Manganese Stearate
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 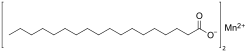
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Manganese(II) stearate, manganese distearate, manganese(2+) dioctadecanoate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C36H70MnO4 | |
| Molar mass | 621.89 |
| Appearance | Pale pink powder |
| Density | g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 359.4 °C (678.9 °F; 632.5 K) |
| insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H312, H315, H319, H332, H335 | |
| Flash point | 162.4 °C (324.3 °F; 435.5 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Manganese stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of manganese and stearic acid with the chemical formula C36H70MnO4.[1][2] The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.[3]
Synthesis
Manganese stearate is synthesized by the reaction of stearic acid with sodium hydroxide, followed by reacting with manganese chloride.[4]
Also, the reaction of manganese(II) acetate with stearic acid.[5]
Physical properties
The compound forms pale pink powder.[6]
Insoluble in water.[6]
Uses
The compound is used in organic synthesis reactions.[6]
Also as an oxidant additive for oxo-biodegradable polymers (for example, high-density polyethylene).[7]
References
- ↑ "Manganese Stearate" (in en). American Elements. https://www.americanelements.com/manganese-stearate-3353-05-7.
- ↑ "NCATS Inxight Drugs — MANGANESE STEARATE" (in en). National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. https://drugs.ncats.io/drug/0276L2MSQ6.
- ↑ "CAS 3353-05-7 Manganese Stearate - Alfa Chemistry". alfa-chemistry.com. https://www.alfa-chemistry.com/product/manganese-stearate-cas-3353-05-7-285018.html.
- ↑ Aras, Neny Rasnyanti M.; Arcana, I Made (2015). "Synthesis of manganese stearate for high density polyethylene (HDPE) and its biodegradation". AIP Conference Proceedings: 070024. doi:10.1063/1.4930728. https://aip.scitation.org/doi/abs/10.1063/1.4930728?journalCode=apc. Retrieved 6 March 2023.
- ↑ "manganese stearate" (in en). chemsrc.com. https://www.chemsrc.com/en/cas/3353-05-7_88892.html.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 "Manganese Stearate | CAS 3353-05-7" (in en). Santa Cruz Biotechnology. https://www.scbt.com/p/manganese-stearate-3353-05-7.
- ↑ Roy, Prasun Kumar; Singh, Priyanka; Kumar, Devendra; Rajagopal, Chitra (2010). "Manganese stearate initiated photo-oxidative and thermo-oxidative degradation of LDPE, LLDPE and their blends". Journal of Applied Polymer Science: NA–NA. doi:10.1002/app.31252.
 |
Categories: [Stearates] [Manganese compounds]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 09/05/2023 13:29:00 | 15 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Manganese_stearate | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed:
 KSF
KSF