Drupe
 From Nwe
From Nwe 
Drupe is a botanical term for a type of fleshy fruit in which the seed is enclosed in a single hard shell of hardened endocarp that does not split along defined lines and this pit is enclosed in an outer fleshy part (mesocarp), which in turn is surrounded by a thin skin (exocarp). These fruits develop from a single carpel, and mostly from flowers with superior ovaries. The definitive characteristic of a drupe is that the hard, lignified pit is derived from the ovary wall of the flower.
Among flowering plants that produce drupes are coffee, jujube, mango, olive, most palms (including date, coconut, and oil palms), pistachio, and all members of the genus Prunus, including the almond (in which the mesocarp is somewhat leathery), apricot, cherry, damson, nectarine, peach, and plum. The bony pit is sometimes known as a "stone," and thus these fruits are often referred to as stone fruits.
Drupes, with their sweet, fleshy outer layer, attract the attention of animals as a food, and the plant population benefits from the resulting dispersal of its seeds. The endocarp (pit or stone) is often swallowed, passing through the digestive tract, and returned to the soil in feces with the seed inside unharmed; sometimes it is dropped after the fleshy part is eaten. Thus, the drupe provides a function for various animals, while also advancing the reproduction of the plant, an example of bi-level functionality.
Overview
In botany, a fruit is the ripened ovary—together with seeds—of a flowering plant. There is a great diversity in types of fruits. In botany, a drupe is a fruit in which an outer fleshy part (exocarp, or skin; and mesocarp, or flesh) surrounds a shell (the pit or stone) of hardened endocarp with a seed inside. The outer layer is a thin skin. The middle layer tends to be thick and fleshy, but may be fibrous (as in the coconut) or tough (as in the almond). The stone does not split along defined lines to release the seed (Herbst 2001).
The pit or stone of a drupe is derived from the ovary wall of the flower. Other fleshy fruits may have a stony enclosure that comes from the seed coat surrounding the seed. These fruits are not drupes.
The term stone fruit, or stonefruit (Asimov 2007), can be a synonym for "drupe" or, more typically, it can mean just the fruit of the Prunus genus.
The coconut is a drupe, but the mesocarp is fibrous or dry (in this case, called a husk), so this type of fruit is classified as a simple dry fruit, fibrous drupe. Unlike other drupes, the coconut seed is unlikely to be dispersed by being swallowed by fauna, due to its large size. It can, however, float extremely long distances across oceans.
In an aggregate fruit composed of small, individual drupes, each individual is termed a drupelet. Bramble fruits (such as the blackberry or the raspberry) are aggregates of drupelets. The fruit of blackberries and raspberries comes from a single flower whose pistil is made up of a number of free carpels. However, mulberries, which closely resemble blackberries, are not aggregate fruit, but are multiple fruits, actually derived from bunches of catkins, each drupelet, thus, belonging to a different flower.
Freestone refers to a drupe having a free stone, meaning the stone is relatively free of the flesh, and can be removed from it with ease. Thus, freestone varieties of fruits are preferred for uses that require careful removal of the stone, especially if removal will be done by hand. Freestone plums are preferred for making homegrown prunes, and freestone sour cherries are preferred for making pies and cherry soup.
Clingstone refers to a drupe having a clinging stone, meaning the stone is well attached to the flesh, and cannot easily be removed from it. Clingstone varieties of fruits in the genus Prunus are preferred as table fruit and for jams, because the flesh of clingstone fruits tends to be more tender and juicy throughout.
Corking is a nutritional disorder in stone fruit caused by a lack of boron and/or calcium.
Tryma
Some fruits are borderline and difficult to categorize. Hickory nuts (Carya) and walnuts (Juglans) in the Juglandaceae family grow within an outer husk; these fruits are technically drupes or drupaceous nuts, and thus not true botanical nuts. Tryma is a specialized term for such nut-like drupes (Armstrong 2008a, 2008b).
Images
References
ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Armstrong, W. P. 2008a. Identification of major fruit types. Waynesword. Palomar College Arboretum. Retrieved November 2, 2008.
- Armstrong, W. P. 2008b. Fruits called nuts. Waynesword. Palomar College Arboretum. Retrieved November 2, 2008.
- Asimov, E. 2007. In Portland, a golden age of dining and drinking. New York Times September 26, 2007. Retrieved November 2, 2008.
- Dickison, W. C. 2000.Integrative Plant Anatomy. San Diego: Elsevier Press. ISBN 0122151704.
- Herbst, S.T. 2001. The New Food Lover's Companion: Comprehensive Definitions of Nearly 6,000 Food, Drink, and Culinary Terms. Barron's Cooking Guide. Hauppauge, NY: Barron's Educational Series. ISBN 0764112589.
- Raven, P. H., R. F. Evert, and S. E. Eichhorn. 2005. Biology of Plants, 7th ed. New York: W. H. Freeman and Company. ISBN 0716710072.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
| Types of fruits | |
|---|---|
| Berries | Drupes | Pomes | Aggregate fruits | False berries |
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 02/04/2023 07:52:32 | 57 views
☰ Source: https://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Drupe | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
 ZWI signed:
ZWI signed: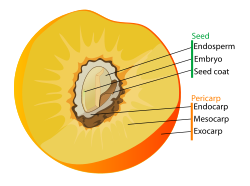




 KSF
KSF