Hafnium(Iii) Iodide
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 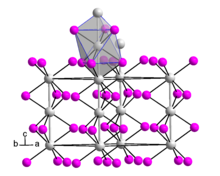
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Hafnium triiodide
| |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula
|
HfI3 |
| Molar mass | 559.20 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | black crystals[1] |
| Melting point | decomposes |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Hafnium(III) chloride Hafnium(III) bromide |
Other cations
|
Titanium(III) iodide Zirconium(III) iodide |
Related compounds
|
Hafnium(IV) iodide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Hafnium(III) iodide is an inorganic compound of hafnium and iodine with the formula Hf I3. It is a black solid.[2]
Preparation
Like other group 4 trihalides, hafnium(III) iodide can be prepared from hafnium(IV) iodide by high-temperature reduction with hafnium metal, although incomplete reaction and contamination of the product with excess metal often occurs.[2]
- 3 Hf I4 + Hf → 4 Hf I3
Other metals can be used as the reducing agent, for example aluminium. The product is often nonstoichiometric, with the compositions Hf I3.2–3.3 and Hf I3.0–3.5 reported.[3][4]
Structure and bonding
Hafnium(III) iodide adopts the same crystal structure as zirconium(III) iodide.[5] This is very similar to the β-TiCl3 structure.[2] The structure is based on hexagonal close packing of iodide ions with one third of the octahedral interstices occupied by Hf3+ ions.[2] It consists of parallel chains of face-sharing {HfI6} octahedra.[5]
Hafnium(III) iodide has a lower magnetic moment than is expected for the d1 metal ion Hf3+, indicating non-negligible Hf–Hf bonding.[2] The Hf–Hf separation was originally reported to be 3.295 Å,[6] but a subsequent study of nonstoichiometric hafnium(III) iodide indicated a lower symmetry structure.[3]
Reactivity
Like the chloride and bromide, hafnium(III) iodide is a powerful enough reducing agent to reduce water and therefore does not have any aqueous chemistry.[2]
References
- ↑ William M. Haynes, ed (2013). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (93rd ed.). CRC Press. p. 4–66. ISBN 978-1466571143.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 965. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Struss, Arthur W.; Corbett, John D. (1969). "Lower halides of hafnium. Nonstoichiometric hafnium triiodide phase". Inorg. Chem. 8 (2): 227–232. doi:10.1021/ic50072a009.
- ↑ Clark, R. J. H.; Bradley, D. C.; Thornton, P. (2013). The Chemistry of Titanium, Zirconium and Hafnium Pergamon Texts in Inorganic Chemistry. Elsevier. p. 432. ISBN 978-1-4831-5921-8.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Wells, A. F. (1984). Structural Inorganic Chemistry (5th ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 418–419. ISBN 978-0-19-965763-6.
- ↑ Dahl, Lawrence F.; Chiang, Tao-I; Seabaugh, Pyrtle W.; Larsen, Edwin M. (1964). "Structural Studies of Zirconium Trihalides and Hafnium Triiodide". Inorg. Chem. 3 (9): 1236–1242. doi:10.1021/ic50019a008.
| HI | He | ||||||||||||||||
| LiI | BeI2 | BI3 | CI4 | NI3 | I2O4, I2O5, I4O9 |
IF, IF3, IF5, IF7 |
Ne | ||||||||||
| NaI | MgI2 | AlI3 | SiI4 | PI3, P2I4 |
S | ICl, ICl3 |
Ar | ||||||||||
| KI | CaI2 | Sc | TiI4 | VI3 | CrI3 | MnI2 | FeI2 | CoI2 | NiI2 | CuI | ZnI2 | Ga2I6 | GeI2, GeI4 |
AsI3 | Se | IBr | Kr |
| RbI | SrI2 | YI3 | ZrI4 | NbI5 | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | AgI | CdI2 | InI3 | SnI4, SnI2 |
SbI3 | TeI4 | I | Xe |
| CsI | BaI2 | HfI4 | TaI5 | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | AuI | Hg2I2, HgI2 |
TlI | PbI2 | BiI3 | Po | AtI | Rn | |
| Fr | RaI2 | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | SmI2 | Eu | Gd | TbI3 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac | ThI4 | Pa | UI3, UI4 |
Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | EsI3 | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
 |
Categories: [Hafnium compounds] [Iodides] [Metal halides]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 07/14/2024 02:08:23 | 3 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Hafnium(III)_iodide | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF