Lithium Oxalate
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 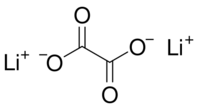
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Lithium oxalate
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula
|
Li 2C 2O 4 |
| Molar mass | 101.90 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless crystalline solid |
| Density | 2.12 g/cm3 |
Solubility in water
|
6.6 g per 100 g of water |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | WARNING |
GHS hazard statements
|
H302, H312 |
GHS precautionary statements
|
P264, P270, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P312, P322, P330, P363, P501 |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
- SizeSet
Lithium oxalate is an organic compound with the chemical formula Li
2C
2O
4. It is a salt of lithium metal and oxalic acid.[3][4] It consists of lithium cations Li+
and oxalate anions C
2O2−
4. Lithium oxalate is soluble in water and converts to lithium oxide when heated.[5]
Synthesis
One of the methods of synthesis is the reaction of direct neutralization of oxalic acid with lithium hydroxide:
- 2 LiOH + H
2C
2O
4 → Li
2C
2O
4 + 2 H
2O
Properties
The compound crystallizes in the monoclinic system, cell parameters a = 3.400 Å, b = 5.156 Å, c = 9.055 Å, β = 95.60°, Z = 4.[3]
Lithium oxalate decomposes when heated at 410–500 °C (770–932 °F; 683–773 K):
- Li
2C
2O
4 → Li
2CO
3 + CO
Applications
In pyrotechnics, the compound is used to color the flame red.[6]
References
- ↑ "553-91-3 | Sigma-Aldrich". Sigma Aldrich. https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/RU/ru/search/553-91-3?focus=products&page=1&perPage=30&sort=relevance&term=553-91-3&type=cas_number.
- ↑ "di-Lithium oxalate". Merck Millipore. https://www.merckmillipore.com/RU/ru/product/di-Lithium-oxalate,MDA_CHEM-822085?ReferrerURL=https://www.google.ru/.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Beagley, B.; Small, R. W. H. (1964-06-10). "The structure of lithium oxalate" (in en). Acta Crystallographica 17 (6): 783–788. doi:10.1107/S0365110X64002079. https://scripts.iucr.org/cgi-bin/paper?a04249. Retrieved 15 June 2021.
- ↑ Solchenbach, Sophie; Wetjen, Morten; Pritzl, Daniel; Schwenke, K. Uta; Gasteiger, Hubert A. (2018). "Lithium Oxalate as Capacity and Cycle-Life Enhancer in LNMO/Graphite and LNMO/SiG Full Cells" (in en). Journal of the Electrochemical Society 165 (3): A512–A524. doi:10.1149/2.0611803jes. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1149/2.0611803jes. Retrieved 15 June 2021.
- ↑ "Lithium Oxalate" (in en). Millipore-Sigma. https://www.emdmillipore.com/CA/en/product/di-Lithium-oxalate,MDA_CHEM-822085.
- ↑ Koch, Ernst-Christian (2009). "Is it possible to Obtain a Deep Red Pyrotechnic Flame Based on Lithium?". 36th International Pyrotechnics Seminar. doi:10.13140/2.1.1657.0567. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/268211790. Retrieved 15 June 2021.
 |
Categories: [Inorganic compounds] [Oxalates]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 05/07/2025 15:01:54 | 10 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Lithium_oxalate | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
✘
ZWI is not signed. [what is this?]

 KSF
KSF