Coronary Artery Aneurysm
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki | Coronary artery aneurysm | |
|---|---|
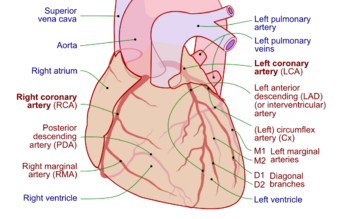 | |
| Coronary arteries | |
| Causes | atherosclerosis, Kawasaki disease, coronary catheterization. |
| Diagnostic method | coronary angiography |
| Treatment | medical management, surgical excision, coronary bypass grafting (CABG), and percutaneous coronary interventions[1] |
Coronary artery aneurysm is an abnormal dilatation of part of the coronary artery. This rare disorder occurs in about 0.3–4.9% of patients who undergo coronary angiography.[2]
Signs and symptoms
Causes
Acquired causes include atherosclerosis in adults,[3] Kawasaki disease in children[4] and coronary catheterization. With the invention of drug eluting stents, there has been more cases implying stents lead to coronary aneurysms. The pathophysiology, although not completely understood, might be comparable to that of aneurysms of larger vessels. This includes disruption of the arterial media, weakening of the arterial wall, increased wall strain and slow dilatation of the coronary artery portion.[2]
It can also be congenital.[5][6] The following risk factors are thought to be associated with coronary artery aneurysms:
- Individual's genetic make-up, especially in patients with congenital coronary artery aneurysms
- Coronary artery disease (atherosclerosis)
- Vasculitic and connective tissue diseases (Kawasaki and Marfan)
- Intracoronary manipulation leading to local wall stress (stent placement, angioplasty, brachytherapy)
- Post-infectious as a consequence of direct wall infiltration or immune complex deposition[7]
Diagnosis
It is often found coincidentally on coronary angiography.[8] Other modalities that can be used to diagnose a coronary artery aneurysm include echocardiography, magnetic resonance imaging and computerized tomography. Although coronary angiography remains to be the gold standard, the invasive procedure comes with its associated risks, is more expensive than other modalities and the size of the aneurysm might be miscalculated if there is a thrombus in place.[2]
Treatment
Treatment for coronary artery aneurysm include medical management, surgery and percutaneous intervention. Underlying coronary artery risk factors should be addressed in patients with atherosclerosis and proper guideline-mediated medications should be started. In those with risk for embolism or thrombosis, anti-platelet or anticoagulation therapy should be contemplated.[citation needed]
In patients with Kawasaki disease prompt administration of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) therapy should be given to prevent complication of coronary artery aneurysm.[9]
Prognosis
Generally, it has a good prognosis.[8] In Kawasaki's disease, untreated, there is a 1–2% death rate, from cardiac causes.[citation needed]
The prognosis of coronary artery aneurysm is dependent on its diameter. The smaller the aneurysm the better the prognosis. There is less risk for ischemic myocardial damage and mortality with smaller aneurysms. Aneurysms with an internal diameter > 8 mm have poorer outcomes, since these aneurysms can be occluded and be associated with complications such as arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, or sudden death.[2]
See also
- Aneurysm
- Coronary artery ectasia
References
- ↑ Kawsara, Akram; Núñez Gil, Iván J.; Alqahtani, Fahad; Moreland, Jason; Rihal, Charanjit S.; Alkhouli, Mohamad (2018-07-09). "Management of Coronary Artery Aneurysms". JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions 11 (13): 1211–1223. doi:10.1016/j.jcin.2018.02.041. ISSN 1936-8798. PMID 29976357.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Sheikh, Azeem S.; Hailan, Ahmed; Kinnaird, Tim; Choudhury, Anirban; Smith, David (2019). "Coronary Artery Aneurysm: Evaluation, Prognosis, and Proposed Treatment Strategies". Heart Views 20 (3): 101–108. doi:10.4103/HEARTVIEWS.HEARTVIEWS_1_19. ISSN 1995-705X. PMID 31620255.
- ↑ "Coronary artery aneurysm: a review and hypothesis regarding etiology". Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 132 (5): 823–8. May 2008. doi:10.5858/2008-132-823-CAAARA. PMID 18466032. https://www.archivesofpathology.org/doi/full/10.1043/1543-2165(2008)132[823:CAAARA]2.0.CO;2.
- ↑ "Coronary artery aneurysm induced by Kawasaki disease in children show features typical senescence". Circ. J. 71 (5): 709–15. May 2007. doi:10.1253/circj.71.709. PMID 17456996.
- ↑ "Congenital coronary artery aneurysms". Br Heart J 36 (4): 329–35. April 1974. doi:10.1136/hrt.36.4.329. PMID 4842623.
- ↑ "MRI of congenital coronary artery aneurysm". Br J Radiol 73 (867): 322–4. March 2000. doi:10.1259/bjr.73.867.10817051. PMID 10817051.
- ↑ Kawsara, Akram; Núñez Gil, Iván J.; Alqahtani, Fahad; Moreland, Jason; Rihal, Charanjit S.; Alkhouli, Mohamad (2018-07-09). "Management of Coronary Artery Aneurysms". JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions 11 (13): 1211–1223. doi:10.1016/j.jcin.2018.02.041. ISSN 1876-7605. PMID 29976357.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Coronary artery aneurysm: a review". Clin Cardiol 29 (10): 439–43. October 2006. doi:10.1002/clc.4960291005. PMID 17063947.
- ↑ Abou Sherif, Sara; Ozden Tok, Ozge; Taşköylü, Özgür; Goktekin, Omer; Kilic, Ismail Dogu (2017-05-05). "Coronary Artery Aneurysms: A Review of the Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment". Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine 4: 24. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2017.00024. ISSN 2297-055X. PMID 28529940.
External links
| Classification | D
|
|---|
 |
Categories: [Heart diseases]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 09/19/2023 08:39:23 | 2 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Medicine:Coronary_artery_aneurysm | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed:
 KSF
KSF