Legality Of Polygamy
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 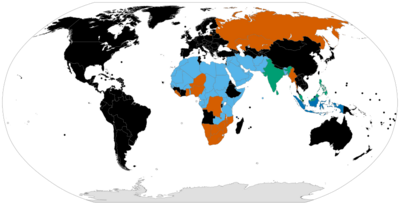
- In Lebanon, Malaysia, Philippines and Singapore polygamy is only legal for Muslims.
- In Nigeria and South Africa, polygamous marriages under customary law and for Muslims are legally recognized.
- In Mauritius, polygamous unions have no legal recognition. Muslim men may, however, "marry" up to four women, but they do not have the legal status of wives.
The legal status of polygamy varies widely around the world. Polygyny is legal in 58 out of nearly 200 sovereign states, the vast majority of them being Muslim-majority countries in Africa and Asia. Polyandry is illegal in virtually every country.[citation needed] A number of countries permit polygyny among Muslims in their communities. Some countries that permit polygyny have restrictions, such as requiring the first wife to give her consent.
In countries that ban polygamy, the offence is commonly called bigamy, though the penalty varies between jurisdictions. In some countries where polygamy is illegal, the prohibition is not enforced.
Countries that recognize polygamous marriages
Africa
 Algeria[1]
Algeria[1] Cameroon[2]
Cameroon[2] Chad[3]
Chad[3] Central African Republic[4]
Central African Republic[4] Republic of the Congo[5]
Republic of the Congo[5] Djibouti[6]
Djibouti[6] Egypt[7]
Egypt[7] Gabon:[8] Both men and women can join in polygamous marriage with the other gender under Gabonese law. In practice, the right to multiple spouses is reserved for men only.[9]
Gabon:[8] Both men and women can join in polygamous marriage with the other gender under Gabonese law. In practice, the right to multiple spouses is reserved for men only.[9] The Gambia[10]
The Gambia[10] Guinea[11]
Guinea[11] Libya[12][13][14]
Libya[12][13][14] Kenya: Polygymy legal under legislation passed in 2014.[15]
Kenya: Polygymy legal under legislation passed in 2014.[15] Mali[16]
Mali[16] Mauritania[17]
Mauritania[17] Morocco[18]
Morocco[18] Nigeria (only in some states)[19]
Nigeria (only in some states)[19] São Tomé and Príncipe[20]
São Tomé and Príncipe[20] Senegal[21]
Senegal[21] Somalia[22]
Somalia[22] South Sudan[23]
South Sudan[23] Sudan[24]
Sudan[24] Eswatini[25]
Eswatini[25] Togo[26]
Togo[26] Tanzania[27]
Tanzania[27] Uganda[28]
Uganda[28] Zambia[29]
Zambia[29]
Asia
.svg.png) Afghanistan[30]
Afghanistan[30] Bahrain[31]
Bahrain[31] Bangladesh[32]
Bangladesh[32] Bhutan[33][34]
Bhutan[33][34] Brunei[35]
Brunei[35] Indonesia (except for in the provinces of Maluku, North Maluku, Papua, and West Papua) [36]
Indonesia (except for in the provinces of Maluku, North Maluku, Papua, and West Papua) [36] Iran[37]
Iran[37] Iraq (except for in Iraqi Kurdistan)[38]
Iraq (except for in Iraqi Kurdistan)[38] Jordan[39]
Jordan[39] Kuwait[40]
Kuwait[40] Lebanon[41]
Lebanon[41] Maldives[42]
Maldives[42] Oman[43]
Oman[43] Qatar[44]
Qatar[44] Pakistan[45]
Pakistan[45] Saudi Arabia[46]
Saudi Arabia[46] Sri Lanka[47][48][49]
Sri Lanka[47][48][49] Syria (except in Syrian Kurdistan)[50]
Syria (except in Syrian Kurdistan)[50] United Arab Emirates[51]
United Arab Emirates[51] Yemen[52]
Yemen[52]
Oceania
 Solomon Islands[53]
Solomon Islands[53]
Countries that only recognize polygamous marriages for Muslims
Note: These countries are included separately because they have specific legislation aimed only at Muslims.
Asia
 Malaysia[54]
Malaysia[54] Philippines[55]
Philippines[55] Singapore.
Singapore. India.
India.
Countries that do not recognize polygamous marriages
Africa
- Benin[56]
- Côte d'Ivoire: Polygamy may be punishable by six months to three years imprisonment, or a fine of CFA 50,000 to CFA 500,000 (US$80 to US$800).[57]
- Eritrea: Illegal since 1977, after 2015 polygamy is punishable with "a definite term of imprisonment of not less than 6 months and not more than 12 months, or a fine of 20,001 – 50,000 Nakfas."[58]
- Ethiopia[59][60]
- Seychelles
- Tunisia, where it has been banned since 1956[61]
Under customary law
- Botswana[62]
- Lesotho[63]
- Liberia[64]
- Malawi[65]
- Namibia[66]
- Niger[67]
- Nigeria (only in some states):[68] Recognized in all northern Sharia states
- Sierra Leone[69]
- South Africa:[70] Recognized under customary law, and recognised for civil purposes in terms of the Recognition of Customary Marriages Act.
- Zimbabwe[71]
Illegal de jure but still practiced
- Angola[72]
- Burkina Faso [73]
- Burundi[74]
- Cabo Verde[75]
- Democratic Republic of the Congo[76]
- Equatorial Guinea[77][78][79]
- Ghana[80][81]
- Madagascar [82]
- Mauritius
- Mayotte (French territory) (not criminalized): Considered to be de facto illegal since a referendum sponsored by France in March 2009, forcing the island to comply with the French laws.[83][84] However, pre-existing Muslim marriages are currently still valid.
- Mozambique[85]
- Rwanda[86]
Americas
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Argentina
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Belize
- Bolivia
- Brazil: Bigamy is illegal but the practice is decriminalized, having led to newsworthy accounts of cohabitation.[87]
- Canada: All forms of polygamy, and some informal multiple sexual relationships, are illegal under section 293 of the Criminal Code.[88] Bigamy is banned by section 290.[89] However, for a long time, the law banning polygamy has not been efficient. As of January 2009, no person had been successfully prosecuted, i.e. convicted, in over sixty years.[90] In 2009, two acquittals on polygamy charges, arising out of the town of Bountiful, British Columbia, prompted the government of British Columbia to pose a reference question to the Supreme Court of British Columbia (i.e., the superior trial court). The reference questions asked if criminalisation of polygamy was consistent with the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms; and, if so, under what circumstances could people be legally punished for polygamy.[91] In November 2011 the court released its 335 page long decision, which was that the criminal offence of polygamy is indeed constitutional, but that it should not be used to prosecute minors for having taken part of a polygamous marriage.[92] Chief Justice Robert Bauman conceded that there is a conflict between this law and some civil right principles, but stated that there are other and "more important" issues which in this case take precedence. He wrote (as quoted by CBC news[92]): "I have concluded that this case is essentially about harm. More specifically, Parliament's reasoned apprehension of harm arising out of the practice of polygamy. This includes harm to women, to children, to society and to the institution of monogamous marriage." Bauman argued that there are cases where the "wives" (who may be rather young; sometimes as young as 12 years) are abducted and abused, but because they believe in a faith promoting polygamy, they are not willing to bring complaints to the authorities. He reasons that these offences sometimes may be stopped by applying anti-polygamy legislation. The decision was welcomed by the Attorney General of British Columbia, and by a representative for the group Stop Polygamy in Canada. Likewise, according to the CBC news,[92] some polyamorous groups in Canada expressed their relief, since Bauman had stated that the law shouldn't apply to them unless they decide to formalize their unions. Women's rights were central to decision.[92]
- Chile
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Cuba
- Dominica
- Dominican Republic
- Ecuador
- El Salvador
- Grenada
- Guatemala
- Guyana
- Haiti
- Honduras
- Jamaica
- Mexico
- Nicaragua
- Panama
- Paraguay
- Peru
- St. Kitts and Nevis
- St. Lucia
- St. Vincent and The Grenadines
- Suriname
- Trinidad and Tobago
- United States: Polygamy is illegal in all 50 states[93] however in Utah, in February, 2020, the law was significantly changed in the House and Senate to reduce polygamy to the status of a traffic ticket.[4] It is still illegal federally according to the Edmunds Act . From about 1847 to 1857, in what is now the state of Utah, many Mormons practiced polygamy, which was widely condemned in the rest of the US. The US federal government threatened The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) and made polygamy illegal through the enforcement of Acts of Congress such as the Morrill Anti-Bigamy Act. The LDS Church formally outlawed the practice in 1890, in a document labeled 'The Manifesto'.[90][94] Small splinter groups from the LDS Church, such as Fundamentalist Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-Day Saints and the Apostolic United Brethren still practice polygamy and awareness has been increased through television dramas such as Big Love and reality shows such as Sister Wives. Among American Muslims, a small minority of around 50,000 to 100,000 people are estimated to live in families with a husband maintaining an informal polygamous relationship.[93]
- Uruguay
- Venezuela
Asia
- Nepal
- China: Polygamy is illegal under Marriage Law passed in 1980, which replaced a similar 1950 prohibition.[95] In Hong Kong, polygamy ended with the passing of the Marriage Act of 1971.
- Israel: Polygamy has been banned for all confessional communities since at least 1959.[96]
- Japan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Mongolia
- Myanmar[97]
- North Korea[98]
- South Korea
- Taiwan: Polygamy is illegal by the 1930 ROC civil law.[99]
- Tajikistan
- Turkey: Polygamy was criminalized in 1926 with the adoption of the Turkish Civil Code, part of Atatürk's secularist reforms. Penalties for polygamy are imprisonment of up to 5 years.[100] Turkey has long been known for its promotion of secularism,[101][102][103] and has introduced measures establishing stricter bars against polygamy; these were passed by the ruling moderate Islamist AK Parti as well. In March 2009, AK Parti effectively banned polygamists from entering or living in the country.[104]
- Turkmenistan
- Uzbekistan
- Vietnam
Under customary law
- Palestine[105]
Illegal de jure but still practiced
- Cambodia[106]
- Israel: polygamy was criminalized in 1977, but the law is not consistently enforced and polygamy is still practiced by Israeli Bedouins.[107]
- Kazakhstan[108]
- Laos
- Russia:[109][110] Factual polygamy and sexual relationships with several adult partners are not punishable in accordance with current[timeframe?] revisions of Criminal Code of Russia and Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses. But multiple marriage can't be registered and officially recognised by Russian authorities because Family Code of Russia (section 14 and others) prohibits registration of marriage if one of the persons is in another registered marriage in Russia or another country. Polygamy is tolerated in predominantly Muslim republics such as Chechnya, Ingushetia, and Dagestan.[111][failed verification]
- Thailand[112]
- Timor-Leste[113]
Europe
- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria: Illegal and punishable with up to three years imprisonment.[114]
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland: The official prosecutor is obliged to take all cases to a court where more two persons are married to each other and such relationships cease to exist after the court has decided it.[115] Polygamic marriages performed abroad may be recognized only in narrow occasions, for instance in child custody matters.[116]
- France: Civil marriage registry illegal.
- Georgia
- Germany: Illegal, legally punishable with fine or prison time up to three years.[117] Polygamous marriages contracted abroad are legal, however the German authorities announced plans to close this legal loophole.[118]
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland:[119] The Catholic Church in Ireland allowed someone with a church annulment but no civil annulment to remarry in church; such a marriage was legally null and bigamous but no prosecutions were brought.[120][121] The practice ended after the 1996 legalisation of divorce.[120] In 2017, the Supreme Court ruled that if someone had two legal marriages abroad, only the first was legal in Ireland, though 'that did not necessarily mean [the second] marriage "can never have legal consequences [in Ireland]"'.[122]
- Italy
- Kosovo
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands: Marriage between more than two individuals prohibited; however, a samenlevingscontract may include more than two partners. It legally accepts immigrants who are in such a union from a country where it is legal; e.g. if a man with two wives immigrates to The Netherlands, all three will be legally recognized.[123]
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania: Bigamy, defined as marriage conducted by a person which is already married, is punishable by up to 2 years in prison or fine. Knowingly marrying a married person is punishable by up to 1 year in prison or by fine.[124]
- Russian Federation
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden: Sweden recognizes polygamous marriages performed abroad, and all spouses are subsequently registered as spouses in the population register, but other spouses than the first spouse may not always be recognized in all occasions.[125][126][127] Only the first spouse is recognized as a spouse when decisions are made on residence permits and social security.[125] A Swede may have four spouses registered at most.[126]
- Switzerland: Polygamy is illegal by law. But polygamous marriage conducted in another country may be accepted or rejected on a case-by-case basis.[128]
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom: Foreign polygamous marriages grant some welfare benefits only, but this is being phased out with the introduction of Universal Credit.[129] Polygamy is treated as bigamy if a second marriage (or civil partnership) is contracted in the United Kingdom. No legal recognition is extended to spouses of subsequent marriages after the first marriage is recognised even when subsequent marriages are contracted abroad.
- Vatican City (Holy See)
Oceania
- Australia: Polygamous marriages cannot be performed in Australia, but polygamous relationships are still common within some indigenous Australian communities.[130][131] Polygamous marriages entered into abroad are recognised for limited purposes[which?] only.[132]
- Fiji
- Kiribati
- Marshall Islands
- Micronesia
- Nauru
- New Zealand: Polygamous marriages cannot be performed in New Zealand, but are permissible if they are legally performed in a country that permits polygamy.
- Palau
- Papua New Guinea
- Samoa
- Tonga
- Tuvalu
- Vanuatu
Current legislation
In most countries, a person who marries a person while still being lawfully married to another commits bigamy, a criminal offence, though penalties vary between jurisdictions. In addition, the second and subsequent marriages are considered legally null and void.
The United Kingdom, Australia, and New Zealand permit some benefits for spouses of polygamous marriages performed abroad. On a case-by-case basis, Sweden recognizes polygamous marriages performed abroad but without giving residence or social security rights to other spouses.[125][126] In Switzerland polygamous marriages conducted abroad may be accepted or rejected on a case-by-case basis;[133] see § Europe. In the Canadian province of Saskatchewan, which allows simultaneous, additional marital rights and obligations for already married persons, prior to married persons becoming divorced from their existing spouse.[134]
The vast majority of Muslim majority sovereign states recognize polygamous marriages: these states span from West Africa to Southeast Asia, with exceptions of Israel, Turkey and Tunisia.[135] The Palestinian territories — consisting of West Bank and Gaza Strip — permit polygamous unions for Muslim citizens of the territories.[136]
Predominantly Christian nations usually do not allow polygamy, with a handful of exceptions such as the Republic of the Congo, Uganda, and Zambia.
Almost a dozen countries that do not permit polygamous civil marriages recognize polygamous marriages under customary law. All the northern states in Nigeria governed by Islamic Sharia law recognize polygamous marriages. The autonomous regions of Somaliland and Puntland in northern Somalia also recognize polygamy, as does the country's Transitional Federal Government itself, since the country is governed by Sharia law. The recently independent country of Southern Sudan also recognizes polygamy.
Polyandry is de facto the norm in rural areas of Tibet, although it is illegal under Chinese family law. Polygamy continues in Bhutan[34] in various forms as it has since ancient times. It is also found in parts of Nepal,[137] despite its formal illegality in the country.[138]
Debates of legalizing polygamous marriages continue in Central Asian countries.[citation needed]
Civil unions
Brazil – A legally married person or a married couple cohabiting with one or more sexual partner(s) is prohibited by law as bigamy, which is punishable by two to six years of imprisonment,[139] and is valid for every Brazilian citizen, including naturalized ones.
In 5 May 2011 long-term cohabitation between non-married persons, known as união estável ("stable union"), was extended to same-sex couples, recognized as a family entity and granted all 112 rights of married couples – its only legal difference from marriage is that it does not change individual civil status from single to married.[citation needed]
One of such uniões estáveis, in Tupã, São Paulo, was registered involving a man and two women, as reported in August 2012.[140] A second união estável-bound trio took place in the city of Rio de Janeiro, this time between three women, in October 2015.[141][142]
International law
In 2000, the United Nations Human Rights Committee reported that polygamy violates the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), citing concerns that the lack of "equality of treatment with regard to the right to marry" meant that polygamy, restricted to polygyny in practice, violates the dignity of women and should be outlawed.[143] Specifically, the reports to UN Committees have noted violations of the ICCPR due to these inequalities[144] and reports to the General Assembly of the UN have recommended it be outlawed.[145][146]
Some countries where polygamy is legal are not signatories of ICCPR, including Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Oman, Malaysia, Brunei and South Sudan; so that ICCPR does not apply to these countries.[147] It has been argued by the Department of Justice of Canada that polygyny is a violation of international human rights law.[148]
Notable legislation
The tables below cover recent pieces of legislation that have been either debated, proposed or voted on; all of which concern a form of polygamous union.
To permit polygamy
| Country | Date | Polygamous union | Upper House | Lower House | Head of State | Final outcome | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | Yes | No | |||||
| 1963 | Polygamous civil marriage (revoke of prohibitions)[149] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| 1987 or earlier | Foreign marriages may receive benefits payments, being phased out[129] | |||||||
| 1994 | Customary law (recognizes polygamous unions)[150] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| 1998 | Polygamous civil marriage [151] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| 1998 | Customary marriage (civil recognition)[152] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| 2003 | Customary law (recognizes polygamous unions)[153] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| 2004 | Pension benefits to wives of a deceased president[154] | - | Failed | - | ||||
| 2005 | Polygamous civil marriage (easing of laws; plus restrictions) | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| 2007 | Polygamous civil marriage[155] | Failed | - | - | - | |||
| 2007 | Polygamous civil marriage[155] | Failed | - | - | - | |||
| 2007 | Polygamous civil marriage | Failed | - | - | - | |||
| 2007 | Polygamous civil marriage | Failed | - | - | - | |||
| 2007 | Polygamous civil marriage | Failed | - | - | - | |||
| June 2008 | Polygamous civil marriage[156] | Failed | - | - | - | |||
| September 2008 | Polygamous civil marriage (easing of laws)[157] | Failed | - | - | - | |||
| July 2009 | Polygamous civil marriage[158] | Proposed | - | - | - | - | ||
| 2009 | Polygamous civil marriage | Proposed | - | - | - | - | ||
| March 2014 | Polygamous civil marriage | Passed[15] | - | - | - | |||
To outlaw polygamy
| Country | Date | Prohibition type | Upper House | Lower House | Head of State | Final outcome | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | Yes | No | |||||
| July 1862 | Morrill Anti-Bigamy Act, which made polygamy a misdemeanor offense in US territories and other areas where the federal government has exclusive jurisdiction. | ' | ' | Signed | ||||
| March 1882 | Edmunds Act, which reinforced Morrill by making polygamy a felony in the jurisdictions covered by Morrill; also prohibited "bigamous" or "unlawful cohabitation" as a misdemeanor offense, which removed the need to prove that actual marriages had occurred in order to obtain convictions on polygamy related charges. | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| October 1921 | Outlaws polygamy[159] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| October 1935 | Outlaws polygamy; polygamous marriage[160] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| October 1950 | Outlaws polygamy | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| 1953 | Restrictions on polygamous marriage[149] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| 1955 | Outlaws polygamy and polygamous marriages for Hindus only[161] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| 1956 | Ban on polygamy; polygamous marriages[162] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| 1959 | Ban on polygamy; polygamous marriage[149] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| 1964 | New penal code outlaws polygamy; polygamous marriages (upholds existing) | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| 1971 | Outlaws polygamy[163] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| 1977 | Outlaws polygamy; polygamous marriage (districts under Sharia exempt)[164] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| 1979 | Restrictions on polygamous marriage; ease of divorce laws[162] | Passed; abrogated | - | - | - | |||
| 1985 | Restrictions on polygamous marriage (less liberal)[162] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| 1993 | Outlaws family reunion for polygamist immigrants[165] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| December 2003 | Outlaws polygamy[166] | Failed | - | - | ||||
| 2003 | Restrictions on polygamous marriage[162] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| August 2004 | New penal code outlaws polygamy; polygamous marriages (upholds existing)[167] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| February 2005 | Restrictions on polygamous marriage (heavy restrictions)[168] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| July 2005 | Outlaws polygamy[169] | Failed | - | - | ||||
| 2007 | Bans civil servants from living polygamously[170] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| May 2008 | Restrictions on polygamous marriage (heavy restrictions)[citation needed] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| June 2008 | Outlaws polygamy[166] | Failed | - | - | ||||
| Nov. 2008 | Outlaws polygamy except in selective circumstances[171] | Passed | Passed | Signed | ||||
| March 2009 | 2009 Mahoran status referendum (passage outlaws polygamy)[172] | Territory-wide referendum | ||||||
| May 2009 | Disallows polygamists from immigrating into the country[173][failed verification] | |||||||
| July 2009 | Restrictions on polygamous marriage[174] | Pending | Pending | - | - | |||
| July 2009 | Ban on polygamy and polygamous customary marriages | Proposed | - | - | - | - | ||
See also
- Polygamy
- List of polygamy court cases
Notes
References
- ↑ "Algeria – Researched and compiled by the Refugee Documentation Centre of Ireland on 22 July 2011 : Information on forced marriages and polygamous marriages, including the treatment of women" (PDF). http://www.refworld.org/pdfid/4e3ba9212.pdf. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "In modern Cameroon polygamy doesn’t pay - csmonitor.com". 10 February 2009. Archived from the original on 10 February 2009. https://web.archive.org/web/20090210233657/http://features.csmonitor.com/backstory/2008/11/13/in-modern-cameroon-polygamy-doesn’t-pay/.
- ↑ "Christian Polygamy In Chad Africa". Christian Polygamy Society. December 2011. Archived from the original on 2 July 2012. https://web.archive.org/web/20120702033824/http://www.internationalchristianpolygamysociety.org/2011/12/christian-polygamy-in-chad-africa/.
- ↑ OECD (20 February 2010). Atlas of Gender and Development How Social Norms Affect Gender Equality in non-OECD Countries. OECD Publishing. p. 206. ISBN 9264077472. https://books.google.com/books?id=4QQlVW1rOsIC&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q&f=false. "The practice of polygamy is legal in the Central African Republic but faces growing resistance among educated women"
- ↑ "Republic Of Congo Responds To Questions Raised In Women’S Anti-Discrimination Committee | Meetings Coverage And Press Releases". 2003-01-29. https://www.un.org/News/Press/docs/2003/wom1383.doc.htm. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Women’s rights protection instruments ratified by Djibouti" (PDF). http://www.africa4womensrights.org/public/Dossier_of_Claims/Djibouti-UK.pdf. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ Primo, Valentina (27 September 2015). "Polygamy in Egypt: Why I Decided to Marry a Second Wife". carioscene. http://www.cairoscene.com/In-Depth/Polygamy-in-Egypt-Why-I-Decided-to-marry-a-Second-Wife?fb_comment_id=995923153763398_999873900034990#faba49c86231cc. "We all know male polygamy is legal."
- ↑ "Gender Equality and Social Institutions in Gabon". Social Institutions & Gender Index, genderindex.org. 2007. http://genderindex.org/country/gabon. Retrieved 2009-04-27.
- ↑ "African Women's Rights Observatory > Country Specific Information - Gabon". http://www1.uneca.org/awro/CountrySpecificInformationGabon.aspx. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ pt. "Polygamy in Gambia". http://www.accessgambia.com/information/polygamy.html. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Guinea | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/guinea. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Libyan men now allowed to remarry without consent of first wife: court rule". English.alarabiya.net. http://english.alarabiya.net/articles/2013/02/07/264927.html. Retrieved 29 October 2014.
- ↑ "Polygamy in Libya — and beyond". Salon.com. http://www.salon.com/2011/11/06/polygamy_in_libya_and_beyond/. Retrieved 29 October 2014.
- ↑ "Libya's Women Activists Outraged by Court Ruling on Wives". VOA. http://www.voanews.com/content/libyas-women-activists-outraged-by-court-ruling-on-multimple-wives/1611645.html. Retrieved 29 October 2014.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 "Kenyan parliament passes polygamy law". Al Jazeera. 21 March 2014. http://www.aljazeera.com/news/africa/2014/03/kenyan-parliament-passes-polygamy-law-201432116656522465.html.
- ↑ "Mali: polygamy, including conditions to be met for a man to be able to marry a second wife; divorce, specifically when a woman requests a divorce, including the grounds and treatment of women by society and the authorities (2012-December 2013)". http://www.refworld.org/docid/53ecb7c74.html. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Mauritania | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/mauritania#_ftn17. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ Medini, Mona (23 January 2015). "Polygamy: How Moroccans trick to have a second wife". MBC Times. http://www.mbctimes.com/english/life/polygamy-how-moroccans-trick-to-have-a-second-wife. "[Polygamy] legally becomes theoretically almost impossible if not completely impossible."
- ↑ Itoro E. Akpan-Iquot. "Traditional marriage in Nigeria: Polygamy". Migerianwomenworld.com. http://nigerianwomenworld.com/highlights/traditional-marriage-in-nigeria.php. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
- ↑ "Gay Life in São Tomé and Príncipe". http://www.globalgayz.com/gay-life-in-sao-tome-and-principe/. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Senegal | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/senegal. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Acceptance of Polygamy Slowly Changes in Muslim Africa", VOANews.com (Voice of America), 12 March 2007, http://www.voanews.com/english/archive/2007-03/2007-03-12-voa14.cfm
- ↑ "Is polygamy corrupting South Sudan?". 11 February 2015. http://www.dailysabah.com/africa/2015/02/11/is-polygamy-corrupting-south-sudan. "Polygamy is commonly practiced in many African societies, including South Sudan."
- ↑ "AFRICA | Sudan pushes polygamy". BBC News. 2001-08-15. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/1493309.stm. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ Refugees, United Nations High Commissioner for. "Refworld - Swaziland: Laws and customs in Swaziland regarding polygamy". http://www.refworld.org/docid/3ae6ad7a6c.html.
- ↑ United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. "Togo: Polygamy among the country's ruling elite". http://www.refworld.org/docid/4f97dc762.html. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Divorce and Polygamy in Tanzania" (PDF). http://ecommons.luc.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1014&context=social_justice. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Uganda | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/uganda. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Zambia | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/zambia. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ Nordland, Rod; Sukhanyar, Jawad (7 November 2015). "Afghan Mullah Leading Stoning Inquiry Condones Practice". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2015/11/08/world/asia/afghan-mullah-leading-stoning-inquiry-condones-practice.html. Retrieved 1 November 2016.
- ↑ "Freedom House: Women's Rights in Bahrain 2009 | Bahrain Center for Human Rights". 2009-03-18. http://www.bahrainrights.org/en/node/2798. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Bangladesh | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/bangladesh. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Bhutan | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/bhutan. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 French, Patrick (1 March 2008). "Bhutan: Last wonder". The Daily Telegraph (London). https://www.telegraph.co.uk/culture/3671552/Bhutan-Small-wonder.html. Retrieved 21 October 2010.
- ↑ "Laws of Brunei" (PDF). https://www.ftcam.de/ft_files/Scheidung_BruneiDarussalam1.pdf. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Indonesia | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/indonesia. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Iran, Islamic Rep. | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/iran-islamic-rep. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ Bassem, Wassim (26 January 2015). "Rising incomes mean many Iraqi men marry multiple wives". http://www.al-monitor.com/pulse/originals/2015/01/iraq-polygamy-men-marriage-society.html#ixzz4UKf4Y9px.
- ↑ "Marriage in Jordan - U.S. Embassy in Jordan". https://jo.usembassy.gov/u-s-citizen-services/local-resources-of-u-s-citizens/marriage-in-jordan/.
- ↑ Chaleby, Kutaiba (1985). "Women of Polygamous Marriages in an Inpatient Psychiatric Service in Kuwait". The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 173 (1): 56–8. doi:10.1097/00005053-198501000-00009. PMID 3965613.
- ↑ "Interview: Women Unequal Under Lebanon’s Law". 19 January 2015. https://www.hrw.org/news/2015/01/19/interview-women-unequal-under-lebanons-law.
- ↑ "Maldives divorce rate soars". 2003-10-31. http://www.unmarriedamerica.org/members/news/2003/October-News/Maldives_divorce_rate_soar.html. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Oman | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/oman. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Pakistan | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/pakistan. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Saudi Arabia | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/saudi-arabia. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ Weber, Stephanie (16 December 2015). "Yes, There Is a Marriage Practice Where Women Have Multiple Husbands". Modern Notion. http://modernnotion.com/polyandry-when-women-have-multiple-husbands/. "In Sri Lanka, however, polyandry is actually protected under law. Under the Kandyan Marriage Law, women are permitted to be married to multiple men. In modern Sri Lanka, the practice often starts with a monogamous relationship that then expands with a partner of the wife’s choosing."
- ↑ "Marriage and Divorce (Kandyan) : Chapter 132" (PDF). http://www.commonlii.org/lk/legis/consol_act/mad132209.pdf. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ Zeitzen, Miriam (1 Apr 2008). Polygamy: A Cross-Cultural Analysis. Berg.. p. 64. ISBN 9781847883711. https://books.google.com/books?id=tMivAwAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Syrian Arab Republic | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/syrian-arab-republic. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in United Arab Emirates | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/united-arab-emirates. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Yemen | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/yemen. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Solomon Islands : Gender and Investment Climate Reform Assessment" (PDF). https://www.ifc.org/wps/wcm/connect/0465238049fb0beca26eebd1a5d13d27/IFC_Gender+and+Inv+Climate+Reform+Assessments+_SolomonIslands.pdf?MOD=AJPERES. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "What are the types of marriages in Malaysia? - Marriage - Lawyerment Knowledge Base". 2016-11-16. http://www.lawyerment.com/library/kb/Families/Marriage/1019.htm. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Philippines - Muslim Filipinos". http://countrystudies.us/philippines/38.htm.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Benin | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/benin. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Cote d'Ivoire | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://genderindex.org/country/cote-d039ivoire. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "PENAL CODE OF THE STATE OF ERITREA" (PDF). http://www.refworld.org/pdfid/55a51ccc4.pdf. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Microsoft Word - Q14320 Ethiopia" (PDF). https://www.justice.gov/sites/default/files/eoir/legacy/2013/06/11/marriage_2.pdf. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "BIGAMOUS MARRIAGE AND THE DIVISION OF COMMON PROPERTY UNDER THE ETHIOPIAN LAW: REGULATORY CHALLENGES AND OPTIONS". http://www.ajol.info/index.php/olj/article/download/107617/97469. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ Tunisian women free to marry non-Muslims, BBC, 16 Sept 2017
- ↑ "Women’s rights protection instruments ratified by Botswana" (PDF). http://www.africa4womensrights.org/public/Dossier_of_Claims/BotswanaENG.pdf. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Concluding observations on the combined initial to fourth periodic reports of Lesotho" (PDF). http://tbinternet.ohchr.org/Treaties/CEDAW/Shared Documents/LSO/CEDAW_C_LSO_CO_1-4_Add-2_22348_E.pdf. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Liberia | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/liberia. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Malawi | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/malawi. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Namibia | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/namibia. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Niger | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/niger. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Nigeria | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/nigeria. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ CEDAW (2007), Responses to the List of Issues And Questions with Regard to the Consideration of the Combined Initial, Second, Third, Fourth and Fifth Periodic Reports: Sierra Leone, CEDAW/C/SLE/Q/5/Add. 1, CEDAW, New York, NY, p. 17.
- ↑ "Gender Equality in South Africa | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/south-africa. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Zimbabwe". 2007-03-06. https://2001-2009.state.gov/g/drl/rls/hrrpt/2006/78765.htm. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ Almeida, Henrique (14 July 2009). "Polygamy in Angola isn't legal, but it is common". http://in.reuters.com/article/idINIndia-41030220090714. "Although Angolan law condemns polygamy, or multiple marriages, the practice is widespread in a country with a large share of female-headed households and where woman are often left alone to care for their children."
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Burkina Faso | Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". http://www.genderindex.org/country/burkina-faso. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ Jensen Arnett, Jeffrey (2007). International encyclopedia of adolescence: A-J, index, Volume 1. Taylor & Francis. p. 123. ISBN 0415966671. https://books.google.com/books?id=lA606koL3EQC&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- ↑ Rego, Márcia (8 April 2015). The Dialogic Nation of Cape Verde: Slavery, Language, and Ideology. Lexington Books. p. 33. ISBN 0739193783. https://books.google.com/books?id=ND19CAAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q&f=false. "family structure in Santiago (and in much of Cape Verde) is characterized by informal polygamy"
- ↑ "Immigration and Refugee Board of Canada : Responses to Information Requests" (PDF). https://www.justice.gov/sites/default/files/eoir/legacy/2014/08/04/COD104852.E.pdf. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Examining the Life of Women in Western Africa" (PDF). http://www.uoregon.edu/~aweiss/intl421_521/CEDAW_Report_West_Africa.pdf. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Abdullahi Ahmed An-Na'im". http://www.law.emory.edu/ifl/region/westafrica.html. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ [2]
- ↑ "Gender Equality in Ghana - Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI)". Genderindex.org. http://genderindex.org/country/ghana. Retrieved 24 September 2015.
- ↑ "Ghana". Law.emory.edu. http://www.law.emory.edu/ifl/legal/ghana.htm. Retrieved 24 September 2015.
- ↑ OECD (2010). Atlas of Gender and Development: How Social Norms Affect Gender Equality in non-OECD Countries. Paris: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Development Centre.. ISBN 978-92-64-07520-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=KjGk01ZpSQQC.
- ↑ Angelique Chrisafis in Paris (26 March 2009). "Welcome to France: home of sun, sea, sand, polygamy and the Indian Ocean". Guardian (London). https://www.theguardian.com/world/2009/mar/26/mayote-referendum-polygamy-islam. Retrieved 21 October 2010.
- ↑ "Muslim island must give up polygamy as price of being part of France". Sydney Morning Herald. 31 March 2009. http://www.smh.com.au/world/muslim-island-must-give-up-polygamy-as-price-of-being-part-of-france-20090330-9h3j.html. Retrieved 21 October 2010.
- ↑ Mwareya, Ray (5 July 2016). "Widows without sons in Mozambique accused of sorcery and robbed of land". https://www.reuters.com/article/us-mozambique-widows-polygamy-idUSKCN0ZL0T6. "Although polygamy is prohibited in Mozambique there is no punishment. Across the country nearly a third of married women are thought to be in polygamous marriages, according to a NORAD survey."
- ↑ "Archived copy". http://www.servat.unibe.ch/law/icl/rw00000_.html.
- ↑ "Polygamy is Brazil's latest contribution to sexual revolution". https://www.efe.com/efe/english/life/polygamy-is-brazil-s-latest-contribution-to-sexual-revolution/50000263-2893262. Retrieved 2018-07-02.
- ↑ "Criminal Code". http://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/acts/C-46/section-293.html#docCont. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Criminal Code". http://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/acts/C-46/section-290.html#docCont. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ 90.0 90.1 Lak, Daniel (21 January 2009). "Polygamy in Canada". CBC News. http://www.cbc.ca/canada/story/2009/01/21/f-polygamy.html. Retrieved 23 July 2009.
- ↑ "Crown wants polygamy testimony off internet". CBC News. 26 November 2010. https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/british-columbia/crown-wants-polygamy-testimony-off-internet-1.868125?ref.
- ↑ 92.0 92.1 92.2 92.3 "Canada's polygamy laws upheld by B.C. Supreme Court". CBC news. 23 November 2011. http://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/british-columbia/story/2011/11/23/bc-polygamy-ruling-supreme-court.html.
- ↑ 93.0 93.1 Barbara Bradley Hagerty (27 May 2008). "Some Muslims in U.S. Quietly Engage in Polygamy". National Public Radio: All Things Considered. https://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=90857818. Retrieved 23 July 2009.
- ↑ Lyman, Edward Leo (1994), "Statehood for Utah", in Powell, Allan Kent, Utah History Encyclopedia, Salt Lake City, Utah: University of Utah Press, ISBN 0874804256, OCLC 30473917, archived from the original on 1 November 2013, https://web.archive.org/web/20131101131036/http://www.uen.org/utah_history_encyclopedia/s/STATEHOOD.html
- ↑ "Marriage Law of the People's Republic of China". http://www.lawinfochina.com/display.aspx?lib=law&id=11.
- ↑ The English Law of Bigamy in a Multi-Confessional Society: The Israel Experience by P Shifman.
- ↑ "Myanmar's president signs off on polygamy law seen as targeting Muslims". Aljazeera. August 2015. http://america.aljazeera.com/articles/2015/8/31/myanmars-president-signs-off-on-law-seen-as-targeting-muslims.html.
- ↑ Chin Kim (1973). "Law of Marriage and Divorce in North Korea". The International Lawyer 7 (4): 910. OCLC 759928863.
- ↑ "民法-結婚要件之研析". http://www.shs.edu.tw/works/essay/2008/03/2008032917040336.pdfSHS.edu.tw.[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
- ↑ "Polygamy Fosters Culture Clashes (and Regrets) in Turkey", New York Times, 10 July 2006
- ↑ ""Turkey Between Secularism and Islamism" by Jacob M. Landau". http://www.jcpa.org/jl/vp352.htm.
- ↑ "Turkey's secularism 'threatened'", BBC
- ↑ Alev Çinar, "Modernity, Islam, and Secularism in Turkey"
- ↑ "Polygamy in Turkey", Polygamy 411, May 2009
- ↑ "Abdullahi Ahmed An-Na'im". http://www.law.emory.edu/ifl/legal/palestine.htm#text. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ Mony, Keo (5 February 2008). "Cambodian Marriage". https://ethnomed.org/culture/cambodian/cambodian-marriage/. "The modern constitution forbids polygamy; some say it is commonly practiced more often when family economics permit."
- ↑ Ben Zikri, Almog (25 November 2018). "Out of Over 300 Polygamy Cases in Israel in 2018, 16 Reached Indictments" (in en). Haaretz. https://www.haaretz.com/israel-news/out-of-over-300-cases-in-2018-against-polygamy-16-reached-indictments-1.6680885. Retrieved 14 May 2019.
- ↑ "Here Come The Brides". https://www.rferl.org/a/1144507.html.
- ↑ "Russians beating demographics with polygamy". RT. 26 July 2011. http://www.rt.com/news/russia-three-andrey-love/. Retrieved 6 August 2012.
- ↑ Mira Katbamna (26 October 2009). "'Half a good man is better than none at all'". The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/education/2009/oct/27/polygamy-study-russia-central-asia. Retrieved 6 August 2012.
- ↑ Osborn, Andrew (2006-01-14). "War-ravaged Chechnya needs polygamy, says its leader". The Independent (London). Archived from the original on 2006-01-17. https://web.archive.org/web/20060117043122/http://news.independent.co.uk/europe/article338474.ece.
- ↑ Chintana Yossoonthorn, Women in Thailand, Proceedings of the Peace Corps Conference on Women and Development Bangkok, 1979, p. 11.
- ↑ "Timor-Leste : Discriminatory family code" (PDF). http://www.genderindex.org/sites/default/files/datasheets/TL.pdf. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Bulgarian Penal Code, art. 179". http://www.vks.bg/vks_p04_04.htm#Раздел I$. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- ↑ http://www.finlex.fi/en/laki/kaannokset/1929/en19290234.pdf
- ↑ "FINLEX ® - Hallituksen esitykset: HE 44/2001". http://www.finlex.fi/fi/esitykset/he/2001/20010044.
- ↑ "§172 StGB". http://dejure.org/gesetze/StGB/172.html.
- ↑ Bewarder, Manuel (2019-05-04). "Polygamie: Einbürgerung bleibt trotz Mehrehe möglich". https://www.welt.de/politik/article192948725/Polygamie-Einbuergerung-bleibt-trotz-Mehrehe-moeglich.html.
- ↑ "Offences Against The Person Act, 1861". Irish Statute Book. pp. Section 57. http://www.irishstatutebook.ie/eli/1861/act/100/enacted/en/print.html#sec57. Retrieved 15 June 2017.
- ↑ 120.0 120.1 Maogoto, Jackson Nyamuya; Anolak, Helena (2009). "Legalising Divorce in the Republic of Ireland: A Canonical Harness to the Legal Liberation of the Right to Marriage Among the Disenfranchised". SSRN Electronic Journal. doi:10.2139/ssrn.1465343. ISSN 1556-5068.
- ↑ Shatter, Alan (5 October 1995). "Fifteenth Amendment of the Constitution (No. 2) Bill, 1995: Committee Stage.". Select Committee on Legislation and Security Debate. Oireachtas. http://oireachtasdebates.oireachtas.ie/debates authoring/debateswebpack.nsf/committeetakes/JUS1995100500003#N210. Retrieved 15 June 2017. "The State does not recognise church decrees of annulment. In effect, all marriages celebrated after a church decree of annulment are bigamous and priests celebrating these marriages are accessories before the fact to bigamy and liable to criminal prosecution. ... we have turned a blind eye to the celebration of bigamous marriages and abandoned couples who celebrate them to a legal limbo for so many years."
- ↑ Carolan, Mary (15 June 2017). "First marriage of Lebanese man with two wives recognised under Irish law". The Irish Times. http://www.irishtimes.com/news/crime-and-law/courts/supreme-court/first-marriage-of-lebanese-man-with-two-wives-recognised-under-irish-law-1.3120790. Retrieved 15 June 2017.
- ↑ Geysegom (1997). Samenlevingscontracten 1997: focus op het buurtniveauPretekst,. pp. 17–19.
- ↑ "Romanian Penal Code, art. 376". http://lege5.ro/Gratuit/gezdmnrzgi/codul-penal-din-2009?pid=135200274&d=2009-07-24#p-135200274. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ↑ 125.0 125.1 125.2 Svenska Dagbladet: Månggifte godkänns – ibland (accessed 15 January 2016)
- ↑ 126.0 126.1 126.2 Aftonbladet: Jodå – månggifte ÄR tillåtet i Sverige (accessed 15 January 2016)
- ↑ "Archived copy". http://www.exponerat.net/tillatet-for-man-att-ha-flera-fruar/.
- ↑ "Archived copy". http://www.rwi.uzh.ch/oe/cimels/Eheschliessungen_im_Ausland.pdf.
- ↑ 129.0 129.1 "House of Commons Library Briefing Note: Polygamy". House of Commons Library. 12 October 2011. http://www.parliament.uk/briefing-papers/sn05051.pdf.
- ↑ "Aboriginal Marriages and Family Structures". Australian Law Reform Commission. https://www.alrc.gov.au/publications/12. Aboriginal Marriages and Family Structures/marriages-aboriginal-societies-today. Retrieved 20 October 2017.
- ↑ "How common is polygamy in Australia? And how does it work?". SBS. 29 May 2012. http://www.sbs.com.au/news/insight/tvepisode/polygamy. Retrieved 20 October 2017.
- ↑ "FAMILY LAW ACT 1975 - SECT 6 Polygamous marriages". http://www.austlii.edu.au/au/legis/cth/consol_act/fla1975114/s6.html.
- ↑ "Eheschliessungen im Ausland" (PDF). http://www.rwi.uzh.ch/oe/cimels/Eheschliessungen_im_Ausland.pdf. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "The Problem of "relationship overlap" in Saskatchewan". 5 January 2011. https://stoppolygamyincanada.wordpress.com/2011/01/05/the-problem-of-relationship-overlap-in-saskatchewan/.
- ↑ "Tunisia: Notable Features: Polygamy". Law.emory.edu. http://www.law.emory.edu/ifl/legal/tunisia.htm. Retrieved 21 October 2010.
- ↑ "Palestinian Marriage Laws". Law.emory.edu. http://www.law.emory.edu/ifl/legal/palestine.htm#text. Retrieved 21 October 2010.
- ↑ Grabianowski, Ed. "How Polygamy Works". People.howstuffworks.com. http://people.howstuffworks.com/polygamy.htm. Retrieved 21 October 2010.
- ↑ "Multiple Damage of Polygamy by Saktida". Boloji.com. 31 October 2004. http://www.boloji.com/wfs2/wfs297.htm. Retrieved 21 October 2010.
- ↑ "DEL2848compilado". http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/decreto-lei/Del2848compilado.htm.
- ↑ "Three-person civil union sparks controversy in Brazil". BBC. https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-latin-america-19402508.
- ↑ "Rio registra primeira união entre 3 mulheres" (in pt). Jornal do Commercio. 17 October 2015. http://jconline.ne10.uol.com.br/canal/cidades/geral/noticia/2015/10/17/rio-registra-primeira-uniao-entre-3-mulheres-204110.php. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- ↑ "Rio registra primeira união estável realizada entre três mulheres" (in pt). O Estado de S. Paulo. 18 October 2015. http://brasil.estadao.com.br/noticias/rio-de-janeiro,rio-registra-primeira-uniao-estavel-entre-3-mulheres,1781538. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- ↑ "Equality of Rights Between Men and Women". University of Minnesota Human Rights Library. http://www1.umn.edu/humanrts/gencomm/hrcom28.htm.
- ↑ "OHCHR report". Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights. http://www2.ohchr.org/english/bodies/hrc/docs/ngos/IHRLS_Chad_95.pdf.
- ↑ "Report of the Human Rights Committee". United Nations General Assembly. http://www.ccprcentre.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/A_63_40_Vol.I_E.pdf.
- ↑ "GENERAL COMMENTS ADOPTED BY THE HUMAN RIGHTS COMMITTEE UNDER ARTICLE 40, PARAGRAPH 4, OF THE INTERNATIONAL COVENANT ON CIVIL AND POLITICAL RIGHTS". United Nations Human Rights Website. Archived from the original on 30 June 2013. https://web.archive.org/web/20130630225551/http://www.unhchr.ch/tbs/doc.nsf/0/13b02776122d4838802568b900360e80.
- ↑ "United Nations Treaty Collection". https://treaties.un.org/Pages/ViewDetails.aspx?src=IND&mtdsg_no=IV-4&chapter=4&lang=en.
- ↑ "POLYGYNY AS A VIOLATION OF INTERNATIONAL HUMAN RIGHTS LAW". Department of Justice, Government of Canada. http://www.justice.gc.ca/eng/rp-pr/other-autre/poly/chap3.html.
- ↑ 149.0 149.1 149.2 "Restricting or banning polygamy, human rights values must stand". The Jakarta Post. Archived from the original on 7 June 2011. https://web.archive.org/web/20110607114419/http://www.thejakartapost.com/news/2007/01/12/restricting-or-banning-polygamy-human-rights-values-must-stand.html. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ "MALAWI : Strategic Country Gender Assessment" (PDF). http://siteresources.worldbank.org/EXTAFRREGTOPGENDER/Resources/MalawiSCGA.pdf. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Middle East | Gadaffi outrage over polygamy bill". BBC News. 25 February 1999. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/285866.stm. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ "Customary marriages now legal". News24. SAPA. 15 November 2000. http://www.news24.com/SouthAfrica/News/Customary-marriages-now-legal-20001115. Retrieved 23 June 2013.
- ↑ "Microsoft Word – news03.2-customary marriage.doc" (PDF). http://www.lac.org.na/projects/grap/Pdf/custmar2003.pdf. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ "Polygamy- To share or not to share? That is the Question" (PDF). http://www.lac.org.na/news/inthenews/pdf/poligamy.pdf. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ 155.0 155.1 Pannier, Bruce (9 March 2007). "Kyrgyzstan: Debate On Legalized Polygamy Continues – Radio Free Europe / Radio Liberty © 2010". Rferl.org. Archived from the original on 26 July 2009. https://web.archive.org/web/20090726054228/http://www.rferl.org/content/Article/1075173.html. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (28 May 2008). "Refworld | Central Asia: Kazakhstan debates polygamy amid regional rise in popularity". UNHCR. http://www.unhcr.org/refworld/publisher,RFERL,,KAZ,4844c1e7c,0.html. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ Sykes, Hugh (2 September 2008). "Middle East | Iran rejects easing polygamy law". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/7594997.stm. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ "OneLove Southern Africa Latest Posts / Blog Profile". http://www.blogcatalog.com/blog/onelove-southern-africa/c1483783b4b34ec42e61016bfa005a02. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. "Refworld | Kyrgyzstan. Political Conditions in the Post-Soviet Era". UNHCR. http://www.unhcr.org/cgi-bin/texis/vtx/refworld/rwmain?page=search&docid=3ae6a60910&skip=0&query=polygamy. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ "Thailand Law Forum: Family Law of Thailand". Thailawforum.com. 1 October 1935. http://www.thailawforum.com/articles/familywimol2.html#f15. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ V.Jayaram (9 January 2007). "Hinduism and Polygamy". Hinduwebsite.com. http://www.hinduwebsite.com/hinduism/h_polygamy.asp. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ 162.0 162.1 162.2 162.3 "Women: Polygamy and Family Law – Valentina M. Donini | Reset Dialogues on Civilizations". Resetdoc.org. http://www.resetdoc.org/EN/Polygamy-family-law.php. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ "The International Encyclopedia of Sexuality: Hong Kong". .hu-berlin.de. 30 June 1997. Archived from the original on 5 November 2006. https://web.archive.org/web/20061105131143/http://www2.hu-berlin.de/sexology/IES/hongkong.html#2. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ [3]
- ↑ Pennink, Adrian (1 April 2001). "Thousands of families in despair as France enforces ban on polygamy – Europe, World". The Independent (London). https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/europe/thousands-of-families-in-despair-as-france-enforces-ban-on-polygamy-689622.html. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ 166.0 166.1 United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. "Refworld | Uganda: Domestic violence, including legislation, statistics and attitudes toward domestic violence; the availability of protection and support services". UNHCR. http://www.unhcr.org/refworld/country,,IRBC,,UGA,456d621e2,49b92b20c,0.html. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. "Refworld | Consideration of reports submitted by States parties under articles 16 and 17 of the Covenant : concluding observations of the Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights : Benin". UNHCR. http://www.unhcr.org/cgi-bin/texis/vtx/refworld/rwmain?page=search&docid=4885cfba0&skip=0&query=polygamy. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. "Refworld | Amnesty International Report 2005 – Morocco/Western Sahara". UNHCR. http://www.unhcr.org/cgi-bin/texis/vtx/refworld/rwmain?page=search&docid=429b27eca&skip=0&query=polygamy. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (17 July 2005). "Refworld | Violence Against Women in Northern Uganda". UNHCR. http://www.unhcr.org/cgi-bin/texis/vtx/refworld/rwmain?page=search&docid=439467214&skip=0&query=polygamy. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ "People's Daily Online – Planned polygamy ban stirs debate in Indonesia". English.peopledaily.com.cn. 6 December 2006. http://english.peopledaily.com.cn/200612/06/eng20061206_329258.html. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ "Polygamy Law Irks Iraq Kurds - ارشيف اسلام اونلاين". 2009-03-02. http://www.islamonline.net/servlet/Satellite?c=Article_C&cid=1226331242817&pagename=Zone-English-News/NWELayout. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ Angelique Chrisafis in Paris (26 March 2009). "Tiny island of the Indian Ocean keen to embrace French rule – 34 years after gaining independence | World news". The Guardian (London). https://www.theguardian.com/world/2009/mar/26/mayote-referendum-polygamy-islam. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ "Polygamy in Turkey - Polygamy 411". http://polygamy411.com/2009/05/08/polygamy-in-turkey/. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ "Indonesia Tightens Polygamy Rules - ارشيف اسلام اونلاين". 2009-03-09. http://www.islamonline.net/servlet/Satellite?c=Article_C&cid=1235628782541&pagename=Zone-English-News/NWELayout. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
Categories: [Marriage law]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 08/18/2024 15:05:09 | 175 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Social:Legality_of_polygamy | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF