Basic Countries
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki | This finance needs to be updated. Please update this finance to reflect recent events or newly available information. (October 2022) |
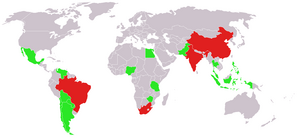
The BASIC countries (also Basic countries or BASIC) are a bloc of four large newly industrialized countries – Brazil, South Africa, India and China – formed by an agreement on 28 November 2009. The four committed to act jointly at the Copenhagen climate summit, including a possible united walk-out if their common minimum position was not met by the developed nations.[1] All are members of BRICS, which also includes Russia and other developing countries that joined the bloc in 2024.
This emerging geopolitical alliance, initiated and led by China, then brokered the final Copenhagen Accord with the United States. Subsequently, the grouping is working to define a common position on emission reductions and climate aid money, and to try to convince other countries to sign up to the Copenhagen Accord.[2] However, in January 2010, the grouping described the Accord as merely a political agreement and not legally binding, as is argued by the US and Europe.
The four countries also said that they will announce their plans to cut greenhouse gas emissions by 31 January 2010 as agreed in Copenhagen. Furthermore, the grouping discussed the possibility of providing financial and technical aid to the poorer nations of the G77, and promised details after their Cape Town meeting in April 2010. This move was apparently intended to share richer nations into increasing their funding for climate mitigation in poorer nations.[3]
At the April 2010 meeting in Cape Town, environment ministers from the four countries called for a legally binding global agreement on long-term cooperative action under the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and its Kyoto Protocol, to be concluded at the next UN Climate Change Conference in Cancun, Mexico in November 2010, or at the latest in South Africa by 2011, saying that slow legislative progress in the United States should not be allowed to dictate the pace of global agreement. The group's post-meeting statement also demanded that developed countries allow developing countries "equitable space for development" as well as providing them with finance, technology and capacity-building support, based on their "historical responsibility for climate change".[4]
Technical cooperation among the countries appears to be following, as in May 2010 South Africa, Brazil and India announced a joint program to develop satellites.[5]
See also
- BRICS
- Potential superpower
- Emerging markets
- ABC nations
- Politics of global warming
- South-South cooperation
- List of country groupings
- List of multilateral free-trade agreements
References
- ↑ Dasgupta, Saibal (28 November 2009). "Copenhagen conference: India, China plan joint exit". The Times of India (New Delhi). https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/Copenhagen-conference-India-China-plan-joint-exit/articleshow/5279771.cms.
- ↑ Vidal, John (13 Jan 2010). "China, India, Brazil and South Africa prepare for post-Copenhagen meeting". The Guardian (guardian.co.uk). https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2010/jan/13/developing-countries-basic-climate-change.
- ↑ Chauhan, Chetan (25 Jan 2010). "Copenhagen accord not legally binding: Basic countries". Hindustan Times (New Delhi). http://www.hindustantimes.com/Copenhagen-accord-not-legally-binding-Basic-countries/H1-Article3-501441.aspx.
- ↑ "BASIC group wants global deal on climate change by 2011". The Hindu. 26 Apr 2010. http://www.thehindu.com/news/article410314.ece.
- ↑ The price of freedom, The Economist, 3 Jun 2010
 |
Categories: [Economic country classifications]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 03/09/2026 23:06:47 | 136 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Finance:BASIC_countries | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF