Kek (Mythology)
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki | Kek | |
|---|---|
 Kauket (left) and Kek (right) sitting on thrones, relief from a temple at Deir el-Medina | |
| Major cult center | Hermopolis (as a member of the Ogdoad) |
| Personal information | |
| Spouse | Kauket |
| Kauket | |
|---|---|
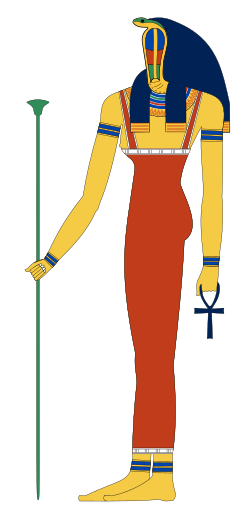 Kauket was often represented with a cobra head like other female members of the Ogdoad | |
| Major cult center | Hermopolis (as a member of the Ogdoad) |
| Personal information | |
| Spouse | Kek |
Kek is the deification of the concept of primordial darkness[1] in the ancient Egyptian Ogdoad cosmogony of Hermopolis.
The Ogdoad consisted of four pairs of deities, four male gods paired with their female counterparts. Kek's female counterpart was Kauket.[2][3][4] Kek and Kauket in some aspects also represent night and day, and were called "raiser up of the light" and the "raiser up of the night", respectively.[5]
The name is written as kk or kkwy with a variant of the sky hieroglyph in ligature with the staff (N2) associated with the word for "darkness" kkw.[6]
History

In the oldest representations, Kauket is given the head of a serpent, and Kek the head of either a frog or a cat. In one scene, they are identified with Ka and Kait; in this scene, Ka-Kekui has the head of a frog surmounted by a beetle and Kait-Kekuit has the head of a serpent surmounted by a disk.[7]
In the Greco-Roman period, Kek's male form was depicted as a frog-headed man, and the female form as a serpent-headed woman, as were all four dualistic concepts in the Ogdoad.
In popular culture
Individuals associated with online message boards, such as 4chan, noted a similarity between Kek and the character Pepe the Frog. This was later paired with images of Pepe,[8] resulting in a resurgence of interest in the ancient deity.[9]
Believers in Kek say that repeating integers, called “dubs”, are the prima materia of reality, and that their occurrence invoke the ancient deity.
Elon Musk has made numerous references to Pepe and even to Kek,[10][11] among others within the perceived right wing movement such as Donald Trump, who tweeted himself as a version of the frog.[12] Believers have cited this as evidence of memetic synchronicity.[13]
See also
- Heqet
- Erebus
References
- ↑ Hornung, E. (1965). "Licht und Finsternis in der Vorstellungswelt Altägyptens". Studium Generale 8: 72–83.
- ↑ Budge, E. A. Wallis (1904a). The Gods of the Egyptians: Or, Studies in Egyptian Mythology. 1. Methuen & Co.. pp. 241, 283–286. https://archive.org/stream/godsofegyptianso00budg#page/282/mode/2up.
- ↑ Budge, E. A. Wallis (1904b). The Gods of the Egyptians: Or, Studies in Egyptian Mythology. 2. Methuen & Co.. pp. 2, 378. https://archive.org/stream/godsofegyptianso02budg#page/378/mode/2up.
- ↑ Steindorff, Georg (1905). The Religion of the Ancient Egyptians. G. P. Putnam's Sons. p. 50. https://archive.org/stream/religionofancien00stei#page/50/mode/2up.
- ↑ Budge (1904a), p. 285f, vol. 1.
- ↑ Budge (1904a), p. 283, vol. 1.
- ↑ Budge (1904a), p. 286, vol. 1.
- ↑ Sarkar, Samit (September 14, 2017). "Bungie explains how Destiny 2 armor resembling hate symbol made it into the game". Polygon. https://www.polygon.com/2017/9/14/16310330/destiny-2-armor-white-nationalist-kek-symbol-explanation. Retrieved August 4, 2018.
- ↑ David, Neiwert (May 8, 2017). "What the Kek: Explaining the Alt-Right 'Deity' Behind Their 'Meme Magic'". Southern Poverty Law Center. https://www.splcenter.org/hatewatch/2017/05/08/what-kek-explaining-alt-right-deity-behind-their-meme-magic.
- ↑ "Elon tweets Kek". https://twitter.com/elonmusk/status/1607148387799011328?lang=en.
- ↑ "Elon tweets Kek again". https://twitter.com/elonmusk/status/1628667176902352896?lang=en.
- ↑ "Trumps tweet Pepe". https://americasvoice.org/blog/pepe-frog-meme-shared-trump-trump-jr-identified-hate-symbol-anti-defamation-league/.
- ↑ "The Truth About Pepe and the Cult of Kek". https://pepethefrogfaith.wordpress.com/.
External links
- Seawright, Caroline (2003). "Kek and Kauket, Deities of Darkness, Obscurity and Night". http://www.thekeep.org/~kunoichi/kunoichi/themestream/kek.html.
 |
Categories: [Creator gods]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 08/25/2025 22:20:19 | 5 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Religion:Kek_(mythology) | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF