.jpg)
1683 map by French cartographer Alain Manesson Mallet from his publication Description de L'Univers. Shows a sea below both the Atlantic and Pacific oceans at a time when Tierra del Fuego was believed joined to Antarctica. Sea is named Mer Magellanique after Ferdinand Magellan.

Samuel Dunn's 1794 General Map of the World or Terraqueous Globe shows a Southern Ocean (but meaning what is today named the South Atlantic) and a Southern Icy Ocean.

A New Map of Asia, from the Latest Authorities, by John Cary, Engraver, 1806, shows the Southern Ocean lying to the south of both the Indian Ocean and Australia.
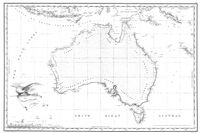
Freycinet Map of 1811 – resulted from the 1800–1803 French Baudin expedition to Australia and was the first full map of Australia ever to be published. In French, the map named the ocean immediately below Australia as the Grand Océan Austral ('Great Southern Ocean').
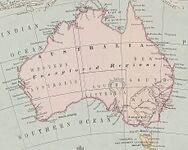
1863 map of Australia shows the Southern Ocean lying immediately to the south of Australia.
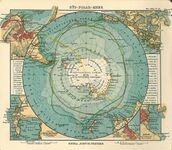
1906 map by German publisher Justus Perthes showing Antarctica encompassed by an Antarktischer (Sudl. Eismeer) Ocean – the 'Antarctic (South Arctic) Ocean'.
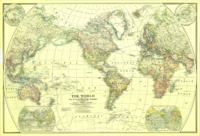
Map of The World in 1922 by the National Geographic Society showing the Antarctic (Southern) Ocean.
Southern Ocean
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 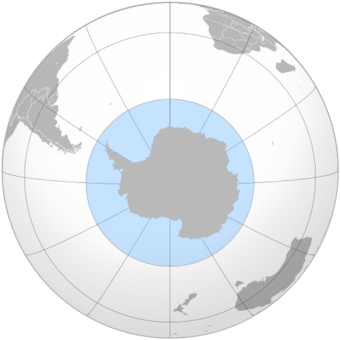
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean,[1][note 4] comprises the southernmost waters of the world ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica.[5] With a size of 20,327,000 km2 (7,848,000 sq mi), it is regarded as the second-smallest of the five principal oceanic divisions: smaller than the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans but larger than the Arctic Ocean.[6]
The maximum depth of the Southern Ocean, using the definition that it lies south of 60th parallel, was surveyed by the Five Deeps Expedition in early February 2019. The expedition's multibeam sonar team identified the deepest point at 60° 28' 46"S, 025° 32' 32"W, with a depth of 7,434 metres (24,390 ft). The expedition leader and chief submersible pilot Victor Vescovo, has proposed naming this deepest point in the Southern Ocean the "Factorian Deep", based on the name of the crewed submersible DSV Limiting Factor, in which he successfully visited the bottom for the first time on February 3, 2019.[7]
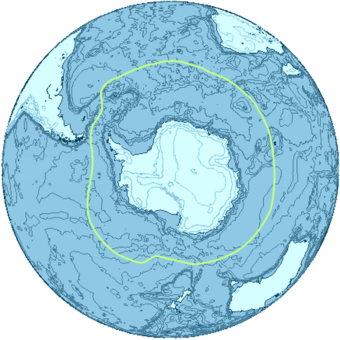
By way of his voyages in the 1770s, James Cook proved that waters encompassed the southern latitudes of the globe. Yet, geographers have often disagreed on whether the Southern Ocean should be defined as a body of water bound by the seasonally fluctuating Antarctic Convergence - an oceanic zone where cold, northward flowing waters from the Antarctic mix with warmer Subantarctic waters,[8] or not defined at all, with its waters instead treated as the southern limits of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) finally settled the debate after the full importance of Southern Ocean overturning circulation had been ascertained, and the term Southern Ocean now defines the body of water which lies south of the northern limit of that circulation.[9]
The Southern Ocean overturning circulation is important is because it makes up the second half of the global thermohaline circulation, with the other half being the much-better known Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC).[10] Much like AMOC, it has also been substantially affected by climate change, in ways that have increased ocean stratification,[11] and which may also result in the circulation substantially slowing or even passing a tipping point and collapsing outright. The latter would have adverse impacts on global weather and the functioning of marine ecosystems in the Southern Ocean which would unfold over centuries.[12][13] Further, the ongoing warming is already changing marine ecosystems in the Southern Ocean.[14]
Definitions and use
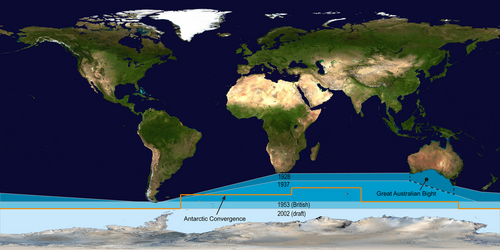
Borders and names for oceans and seas were internationally agreed when the International Hydrographic Bureau, the precursor to the IHO, convened the First International Conference on 24 July 1919. The IHO then published these in its Limits of Oceans and Seas, the first edition being 1928. Since the first edition, the limits of the Southern Ocean have moved progressively southwards; since 1953, it has been omitted from the official publication and left to local hydrographic offices to determine their own limits.
The IHO included the ocean and its definition as the waters south of the 60th parallel south in its 2000 revisions, but this has not been formally adopted, due to continuing impasses about some of the content, such as the naming dispute over the Sea of Japan. The 2000 IHO definition, however, was circulated in a draft edition in 2002, and is used by some within the IHO and by some other organizations such as the CIA World Factbook and Merriam-Webster.[6][15]
The Australian Government regards the Southern Ocean as lying immediately south of Australia (see ).[16][17]
The National Geographic Society recognized the ocean officially in June 2021.[18][19] Prior to this, it depicted it in a typeface different from the other world oceans; instead, it shows the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans extending to Antarctica on both its print and online maps.[20][21] Map publishers using the term Southern Ocean on their maps include Hema Maps[22] and GeoNova.[23]
Pre-20th century
.jpg)
"Southern Ocean" is an obsolete name for the Pacific Ocean or South Pacific, coined by the Spanish explorer Vasco Núñez de Balboa, the first European to discover the Pacific, who approached it from the north in Panama.[24] The "South Seas" is a less archaic synonym. A 1745 British Act of Parliament established a prize for discovering a Northwest Passage to "the Western and Southern Ocean of America".[25]
Authors using "Southern Ocean" to name the waters encircling the unknown southern polar regions used varying limits. James Cook's account of his second voyage implies New Caledonia borders it.[26] Peacock's 1795 Geographical Dictionary said it lay "to the southward of America and Africa";[27] John Payne in 1796 used 40 degrees as the northern limit;[28] the 1827 Edinburgh Gazetteer used 50 degrees.[29] The Family Magazine in 1835 divided the "Great Southern Ocean" into the "Southern Ocean" and the "Antarctick [sic] Ocean" along the Antarctic Circle, with the northern limit of the Southern Ocean being lines joining Cape Horn, the Cape of Good Hope, Van Diemen's Land and the south of New Zealand.[30]
The United Kingdom's South Australia Act 1834 described the waters forming the southern limit of the new province of South Australia as "the Southern Ocean". The Colony of Victoria's Legislative Council Act 1881 delimited part of the division of Bairnsdale as "along the New South Wales boundary to the Southern ocean".[31]
1928 delineation
In the 1928 first edition of Limits of Oceans and Seas, the Southern Ocean was delineated by land-based limits: Antarctica to the south, and South America, Africa, Australia, and Broughton Island, New Zealand to the north.
The detailed land-limits used were from Cape Horn in Chile eastwards to Cape Agulhas in Africa, then further eastwards to the southern coast of mainland Australia to Cape Leeuwin, Western Australia. From Cape Leeuwin, the limit then followed eastwards along the coast of mainland Australia to Cape Otway, Victoria, then southwards across Bass Strait to Cape Wickham, King Island, along the west coast of King Island, then the remainder of the way south across Bass Strait to Cape Grim, Tasmania.
The limit then followed the west coast of Tasmania southwards to the South East Cape and then went eastwards to Broughton Island, New Zealand, before returning to Cape Horn.[32]
1937 delineation

The northern limits of the Southern Ocean were moved southwards in the IHO's 1937 second edition of the Limits of Oceans and Seas. From this edition, much of the ocean's northern limit ceased to abut land masses.
In the second edition, the Southern Ocean then extended from Antarctica northwards to latitude 40°S between Cape Agulhas in Africa (long. 20°E) and Cape Leeuwin in Western Australia (long. 115°E), and extended to latitude 55°S between Auckland Island of New Zealand (165 or 166°E east) and Cape Horn in South America (67°W).[33]
As is discussed in more detail below, prior to the 2002 edition the limits of oceans explicitly excluded the seas lying within each of them. The Great Australian Bight was unnamed in the 1928 edition, and delineated as shown in the figure above in the 1937 edition. It therefore encompassed former Southern Ocean waters—as designated in 1928—but was technically not inside any of the three adjacent oceans by 1937.
In the 2002 draft edition, the IHO have designated 'seas' as being subdivisions within 'oceans', so the Bight would have still been within the Southern Ocean in 1937 if the 2002 convention were in place then. To perform direct comparisons of current and former limits of oceans it is necessary to consider, or at least be aware of, how the 2002 change in IHO terminology for 'seas' can affect the comparison.
1953 delineation
The Southern Ocean did not appear in the 1953 third edition of Limits of Oceans and Seas, a note in the publication read:
The Antarctic or Southern Ocean has been omitted from this publication as the majority of opinions received since the issue of the 2nd Edition in 1937 are to the effect that there exists no real justification for applying the term Ocean to this body of water, the northern limits of which are difficult to lay down owing to their seasonal change. The limits of the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans have therefore been extended South to the Antarctic Continent.
Hydrographic Offices who issue separate publications dealing with this area are therefore left to decide their own northern limits (Great Britain uses Latitude of 55 South.)[34]:4
Instead, in the IHO 1953 publication, the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans were extended southward, the Indian and Pacific Oceans (which had not previously touched pre 1953, as per the first and second editions) now abutted at the meridian of South East Cape, and the southern limits of the Great Australian Bight and the Tasman Sea were moved northwards.[34]
2002 draft delineation
The IHO readdressed the question of the Southern Ocean in a survey in 2000. Of its 68 member nations, 28 responded, and all responding members except Argentina agreed to redefine the ocean, reflecting the importance placed by oceanographers on ocean currents. The proposal for the name Southern Ocean won 18 votes, beating the alternative Antarctic Ocean. Half of the votes supported a definition of the ocean's northern limit at the 60th parallel south—with no land interruptions at this latitude—with the other 14 votes cast for other definitions, mostly the 50th parallel south, but a few for as far north as the 35th parallel south. Notably the Southern Ocean Observing System collates data from latitudes higher than 40 degrees south.
A draft fourth edition of Limits of Oceans and Seas was circulated to IHO member states in August 2002 (sometimes referred to as the "2000 edition" as it summarized the progress to 2000).[36] It has yet to be published due to 'areas of concern' by several countries relating to various naming issues around the world – primarily the Sea of Japan naming dispute – and there have been various changes, 60 seas were given new names, and even the name of the publication was changed.[37] A reservation had also been lodged by Australia regarding the Southern Ocean limits.[38] Effectively, the third edition—which did not delineate the Southern Ocean leaving delineation to local hydrographic offices—has yet to be superseded.
Despite this, the fourth edition definition has partial de facto usage by many nations, scientists, and organisations such as the U.S. (the CIA World Factbook uses "Southern Ocean", but none of the other new sea names within the "Southern Ocean", such as the "Cosmonauts Sea") and Merriam-Webster,[6][15][21] scientists and nations – and even by some within the IHO.[39] Some nations' hydrographic offices have defined their own boundaries; the United Kingdom used the 55th parallel south for example.[34] Other organisations favour more northerly limits for the Southern Ocean. For example, Encyclopædia Britannica describes the Southern Ocean as extending as far north as South America, and confers great significance on the Antarctic Convergence, yet its description of the Indian Ocean contradicts this, describing the Indian Ocean as extending south to Antarctica.[40][41]
Other sources, such as the National Geographic Society, show the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian oceans as extending to Antarctica on its maps, although articles on the National Geographic web site have begun to reference the Southern Ocean.[21]
A radical shift from past IHO practices (1928–1953) was also seen in the 2002 draft edition when the IHO delineated 'seas' as being subdivisions that lay within the boundaries of 'oceans'. While the IHO are often considered the authority for such conventions, the shift brought them into line with the practices of other publications (e.g. the CIA World Fact Book) which already adopted the principle that seas are contained within oceans. This difference in practice is markedly seen for the Pacific Ocean in the adjacent figure. Thus, for example, previously the Tasman Sea between Australia and New Zealand was not regarded by the IHO as being part of the Pacific, but as of the 2002 draft edition it is.
The new delineation of seas being subdivisions of oceans has avoided the need to interrupt the northern boundary of the Southern Ocean where intersected by Drake Passage which includes all of the waters from South America to the Antarctic coast, nor interrupt it for the Scotia Sea, which also extends below the 60th parallel south. The new delineation of seas has also meant that the long-time named seas around Antarctica, excluded from the 1953 edition (the 1953 map did not even extend that far south), are 'automatically' part of the Southern Ocean.

Australian standpoint
In Australia, cartographical authorities define the Southern Ocean as including the entire body of water between Antarctica and the south coasts of Australia and New Zealand, and up to 60°S elsewhere.[42] Coastal maps of Tasmania and South Australia label the sea areas as Southern Ocean[43] and Cape Leeuwin in Western Australia is described as the point where the Indian and Southern Oceans meet.[44]
History of exploration
Unknown southern land
Exploration of the Southern Ocean was inspired by a belief in the existence of a Terra Australis – a vast continent in the far south of the globe to "balance" the northern lands of Eurasia and North Africa – which had existed since the times of Ptolemy. The rounding of the Cape of Good Hope in 1487 by Bartolomeu Dias first brought explorers within touch of the Antarctic cold, and proved that there was an ocean separating Africa from any Antarctic land that might exist.[45] Ferdinand Magellan, who passed through the Strait of Magellan in 1520, assumed that the islands of Tierra del Fuego to the south were an extension of this unknown southern land. In 1564, Abraham Ortelius published his first map, Typus Orbis Terrarum, an eight-leaved wall map of the world, on which he identified the Regio Patalis with Locach as a northward extension of the Terra Australis, reaching as far as New Guinea.[46][47]
European geographers continued to connect the coast of Tierra del Fuego with the coast of New Guinea on their globes, and allowing their imaginations to run riot in the vast unknown spaces of the south Atlantic, south Indian and Pacific oceans they sketched the outlines of the Terra Australis Incognita ("Unknown Southern Land"), a vast continent stretching in parts into the tropics. The search for this great south land was a leading motive of explorers in the 16th and the early part of the 17th centuries.[45]
The Spaniard Gabriel de Castilla, who claimed having sighted "snow-covered mountains" beyond the 64° S in 1603, is recognized as the first explorer that discovered the continent of Antarctica, although he was ignored in his time.
In 1606, Pedro Fernández de Quirós took possession for the king of Spain all of the lands he had discovered in Australia del Espiritu Santo (the New Hebrides) and those he would discover "even to the Pole".[45]
Francis Drake, like Spanish explorers before him, had speculated that there might be an open channel south of Tierra del Fuego. When Willem Schouten and Jacob Le Maire discovered the southern extremity of Tierra del Fuego and named it Cape Horn in 1615, they proved that the Tierra del Fuego archipelago was of small extent and not connected to the southern land, as previously thought. Subsequently, in 1642, Abel Tasman showed that even New Holland (Australia) was separated by sea from any continuous southern continent.[45]
South of the Antarctic Convergence
File:Edmond Halley, 1656-1742, Astronomer Royal RMG BHC2734.tiff The visit to South Georgia by Anthony de la Roché in 1675 was the first-ever discovery of land south of the Antarctic Convergence, i.e. in the Southern Ocean/Antarctic.[48][49] Soon after the voyage cartographers started to depict "Roché Island", honouring the discoverer. James Cook was aware of la Roché's discovery when surveying and mapping the island in 1775.[50]
Edmond Halley's voyage in HMS Paramour for magnetic investigations in the South Atlantic met the pack ice in 52° S in January 1700, but that latitude (he reached 140 mi [230 km] off the north coast of South Georgia) was his farthest south. A determined effort on the part of the French naval officer Jean-Baptiste Charles Bouvet de Lozier to discover the "South Land" – described by a half legendary "sieur de Gonneyville" – resulted in the discovery of Bouvet Island in 54°10′ S, and in the navigation of 48° of longitude of ice-cumbered sea nearly in 55° S in 1730.[45]
In 1771, Yves Joseph Kerguelen sailed from France with instructions to proceed south from Mauritius in search of "a very large continent". He lighted upon a land in 50° S which he called South France, and believed to be the central mass of the southern continent. He was sent out again to complete the exploration of the new land, and found it to be only an inhospitable island which he renamed the Isle of Desolation, but which was ultimately named after him.[45]
South of the Antarctic Circle

The obsession of the undiscovered continent culminated in the brain of Alexander Dalrymple, the brilliant and erratic hydrographer who was nominated by the Royal Society to command the Transit of Venus expedition to Tahiti in 1769. The command of the expedition was given by the admiralty to Captain James Cook. Sailing in 1772 with Resolution, a vessel of 462 tons under his own command and Adventure of 336 tons under Captain Tobias Furneaux, Cook first searched in vain for Bouvet Island, then sailed for 20 degrees of longitude to the westward in latitude 58° S, and then 30° eastward for the most part south of 60° S, a lower southern latitude than had ever been voluntarily entered before by any vessel. On 17 January 1773 the Antarctic Circle was crossed for the first time in history and the two ships reached 67° 15' S by 39° 35' E, where their course was stopped by ice.[45]

Cook then turned northward to look for French Southern and Antarctic Lands, of the discovery of which he had received news at Cape Town, but from the rough determination of his longitude by Kerguelen, Cook reached the assigned latitude 10° too far east and did not see it. He turned south again and was stopped by ice in 61° 52′ S by 95° E and continued eastward nearly on the parallel of 60° S to 147° E. On 16 March, the approaching winter drove him northward for rest to New Zealand and the tropical islands of the Pacific. In November 1773, Cook left New Zealand, having parted company with the Adventure, and reached 60° S by 177° W, whence he sailed eastward keeping as far south as the floating ice allowed. The Antarctic Circle was crossed on 20 December and Cook remained south of it for three days, being compelled after reaching 67° 31′ S to stand north again in 135° W.[45]
A long detour to 47° 50′ S served to show that there was no land connection between New Zealand and Tierra del Fuego. Turning south again, Cook crossed the Antarctic Circle for the third time at 109° 30′ W before his progress was once again blocked by ice four days later at 71° 10′ S by 106° 54′ W. This point, reached on 30 January 1774, was the farthest south attained in the 18th century. With a great detour to the east, almost to the coast of South America, the expedition regained Tahiti for refreshment. In November 1774, Cook started from New Zealand and crossed the South Pacific without sighting land between 53° and 57° S to Tierra del Fuego; then, passing Cape Horn on 29 December, he rediscovered Roché Island renaming it Isle of Georgia, and discovered the South Sandwich Islands (named Sandwich Land by him), the only ice-clad land he had seen, before crossing the South Atlantic to the Cape of Good Hope between 55° and 60°. He thereby laid open the way for future Antarctic exploration by exploding the myth of a habitable southern continent. Cook's most southerly discovery of land lay on the temperate side of the 60th parallel, and he convinced himself that if land lay farther south it was practically inaccessible and without economic value.[45]
Voyagers rounding Cape Horn frequently met with contrary winds and were driven southward into snowy skies and ice-encumbered seas; but so far as can be ascertained none of them before 1770 reached the Antarctic Circle, or knew it, if they did.
In a voyage from 1822 to 1824, James Weddell commanded the 160-ton brig Jane, accompanied by his second ship Beaufoy captained by Matthew Brisbane. Together they sailed to the South Orkneys where sealing proved disappointing. They turned south in the hope of finding a better sealing ground. The season was unusually mild and tranquil, and on 20 February 1823 the two ships reached latitude 74°15' S and longitude 34°16'45″ W the southernmost position any ship had ever reached up to that time. A few icebergs were sighted but there was still no sight of land, leading Weddell to theorize that the sea continued as far as the South Pole. Another two days' sailing would have brought him to Coat's Land (to the east of the Weddell Sea) but Weddell decided to turn back.[52]
First sighting of land

The first land south of the parallel 60° south latitude was discovered by the Englishman William Smith, who sighted Livingston Island on 19 February 1819. A few months later Smith returned to explore the other islands of the South Shetlands archipelago, landed on King George Island, and claimed the new territories for Britain.
In the meantime, the Spanish Navy ship San Telmo sank in September 1819 when trying to cross Cape Horn. Parts of her wreckage were found months later by sealers on the north coast of Livingston Island (South Shetlands). It is unknown if some survivor managed to be the first to set foot on these Antarctic islands.
The first confirmed sighting of mainland Antarctica cannot be accurately attributed to one single person. It can, however, be narrowed down to three individuals. According to various sources,[53][54][55] three men all sighted the ice shelf or the continent within days or months of each other: Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen, a captain in the Russian Imperial Navy; Edward Bransfield, a captain in the Royal Navy; and Nathaniel Palmer, an American sailor out of Stonington, Connecticut. It is certain that the expedition, led by von Bellingshausen and Lazarev on the ships Vostok and Mirny, reached a point within 32 km (20 mi) from Princess Martha Coast and recorded the sight of an ice shelf at [ ⚑ ] 69°21′28″S 2°14′50″W / 69.35778°S 2.24722°W[56] that became known as the Fimbul Ice Shelf. On 30 January 1820, Bransfield sighted Trinity Peninsula, the northernmost point of the Antarctic mainland, while Palmer sighted the mainland in the area south of Trinity Peninsula in November 1820. Von Bellingshausen's expedition also discovered Peter I Island and Alexander I Island, the first islands to be discovered south of the circle.
Antarctic expeditions

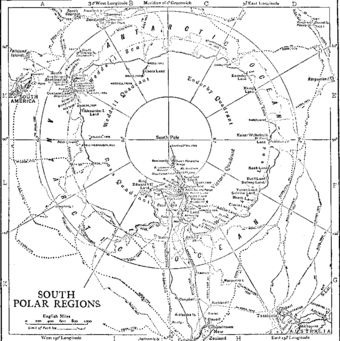
In December 1839, as part of the United States Exploring Expedition of 1838–42 conducted by the United States Navy (sometimes called "the Wilkes Expedition"), an expedition sailed from Sydney, Australia, on the sloops-of-war USS Vincennes and USS Peacock, the brig USS Porpoise, the full-rigged ship Relief, and two schooners Sea Gull and USS Flying Fish. They sailed into the Antarctic Ocean, as it was then known, and reported the discovery "of an Antarctic continent west of the Balleny Islands" on 25 January 1840. That part of Antarctica was later named "Wilkes Land", a name it maintains to this day.
Explorer James Clark Ross passed through what is now known as the Ross Sea and discovered Ross Island (both of which were named for him) in 1841. He sailed along a huge wall of ice that was later named the Ross Ice Shelf. Mount Erebus and Mount Terror are named after two ships from his expedition: HMS Erebus and HMS Terror.[57]

The Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition of 1914, led by Ernest Shackleton, set out to cross the continent via the pole, but their ship, Endurance, was trapped and crushed by pack ice before they even landed. The expedition members survived after an epic journey on sledges over pack ice to Elephant Island. Then Shackleton and five others crossed the Southern Ocean, in an open boat called James Caird, and then trekked over South Georgia to raise the alarm at the whaling station Grytviken.
In 1946, US Navy Rear Admiral Richard E. Byrd and more than 4,700 military personnel visited the Antarctic in an expedition called Operation Highjump. Reported to the public as a scientific mission, the details were kept secret and it may have actually been a training or testing mission for the military. The expedition was, in both military or scientific planning terms, put together very quickly. The group contained an unusually high amount of military equipment, including an aircraft carrier, submarines, military support ships, assault troops and military vehicles. The expedition was planned to last for eight months but was unexpectedly terminated after only two months. With the exception of some eccentric entries in Admiral Byrd's diaries, no real explanation for the early termination has ever been officially given.
Captain Finn Ronne, Byrd's executive officer, returned to Antarctica with his own expedition in 1947–1948, with Navy support, three planes, and dogs. Ronne disproved the notion that the continent was divided in two and established that East and West Antarctica was one single continent, i.e. that the Weddell Sea and the Ross Sea are not connected.[58] The expedition explored and mapped large parts of Palmer Land and the Weddell Sea coastline, and identified the Ronne Ice Shelf, named by Ronne after his wife Edith "Jackie" Ronne.[59] Ronne covered 3,600 miles (5,790 km) by ski and dog sled – more than any other explorer in history.[60] The Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition discovered and mapped the last unknown coastline in the world and was the first Antarctic expedition to ever include women.[61]
Recent history

The Antarctic Treaty was signed on 1 December 1959 and came into force on 23 June 1961. Among other provisions, this treaty limits military activity in the Antarctic to the support of scientific research.
The first person to sail single-handed to Antarctica was the New Zealander David Henry Lewis, in 1972, in a 10-metre (30 ft) steel sloop Ice Bird.
A baby, named Emilio Marcos de Palma, was born near Hope Bay on 7 January 1978, becoming the first baby born on the continent. He also was born further south than anyone in history.[62]
The MV Explorer was a cruise ship operated by the Swedish explorer Lars-Eric Lindblad. Observers point to Explorer's 1969 expeditionary cruise to Antarctica as the frontrunner for today's[when?] sea-based tourism in that region.[63][64] Explorer was the first cruise ship used specifically to sail the icy waters of the Antarctic Ocean and the first to sink there[65] when she struck an unidentified submerged object on 23 November 2007, reported to be ice, which caused a 10 by 4 inches (25 by 10 cm) gash in the hull.[66] Explorer was abandoned in the early hours of 23 November 2007 after taking on water near the South Shetland Islands in the Southern Ocean, an area which is usually stormy but was calm at the time.[67] Explorer was confirmed by the Chilean Navy to have sunk at approximately position: 62° 24′ South, 57° 16′ West,[68] in roughly 600 m of water.[69]
British engineer Richard Jenkins designed an unmanned "saildrone"[70] that completed the first autonomous circumnavigation of the Southern Ocean on 3 August 2019 after 196 days at sea.[71]
The first completely human-powered expedition on the Southern Ocean was accomplished on 25 December 2019 by a team of rowers comprising captain Fiann Paul (Iceland), first mate Colin O'Brady (US), Andrew Towne (US), Cameron Bellamy (South Africa), Jamie Douglas-Hamilton (UK) and John Petersen (US).[72]
Geography
The Southern Ocean, geologically the youngest of the oceans, was formed when Antarctica and South America moved apart, opening the Drake Passage, roughly 30 million years ago. The separation of the continents allowed the formation of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current.
With a northern limit at 60°S, the Southern Ocean differs from the other oceans in that its largest boundary, the northern boundary, does not abut a landmass (as it did with the first edition of Limits of Oceans and Seas). Instead, the northern limit is with the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans.
One reason for considering it as a separate ocean stems from the fact that much of the water of the Southern Ocean differs from the water in the other oceans. Water gets transported around the Southern Ocean fairly rapidly because of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current which circulates around Antarctica. Water in the Southern Ocean south of, for example, New Zealand, resembles the water in the Southern Ocean south of South America more closely than it resembles the water in the Pacific Ocean.
The Southern Ocean has typical depths of between 4,000 and 5,000 m (13,000 and 16,000 ft) over most of its extent with only limited areas of shallow water. The Southern Ocean's greatest depth of 7,236 m (23,740 ft) occurs at the southern end of the South Sandwich Trench, at 60°00'S, 024°W. The Antarctic continental shelf appears generally narrow and unusually deep, its edge lying at depths up to 800 m (2,600 ft), compared to a global mean of 133 m (436 ft).
Equinox to equinox in line with the sun's seasonal influence, the Antarctic ice pack fluctuates from an average minimum of 2.6 million square kilometres (1.0×106 sq mi) in March to about 18.8 million square kilometres (7.3×106 sq mi) in September, more than a sevenfold increase in area.
Sub-divisions of the Southern Ocean
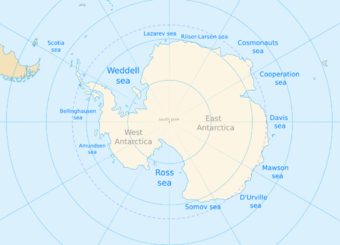
Sub-divisions of oceans are geographical features such as "seas", "straits", "bays", "channels", and "gulfs". There are many sub-divisions of the Southern Ocean defined in the never-approved 2002 draft fourth edition of the IHO publication Limits of Oceans and Seas. In clockwise order these include (with sector):
- Weddell Sea (57°18'W – 12°16'E)
- King Haakon VII Sea[note 5] (20°W – 45°E)
- Lazarev Sea (0° – 14°E)
- Riiser-Larsen Sea (14° – 30°E)
- Cosmonauts Sea (30° – 50°E)
- Cooperation Sea (59°34' – 85°E)
- Davis Sea (82° – 96°E)
- Mawson Sea (95°45' – 113°E)
- Dumont D'Urville Sea (140°E)
- Somov Sea (150° – 170°E)
- Ross Sea (166°E – 155°W)
- Amundsen Sea (102°20′ – 126°W)
- Bellingshausen Sea (57°18' – 102°20'W)
- Part of the Drake Passage[note 6] (54° – 68°W)
- Bransfield Strait (54° – 62°W)
- Part of the Scotia Sea[note 7] (26°30' – 65°W)
A number of these such as the 2002 Russian-proposed "Cosmonauts Sea", "Cooperation Sea", and "Somov (mid-1950s Russian polar explorer) Sea" are not included in the 1953 IHO document which remains currently in force,[34] because they received their names largely originated from 1962 onward. Leading geographic authorities and atlases do not use these latter three names, including the 2014 10th edition World Atlas from the United States' National Geographic Society and the 2014 12th edition of the British Times Atlas of the World, but Soviet and Russian-issued maps do.[73][74]
Biggest seas in Southern Ocean
Top large seas:[75][76][77]
- Weddell Sea – 2,800,000 km2 (1,100,000 sq mi)
- Somov Sea – 1,150,000 km2 (440,000 sq mi)
- Riiser-Larsen Sea – 1,138,000 km2 (439,000 sq mi)
- Lazarev Sea – 929,000 km2 (359,000 sq mi)
- Scotia Sea – 900,000 km2 (350,000 sq mi)
- Cosmonauts Sea – 699,000 km2 (270,000 sq mi)
- Ross Sea – 637,000 km2 (246,000 sq mi)
- Bellingshausen Sea – 487,000 km2 (188,000 sq mi)
- Mawson Sea – 333,000 km2 (129,000 sq mi)
- Cooperation Sea – 258,000 km2 (100,000 sq mi)
- Amundsen Sea – 98,000 km2 (38,000 sq mi)
- Davis Sea – 21,000 km2 (8,100 sq mi)
- D'Urville Sea
- King Haakon VII Sea
Natural resources

The Southern Ocean probably contains large, and possibly giant, oil and gas fields on the continental margin. Placer deposits, accumulation of valuable minerals such as gold, formed by gravity separation during sedimentary processes are also expected to exist in the Southern Ocean.[5]
Manganese nodules are expected to exist in the Southern Ocean. Manganese nodules are rock concretions on the sea bottom formed of concentric layers of iron and manganese hydroxides around a core. The core may be microscopically small and is sometimes completely transformed into manganese minerals by crystallization. Interest in the potential exploitation of polymetallic nodules generated a great deal of activity among prospective mining consortia in the 1960s and 1970s.[5]
The icebergs that form each year around in the Southern Ocean hold enough fresh water to meet the needs of every person on Earth for several months. For several decades there have been proposals, none yet to be feasible or successful, to tow Southern Ocean icebergs to more arid northern regions (such as Australia) where they can be harvested.[78]
Natural hazards
.jpg)
Icebergs can occur at any time of year throughout the ocean. Some may have drafts up to several hundred meters; smaller icebergs, iceberg fragments and sea-ice (generally 0.5 to 1 m thick) also pose problems for ships. The deep continental shelf has a floor of glacial deposits varying widely over short distances.
Sailors know latitudes from 40 to 70 degrees south as the "Roaring Forties", "Furious Fifties" and "Shrieking Sixties" due to high winds and large waves that form as winds blow around the entire globe unimpeded by any land-mass. Icebergs, especially in May to October, make the area even more dangerous. The remoteness of the region makes sources of search and rescue scarce.
Physical oceanography
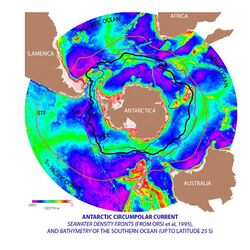
Antarctic Circumpolar Current and Antarctic Convergence
While the Southern is the second smallest ocean it contains the unique and highly energetic Antarctic Circumpolar Current which moves perpetually eastward – chasing and joining itself, and at 21,000 km (13,000 mi) in length – it comprises the world's longest ocean current, transporting 130 million cubic metres per second (4.6×109 cu ft/s) of water – 100 times the flow of all the world's rivers.[79]
Several processes operate along the coast of Antarctica to produce, in the Southern Ocean, types of water masses not produced elsewhere in the oceans of the Southern Hemisphere. One of these is the Antarctic Bottom Water, a very cold, highly saline, dense water that forms under sea ice. Another is Circumpolar Deep Water, a mixture of Antarctic Bottom Water and North Atlantic Deep Water.
Associated with the Circumpolar Current is the Antarctic Convergence encircling Antarctica, where cold northward-flowing Antarctic waters meet the relatively warmer waters of the subantarctic, Antarctic waters predominantly sink beneath subantarctic waters, while associated zones of mixing and upwelling create a zone very high in nutrients. These nurture high levels of phytoplankton with associated copepods and Antarctic krill, and resultant foodchains supporting fish, whales, seals, penguins, albatrosses and a wealth of other species.[80]
The Antarctic Convergence is considered to be the best natural definition of the northern extent of the Southern Ocean.
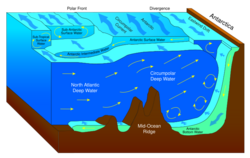
Upwelling
Large-scale upwelling is found in the Southern Ocean. Strong westerly (eastward) winds blow around Antarctica, driving a significant flow of water northwards. This is actually a type of coastal upwelling. Since there are no continents in a band of open latitudes between South America and the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, some of this water is drawn up from great depths. In many numerical models and observational syntheses, the Southern Ocean upwelling represents the primary means by which deep dense water is brought to the surface. Shallower, wind-driven upwelling is also found off the west coasts of North and South America, northwest and southwest Africa, and southwest and southeast Australia, all associated with oceanic subtropical high pressure circulations.
Some models of the ocean circulation suggest that broad-scale upwelling occurs in the tropics, as pressure driven flows converge water toward the low latitudes where it is diffusively warmed from above. The required diffusion coefficients, however, appear to be larger than are observed in the real ocean. Nonetheless, some diffusive upwelling does probably occur.
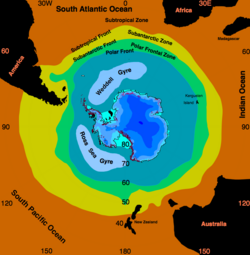
Ross and Weddell Gyres
The Ross Gyre and Weddell Gyre are two gyres that exist within the Southern Ocean. The gyres are located in the Ross Sea and Weddell Sea respectively, and both rotate clockwise. The gyres are formed by interactions between the Antarctic Circumpolar Current and the Antarctic Continental Shelf.
Sea ice has been noted to persist in the central area of the Ross Gyre.[81] There is some evidence that global warming has resulted in some decrease of the salinity of the waters of the Ross Gyre since the 1950s.[82]
Due to the Coriolis effect acting to the left in the Southern Hemisphere and the resulting Ekman transport away from the centres of the Weddell Gyre, these regions are very productive due to upwelling of cold, nutrient rich water.
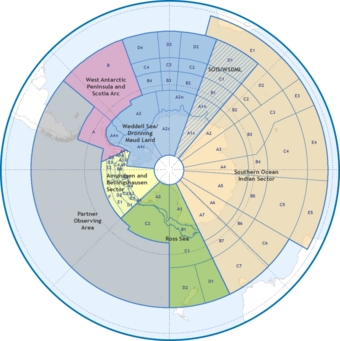
Observations
Observation of the Southern Ocean is coordinated through the Southern Ocean Observing System (SOOS).[83][84] This provides access to meta data for a significant proportion of the data collected in the regions over the past decades including hydrographic measurements and ocean currents. The data provision is set up to emphasize records that are related to Essential Ocean Variables (EOVs)[85] for the ocean region south of 40°S.
Climate
Sea temperatures vary from about −2 to 10 °C (28 to 50 °F). Cyclonic storms travel eastward around the continent and frequently become intense because of the temperature contrast between ice and open ocean. The ocean-area from about latitude 40 south to the Antarctic Circle has the strongest average winds found anywhere on Earth.[86] In winter the ocean freezes outward to 65 degrees south latitude in the Pacific sector and 55 degrees south latitude in the Atlantic sector, lowering surface temperatures well below 0 degrees Celsius. At some coastal points, however, persistent intense drainage winds from the interior keep the shoreline ice-free throughout the winter.
Climate change
Biodiversity

Animals
A variety of marine animals exist and rely, directly or indirectly, on the phytoplankton in the Southern Ocean. Antarctic sea life includes penguins, blue whales, orcas, colossal squids and fur seals. The emperor penguin is the only penguin that breeds during the winter in Antarctica, while the Adélie penguin breeds farther south than any other penguin. The rockhopper penguin has distinctive feathers around the eyes, giving the appearance of elaborate eyelashes. King penguins, chinstrap penguins, and gentoo penguins also breed in the Antarctic.
The Antarctic fur seal was very heavily hunted in the 18th and 19th centuries for its pelt by sealers from the United States and the United Kingdom. The Weddell seal, a "true seal", is named after Sir James Weddell, commander of British sealing expeditions in the Weddell Sea. Antarctic krill, which congregates in large schools, is the keystone species of the ecosystem of the Southern Ocean, and is an important food organism for whales, seals, leopard seals, fur seals, squid, icefish, penguins, albatrosses and many other birds.[87]
The benthic communities of the seafloor are diverse and dense, with up to 155,000 animals found in 1 square metre (10.8 sq ft). As the seafloor environment is very similar all around the Antarctic, hundreds of species can be found all the way around the mainland, which is a uniquely wide distribution for such a large community. Deep-sea gigantism is common among these animals.[88]
A census of sea life carried out during the International Polar Year and which involved some 500 researchers was released in 2010. The research is part of the global Census of Marine Life (CoML) and has disclosed some remarkable findings. More than 235 marine organisms live in both polar regions, having bridged the gap of 12,000 km (7,500 mi). Large animals such as some cetaceans and birds make the round trip annually. More surprising are small forms of life such as mudworms, sea cucumbers and free-swimming snails found in both polar oceans. Various factors may aid in their distribution – fairly uniform temperatures of the deep ocean at the poles and the equator which differ by no more than 5 °C (9.0 °F), and the major current systems or marine conveyor belt which transport egg and larva stages.[89] However, among smaller marine animals generally assumed to be the same in the Antarctica and the Arctic, more detailed studies of each population have often—but not always—revealed differences, showing that they are closely related cryptic species rather than a single bipolar species.[90][91][92]

Birds
The rocky shores of mainland Antarctica and its offshore islands provide nesting space for over 100 million birds every spring. These nesters include species of albatrosses, petrels, skuas, gulls and terns.[93] The insectivorous South Georgia pipit is endemic to South Georgia and some smaller surrounding islands. Freshwater ducks inhabit South Georgia and the Kerguelen Islands.[94]
The flightless penguins are all located in the Southern Hemisphere, with the greatest concentration located on and around Antarctica. Four of the 18 penguin species live and breed on the mainland and its close offshore islands. Another four species live on the subantarctic islands.[95] Emperor penguins have four overlapping layers of feathers, keeping them warm. They are the only Antarctic animal to breed during the winter.[96]
Fish
There are relatively few fish species in few families in the Southern Ocean. The most species-rich family are the snailfish (Liparidae), followed by the cod icefish (Nototheniidae)[97] and eelpout (Zoarcidae). Together the snailfish, eelpouts and notothenioids (which includes cod icefish and several other families) account for almost 9⁄10 of the more than 320 described fish species of the Southern Ocean (tens of undescribed species also occur in the region, especially among the snailfish).[98] Southern Ocean snailfish are generally found in deep waters, while the icefish also occur in shallower waters.[97]
Icefish

Cod icefish (Nototheniidae), as well as several other families, are part of the Notothenioidei suborder, collectively sometimes referred to as icefish. The suborder contains many species with antifreeze proteins in their blood and tissue, allowing them to live in water that is around or slightly below 0 °C (32 °F).[99][100] Antifreeze proteins are also known from Southern Ocean snailfish.[101]
The crocodile icefish (family Channichthyidae), also known as white-blooded fish, are only found in the Southern Ocean. They lack hemoglobin in their blood, resulting in their blood being colourless. One Channichthyidae species, the mackerel icefish (Champsocephalus gunnari), was once the most common fish in coastal waters less than 400 metres (1,312 ft) deep, but was overfished in the 1970s and 1980s. Schools of icefish spend the day at the seafloor and the night higher in the water column eating plankton and smaller fish.[99]
There are two species from the genus Dissostichus, the Antarctic toothfish (Dissostichus mawsoni) and the Patagonian toothfish (Dissostichus eleginoides). These two species live on the seafloor 100–3,000 metres (328–9,843 ft) deep, and can grow to around 2 metres (7 ft) long weighing up to 100 kilograms (220 lb), living up to 45 years. The Antarctic toothfish lives close to the Antarctic mainland, whereas the Patagonian toothfish lives in the relatively warmer subantarctic waters. Toothfish are commercially fished, and overfishing has reduced toothfish populations.[99][102]
Another abundant fish group is the genus Notothenia, which like the Antarctic toothfish have antifreeze in their bodies.[99]
An unusual species of icefish is the Antarctic silverfish (Pleuragramma antarcticum), which is the only truly pelagic fish in the waters near Antarctica.[103]

Mammals
Seven pinniped species inhabit Antarctica. The largest, the elephant seal (Mirounga leonina), can reach up to 4,000 kilograms (8,818 lb), while females of the smallest, the Antarctic fur seal (Arctophoca gazella), reach only 150 kilograms (331 lb). These two species live north of the sea ice, and breed in harems on beaches. The other four species can live on the sea ice. Crabeater seals (Lobodon carcinophagus) and Weddell seals (Leptonychotes weddellii) form breeding colonies, whereas leopard seals (Hydrurga leptonyx) and Ross seals (Ommatophoca rossii) live solitary lives. Although these species hunt underwater, they breed on land or ice and spend a great deal of time there, as they have no terrestrial predators.[104]
The four species that inhabit sea ice are thought to make up 50% of the total biomass of the world's seals.[105] Crabeater seals have a population of around 15 million, making them one of the most numerous large animals on the planet.[106] The New Zealand sea lion (Phocarctos hookeri), one of the rarest and most localised pinnipeds, breeds almost exclusively on the subantarctic Auckland Islands, although historically it had a wider range.[107] Out of all permanent mammalian residents, the Weddell seals live the furthest south.[108]
There are 10 cetacean species found in the Southern Ocean: six baleen whales, and four toothed whales. The largest of these, the blue whale (Balaenoptera musculus), grows to 24 metres (79 ft) long weighing 84 tonnes. Many of these species are migratory, and travel to tropical waters during the Antarctic winter.[109]
.jpg)
Invertebrates
Arthropods
Five species of krill, small free-swimming crustaceans, have been found in the Southern Ocean.[110] The Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) is one of the most abundant animal species on earth, with a biomass of around 500 million tonnes. Each individual is 6 centimetres (2.4 in) long and weighs over 1 gram (0.035 oz).[111] The swarms that form can stretch for kilometres, with up to 30,000 individuals per 1 cubic metre (35 cu ft), turning the water red.[110] Swarms usually remain in deep water during the day, ascending during the night to feed on plankton. Many larger animals depend on krill for their own survival.[111] During the winter when food is scarce, adult Antarctic krill can revert to a smaller juvenile stage, using their own body as nutrition.[110]
Many benthic crustaceans have a non-seasonal breeding cycle, and some raise their young in a brood pouch. Glyptonotus antarcticus is an unusually large benthic isopod, reaching 20 centimetres (8 in) in length weighing 70 grams (2.47 oz). Amphipods are abundant in soft sediments, eating a range of items, from algae to other animals.[88] The amphipods are highly diverse with more than 600 recognized species found south of the Antarctic Convergence and there are indications that many undescribed species remain. Among these are several "giants", such as the iconic epimeriids that are up to 8 cm (3.1 in) long.[112]
Slow moving sea spiders are common, sometimes growing as large as a human hand. They feed on the corals, sponges, and bryozoans that litter the seabed.[88]

Others
Many aquatic molluscs are present in Antarctica. Bivalves such as Adamussium colbecki move around on the seafloor, while others such as Laternula elliptica live in burrows filtering the water above.[88] There are around 70 cephalopod species in the Southern Ocean,[113] the largest of which is the colossal squid (Mesonychoteuthis hamiltoni), which at up to 14 metres (46 ft) is among the largest invertebrate in the world.[114] Squid makes up most of the diet of some animals, such as grey-headed albatrosses and sperm whales, and the warty squid (Moroteuthis ingens) is one of the subantarctic's most preyed upon species by vertebrates.[113]
The sea urchin genus Abatus burrow through the sediment eating the nutrients they find in it.[88] Two species of salps are common in Antarctic waters: Salpa thompsoni and Ihlea racovitzai. Salpa thompsoni is found in ice-free areas, whereas Ihlea racovitzai is found in the high-latitude areas near ice. Due to their low nutritional value, they are normally only eaten by fish, with larger animals such as birds and marine mammals only eating them when other food is scarce.[115]
Antarctic sponges are long-lived and sensitive to environmental changes due to the specificity of the symbiotic microbial communities within them. As a result, they function as indicators of environmental health.[116]
Environment
Current issues
Increased solar ultraviolet radiation resulting from the Antarctic ozone hole has reduced marine primary productivity (phytoplankton) by as much as 15% and has started damaging the DNA of some fish.[117] Illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing, especially the landing of an estimated five to six times more Patagonian toothfish than the regulated fishery, likely affects the sustainability of the stock. Long-line fishing for toothfish causes a high incidence of seabird mortality.
International agreements

All international agreements regarding the world's oceans apply to the Southern Ocean. In addition, it is subject to these agreements specific to the region:
- The Southern Ocean Whale Sanctuary of the International Whaling Commission (IWC) prohibits commercial whaling south of 40 degrees south (south of 60 degrees south between 50 degrees and 130 degrees west). Japan regularly does not recognize this provision, because the sanctuary violates IWC charter. Since the scope of the sanctuary is limited to commercial whaling, in regard to its whaling permit and whaling for scientific research, a Japanese fleet carried out an annual whale-hunt in the region. On 31 March 2014, the International Court of Justice ruled that Japan's whaling program, which Japan has long claimed is for scientific purposes, was a cloak for commercial whaling, and no further permits would be granted.
- Convention for the Conservation of Antarctic Seals is part of the Antarctic Treaty System. It was signed at the conclusion of a multilateral conference in London on 11 February 1972.[118]
- Convention for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR) is part of the Antarctic Treaty System. The Convention was entered into force on 7 April 1982 and its goal is to preserve marine life and environmental integrity in and near Antarctica. It was established in large part due to concerns that an increase in krill catches in the Southern Ocean could have a serious impact on populations of other marine life which are dependent upon krill for food.[119]
Many nations prohibit the exploration for and the exploitation of mineral resources south of the fluctuating Antarctic Convergence,[120] which lies in the middle of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current and serves as the dividing line between the very cold polar surface waters to the south and the warmer waters to the north. The Antarctic Treaty covers the portion of the globe south of sixty degrees south;[121] it prohibits new claims to Antarctica.[122]
The Convention for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources applies to the area south of 60° South latitude as well as the areas further north up to the limit of the Antarctic Convergence.[123]
Economy
Between 1 July 1998 and 30 June 1999, fisheries landed 119,898 tonnes (118,004 long tons; 132,165 short tons), of which 85% consisted of krill and 14% of Patagonian toothfish. International agreements came into force in late 1999 to reduce illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing, which in the 1998–99 season landed five to six times more Patagonian toothfish than the regulated fishery.
Ports and harbors

Major operational ports include: Rothera Station, Palmer Station, Villa Las Estrellas, Esperanza Base, Mawson Station, McMurdo Station, and offshore anchorages in Antarctica.
Few ports or harbors exist on the southern (Antarctic) coast of the Southern Ocean, since ice conditions limit use of most shores to short periods in midsummer; even then some require icebreaker escort for access. Most Antarctic ports are operated by government research stations and, except in an emergency, remain closed to commercial or private vessels; vessels in any port south of 60 degrees south are subject to inspection by Antarctic Treaty observers.
The Southern Ocean's southernmost port operates at McMurdo Station at [ ⚑ ] 77°50′S 166°40′E / 77.833°S 166.667°E. Winter Quarters Bay forms a small harbor, on the southern tip of Ross Island where a floating ice pier makes port operations possible in summer. Operation Deep Freeze personnel constructed the first ice pier at McMurdo in 1973.[124]
Based on the original 1928 IHO delineation of the Southern Ocean (and the 1937 delineation if the Great Australian Bight is considered integral), Australian ports and harbors between Cape Leeuwin and Cape Otway on the Australian mainland and along the west coast of Tasmania would also be identified as ports and harbors existing in the Southern Ocean. These would include the larger ports and harbors of Albany, Thevenard, Port Lincoln, Whyalla, Port Augusta, Port Adelaide, Portland, Warrnambool, and Macquarie Harbour.
Even though organizers of several yacht races define their routes as involving the Southern Ocean, the actual routes don't enter the actual geographical boundaries of the Southern Ocean. The routes involve instead South Atlantic, South Pacific and Indian Ocean.[125][126][127]
See also
- Borders of the oceans
- List of Antarctic and subantarctic islands
- List of countries by southernmost point
- List of seamounts in the Southern Ocean
- Seven Seas
- International Bathymetric Chart of the Southern Ocean
Notes
- ↑ Also a translation of its former French name (Grand Océan Austral) in reference to its position below the Pacific, the "Grand Océan".
- ↑ Used by Dr. Hooker in his accounts of his Antarctic voyages.[4] Also a translation of the ocean's Japanese name Nankyoku Kai (南極海).
- ↑ Also a translation of the ocean's Chinese name Nánbīng Yáng (南冰洋).
- ↑ Historic names include the "South Sea",[2] the "Great Southern Ocean",[3][note 1] the "South Polar Ocean" or "South-Polar Ocean",[note 2] and the "Southern Icy Ocean".[2][note 3]
- ↑ Reservation by Norway: Norway recognizes the name Kong Håkon VII Hav, which covers the sea area adjacent to Dronning Maud Land and stretching from 20°W to 45°E.[36]
- ↑ The Drake Passage is situated between the southern and eastern extremities of South America and the South Shetland Islands, lying north of the Antarctic Peninsula.[36]
- ↑ The Scotia Sea is an area defined by the southeastern extremity of South America and the South Shetland Islands on the west and by South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands to the north and east. As they extend north of 60°S, Drake Passage and the Scotia Sea are also described as forming part of the South Atlantic Ocean.[36]
References
- ↑ EB (1878).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Sherwood, Mary Martha (1823), An Introduction to Geography, Intended for Little Children, 3rd ed., Wellington: F. Houlston & Son, p. 10, https://books.google.com/books?id=u-w7AAAAYAAJ
- ↑ Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). "Great Southern Ocean". Encyclopædia Britannica. 12 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 422.
- ↑ Hooker, Joseph Dalton (1843), Flora Antarctica: The Botany of the Antarctic Voyage, London: Reeve
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 "Geography – Southern Ocean". CIA Factbook. https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/oceans/southern-ocean/. "... the Southern Ocean has the unique distinction of being a large circumpolar body of water totally encircling the continent of Antarctica; this ring of water lies between 60 degrees south latitude and the coast of Antarctica and encompasses 360 degrees of longitude."
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 "Introduction – Southern Ocean". CIA Factbook. https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/oceans/southern-ocean/. "...As such, the Southern Ocean is now the fourth largest of the world's five oceans (after the Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, and Indian Ocean, but larger than the Arctic Ocean)."
- ↑ "Explorer completes another historic submersible dive" (in en). 2019-02-06. https://ftw.usatoday.com/2019/02/explorer-completes-another-historic-submersible-dive.
- ↑ Pyne, Stephen J. (1986). The Ice: A Journey to Antarctica. University of Washington Press.
- ↑ "Do You Know the World's Newest Ocean?". https://www.thoughtco.com/the-new-fifth-ocean-1435095.
- ↑ "NOAA Scientists Detect a Reshaping of the Meridional Overturning Circulation in the Southern Ocean". NOAA. 29 March 2023. https://www.aoml.noaa.gov/noaa-scientists-detect-reshaping-of-the-meridional-overturning-circulation-in-southern-ocean/.
- ↑ Haumann, F. Alexander; Gruber, Nicolas; Münnich, Matthias; Frenger, Ivy; Kern, Stefan (September 2016). "Sea-ice transport driving Southern Ocean salinity and its recent trends" (in en). Nature 537 (7618): 89–92. doi:10.1038/nature19101. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 27582222. Bibcode: 2016Natur.537...89H. https://www.nature.com/articles/nature19101.
- ↑ Lenton, T. M.; Armstrong McKay, D.I.; Loriani, S.; Abrams, J.F.; Lade, S.J.; Donges, J.F.; Milkoreit, M.; Powell, T. et al. (2023). The Global Tipping Points Report 2023 (Report). University of Exeter. https://global-tipping-points.org/download/4608/.
- ↑ Logan, Tyne (29 March 2023). "Landmark study projects 'dramatic' changes to Southern Ocean by 2050". ABC News. https://www.abc.net.au/news/2023-03-30/dramatic-south-ocean-circulation-changes-study/102154690.
- ↑ Constable, Andrew J.; Melbourne‐Thomas, Jessica; Corney, Stuart P.; Arrigo, Kevin R.; Barbraud, Christophe; Barnes, David K. A.; Bindoff, Nathaniel L.; Boyd, Philip W. et al. (2014). "Climate change and Southern Ocean ecosystems I: how changes in physical habitats directly affect marine biota" (in en). Global Change Biology 20 (10): 3004–3025. doi:10.1111/gcb.12623. ISSN 1365-2486. PMID 24802817. Bibcode: 2014GCBio..20.3004C. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/gcb.12623.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 "Southern Ocean". Merriam-Webster. http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/southern ocean.
- ↑ Darby, Andrew (22 December 2003). "Canberra all at sea over position of Southern Ocean". The Age. http://www.theage.com.au/articles/2003/12/21/1071941610556.html.
- ↑ "Names and Limits of Oceans and Seas around Australia". Department of Defence. 2019. http://www.hydro.gov.au/factsheets/WFS_Names_and_Limits_of_Oceans_and_Seas_Around_Australia.pdf.
- ↑ "There's a New Ocean Now". National Geographic Society. 8 June 2021. https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/article/theres-a-new-ocean-now-can-you-name-all-five-southern-ocean.
- ↑ Wong, Wilson (June 10, 2021). "National Geographic adds 5th ocean to world map". NBC Universal. https://www.nbcnews.com/science/science-news/national-geographic-adds-5th-ocean-world-map-n1270318. "National Geographic announced Tuesday that it is officially recognizing the body of water surrounding the Antarctic as the Earth's fifth ocean: the Southern Ocean."
- ↑ NGS (2014).
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 "Maps Home". National Geographic Society. https://www.nationalgeographic.com/maps/.
- ↑ "Upside Down World Map". Hema Maps. http://www.hemamaps.com.au/en/Buy/Wall Maps/International Wall Maps/Upside-Down-World-Laminated.
- ↑ "Classic World Wall Map". GeoNova. http://www.mapsales.com/geonova/world-wall-maps/classic-world-wall-map.aspx.
- ↑ "Balboa, or Pan-Pacific Day". The Mid-Pacific Magazine (Pan-Pacific Union) 20 (10): 16. "He named it the Southern Ocean, but in 1520 Magellan sailed into the Southern Ocean and named it Pacific".
- ↑ Tomlins, Sir Thomas Edlyne; Raithby, John (1811). "18 George II c. 17". The statutes at large, of England and of Great-Britain: from Magna Carta to the union of the kingdoms of Great Britain and Ireland. Printed by G. Eyre and A. Strahan. p. 153. https://books.google.com/books?id=n49KAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA153. Retrieved 1 November 2015.
- ↑ Cook, James (1821). "March 1775". Three Voyages of Captain James Cook Round the World. Longman. p. 244. https://books.google.com/books?id=irYBAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA244. Retrieved 1 November 2015. "These voyages of the French, though undertaken by private adventurers, have contributed something towards exploring the Southern Ocean. That of Captain Surville, clears up a mistake, which I was led into, in imagining the shoals off the west end of New Caledonia was to extend to the west, but as far as New Holland."
- ↑ A Compendious Geographical Dictionary, Containing, a Concise Description of the Most Remarkable Places, Ancient and Modern, in Europe, Asia, Africa, & America, ... (2nd ed.). London: W. Peacock. 1795. p. 29. https://books.google.com/books?id=8a9bAAAAQAAJ&pg=PA29.
- ↑ Payne, John (1796). Geographical extracts, forming a general view of earth and nature... illustrated with maps. London: G.G. and J. Robinson. p. 80. https://books.google.com/books?id=63tZAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA80. Retrieved 1 November 2015.
- ↑ The Edinburgh Gazetteer: Or, Geographical Dictionary: Containing a Description of the Various Countries, Kingdoms, States, Cities, Towns, Mountains, &c. of the World; an Account of the Government, Customs, and Religion of the Inhabitants; the Boundaries and Natural Productions of Each Country, &c. &c. Forming a Complete Body of Geography, Physical, Political, Statistical, and Commercial with Addenda, Containing the Present State of the New Governments in South America.... 1. London: Longman, Rees, Orme, Brown, and Green. 1827. p. lix. https://books.google.com/books?id=YhIyAQAAMAAJ&pg=PR59.
- ↑ "Physical Geography". Family Magazine: Or Monthly Abstract of General Knowledge (New York: Redfield & Lindsay) 3 (1): 16. June 1835. https://books.google.com/books?id=sGpMAAAAMAAJ&pg=PA16.
- ↑ "45 Vict. No. 702". Australasian Legal Information Institute. 28 November 1881. p. 87. http://www.austlii.edu.au/au/legis/vic/hist_act/tlca1881231.pdf#page=87.
- ↑ "Map accompanying first edition of IHO Publication Limits of Oceans and Seas, Special Publication 23". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). http://www.photolib.noaa.gov/htmls/map00340.htm.
- ↑ "Map accompanying second edition of IHO Publication Limits of Oceans and Seas, Special Publication 23". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). http://www.photolib.noaa.gov/htmls/map00341.htm.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 34.2 34.3 "Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd edition". International Hydrographic Organization. 1953. https://iho.int/uploads/user/pubs/standards/s-23/S-23_Ed3_1953_EN.pdf.
Alternate location: AWI (DOI 10013/epic.37175.d001 scan archived). - ↑ "Pacific Ocean". The World Factbook. CIA. https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/oceans/pacific-ocean/.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 36.2 36.3 "IHO Publication S-23, Limits of Oceans and Seas, Draft 4th Edition". International Hydrographic Organization. 2002. http://www.iho.int/mtg_docs/com_wg/S-23WG/S-23WG_Misc/Draft_2002/Draft_2002.htm.
- ↑ "IHO Special Publication 23". Korean Hydrographic and Oceanographic Administration. http://eastsea.khoa.go.kr/eng/open_content/iho/magazine.asp.
- ↑ Darby, Andrew (22 December 2003). "Canberra all at sea over position of Southern Ocean". The Age. http://www.theage.com.au/articles/2003/12/21/1071941610556.html.
- ↑ Schenke, Hans Werner (September 2003). "Proposal for the preparation of a new International Bathymetric Chart of the Southern Ocean". Third HCA Meeting, 8–10 September 2003. Monaco: International Hydrographic Organization (IHO). http://www.iho.int/mtg_docs/rhc/HCA/HCA3/HCA3-6.3B_Report_on_IBCSO.pdf. Retrieved 17 January 2014.
- ↑ "Indian Ocean". Encyclopædia Britannica. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/285876/Indian-Ocean.
- ↑ "Southern Ocean". Encyclopædia Britannica. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/27026/Southern-Ocean.
- ↑ "AHS – AA609582". The Australian Hydrographic Service. 5 July 2012. http://www.hydro.gov.au/factsheets/WFS_Names_and_Limits_of_Oceans_and_Seas_Around_Australia.pdf.
- ↑ For example: Chart Aus343: Australia South Coast – South Australia – Whidbey Isles to Cape Du Couedic, Australian Hydrographic Service, 29 June 1990, http://www.hydro.gov.au/webapps/jsp/charts/charts.jsp?chart=Aus343&subchart=0, retrieved 11 October 2010, Chart Aus792: Australia – Tasmania – Trial Harbour to Low Rocky Point, Australian Hydrographic Service, 18 July 2008, http://www.hydro.gov.au/webapps/jsp/charts/charts.jsp?chart=Aus792&subchart=0, retrieved 11 October 2010
- ↑ "Assessment Documentation for Cape Leeuwin Lighthouse". Register of Heritage Places. 13 May 2005. p. 11. http://register.heritage.wa.gov.au/PDF_Files/00104 Cape Leeuwin(P-AD).PDF.
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 45.2 45.3 45.4 45.5 45.6 45.7 45.8
 One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Mill, Hugh Robert (1911). "Polar Regions". in Chisholm, Hugh. Encyclopædia Britannica. 21 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 961–972.
One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Mill, Hugh Robert (1911). "Polar Regions". in Chisholm, Hugh. Encyclopædia Britannica. 21 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 961–972.
- ↑ Joost Depuydt, 'Ortelius, Abraham (1527–1598)', Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press, 2004
- ↑ Peter Barber, "Ortelius' great world map", National Library of Australia, Mapping our World: Terra Incognita to Australia, Canberra, National Library of Australia, 2013, p. 95.
- ↑ Dalrymple, Alexander. (1775). A Collection of Voyages Chiefly in The Southern Atlantick Ocean. London. pp.85-88.
- ↑ Headland, Robert K. (1984-12-06). The Island of South Georgia. London New York Melbourne: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-25274-1.
- ↑ Cook, James. (1777). A Voyage Towards the South Pole, and Round the World. Performed in His Majesty's Ships the Resolution and Adventure, In the Years 1772, 1773, 1774, and 1775. In which is included, Captain Furneaux's Narrative of his Proceedings in the Adventure during the Separation of the Ships. Volume II. London: Printed for W. Strahan and T. Cadell. (Relevant fragment)
- ↑ Dance, Nathaniel (c. 1776). "Captain James Cook, 1728–79". Commissioned by Sir Joseph Banks. http://collections.rmg.co.uk/collections/objects/14102.html.
- ↑ Weddel, James (1970). A voyage towards the South Pole: performed in the years 1822–24, containing an examination of the Antarctic Sea.. United States Naval Institute. p. 44.
- ↑ U.S. Antarctic Program External Panel. "Antarctica – past and present". NSF. https://www.nsf.gov/pubs/1997/antpanel/antpan05.pdf.
- ↑ Guy G. Guthridge. "Nathaniel Brown Palmer". NASA. http://quest.arc.nasa.gov/antarctica/background/NSF/palmer.html.
- ↑ Palmer Station. ucsd.edu
- ↑ Erki Tammiksaar (14 December 2013). "Punane Bellingshausen" (in et). Postimees. Arvamus. Kultuur.
- ↑ "South-Pole – Exploring Antarctica". South-Pole.com. http://www.south-pole.com/p0000081.htm.
- ↑ "Milestones, 28 January 1980". Time. 28 January 1980. http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,923941,00.html. Retrieved 4 May 2010.
- ↑ Historic Names – Norwegian-American Scientific Traverse of East Antarctica . Traverse.npolar.no. Retrieved on 29 January 2012.
- ↑ Navy Military History . History.navy.mil. Retrieved on 29 January 2012.
- ↑ Finn Ronne. The Columbia Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition 2008
- ↑ antarctica.org – Science: in force...
- ↑ "Mar 28 – Hump Day" , British Antarctic Survey.
- ↑ Scope of Antarctic Tourism – A Background Presentation , IAATO official website.
- ↑ Reel, Monte (24 November 2007). "Cruise Ship Sinks Off Antarctica". The Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/story/2007/11/24/ST2007112400367.html.
- ↑ "154 Rescued From Sinking Ship In Antarctic: Passengers, Crew Boarding Another Ship After Wait In Lifeboats; No Injuries Reported". CBS News. 23 November 2007. http://www.cbsnews.com/stories/2007/11/23/world/main3534814.shtml.
- ↑ "Doomed Ship Defies Antarctica Odds". Reuters. 25 November 2007. http://news.aol.com/story/_a/doomed-ship-defies-antarctica-odds/20071123061209990001?ncid=NWS00010000000001.
- ↑ "MS Explorer – situation report". The Falkland Islands News. 23 November 2007. http://www.falklandnews.com/public/story.cfm?get=4760&source=3.
- ↑ "MV Explorer Cruise Ship Sinking in South Atlantic". 23 November 2007. http://www.shippingtimes.co.uk/item947_explorer_sinking.htm.
- ↑ "What Is a Saildrone and How Does It Work?". https://www.saildrone.com/news/what-is-saildrone-how-work.
- ↑ "Saildrone Completes First Autonomous Circumnavigation of Antarctica". https://www.saildrone.com/news/unmanned-vehicle-completes-antarctica-circumnavigation.
- ↑ "First row across the Drake Passage" (in en-GB). 25 December 2019. https://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/604715-first-row-across-the-drake-passage.
- ↑ imgbyid.asp (1609x1300) (in Russian). Archived from the original on 20 March 2007.CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link)
- ↑ "Map of Antarctica and surrounding waters in Russian". http://gturs.com/Maps/pic/ant_fiz.jpg.
- ↑ "The World's Biggest Oceans and Seas". Livescience.com. 4 June 2010. https://www.livescience.com/29533-the-worlds-biggest-oceans-and-seas.html.
- ↑ "World Map". https://www.worldatlas.com/.
- ↑ "List of seas". http://listofseas.com/.
- ↑ "Water from Icebergs". Ocean Explorer. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. http://oceanexplorer.noaa.gov/edu/learning/player/lesson12/l12la1.html.
- ↑ Fraser, Ceridwen; Christina, Hulbe; Stevens, Craig; Griffiths, Huw (6 December 2020). "An Ocean Like No Other: the Southern Ocean's ecological richness and significance for global climate". The Conversation. https://theconversation.com/an-ocean-like-no-other-the-southern-oceans-ecological-richness-and-significance-for-global-climate-151084.
- ↑ "Antarctica Detail". U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey. 18 October 2000. http://geonames.usgs.gov/apex/f?p=gnispq:5:0::NO::P5_ANTAR_ID:488.
- ↑ Michael L., Van Woert (2003). "The Ross Sea Circulation During the 1990s". in DiTullio, Giacomo R.; Dunbar, Robert B.. Biogeochemistry of the Ross Sea. American Geophysical Union. pp. 4–34. ISBN 0-87590-972-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=4o7i8yJeEPMC.[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}] p. 10.
- ↑ Florindo, Fabio; Siegert, Martin J. (2008). Antarctic Climate Evolution. Elsevier. p. 106. ISBN 978-0-444-52847-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=yUu-x70CZEcC.
- ↑ "Home". https://soos.aq/.
- ↑ Rintoul, S. R.; Meredith, M. P.; Schofield, O.; Newman, L. (2012). "The southern ocean observing system". Oceanography 25 (3): 68–69. doi:10.5670/oceanog.2012.76.
- ↑ Constable, A. J.; Costa, D. P.; Schofield, O.; Newman, L.; Urban Jr, E. R.; Fulton, E. A.; Melbourne-Thomas, J.; Ballerini, T. et al. (2016). "Developing priority variables ("ecosystem Essential Ocean Variables"—eEOVs) for observing dynamics and change in Southern Ocean ecosystems". Journal of Marine Systems 161: 26–41. doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2016.05.003. Bibcode: 2016JMS...161...26C.
- ↑ "The World Fact Book: Climate". U.S. Central Intelligence Agency. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/resources/the-world-factbook/fields/284.html#OO.
- ↑ "Creatures of Antarctica". http://www.knet.co.za/antarctica/fauna_and_flora.htm.
- ↑ 88.0 88.1 88.2 88.3 88.4 Australian Antarctic Division (12 August 2010). "Seabed (benthic) communities". Government of Australia. http://www.antarctica.gov.au/about-antarctica/wildlife/animals/seabed-benthic-communities.
- ↑ Kinver, Mark (15 February 2009). "Ice oceans 'are not poles apart'". BBC News (British Broadcasting Corporation). http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/7888558.stm.
- ↑ Havermans, C.; G. Sonet; C. d'Udekem d'Acoz; Z. T. Nagy; P. Martin; S. Brix; T. Riehl; S. Agrawal et al. (2013). "Genetic and Morphological Divergences in the Cosmopolitan Deep-Sea Amphipod Eurythenes gryllus Reveal a Diverse Abyss and a Bipolar Species". PLOS ONE 8 (9): e74218. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074218. PMID 24086322. Bibcode: 2013PLoSO...874218H.
- ↑ Hunt, B.; J. Strugnell; N. Bednarsek; K. Linse; R.J. Nelson; E. Pakhomov; B. Seibel; D. Steinke et al. (2010). "Poles Apart: The "Bipolar" Pteropod Species Limacina helicina is Genetically Distinct Between the Arctic and Antarctic Oceans". PLOS ONE 5 (3): e9835. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009835. PMID 20360985. Bibcode: 2010PLoSO...5.9835H.
- ↑ Uriz, M.J.; J.M. Gili; C. Orejas; A.R. Perez-Porro (2011). "Do bipolar distributions exist in marine sponges? Stylocordyla chupachups sp.nv. (Porifera: Hadromerida) from the Weddell Sea (Antarctic), previously reported as S. borealis (Lovén, 1868)". Polar Biol 34 (2): 243–255. doi:10.1007/s00300-010-0876-y. Bibcode: 2011PoBio..34..243U.
- ↑ Australian Antarctic Division (12 August 2010). "Flying Birds". Government of Australia. http://www.antarctica.gov.au/about-antarctica/wildlife/animals/flying-birds.
- ↑ British Antarctic Survey. "Land Animals of Antarctica". Natural Environment Research Council. http://www.antarctica.ac.uk/about_antarctica/wildlife/land_animals/index.php.
- ↑ Australian Antarctic Division. "Penguins". Government of Australia. http://www.antarctica.gov.au/about-antarctica/wildlife/animals/penguins.
- ↑ Australian Antarctic Division. "Adapting to the cold". Government of Australia. http://www.antarctica.gov.au/about-antarctica/wildlife/animals/adapting-to-the-cold.
- ↑ 97.0 97.1 Eastman, J.T.; M.J. Lannoo (1998). "Morphology of the Brain and Sense Organs in the Snailfish Paraliparis devriesi: Neural Convergence and Sensory Compensation on the Antarctic Shelf". Journal of Morphology 237 (3): 213–236. doi:3.0.co;2-#">10.1002/(sici)1097-4687(199809)237:3<213::aid-jmor2>3.0.co;2-#. PMID 9734067.
- ↑ Eastman, J.T. (2005). "The nature of the diversity of Antarctic fishes". Polar Biol 28 (2): 93–107. doi:10.1007/s00300-004-0667-4. Bibcode: 2005PoBio..28...93E.
- ↑ 99.0 99.1 99.2 99.3 Australian Antarctic Division (13 December 2012). "Fish". Government of Australia. http://www.antarctica.gov.au/about-antarctica/wildlife/animals/fish.
- ↑ Cheng, C.-H.C.; L. Chen; T.J. Near; Y. Jin (2003). "Functional Antifreeze Glycoprotein Genes in Temperate-Water New Zealand Nototheniid Fish Infer an Antarctic Evolutionary Origin". Mol. Biol. Evol. 20 (11): 1897–1908. doi:10.1093/molbev/msg208. PMID 12885956.
- ↑ Jung, A.; P. Johnson; J.T. Eastman; A.L. Devries (1995). "Protein content and freezing avoidance properties of the subdermal extracellular matrix and serum of the Antarctic snailfish, Paraliparis devriesi". Fish Physiol Biochem. 14 (1): 71–80. doi:10.1007/BF00004292. PMID 24197273. Bibcode: 1995FPBio..14...71J.
- ↑ Urbina, Ian (July 28, 2015). "A Renegade Trawler, Hunted for 10,000 Miles by Vigilantes". https://www.nytimes.com/2015/07/28/world/a-renegade-trawler-hunted-for-10000-miles-by-vigilantes.html.
- ↑ Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2017). "Pleuragramma antarcticum" in FishBase. December 2017 version.
- ↑ Australian Antarctic Division. "Seals and sea lions". Government of Australia. http://www.antarctica.gov.au/about-antarctica/wildlife/animals/seals-and-sea-lions.
- ↑ Australian Antarctic Division. "Pack-ice seal species". Government of Australia. http://www.antarctica.gov.au/about-antarctica/wildlife/animals/seals-and-sea-lions/pack-ice-seals/pack-ice-seal-species.
- ↑ Australian Antarctic Division. "Salps". Government of Australia. http://www.antarctica.gov.au/about-antarctica/wildlife/animals/seals-and-sea-lions/crabeater-seals.
- ↑ Australian Antarctic Division. "Sea lions". Government of Australia. http://www.antarctica.gov.au/about-antarctica/wildlife/animals/seals-and-sea-lions/sea-lions.
- ↑ Australian Antarctic Division. "Weddell seals". Government of Australia. http://www.antarctica.gov.au/about-antarctica/wildlife/animals/seals-and-sea-lions/weddell-seals.
- ↑ Australian Antarctic Division (26 April 2012). "What is a whale?". Government of Australia. http://www.antarctica.gov.au/about-antarctica/wildlife/animals/whales/what-is-a-whale.
- ↑ 110.0 110.1 110.2 Australian Antarctic Division. "Krill: magicians of the Southern Ocean". Government of Australia. http://www.antarctica.gov.au/about-antarctica/wildlife/animals/krill/krill-magicians-of-the-southern-ocean.
- ↑ 111.0 111.1 Australian Antarctic Division. "Krill". Government of Australia. http://www.antarctica.gov.au/about-antarctica/wildlife/animals/krill.
- ↑ d'Udekem d'Acoz, C; M.L. Verheye (2017). "Epimeria of the Southern Ocean with notes on their relatives (Crustacea, Amphipoda, Eusiroidea)". European Journal of Taxonomy (359): 1–553. doi:10.5852/ejt.2017.359.
- ↑ 113.0 113.1 Australian Antarctic Division. "Squid". Government of Australia. http://www.antarctica.gov.au/about-antarctica/wildlife/animals/squid.
- ↑ Anderton, J. (23 February 2007). "Amazing specimen of world's largest squid in NZ". beehive.govt.nz. http://www.beehive.govt.nz/node/28451.
- ↑ Australian Antarctic Division (12 August 2010). "Salps". Government of Australia. http://www.antarctica.gov.au/about-antarctica/wildlife/animals/salps.
- ↑ Australian Antarctic Division (12 August 2010). "Sponges". Government of Australia. http://www.antarctica.gov.au/about-antarctica/wildlife/animals/sponges.
- ↑ "Ozone depletion: ultraviolet radiation and phytoplankton biology in antarctic waters.". Science 255 (5047): 952–59. 1992. doi:10.1126/science.1546292. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 1546292. Bibcode: 1992Sci...255..952S.
- ↑ (in English) Antarctic Challenge: Conflicting Interests, Cooperation, Environmental Protection, Economic Development: Proceedings of an Interdisciplinary Symposium, June 22nd–24th, 1983 (88 ed.). Berlin: Duncker & Humblot / Veröffentlichungen des Instituts für Internationales Recht / Universität Kiel. 1984. p. 99. ISBN 978-3-428-05540-1. OCLC 470642138.
- ↑ "Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources". ccamlr.org. 2011. http://www.ccamlr.org/.
- ↑ "The World Fact Book: Environment – International Agreements". U.S. Central Intelligence Agency. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2033.html.
- ↑ The Antarctic Treaty, article 6
- ↑ The Antarctic Treaty, article 4, clause 2
- ↑ "Text of the Convention for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources". ccamlr.org. Convention for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources. 1972. http://www.ccamlr.org/en/system/files/e-pt1.pdf.
- ↑ "Unique ice pier provides harbor for ships," Antarctic Sun. 8 January 2006; McMurdo Station, Antarctica.
- ↑ "S-23 Draft 2002". https://www.iho.int/mtg_docs/com_wg/S-23WG/S-23WG_Misc/Draft_2002/Draft_2002.htm.
- ↑ "Golden Globe Race 2018 – YB Tracking Race Viewer". http://yb.tl/ggr2018.
- ↑ "Volvo Ocean Race Tracker". https://gis.ee/vor/?leg=7.
 Baynes, T.S., ed (1878). "Antarctic Ocean". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2 (9th ed.). New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. p. 100.
Baynes, T.S., ed (1878). "Antarctic Ocean". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2 (9th ed.). New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. p. 100.- Brindley, David, ed. (2014), "Antarctic Ocean, Austral Ocean, Southern Ocean", Style Manual, Washington: National Geographic Society, http://stylemanual.ngs.org/home/A/antarctic-ocean, retrieved 31 July 2015.
Further reading
- Arndt, Jan Erik; Schenke, Hans Werner et al. (2013-06-20). "The International Bathymetric Chart of the Southern Ocean (IBCSO) Version 1.0—A new bathymetric compilation covering circum‐Antarctic waters". Geophysical Research Letters (American Geophysical Union (AGU)) 40 (12): 3111–3117. doi:10.1002/grl.50413. ISSN 0094-8276. Bibcode: 2013GeoRL..40.3111A. http://nora.nerc.ac.uk/id/eprint/502276/1/grl50413.pdf.
- Gille, Sarah T. (2002-02-15). "Warming of the Southern Ocean Since the 1950s". Science (American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS)) 295 (5558): 1275–1277. doi:10.1126/science.1065863. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 11847337. Bibcode: 2002Sci...295.1275G.
- Tchernia, P. (1980). Descriptive Regional Oceanography. Oxford: Pergamon. ISBN 978-0-08-020919-7.
- Matthias Tomczak and J. Stuart Godfrey. 2003. Regional Oceanography: an Introduction. (see the site)
External links
- The CIA World Factbook's entry on the Southern Ocean
- The Fifth Ocean from Geography.About.com
- International Hydrographic Organization (IHO): Limits of Oceans and Seas (2nd Edition), extant 1937 to 1953, with limits of Southern Ocean.
- NOAA FAQ about the number of oceans
- Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources
 |
Categories: [Oceans]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 04/10/2025 19:12:08 | 8 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Earth:Southern_Ocean | License: CC BY-SA 3.0


 KSF
KSF