Cape (Geography)
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki Short description: Large headland extending into a body of water, usually the sea



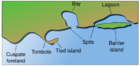
In geography, a cape is a headland, or peninsula or promontory extending into a body of water, usually the sea.[1] A cape usually represents a marked change in trend of the coastline, often making them important landmarks in sea navigation. This also makes them prone to natural forms of erosion, mainly tidal actions, resulting in a relatively short geological lifespan. Capes can be formed by glaciers, volcanoes, and changes in sea level. Erosion plays a large role in each of these methods of formation.[citation needed]
Gallery
-
Cape Cornwall, England
-
Satellite image of Cape Fear, North Carolina
-
Cape MacLear, Malawi
-
Map depicting Cape Horn at the southernmost portion of South America
-
Photograph of Cabo Mayor in Santander, Spain
-
Photograph of Cape Cambell, New Zealand, at sunrise
See also
- Extreme points of Africa
- Extreme points of Asia
- Extreme points of Europe
- Extreme points of North America
- Extreme points of South America
References
- ↑ Whittow, John (1984). Dictionary of Physical Geography. London: Penguin, 1984, p. 80. ISBN 0-14-051094-X.
External links
 |
Categories: [Headlands] [Coastal and oceanic landforms] [Oceanographical terminology]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 01/24/2026 18:39:12 | 79 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Earth:Cape_(geography) | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
✘
ZWI is not signed. [what is this?]


.jpg)





 KSF
KSF