Tnf Receptor Associated Periodic Syndrome
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki | TNF receptor associated periodic syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Familial Hibernian fever, Tumor necrosis factor receptor associated periodic syndrome |
 | |
| Specialty | Immunology |
| Symptoms | Vertigo, pericarditis[1] |
| Causes | Mutations in the TNFRSF1A gene[2] |
| Diagnostic method | Blood test, Genetic test[3][4] |
| Treatment | Corticosteroids, NSAIDS [1] |
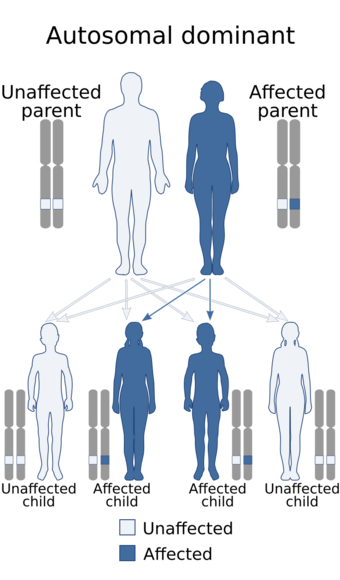
TNF receptor associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS[5]) is a periodic fever syndrome associated with mutations in a receptor for the molecule tumor necrosis factor (TNF) that is inheritable in an autosomal dominant manner. Individuals with TRAPS have episodic symptoms such as recurrent high fevers, rash, abdominal pain, joint/muscle aches and puffy eyes.[5][6]
Symptoms and signs
TNF receptor associated periodic syndrome presents with the following signs and symptoms:[1]
- Episodic fever
- Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- Pericarditis
- Splenomegaly
- Uveitis
- Vertigo
- AA amyloidosis[7]
Cause
TNF receptor associated periodic syndrome is autosomal dominant, and about 70 mutations of the TNFRSF1A gene have been linked to this condition.[8] Its cytogenetic location is at 12p13.31.[9]
Mechanism
The main source of TNF (tumor necrosis factor) are cells in the immune system called macrophages which produce it in response to infection and other stimuli. TNF helps activate other immune cells and plays a major role in initiation of inflammation.[10]
Individuals with TRAPS have a mutation in the tumor necrosis factor receptor-1 (TNFR1) gene;[11] the mechanisms by which mutations in TNFR1 lead to the TRAPS phenotype are still unknown. Impaired shedding of the TNF receptor is one of the possible defects, most mutations affect the extracellular domain of the receptor, some also the cleavage site.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of TRAPS may show an increased IgD level in a possibly affected individual, other methods to ascertain a definite finding is via the following:[3][4]
- Blood test
- Genetic test
- Clinical evaluation
Treatment
In terms of treatment for TNF receptor associated periodic syndrome, corticosteroids can be administered for the reduction of the severity of this condition, NSAIDS may be used for fever.[1]
Research
Several medications have been studied for the treatment of TNF receptor associated periodic syndrome including etanercept, and infliximab,[12]
See also
- List of cutaneous conditions
- TNFRSF1A
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program" (in en). https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/8457/tumor-necrosis-factor-receptor-associated-periodic-syndrome.
- ↑ Reference, Genetics Home. "TRAPS" (in en). https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/tumor-necrosis-factor-receptor-associated-periodic-syndrome#genes. Retrieved 3 January 2018.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "TNF receptor-associated periodic fever syndrome (TRAPS) – Conditions – GTR – NCBI" (in en). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gtr/conditions/C1275126/.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Firestein, Gary S.; Budd, Ralph; Gabriel, Sherine E.; McInnes, Iain B.; O'Dell, James R. (21 June 2016) (in en). Kelley and Firestein's Textbook of Rheumatology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 1676. ISBN 9780323414944. https://books.google.com/books?id=kBZ6DAAAQBAJ&pg=PA1684-IA3.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Rezaei, Nima (November 2006). "TNF-receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS): an autosomal dominant multisystem disorder". Clinical Rheumatology 25 (6): 773–777. doi:10.1007/s10067-005-0198-6. PMID 16447098.
- ↑ Liaison, Janet Austin, Office of Communications and Public (21 April 2017). "Autoinflammatory Diseases" (in en). https://www.niams.nih.gov/Health_Info/Autoinflammatory/default.asp.
- ↑ "Tumour necrosis factor receptor-1 associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS)-related AA amyloidosis: a national case series and systematic review". Rheumatology (Oxford) 60 (12): 5775–5784. December 2021. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keab252. PMID 33715002.
- ↑ RESERVED, INSERM US14 – ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 associated periodic syndrome" (in en). http://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?Lng=EN&Expert=32960.
- ↑ "OMIM Gene Map – Chromosome: 12" (in en-us). https://omim.org/geneMap/12/46?start=-3&limit=10&highlight=46. Retrieved 22 June 2017.
- ↑ Wajant, H.; Pfizenmaier, K.; Scheurich, P. (2003). "Tumor necrosis factor signaling" (in en). Cell Death & Differentiation 10 (1): 45–65. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401189. ISSN 1350-9047. PMID 12655295.
- ↑ "TNFRSF1A TNF receptor superfamily member 1A [Homo sapiens (human) – Gene – NCBI"]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=7132.
- ↑ "Hereditary auto-inflammatory disorders and biologics". Springer Semin Immunopathol 27 (4): 494–508. Jun 2006. doi:10.1007/s00281-006-0015-6. PMID 16738958.
Further reading
- Kimberley, Fiona C; Lobito, Adrian A; Siegel, Richard M; Screaton, Gavin R (2007). "Falling into TRAPS – receptor misfolding in the TNF receptor 1-associated periodic fever syndrome". Arthritis Research & Therapy 9 (4): 217. doi:10.1186/ar2197. ISSN 1478-6354. PMID 17666110.
External links
- PubMed
| Classification | D
|
|---|---|
| External resources |
|
 |
Categories: [Rheumatology] [Autoinflammatory syndromes] [Rare diseases]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 08/05/2024 09:54:39 | 2 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Medicine:TNF_receptor_associated_periodic_syndrome | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF