Nitrogen Monofluoride
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Fluoroimidogen
| |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
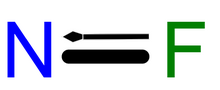
Chemical formula
|
FN |
| Molar mass | 33.005 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
Related isoelectronic
|
Dioxygen, nitroxyl anion |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Nitrogen monofluoride (fluoroimidogen) is a metastable species that has been observed in laser studies. It is isoelectronic with O2. Like boron monofluoride, it is an instance of the rare multiply-bonded fluorine atom.[1][2] It is unstable with respect to its formal dimer, dinitrogen difluoride, as well as to its elements, nitrogen and fluorine.
Nitrogen monofluoride is produced when radical species (H, O, N, CH3) abstracts a fluorine atom from nitrogen difluoride (NF2). Stoichiometrically, the reaction is extremely efficient, regenerating a radical for long-lasting chain propagation. However, radical impurities in the end product also catalyze that product's decomposition. Azide decomposition offers a less-efficient but more pure technique: fluorine azide (which can be formed in situ via reaction of atomic fluorine with hydrazoic acid) decomposes upon shock into NF and N2.[3][4]
Many NF-producing reactions give the product in an excited state with characteristic chemiluminescence. They have thus been investigated for development as a chemical laser.[4][5]
References
- ↑ Davis, Steven J.; Rawlins, Wilson T.; Piper, Lawrence G. (Feb 1989). "Rate coefficient for the H + NF(a1Δ) reaction" (in en) (PDF). The Journal of Physical Chemistry (American Chemical Society) 93 (3): 1078–1082. doi:10.1021/j100340a013. ISSN 0022-3654. https://metastablestates.com/Publications/JPC_93_1078_1989.pdf.
- ↑ Harbison, G. S. (2002). "The Electric Dipole Polarity of the Ground and Low-lying Metastable Excited States of NF". Journal of the American Chemical Society 124 (3): 366–367. doi:10.1021/ja0159261. PMID 11792193.
- ↑ Gmelin-lnstitut für Anorganische Chemie der Max-Planck-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der Wissenschaften (2013) (in en). Gmelin Handbook of Inorganic Chemistry: F Fluorine: Compounds with Oxygen and Nitrogen. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 263–271. ISBN 9783662063392. https://books.google.com/books?id=rpfsCAAAQBAJ&pg=PR263.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Avizonis, Petras V. (2012). "Chemically Pumped Electronic Transition Lasers". in Onorato, Michele. Gas Flow and Chemical Lasers. Plenum Press. pp. 1–19. doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-7067-7_1. ISBN 978-1-4615-7067-7.
- ↑ Kenner, Rex D.; Ogryzlo, Elmer A. (1985). "Chemiluminescence in Gas Phase Reactions; 4. NF(a1Δ) (870, 875 nm) and (b1Σ+) (525–530 nm)". in Burr, John G.. Chemi- and Bioluminescence. Chemical and Biochemical Analysis. 16. Dekker. pp. 84–87. ISBN 0-8247-7277-6.
 |
Categories: [Nitrogen fluorides] [Nitrogen compounds] [Diatomic molecules]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 11/05/2024 15:36:20 | 11 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Nitrogen_monofluoride | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF