Allyl Phenyl Ether
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 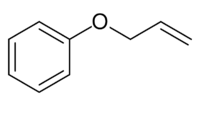
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
[(Prop-2-en-1-yl)oxy]benzene | |
| Other names
(Allyloxy)benzene
3-Phenoxypropene Allyloxybenzene | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula
|
C9H10O |
| Molar mass | 134.178 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Melting point | 90 °C (194 °F; 363 K) |
| Boiling point | 191.7 °C (377.1 °F; 464.8 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
GHS hazard statements
|
H302, H312, H332 |
GHS precautionary statements
|
P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P304+312, P304+340, P312, P322, P330, P363, P501 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
- SizeSet
Allyl phenyl ether is an organic compound with the formula C6H5OCH2CH=CH2. It is a colorless solid.
Preparation
Allyl phenyl ether is prepared by the reaction of sodium phenoxide with allyl bromide:[1]
- C6H5ONa + BrCH2CH=CH2 → C6H5OCH2CH=CH2 + NaBr
The yield is almost quantitative when the reaction is conducted in homogeneous solution using dimethoxyethane. When the reaction is conducted as a slurry in diethyl ether, the predominant product is, after acidic work-up, 2-allylphenol.
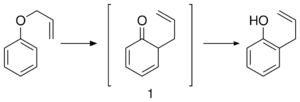
Reactions
Allyl phenyl ether converts to 2-allylphenol in the presence of acid catalysts. This conversion is an example of the Claisen rearrangement.[2][3]
References
- ↑ Kornblum, Nathan; Lurie, Arnold P. (1959). "Heterogeneity as a Factor in the Alkylation of Ambident Anions: Phenoxide Ions1,2". Journal of the American Chemical Society 81 (11): 2705–2715. doi:10.1021/ja01520a030.
- ↑ Martín Castro, Ana M. (2004). "Claisen Rearrangement over the Past Nine Decades". Chemical Reviews 104 (6): 2939–3002. doi:10.1021/cr020703u. PMID 15186185.
- ↑ Yadav, G. D.; Lande, S. V., UDCaT-5: A Novel and Efficient Solid Superacid Catalyst for Claisen Rearrangement of Substituted Allyl Phenyl Ethers. Synthetic Communications 2007, 37 (6), 941-946
 |
Categories: [Phenol ethers] [Phenyl compounds] [Allyl compounds]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 02/01/2024 08:01:57 | 7 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Allyl_phenyl_ether | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
✘
ZWI is not signed. [what is this?]

 KSF
KSF