botulinum neurotoxin -producing clostridia occurrence in canned fish". Journal of Veterinary Research. 66 (4): 605–611. doi:10.2478/jvetres-2022-0060. Archived from the original on December 27, 2023. Retrieved April 7, 2024.
- ↑ Chau R, Kalaitzis JA, Neilan BA (July 2011). "On the origins and biosynthesis of tetrodotoxin" (PDF). Aquatic Toxicology. 104 (1–2): 61–72. Bibcode:2011AqTox.104...61C. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.04.001. PMID 21543051. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 5, 2016. Retrieved February 29, 2016.
- ↑ Jal, S.; Khora, S.S. (October 2015). "An overview on the origin and production of tetrodotoxin, a potent neurotoxin". Journal of Applied Microbiology. 119 (4): 907–916. doi:10.1111/jam.12896. Archived from the original on April 11, 2024. Retrieved April 10, 2024.
- ↑ Pessoa, RBG; de Oliveira, WF; Correia, MTDS; Fontes, A; Coelho, LCBB (2022). "Aeromonas and Human Health Disorders: Clinical Approaches". Frontiers in microbiology. 13: 868890. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.868890. PMID 35711774. Archived from the original on April 1, 2024. Retrieved April 4, 2024.
- ↑ Karlsson, Philip A.; Tano, Eva; Jernberg, Cecilia; Hickman, Rachel A.; Guy, Lionel; Järhult, Josef D.; Wang, Helen (May 13, 2021). "Molecular Characterization of Multidrug-Resistant Yersinia enterocolitica From Foodborne Outbreaks in Sweden". Frontiers in Microbiology. 12: 664665. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2021.664665. ISSN 1664-302X. PMC 8155512. PMID 34054769.
- ↑ Mount M. "Fungi and Mycotoxins" (PDF). vetmed.ucdavis.edu. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 27, 2007. Retrieved August 11, 2007.
- ↑ Awuchi, CG; Ondari, EN; Ogbonna, CU; Upadhyay, AK; Baran, K; Okpala, COR; Korzeniowska, M; Guiné, RPF (June 3, 2021). "Mycotoxins Affecting Animals, Foods, Humans, and Plants: Types, Occurrence, Toxicities, Action Mechanisms, Prevention, and Detoxification Strategies-A Revisit". Foods (Basel, Switzerland). 10 (6). doi:10.3390/foods10061279. PMID 34205122. Archived from the original on October 29, 2022. Retrieved May 8, 2024.
- ↑ "Aflatoxins". Center for Food Safety & Applied Nutrition. Archived from the original on June 10, 2009. Retrieved August 12, 2007.
- ↑ "GASGA Technical Leaflet – 3 Mycotoxins in Grain". Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Archived from the original on January 12, 2017. Retrieved August 12, 2007.
- ↑ "Chapter 2 Foodborne Hazards in Basic Food Safety for Health Workers" (PDF). World Health Organization. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 27, 2007. Retrieved August 12, 2007.
- ↑ "Sec. 683.100 Action Levels for Aflatoxins in Animal Feeds (CPG 7126.33)". Food and Drug Administration. Archived from the original on September 29, 2007. Retrieved August 13, 2007.
- ↑ Henry MH. "Mycotoxins in Feeds: CVM's Perspective". FDA.gov. Archived from the original on January 6, 2012. Retrieved January 1, 2012.
- ↑ Webley DJ, Jackson KL, Mullins JD, Hocking AD, Pitt JI (1997). "Alternaria toxins in weather-damaged wheat and sorghum in the 1995–1996 Australian harvest". Australian Journal of Agricultural Research. 48 (8): 1249–56. doi:10.1071/A97005.
- ↑ Li F, Yoshizawa T (July 2000). "Alternaria mycotoxins in weathered wheat from China". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 48 (7): 2920–4. doi:10.1021/jf0000171. PMID 10898645.
- ↑ Motta SD, Valente Soares LM (July 2001). "Survey of Brazilian tomato products for alternariol, alternariol monomethyl ether, tenuazonic acid and cyclopiazonic acid". Food Additives and Contaminants. 18 (7): 630–4. doi:10.1080/02652030117707. PMID 11469319. S2CID 45938351.
- ↑ Li FQ, Toyazaki N, Yoshizawa T (April 2001). "Production of alternaria mycotoxins by Alternaria alternata isolated from weather-damaged wheat". Journal of Food Protection. 64 (4): 567–71. doi:10.4315/0362-028X-64.4.567. PMID 11307900.
- ↑ Kamle, M; Mahato, DK; Gupta, A; Pandhi, S; Sharma, N; Sharma, B; Mishra, S; Arora, S; Selvakumar, R; Saurabh, V; Dhakane-Lad, J; Kumar, M; Barua, S; Kumar, A; Gamlath, S; Kumar, P (January 23, 2022). "Citrinin Mycotoxin Contamination in Food and Feed: Impact on Agriculture, Human Health, and Detection and Management Strategies". Toxins. 14 (2). doi:10.3390/toxins14020085. PMID 35202113. Archived from the original on April 4, 2023. Retrieved April 9, 2024.
- ↑ Nishie, K.; Cole, R. J.; Dorner, J. W. (January 1988). "Toxicity of citreoviridin". Research Communications in Chemical Pathology and Pharmacology. 59 (1): 31–52. ISSN 0034-5164. Archived from the original on June 16, 2022. Retrieved April 11, 2024.
- ↑ Chang, Perng-Kuang; Ehrlich, Kenneth; Fujii, Isao (November 6, 2009). "Cyclopiazonic Acid Biosynthesis of Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus oryzae". Toxins. 1 (2): 74–99. doi:10.3390/toxins1020074. Archived from the original on January 29, 2022. Retrieved April 13, 2024.
- ↑ Arcella, Davide; Gómez Ruiz, Jose Ángel; Innocenti, Matteo Lorenzo; Roldán, Ruth (July 2017). "Human and animal dietary exposure to ergot alkaloids". EFSA Journal. 15 (7). doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2017.4902. Archived from the original on February 7, 2023. Retrieved April 19, 2024.
- ↑ Marasas WF (1995). "Fumonisins: their implications for human and animal health". Natural Toxins. 3 (4): 193–8, discussion 221. doi:10.1002/nt.2620030405. PMID 7582616.
- ↑ Soriano JM (2004). "Occurrence of fumonisins in foods". Food Research International. 37 (10): 985–1000. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2004.06.009.
- ↑ "CVM and Fumonisins". Food and Drug Administration. Archived from the original on August 12, 2007. Retrieved August 13, 2007.
- ↑ "More contaminated maize meal products withdrawn from sale". Food Standards Agency. Archived from the original on August 13, 2007. Retrieved August 12, 2007.
- ↑ Ekwomadu, TI; Akinola, SA; Mwanza, M (November 9, 2021). "Fusarium Mycotoxins, Their Metabolites (Free, Emerging, and Masked), Food Safety Concerns, and Health Impacts". International journal of environmental research and public health. 18 (22). doi:10.3390/ijerph182211741. PMID 34831498. Archived from the original on March 19, 2023. Retrieved April 9, 2024.
- ↑ Burdock, G. A.; Soni, M. G.; Carabin, I. G. (February 2001). "Evaluation of health aspects of kojic acid in food". Regulatory toxicology and pharmacology: RTP. 33 (1): 80–101. doi:10.1006/rtph.2000.1442. ISSN 0273-2300. Archived from the original on February 28, 2023. Retrieved April 14, 2024.
- ↑ EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain, (CONTAM); Knutsen, HK; Alexander, J; Barregård, L; Bignami, M; Brüschweiler, B; Ceccatelli, S; Cottrill, B; Dinovi, M; Grasl-Kraupp, B; Hogstrand, C; Hoogenboom, LR; Nebbia, CS; Oswald, IP; Petersen, A; Rose, M; Roudot, AC; Schwerdtle, T; Vleminckx, C; Vollmer, G; Wallace, H; De Saeger, S; Eriksen, GS; Farmer, P; Fremy, JM; Gong, YY; Meyer, K; Naegeli, H; Parent-Massin, D; van Egmond, H; Altieri, A; Colombo, P; Eskola, M; van Manen, M; Edler, L (March 2018). "Risks to human and animal health related to the presence of moniliformin in food and feed". EFSA journal. European Food Safety Authority. 16 (3): e05082. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2018.5082. PMID 32625822. Archived from the original on November 3, 2023. Retrieved April 15, 2024.
- ↑ Birkelund, T; Johansen, RF; Illum, DG; Dyrskog, SE; Østergaard, JA; Falconer, TM; Andersen, C; Fridholm, H; Overballe-Petersen, S; Jensen, JS (January 2021). "Fatal 3-Nitropropionic Acid Poisoning after Consuming Coconut Water". Emerging infectious diseases. 27 (1): 278–280. doi:10.3201/eid2701.202222. PMID 33350928. Archived from the original on July 3, 2023. Retrieved April 15, 2024.
- ↑ "Scientific Opinion on risks for animal and public health related to the presence of nivalenol in food and feed". European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) Journal. 11 (6): 1–5. 2013. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2013.3262.
- ↑ "20th Australian Total Diet Survey – Part B". Food Standards Australia New Zealand. Archived from the original on September 2, 2007. Retrieved August 13, 2007.
- ↑ 62.0 62.1 "Worldwide regulations for mycotoxins in food and feed in 2003". FAO FOOD AND NUTRITION PAPER 81. Archived from the original on September 10, 2007. Retrieved August 13, 2007.
- ↑ "Patulin in Apple Juice, Apple Juice Concentrates and Apple Juice Products". Food and Drug Administration. Archived from the original on September 12, 2007. Retrieved August 16, 2007.
- ↑ Jordan, T. W. (July 2020). "The cellular and molecular toxicity of sporidesmin". New Zealand Veterinary Journal. 68 (4): 203–213. doi:10.1080/00480169.2020.1729268. ISSN 1176-0710. Archived from the original on June 17, 2022. Retrieved April 17, 2024.
- ↑ Viegas, C; Nurme, J; Piecková, E; Viegas, S (July 9, 2018). "Sterigmatocystin in foodstuffs and feed: aspects to consider". Mycology. 11 (2): 91–104. doi:10.1080/21501203.2018.1492980. PMID 32923018. Archived from the original on April 18, 2024. Retrieved April 16, 2024.
- ↑ Sabater-Vilar M, Nijmeijer S, Fink-Gremmels J (November 2003). "Genotoxicity assessment of five tremorgenic mycotoxins (fumitremorgen B, paxilline, penitrem A, verruculogen, and verrucosidin) produced by molds isolated from fermented meats". Journal of Food Protection. 66 (11): 2123–9. doi:10.4315/0362-028X-66.11.2123. PMID 14627292.
- ↑ Adejumo TO, Hettwer U, Karlovsky P (May 2007). "Occurrence of Fusarium species and trichothecenes in Nigerian maize". International Journal of Food Microbiology. 116 (3): 350–7. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.02.009. PMID 17412440.
- ↑ Mazur LJ, Kim J (December 2006). "Spectrum of noninfectious health effects from molds". Pediatrics. 118 (6): e1909-26. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-2829. PMID 17142508.
- ↑ Froquet R, Sibiril Y, Parent-Massin D (February 2001). "Trichothecene toxicity on human megakaryocyte progenitors (CFU-MK)". Human & Experimental Toxicology. 20 (2): 84–9. doi:10.1191/096032701677428611. PMID 11327514. S2CID 37767457.
- ↑ Joffe AZ, Yagen B (February 1977). "Comparative study of the yield of T-2 toxic produced by Fusarium poae, F. sporotrichioides and F. sporotrichioides var. tricinctum strains from different sources". Mycopathologia. 60 (2): 93–7. doi:10.1007/bf00490378. PMID 846559. S2CID 39431820.
- ↑ Hay RJ (April 2007). "Fusarium infections of the skin". Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases. 20 (2): 115–7. doi:10.1097/QCO.0b013e328014392d. PMID 17496567.
- ↑ "Guidance for Industry and FDA – Letter to State Agricultural Directors, State Feed Control Officials, and Food, Feed, and Grain Trade Organizations". Food and Drug Administration. Archived from the original on June 9, 2007. Retrieved August 13, 2007.
- ↑ Hohn, Thomas M. "Trichothecene-resistant transgenic plants". U.S. Patent 6,646,184. Priority date March 31, 1999.
- ↑ Han, X; Huangfu, B; Xu, T; Xu, W; Asakiya, C; Huang, K; He, X (June 2, 2022). "Research Progress of Safety of Zearalenone: A Review". Toxins. 14 (6). doi:10.3390/toxins14060386. PMID 35737047. Archived from the original on April 18, 2024. Retrieved April 16, 2024.
- ↑ Zinedine, Abdellah; Ruiz, Maria-Jose (January 2014). "Zearalenone". Mycotoxins and their Implications in Food Safety. Future Science Ltd: 52–66. doi:10.4155/ebo.13.660. Archived from the original on April 18, 2024. Retrieved April 16, 2024.
- ↑ O’Shea, Helen; Blacklaws, Barbara A.; Collins, Patrick J.; McKillen, John; Fitzgerald, Rose (2019). "Viruses Associated With Foodborne Infections". Reference Module in Life Sciences. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-809633-8.90273-5. Archived from the original on July 6, 2022. Retrieved April 9, 2024.
- ↑ Bosch, Albert; Gkogka, Elissavet; Le Guyader, Françoise S.; Loisy-Hamon, Fabienne; Lee, Alvin; van Lieshout, Lilou; Marthi, Balkumar; Myrmel, Mette; Sansom, Annette; Schultz, Anna Charlotte; Winkler, Anett; Zuber, Sophie; Phister, Trevor (November 2018). "Foodborne viruses: Detection, risk assessment, and control options in food processing". International Journal of Food Microbiology. 285: 110–128. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.06.001. Archived from the original on December 8, 2023. Retrieved April 25, 2024.
- ↑ Greening, Gail E.; Cannon, Jennifer L. (2016). "Human and Animal Viruses in Food (Including Taxonomy of Enteric Viruses)". Viruses in Foods: 5–57. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-30723-7_2.
- ↑ Dubois E, Hennechart C, Deboosère N, Merle G, Legeay O, Burger C, et al. (April 2006). "Intra-laboratory validation of a concentration method adapted for the enumeration of infectious F-specific RNA coliphage, enterovirus, and hepatitis A virus from inoculated leaves of salad vegetables". International Journal of Food Microbiology. 108 (2): 164–71. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2005.11.007. PMID 16387377.
- ↑ Schmidt HM. "Improving the microbilological quality and safety of fresh-cut tomatoes by low dose dlectron beam irradiation – Master thesis" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on September 27, 2007. Retrieved August 11, 2007.
- ↑ Waqar, Sana; Sharma, Bashar; Koirala, Janak (2024). "Hepatitis E". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on May 17, 2022. Retrieved April 2, 2024.
- ↑ "Norovirus". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. March 14, 2024. Archived from the original on November 1, 2017. Retrieved April 12, 2024.
- ↑ Omatola, CA; Olaniran, AO (April 22, 2022). "Rotaviruses: From Pathogenesis to Disease Control-A Critical Review". Viruses. 14 (5). doi:10.3390/v14050875. PMID 35632617. Archived from the original on November 10, 2023. Retrieved April 12, 2024.
- ↑ K D Murrell (August 2013). "Zoonotic foodborne parasites and their surveillance". Revue Scientifique et Technique (International Office of Epizootics). 32 (2): 559–569. PMID 24547659. Archived from the original on June 16, 2022. Retrieved August 9, 2022.
- ↑ "Taxonomy browser (Platyhelminthes)". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on February 20, 2023. Retrieved April 26, 2024.
- ↑ Reblánová, M.; Špakulová, M.; Orosová, M.; Bazsalovicsová, E.; Rajský, D. (June 1, 2010). "A description of karyotype of the giant liver fluke Fascioloides magna (Trematoda, Platyhelminthes) and a review of Fasciolidae cytogenetics". Helminthologia. 47 (2): 69–75. doi:10.2478/s11687-010-0012-0. ISSN 1336-9083. Archived from the original on April 27, 2024. Retrieved April 26, 2024.
- ↑ Britannica (2021). "Nematode". Archived from the original on July 12, 2022. Retrieved August 9, 2022.
- ↑ Solis, Addison (June 16, 2018). Food Microbiology. Scientific e-Resources. p. 24. ISBN 978-1-83947-159-9. Archived from the original on April 24, 2024. Retrieved April 21, 2024.
- ↑ Mithöfer, Axel; Boland, Wilhelm (June 2, 2012). "Plant Defense Against Herbivores: Chemical Aspects". Annual Review of Plant Biology. 63 (1): 431–450. doi:10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103854. ISSN 1543-5008. Archived from the original on March 26, 2024. Retrieved April 20, 2024.
- ↑ "Food Poisoning from Marine Toxins | CDC Yellow Book 2024". wwwnc.cdc.gov. Archived from the original on April 3, 2024. Retrieved April 5, 2024.
- ↑ Jansen, Suze A.; Kleerekooper, Iris; Hofman, Zonne L. M.; Kappen, Isabelle F. P. M.; Stary-Weinzinger, Anna; van der Heyden, Marcel A. G. (September 2012). "Grayanotoxin Poisoning: 'Mad Honey Disease' and Beyond". Cardiovascular Toxicology. 12 (3): 208–215. doi:10.1007/s12012-012-9162-2. Archived from the original on July 26, 2019. Retrieved April 19, 2024.
- ↑ Hedberg CW, Fishbein DB, Janssen RS, Meyers B, McMillen JM, MacDonald KL, et al. (April 1987). "An outbreak of thyrotoxicosis caused by the consumption of bovine thyroid gland in ground beef". The New England Journal of Medicine. 316 (16): 993–8. doi:10.1056/NEJM198704163161605. PMID 3561455.
- ↑ Parmar MS, Sturge C (September 2003). "Recurrent hamburger thyrotoxicosis". Canadian Medical Association Journal. 169 (5): 415–7. PMC 183292. PMID 12952802.
- ↑ Broome MR, Peterson ME, Kemppainen RJ, Parker VJ, Richter KP (January 2015). "Exogenous thyrotoxicosis in dogs attributable to consumption of all-meat commercial dog food or treats containing excessive thyroid hormone: 14 cases (2008-2013)". Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association. 246 (1): 105–11. doi:10.2460/javma.246.1.105. PMID 25517332.
- ↑ Hendriks LE, Looij BJ (March 2010). "Hyperthyroidism caused by excessive consumption of sausages". The Netherlands Journal of Medicine. 68 (3): 135–7. PMID 20308711.
- ↑ Kinney JS, Hurwitz ES, Fishbein DB, Woolf PD, Pinsky PF, Lawrence DN, et al. (January 1988). "Community outbreak of thyrotoxicosis: epidemiology, immunogenetic characteristics, and long-term outcome". The American Journal of Medicine. 84 (1): 10–8. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(88)90002-2. PMID 3257352.
- ↑ "Foodborne Poisoning (Mushroom Toxin)Investigation Overview" (PDF). ncdhhs.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 31, 2023. Retrieved April 19, 2024.
- ↑ Watier-Grillot, Stéphanie; Larréché, Sébastien; Mazuet, Christelle; Baudouin, Frédéric; Feraudet-Tarisse, Cécile; Holterbach, Lise; Dia, Aïssata; Tong, Christelle; Bourget, Laure; Hery, Sophie; Pottier, Emmanuel; Bouilland, Olivier; Tanti, Marc; Merens, Audrey; Simon, Stéphanie; Diancourt, Laure; Chesnay, Aurélie; Pommier de Santi, Vincent (July 13, 2023). "From Foodborne Disease Outbreak (FBDO) to Investigation: The Plant Toxin Trap, Brittany, France, 2018". Toxins. 15 (7): 457. doi:10.3390/toxins15070457. Archived from the original on April 21, 2024. Retrieved April 19, 2024.
- ↑ "The Unwelcome Toxins in Our Food – Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids (PAs)". sfa.gov. Archived from the original on April 19, 2024. Retrieved April 18, 2024.
- ↑ Watkins, Sharon M. (September 2008). "Neurotoxic Shellfish Poisoning". Marine Drugs. 6 (3): 430–455. doi:10.3390/md20080021. Archived from the original on August 16, 2023. Retrieved April 18, 2024.
- ↑ Nguyen, HoanVu N.; Smith, Matthew E.; Swoboda, Henry D. (2024). "Shellfish Toxicity". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on November 4, 2022. Retrieved April 18, 2024.
- ↑ Clark, RF; Williams, SR; Nordt, SP; Manoguerra, AS (1999). "A review of selected seafood poisonings" (PDF). Undersea & Hyperbaric Medicine. 26 (3): 175–84. PMID 10485519. Archived from the original on June 17, 2012.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ↑ "Scombrotoxin Poisoning and Decomposition". FDA. 2024. Archived from the original on July 25, 2023. Retrieved April 18, 2024.
- ↑ Al Dhuhaibat, Zahra k; Zarzour, Talal (January 10, 2023). "Tetrodotoxin Poisoning Due to Pufferfish Ingestion in the United Arab Emirates". Cureus. doi:10.7759/cureus.33627. Archived from the original on April 21, 2024. Retrieved April 18, 2024.
- ↑ Kreis, Wolfgang (August 2017). "The Foxgloves (Digitalis) Revisited". Planta Medica. 83 (12/13): 962–976. doi:10.1055/s-0043-111240. ISSN 0032-0943. Archived from the original on April 15, 2024. Retrieved April 19, 2024.
- ↑ Adams, Clive E (April 1, 2010). "James Crichton Browne and controlled evaluation of drug treatment for mental illness". Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. 103 (4): 160–161. doi:10.1258/jrsm.2009.09k073. Archived from the original on April 21, 2024. Retrieved April 19, 2024.
- ↑ Sitammagari, Kranthi K.; Masood, Wajeed (2024). "Creutzfeldt Jakob Disease". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on November 9, 2023. Retrieved April 7, 2024.
- ↑ Brend, W. A. (May 25, 1934). "THE PTOMAINE-POISONING MYTH". The Spectator. Archived from the original on March 17, 2022. Retrieved August 9, 2022.
- ↑ Oxford English Dictionary (First ed.). London: Oxford University Press. 1933. p. 1557.
- ↑ Merck's Bulletin, Volume 5 Archived April 27, 2021, at the Wayback Machine, William Henry Porter, 1892.
- ↑ Lancet, 3 Oct 1891, page 752
- ↑ "Report Next Week," Archived March 17, 2022, at the Wayback Machine Evening Independent (Massillon, OH), July 22, 1932, pg. 6
- ↑ "Medicine: Potato Salad," Time, August 1, 1932.
- ↑ "Poisoning Hits 150 in Chicago". Kenosha Evening News. May 27, 1944. Archived from the original on April 27, 2021. Retrieved August 9, 2022.
- ↑ Zhernov, Yury V.; Simanduyev, Mark Y.; Zaostrovtseva, Olga K.; Semeniako, Ekaterina E.; Kolykhalova, Kseniia I.; Fadeeva, Inna A.; Kashutina, Maria I.; Vysochanskaya, Sonya O.; Belova, Elena V.; Shcherbakov, Denis V.; Sukhov, Vitaly A.; Sidorova, Ekaterina A.; Mitrokhin, Oleg V. (January 2023). "Molecular Mechanisms of Scombroid Food Poisoning". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 24 (1): 809. doi:10.3390/ijms24010809. ISSN 1422-0067.
- ↑ "What You Need to Know about Foodborne Illnesses". FDA. 2024. Archived from the original on February 2, 2024. Retrieved April 10, 2024.
- ↑ "Fight Off Food Poisoning". NIH News in Health. May 12, 2017. Archived from the original on October 2, 2023. Retrieved April 27, 2024.
- ↑ Rachel M Lee, Justin Lessler, Rose A Lee, Kara E Rudolph, Nicholas G Reich, Trish M Perl, and Derek AT Cummings (September 2013). "Incubation periods of viral gastroenteritis: a systematic review". BMC Infectious Diseases. 13: 446. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-13-446. PMC 3849296. PMID 24066865.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - ↑ "Food-Related Diseases". US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. March 29, 2018. Archived from the original on November 9, 2010. Retrieved August 9, 2022.
- ↑ 120.0 120.1 120.2 Greig JD. "Infective Doses and Pathogen Carriage". ResearchGate.
- ↑ Owens, Michael D (January 2014) Salmonella Infection in Emergency Medicine Archived October 11, 2008, at the Wayback Machine. emedicine.com
- ↑ Kurtz, Jonathan R; Goggins, J. Alan; McLachlan, James B. (October 2017). "Salmonella infection: Interplay between the bacteria and host immune system". Immunology Letters. 190: 42–50. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2017.07.006. Archived from the original on September 23, 2022. Retrieved April 27, 2024.
- ↑ Leung, Alexander K.C.; Leung, Amy A.M.; Wong, Alex H.C.; Hon, Kam L. (August 5, 2019). "Travelers' Diarrhea: A Clinical Review". Recent Patents on Inflammation & Allergy Drug Discovery. 13 (1): 38–48. doi:10.2174/1872213X13666190514105054. Archived from the original on January 5, 2024. Retrieved April 8, 2024.
- ↑ "DIAGNOSTIC TOOLS FOR FOODBORNE ILLNESS". FDA. Archived from the original on March 5, 2021. Retrieved March 31, 2024.
- ↑ "Tracking and Tracing of Food". FDA. 2024. Archived from the original on September 21, 2023. Retrieved April 28, 2024.
- ↑ Procedures to Investigate Foodborne Illness. Springer Science & Business Media. July 8, 2011. p. 29. ISBN 978-1-4419-8396-1. Archived from the original on April 30, 2024. Retrieved April 28, 2024.
- ↑ "FDA Says Viruses Safe for Treating Meat". Archived from the original on August 25, 2006. Retrieved September 2, 2014.
- ↑ DeRusha J (November 9, 2010). "Good Question: Does Washing Fruit Do Anything?". Archived from the original on April 28, 2021. Retrieved September 18, 2016.
- ↑ How Temperatures Affect Food Archived February 25, 2021, at the Wayback Machine. U.D. Department of Agriculture
- ↑ FAO/WHO (2006). World Health Organization (ed.). "Enterobacter sakazakii and Salmonella in powdered infant formula" (Meeting report). Microbiological risk assessment series 10. Archived from the original on April 2, 2015.
- ↑ Scallan E, Griffin PM, Angulo FJ, Tauxe RV, Hoekstra RM (January 2011). "Foodborne illness acquired in the United States--unspecified agents". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 17 (1): 16–22. doi:10.3201/eid1701.P21101. PMC 3204615. PMID 21192849.
- ↑ 132.0 132.1 132.2 Scallan E, Hoekstra RM, Angulo FJ, Tauxe RV, Widdowson MA, Roy SL, et al. (January 2011). "Foodborne illness acquired in the United States--major pathogens". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 17 (1): 7–15. doi:10.3201/eid1701.P11101. PMC 3375761. PMID 21192848.
- ↑ "Obama Proposes Single Overseer for Food Safety". The New York Times. February 20, 2015. Archived from the original on June 16, 2022. Retrieved February 22, 2015.
According to the C.D.C., an estimated 87 million Americans are sickened each year by contaminated food, 371,000 are hospitalized with food-related illness and 5,700 die from food-related disease
- ↑ 134.0 134.1 Sabrina Tavernise (July 26, 2013). "F.D.A. Says Importers Must Audit Food Safety". The New York Times. Archived from the original on July 27, 2013. Retrieved July 27, 2013.
One in every six Americans becomes ill from eating contaminated food each year, Dr. Margaret A. Hamburg, F.D.A. commissioner, estimated. About 130,000 are hospitalized and 3,000 die.
- ↑ 135.0 135.1 Stephanie Strom (January 4, 2013). "F.D.A. Offers Sweeping Rules to Fight Food Contamination". The New York Times. Archived from the original on January 4, 2013. Retrieved January 5, 2013.
One in six Americans becomes ill from eating contaminated food each year, the government estimates; of those, roughly 130,000 are hospitalized and 3,000 die.
- ↑ 136.0 136.1 136.2 "Annual Report of the Chief Scientist 2012/13" (PDF). Food Standards Agency. England. 2013. Archived (PDF) from the original on February 24, 2021. Retrieved August 9, 2022.
- ↑ 137.0 137.1 Liebling A, Maruna S, McAra L (2017). The Oxford Handbook of Criminology. Oxford University Press. p. 290. ISBN 978-0-19-871944-1. Archived from the original on August 23, 2022. Retrieved August 9, 2022.
- ↑ 138.0 138.1 138.2 "Report of the French sanitary agencies" (PDF) (in français). INVS/Afssa. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 3, 2016. Retrieved October 6, 2004.
- ↑ 139.0 139.1 139.2 "Summary of Report of the French sanitary agencies" (PDF) (in français). INVS/Afssa. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 3, 2016. Retrieved October 6, 2004.
- ↑ 140.0 140.1 "23 million people falling ill from unsafe food each year in Europe is just the tip of the iceberg". www.who.int. Archived from the original on May 21, 2023. Retrieved April 30, 2024.
- ↑ "Morbidité et mortalité dues aux maladies infectieuses d'origine alimentaire en France". www.santepubliquefrance.fr (in français). Archived from the original on January 27, 2021. Retrieved April 30, 2024.
- ↑ 142.0 142.1 Kirk M, et al. "Foodborne illness in Australia: Annual incidence circa 2010 pp7-9". Australia Department of Health. Australian National University. Archived from the original on August 23, 2022. Retrieved September 13, 2015.
- ↑ "Food poisoning". NSW Food authority. Archived from the original on March 16, 2024. Retrieved April 30, 2024.
- ↑ "Food borne illness in Australia" (PDF). OzFoodNet.
- ↑ Astridge K, McPherson M, Kirk M, et al. (2011). "Foodborne disease outbreaks in Australia 2001-2009". Food Australia. 63 (12): 44–50.
- ↑ "Food Hygiene". BUPA. Archived from the original on December 11, 2015. Retrieved September 13, 2015.
- ↑ "Food Safety Newsletter: 2022 FoodNet Report". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. June 29, 2023. Archived from the original on December 16, 2023. Retrieved April 22, 2024.
- ↑ Ford, Laura; Self, Julie L.; Wong, Karen K.; Hoekstra, Robert M.; Tauxe, Robert V.; Rose, Erica Billig; Bruce, Beau B. "Power Law for Estimating Underdetection of Foodborne Disease Outbreaks, United States - Volume 30, Number 2—February 2024 - Emerging Infectious Diseases journal - CDC". doi:10.3201/eid3002.230342. Archived from the original on February 23, 2024. Retrieved April 30, 2024.
- ↑ "Aberdeen's typhoid outbreak remembered 50 years on". BBC News. April 11, 2014. Archived from the original on September 4, 2022. Retrieved April 6, 2024.
- ↑ Smith, David F.; Diack, H. Lesley and Pennington, T. Hugh (2005) Food Poisoning, Policy and Politics : Corned Beef and Typhoid in Britain in the 1960s. Boydell Press. ISBN 1-84383-138-4[page needed]
- ↑ Brian Deer (February 24, 1985). "Food poison deaths probe may reveal NHS flaws". The Sunday Times. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved August 9, 2022.
- ↑ "BBC News - Health - Sheriff criticises E. coli butcher". Archived from the original on January 8, 2007. Retrieved August 9, 2022.
- ↑ Cowden JM, Ahmed S, Donaghy M, Riley A (June 2001). "Epidemiological investigation of the central Scotland outbreak of Escherichia coli O157 infection, November to December 1996". Epidemiology and Infection. 126 (3): 335–41. doi:10.1017/S0950268801005520. PMC 2869700. PMID 11467789.
- ↑ "The Food Standards Agency: A Force for Change". gov.uk. Food Standards Agency, United Kingdom. January 14, 1998. Archived from the original on February 26, 2010. Retrieved August 14, 2016.
- ↑ Hardy A (January 13, 2016). "Food Poisoning: An On-going Saga". History and Policy. History and Policy. Archived from the original on December 27, 2021. Retrieved July 4, 2016.
- ↑ "Meat Produced by Advanced Meat/Bone Separation Machinery and Meat Recovery (AMR) Systems". Federal Register. U.S. National Archive and Records Administration. January 12, 2004. Archived from the original on August 17, 2016. Retrieved July 3, 2016.
- ↑ "Healthy People 2010 Home Page". Archived from the original on March 10, 2017. Retrieved August 9, 2022.
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control Prevention (CDC) (April 2008). "Preliminary FoodNet data on the incidence of infection with pathogens transmitted commonly through food--10 states, 2007". MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 57 (14): 366–70. PMID 18401330. Archived from the original on June 15, 2017. Retrieved August 9, 2022.
- ↑ Severson G (June 15, 2018). "Why are we seeing so many food recalls?". KARE 11. Archived from the original on August 23, 2022. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ↑ "Microbiological risk assessment" (PDF). WHO. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 21, 2024. Retrieved April 20, 2024.
- ↑ "FAO/WHO guide for application of risk analysis principles and procedures during food safety emergencies" (PDF). fao. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 18, 2023. Retrieved April 20, 2024.
- ↑ "International food safety authorities network". www.who.int. Archived from the original on April 17, 2024. Retrieved April 21, 2024.
- ↑ Multicriteria-based ranking for risk management of foodborne parasites. Microbiological Risk Assessment Series No. 23. FAO/WHO. 2014. ISBN 978-92-5-108199-0. Archived from the original on August 18, 2022. Retrieved August 9, 2022.
- ↑ Bouwknegt M, Devleesschauwer B, Graham H, Robertson LJ, van der Giessen JW (March 2018). "Prioritisation of foodborne parasites in Europe, 2016". Euro Surveillance. 23 (9). doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2018.23.9.17-00161. PMC 5840924. PMID 29510783.
- ↑ "Microbiological criteria - European Commission". food.ec.europa.eu. Archived from the original on March 26, 2024. Retrieved April 28, 2024.
- ↑ "ISO 15216-2:2019". ISO. Archived from the original on September 23, 2023. Retrieved April 28, 2024.
- ↑ "Committee | CODEXALIMENTARIUS FAO-WHO". www.fao.org. Archived from the original on September 26, 2023. Retrieved April 28, 2024.
Further reading[edit | edit source]
Periodicals[edit | edit source]
- International Journal of Food Microbiology Archived January 2, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, ISSN 0168-1605, Elsevier
- Foodborne Pathogens and Disease Archived March 9, 2021, at the Wayback Machine, ISSN 1535-3141, Mary Ann Liebert, Inc.
- Mycopathologia, ISSN 1573-0832 (electronic), ISSN 0301-486X (paper), Springer
Books[edit | edit source]
- Hocking AD, Pitt JI, Samson RA, Thrane U (2005). Advances in Food Mycology. Springer. ISBN 978-0-387-28385-2. Archived from the original on April 27, 2021. Retrieved August 9, 2022. ISBN 978-0-387-28391-3 (electronic).
- Hobbs BC (1993). Food Poisoning and Food Hygiene. British Medical Bulletin. Vol. 7. Edward Arnold. pp. 167–70. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a073825. ISBN 978-0-340-53740-4. PMID 14821218.
- Riemann HP, Cliver DO (2006). FoodBorne Infections and Intoxications. Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-588365-8. Archived from the original on April 27, 2021. Retrieved August 9, 2022.
- Smith JL (2005). Fratamico PM, Bhunia AK, Smith JL (eds.). Foodborne Pathogens: Microbiology And Molecular Biology. Horizon Scientific Press. ISBN 978-1-904455-00-4.
External links[edit | edit source]
- Foodborne diseases, emerging, WHO, Fact sheet N°124, revised January 2002
- Foodborne illness information pages Archived December 30, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, NSW Food Authority
- Food safety and foodborne illness, WHO, Fact sheet N°237, revised January 2002
- UK Health protection Agency
- US PulseNet Archived September 14, 2022, at the Wayback Machine
- Food poisoning Archived October 25, 2017, at the Wayback Machine from NHS Direct Online
- Food Safety Network hosted at the University of Guelph, Canada.
- Food Standard Agency website Archived May 11, 2019, at the Wayback Machine
Categories: [Food safety] [Foodborne illnesses] [Health disasters]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 06/19/2024 19:55:59 | 5 views
☰ Source: https://mdwiki.org/wiki/Foodborne_illness | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF