Abcn
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 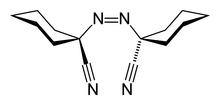
| |
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
1,1′-Diazene-1,2-diyldicyclohexanecarbonitrile | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | ACHN |
Beilstein Reference
|
960744 |
| ChemSpider |
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| UN number | 3226 |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula
|
C14H20N4 |
| Molar mass | 244.342 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 114 to 118[1] °C (237 to 244 °F; 387 to 391 K) decomposes near 80 °C |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements
|
H242, H315, H319, H335 |
GHS precautionary statements
|
P261, P305+351+338 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
1,1′-Azobis(cyclohexanecarbonitrile) or ACHN is a radical initiator.[1] The molecular formula is NCC6H10N=NC6H10CN. It is a white solid that is soluble in aromatic solvents.[2]
ACHN has a 10-hour half-life in toluene at 88 °C.[1]
See also
- Azobisisobutylonitrile (AIBN) is another commonly used free radical initiator
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1,1′-Azobis(cyclohexanecarbonitrile) at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Steven A. Kates, Fernando Albericio (2001). "1,1'-Azobis-1-cyclohexanenitrile". E-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.ra120.
 |
Categories: [Azo compounds] [Nitriles] [Radical initiators]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 08/24/2024 01:17:50 | 2 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:ABCN | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
✘
ZWI is not signed. [what is this?]

 KSF
KSF