Aceturic Acid
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 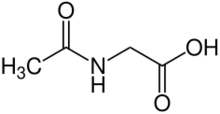
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Acetamidoacetic acid | |
| Other names
Acetylglycine
N-Acetylglycine 2-Acetamidoacetic acid Acetylglycocoll | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | AcGly |
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| DrugBank |
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula
|
C4H7NO3 |
| Molar mass | 117.104 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White powder or needles |
| Melting point | 206 to 208 °C (403 to 406 °F; 479 to 481 K) |
Solubility in water
|
2.7% at 15 °C |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
N-Acetylglycinamide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Aceturic acid (N-acetylglycine) is a derivative of the amino acid glycine. The conjugate base of this carboxylic acid is called aceturate, a term used for its esters and salts.
Preparation
Aceturic acid can be prepared by warming glycine either with a slight excess of acetic anhydride in benzene,[1] or with an equal molar amount of acetic anhydride in glacial (concentrated) acetic acid.[2]
See also
- Aceglutamide (α-N-Acetylglutamine)
- N-Acetylaspartic acid
- N-Acetylcysteine
- N-Acetylglutamic acid
- N-Acetylleucine
- Nε-Acetyllysine
- N-Acetyltyrosine
- Aceburic acid
References
- ↑ Curtius, Th.; Radenhausen, R. (1895). "Hydrazide und Azide organischer Säuren. X Abhandlung. 35. Ueber Hydrazide substituirter Amidosäuren und das Hydrazid der Fumarsäure". J. Prakt. Chem. 52 (1): 433–454. doi:10.1002/prac.18950520134. https://zenodo.org/record/1427988.
- ↑ Dakin, H. D. (1929). "The Condensation of Aromatic Aldehydes with Glycine and Acetylglycine". J. Biol. Chem. 82 (2): 439–446. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(20)78291-8. http://www.jbc.org/content/82/2/439.full.pdf.
 |
Categories: [Acetamides]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 03/11/2024 02:22:40 | 3 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Aceturic_acid | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
✘
ZWI is not signed. [what is this?]

 KSF
KSF